Hitler
 When Hitler began his reign of terror on the Jewish people, along with several other groups that he considered undesirables…the groups who were not of the “Aryan Race,” he proceeded to do unspeakable things to these poor people who could not fight back because they had no weapons. They were a peace-loving people who were just trying to get along with those around them, and those in power. Unfortunately, Hitler didn’t care if they were peace-loving, if they wanted to get along, or be cooperative. Their only crime was that they were not of the “Aryan Race.” For anyone who doesn’t really understand the concept of Aryan, it is this: “The Aryan race is a historical race concept which emerged in the period of the late 19th century and mid-20th century to describe people of Indo-European heritage as a racial grouping.”
When Hitler began his reign of terror on the Jewish people, along with several other groups that he considered undesirables…the groups who were not of the “Aryan Race,” he proceeded to do unspeakable things to these poor people who could not fight back because they had no weapons. They were a peace-loving people who were just trying to get along with those around them, and those in power. Unfortunately, Hitler didn’t care if they were peace-loving, if they wanted to get along, or be cooperative. Their only crime was that they were not of the “Aryan Race.” For anyone who doesn’t really understand the concept of Aryan, it is this: “The Aryan race is a historical race concept which emerged in the period of the late 19th century and mid-20th century to describe people of Indo-European heritage as a racial grouping.”
When Hitler, invaded Poland, he quickly began to turn people against the Jewish people. These people had been living as a part of a community, making an important contribution to Polish society. Hitler began by polluting the minds of the young people first, and then the older people against the Jewish people, saying that they were thieves, and that everything they owned rightfully belonged to the “Aryan” people. Many of the people bought into Hitler’s lies and hatred, but there were those who did not. The problem was that even those who did not agree to help the Jews, had to be careful, because if they didn’t turn in those who helped, it was considered harboring criminals. If they were caught helping the Jews, they could be sent to the work camps or executed.
Since the German invasion of Poland in 1939, the Jewish population had been either forced into ghettos, transported to concentration and labor camps, or murdered. Jewish homes and shops were confiscated and synagogues were burned to the ground. By 1942, things were getting really tough in Warsaw, but a group of Polish Christians refused to stand by and do nothing. So, they put their own lives at risk when they set up the Council for the Assistance of the Jews. The group was led by two women, Zofia Kossak and Wanda Filipowicz. Word about the Jews’ fate finally leaked out in June of 1942, when a Warsaw underground newspaper, the Liberty Brigade, made public the news that tens of thousands of Jews were being gassed at Chelmno, a death camp in Poland. It had been almost seven months since the extermination of prisoners had begun.
At first, people didn’t believe what they heard about the “Final Solution,” which was the mass extermination of European Jewry and the growing network of extermination camps in Poland. Soon, it was difficult to deny. Nevertheless, little was done to stop it. Angry speeches from politicians, followed by threats of postwar reprisals, were heard in places outside Poland. Within Poland, non-Jewish Poles were themselves often the objects of persecution and forced labor at the hands of their Nazi occupiers. Because they were Slavs, they too were considered “inferior” to the Aryan Germans, and therefore, only good as servants and slaves…according to the Nazis anyway. Zofia Kossak and Wanda Filipowicz didn’t care that they could lose their lives, what was going on, was wrong and they could not stand by and do nothing. These two Polish Christians were determined to do what they could to protect their Jewish neighbors.
History says that both women died in 1968, but it is unclear what caused Kossak and Filipowicz’s deaths. It is also unclear whether their mission was to protect the Polish Jews was successful. No matter what the outcome of their plan was, they did the right thing. They saw something that wasn’t right, and they tried to do something to correct the situation. Kossak and Filipowicz were not alone in their struggle to help either. Just two days after the Council was established, the SS, Hitler’s “political” terror police force, rounded up 23 men,  women, and children, and locked some in a cottage and some in a barn. Then they burned them alive. Their crime: suspicion of harboring Jews. They were not convicted or tried, they were just murdered.
women, and children, and locked some in a cottage and some in a barn. Then they burned them alive. Their crime: suspicion of harboring Jews. They were not convicted or tried, they were just murdered.
The Nazi death machine proved overwhelming, even with the bravery of some Polish Christians, and Jewish resistance fighters within the Warsaw ghetto, who rebelled in 1943. Some of the Polish Jews found refuge among their Christian neighbors, in an attempt to elude the SS. Poland became the killing ground for not only Poland’s Jewish citizens, but much of Europe’s as well…approximately 4.5 million Jews were killed in Poland’s death and labor camps by the end of World War II.
 Sometimes, it’s a close call that saves the life of a person, because a difference of inches could have meant the difference between life and death. That was the case for young Corporal Adolf Hitler when he was temporarily blinded on October 14, 1918, by a gas shell that was close enough to temporarily blind him, but unfortunately for the rest of the world, not close enough to kill him. The British shell was part of an attack at Ypres Salient in Belgium, and in the aftermath, Hitler found himself evacuated to a German military hospital at Pasewalk, in Pomerania. Of course, Hitler considered this a great good fortune, with the exception of the temporary blindness. I find myself wishing that the shell had been closer, because the difference of inches could have changed the world, and especially the victims of the Holocaust.
Sometimes, it’s a close call that saves the life of a person, because a difference of inches could have meant the difference between life and death. That was the case for young Corporal Adolf Hitler when he was temporarily blinded on October 14, 1918, by a gas shell that was close enough to temporarily blind him, but unfortunately for the rest of the world, not close enough to kill him. The British shell was part of an attack at Ypres Salient in Belgium, and in the aftermath, Hitler found himself evacuated to a German military hospital at Pasewalk, in Pomerania. Of course, Hitler considered this a great good fortune, with the exception of the temporary blindness. I find myself wishing that the shell had been closer, because the difference of inches could have changed the world, and especially the victims of the Holocaust.
Like many young men of the period, Hitler was drafted for Austrian military service, but when he reported, he was turned down due to lack of fitness. In the summer of 1914, Hitler had moved to Munich. When World War I began, he asked for and received special permission to enlist as a German soldier. It all seemed like a noble thing to do. Hitler was a member of the 16th Bavarian Reserve Infantry Regiment. He traveled to France in October 1914. There, he saw heavy action during the First Battle of Ypres, earning the Iron Cross that December for dragging a wounded comrade to safety. These things rather surprise me, give Hitler’s reputation for thinking only of himself.
Over the course of the next two years, Hitler took part in some of the fiercest struggles of the war, including  the Battle of Neuve Chapelle, the Second Battle of Ypres and the Battle of the Somme. He was wounded in the leg by a shell blast on October 7, 1916, near Bapaume, France. Following his hospital stay. Hitler was sent to recover near Berlin, after which he returned to his old unit by February 1917. According to Hans Mend, a comrade of Hitler, he was given to rants on the dismal state of morale and dedication to the cause on the home front in Germany. According to Mend, “He sat in the corner of our mess holding his head between his hands in deep contemplation. Suddenly he would leap up, and running about excitedly, say that in spite of our big guns victory would be denied us, for the invisible foes of the German people were a greater danger than the biggest cannon of the enemy.” It would seem that Hitler’s crazed mind was beginning to present itself. As I look at a picture of Hitler as a young man, I wonder what happened to him that changed him so much. Yung Hitler didn’t look like the crazed, evil dictator the world knew
the Battle of Neuve Chapelle, the Second Battle of Ypres and the Battle of the Somme. He was wounded in the leg by a shell blast on October 7, 1916, near Bapaume, France. Following his hospital stay. Hitler was sent to recover near Berlin, after which he returned to his old unit by February 1917. According to Hans Mend, a comrade of Hitler, he was given to rants on the dismal state of morale and dedication to the cause on the home front in Germany. According to Mend, “He sat in the corner of our mess holding his head between his hands in deep contemplation. Suddenly he would leap up, and running about excitedly, say that in spite of our big guns victory would be denied us, for the invisible foes of the German people were a greater danger than the biggest cannon of the enemy.” It would seem that Hitler’s crazed mind was beginning to present itself. As I look at a picture of Hitler as a young man, I wonder what happened to him that changed him so much. Yung Hitler didn’t look like the crazed, evil dictator the world knew
Hitler continued to earn citations for bravery over the next year, including an Iron Cross 1st Class for “personal bravery and general merit” in August 1918 for single-handedly capturing a group of French soldiers hiding in a shell hole during the final German offensive on the Western Front. Then, on October 14, 1918, Hitler received the injury that put an end to his service in World War I. He learned of the German surrender while recovering at Pasewalk. Hitler was furious and frustrated by the news. He said, “I staggered and stumbled back to my  ward and buried my aching head between the blankets and pillow.” Hitler felt he and his fellow soldiers had been betrayed by the German people. I’m amazed that he did not put them in the camps too. In 1941, Hitler as Führer would reveal the degree to which his career and its terrible legacy had been shaped by the World War I, writing that “I brought back home with me my experiences at the front; out of them I built my National Socialist community.”
ward and buried my aching head between the blankets and pillow.” Hitler felt he and his fellow soldiers had been betrayed by the German people. I’m amazed that he did not put them in the camps too. In 1941, Hitler as Führer would reveal the degree to which his career and its terrible legacy had been shaped by the World War I, writing that “I brought back home with me my experiences at the front; out of them I built my National Socialist community.”
When I think of what might have been, but for a difference of inches, I find it very ironic. If that shell had hit just a few inches closer, perhaps Hitler would have died a hero in his nation, before he could become the epitome of evil…to the world, and to many of his own people. I suppose World War I and II, as well as the other wars, would have still happened, but maybe, quite likely, the Holocaust would not have happened. Just a few inches. If only.
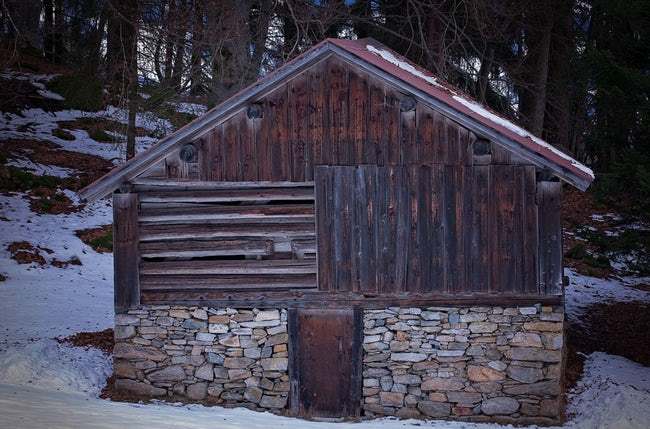 Being Jewish during the Holocaust meant doing whatever it took to survive. For some, that means hiding in walls or changing one’s identity, then so be it. Still, there were other Jews who had no way of doing either of these things, so they had to make due with what they had. The path to freedom and life was a difficult one, no matter what path they chose. There were close calls, starvation, fear, and a lot of quiet. Two families decided that they had no choice, but to take refuge in a hayloft over a pigsty offered by the owner, Francisca Halamajowa, a kindly Polish Catholic woman, and her daughter, Helena, who protected these families.
Being Jewish during the Holocaust meant doing whatever it took to survive. For some, that means hiding in walls or changing one’s identity, then so be it. Still, there were other Jews who had no way of doing either of these things, so they had to make due with what they had. The path to freedom and life was a difficult one, no matter what path they chose. There were close calls, starvation, fear, and a lot of quiet. Two families decided that they had no choice, but to take refuge in a hayloft over a pigsty offered by the owner, Francisca Halamajowa, a kindly Polish Catholic woman, and her daughter, Helena, who protected these families.
The Malkin and Kinder families went into hiding in 1942, just before the town’s Jewish ghetto was liquidated, but unfortunately, after 4 year old Fay Malkin’s father and others were killed in an old brick factory nearby. Years later in 2011, Fay Malkin told of the heroic acts of Halamajowa. Fay Malkin almost died shortly before her 5th birthday, while hiding in that hayloft. She told the Holocaust remembrance gathering at UJA-Federation of New York on May 3rd: “Hitler didn’t win, we’re here.” Malkin tells of the 20 months that the family and two other families stayed hidden in order to stay alive…and to protect their protectors, who would have also lost their lives if they were caught.
The families worried that 4-year-old Fay would give them away with her crying. The little girl promised not to cry, but that is really a lot to ask of a little girl. Malkin couldn’t control herself once in the hayloft. After trying many other approaches, the adults finally made the excruciating decision to poison little Fay in order to save the rest. Malkin would have almost certainly been killed, if they were discovered. Malkin said her memory of the incident is faint, but she remembers pushing out the pill put in her mouth. Just before she was put in a bag to be buried, a doctor who was among those hiding felt a slight pulse. She was saved. “I became the miracle child,” she said. Having lived with the story her whole life, Fay smiled when she said that her crying after that was controlled by pillows. The families were saved, not only because of the kindness and courage of their fellow townspeople, but by the miracle of a little child that didn’t die. I realize that the fact that little Fay Malkin lived through the attempted poisoning may not seem like something that saved the families, but in reality, how could they have lived with themselves? Yes, they would have been alive, but they would have been almost as bad as the Nazis who were trying to kill them.
The Malkin family lived in Sokal, then part of Poland…now in Ukraine. Before World War II, there were 6,000 Jews in Sokal. By the end of the war, only about 30 had survived, and half of them were sheltered by Halamajowa. For 20 months, the families stayed in that tiny hayloft…never daring to leave or even make a sound. Halamajowa and her daughter, Helena, risked their lives by feeding them surreptitiously and otherwise helping them, all the while disguising their actions from her neighbors and the occupying German army. In July 1944, the town was liberated by the Soviets. When the Malkin and Kindler families were finally able to come down from the hayloft, they learned that Halamajowa had also been sheltering another Jewish family in a hole dug under her kitchen floor. What these two women did was above and beyond expectation, and very brave.
Of course, most Jews never spoke of the experience. They didn’t want to get anyone in trouble, and their 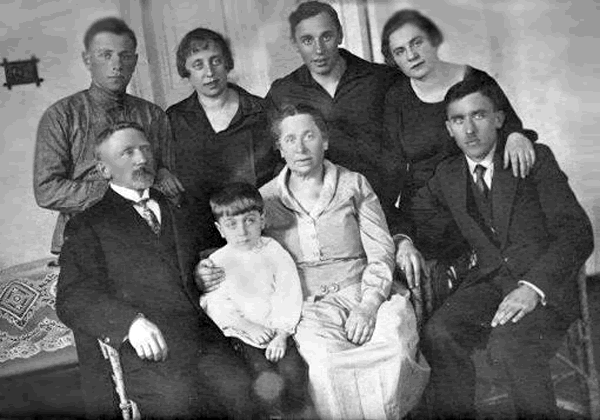 protectors felt the same way. They didn’t trust the government, even with the war over. Halamajowa died in Russia in 1960…never having revealed her secrets. Nevertheless, in 1986 she was honored at Yad Vashem as a Righteous Gentile…a fitting title. In 2007, Malkin, Maltz, and several others from the hayloft and celler families, returned to Sokal. The trip was part of a film project that led to No. 4 Street of Our Lady. A basis for the film was the diary kept by Fay’s cousin, Moshe Maltz. Malkin said it was important but highly emotional going back to Sokal, especially seeing where her father was killed. Included in the group traveling there were the two granddaughters of Halamajowa, who now live in Connecticut. I’m sure it was very emotional.
protectors felt the same way. They didn’t trust the government, even with the war over. Halamajowa died in Russia in 1960…never having revealed her secrets. Nevertheless, in 1986 she was honored at Yad Vashem as a Righteous Gentile…a fitting title. In 2007, Malkin, Maltz, and several others from the hayloft and celler families, returned to Sokal. The trip was part of a film project that led to No. 4 Street of Our Lady. A basis for the film was the diary kept by Fay’s cousin, Moshe Maltz. Malkin said it was important but highly emotional going back to Sokal, especially seeing where her father was killed. Included in the group traveling there were the two granddaughters of Halamajowa, who now live in Connecticut. I’m sure it was very emotional.
 There is good that comes from science, and there is bad too, unfortunately. Things like weapons of warfare would most likely fall into the bad that comes from science. Still, weapons are necessary, and maybe it isn’t the weapon that is bad, but rather the user. Wernher von Braun was a rocket scientist in Hitler’s Germany. His job was to build bigger and more dangerous weapons. The V-2 missile was the culmination of von Braun’s work so far. On October 3, 1942, von Braun tested the V-2 missile. The missile was fired successfully from Peenemunde, as island off Germany’s Baltic coast. It traveled 118 miles in that test; and later, in evil weapon style, it proved extraordinarily deadly in the war. The V-2 missile was the precursor to the Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) of the postwar era.
There is good that comes from science, and there is bad too, unfortunately. Things like weapons of warfare would most likely fall into the bad that comes from science. Still, weapons are necessary, and maybe it isn’t the weapon that is bad, but rather the user. Wernher von Braun was a rocket scientist in Hitler’s Germany. His job was to build bigger and more dangerous weapons. The V-2 missile was the culmination of von Braun’s work so far. On October 3, 1942, von Braun tested the V-2 missile. The missile was fired successfully from Peenemunde, as island off Germany’s Baltic coast. It traveled 118 miles in that test; and later, in evil weapon style, it proved extraordinarily deadly in the war. The V-2 missile was the precursor to the Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) of the postwar era.
German scientists, led by von Braun, had been working on the development of these long-range missiles since the 1930s. I don’t know if von Braun was doing this work by choice, which would make him very likely as evil as the weapons of destruction he made, or whether, like so many of the German people under Hitler’s evil rule, he simply had no say in the matter. Whatever the case may be, von Braun was good at what he did. The science, which clearly must have fascinated him, was a work to which he was well suited. He understood it. He knew how to make it do hat he wanted it to do, and become what he wanted it to become…or, at least what he was told to make it become. Still, it took time to perfect. Three trial launches had already failed. The fourth in the series, known as A-4,  finally saw the V-2, a 12-ton rocket capable of carrying a one-ton warhead, successfully launched. I wonder just how much pressure was on von Braun at that fourth launch attempt. Could it have cost him his life, or his freedom, if he did not successfully create this weapon that Hitler wanted so badly.
finally saw the V-2, a 12-ton rocket capable of carrying a one-ton warhead, successfully launched. I wonder just how much pressure was on von Braun at that fourth launch attempt. Could it have cost him his life, or his freedom, if he did not successfully create this weapon that Hitler wanted so badly.
The V-2 was unique in several ways. First, it was virtually impossible to intercept, making it a serious threat to anyone it was aimed at. Upon launching, the missile rises six miles straight up. Then, it proceeds on an arced course, cutting off its own fuel according to the range desired. The missile then tips over and falls on its target-at a speed of almost 4,000 miles per hour. That would make it extremely difficult to blow up in flight, since hitting something moving at that speed would take serious accuracy, and heat seeking missiles were not developed yet. The missile hits with such force that it burrows itself several feet into the ground before exploding. In addition, the missile had the potential of flying a distance of 200 miles, and the launch pads were portable, making them impossible to detect before firing.
September 6, 1944 became the first real use of the V-2, when two missiles were fired at Paris. On September 8, two more were fired at England, which would be followed by more than 1,100 more during the next six months. More than 2,700 British citizens died because of the rocket attacks. After the war, both the United States and the Soviet Union captured samples of the rockets for reproduction. They also captured the scientists  responsible for their creation. Following the war, von Braun was secretly moved to the United States, along with about 1,600 other German scientists, engineers, and technicians, as part of Operation Paperclip. He worked for the United States Army on an intermediate-range ballistic missile program, and he developed the rockets that launched the United States’ first space satellite Explorer 1.
responsible for their creation. Following the war, von Braun was secretly moved to the United States, along with about 1,600 other German scientists, engineers, and technicians, as part of Operation Paperclip. He worked for the United States Army on an intermediate-range ballistic missile program, and he developed the rockets that launched the United States’ first space satellite Explorer 1.
His group was assimilated into NASA, where he served as director of the newly formed Marshall Space Flight Center and as the chief architect of the Saturn V super heavy-lift launch vehicle that propelled the Apollo spacecraft to the Moon. He also advocated for a human mission to Mars. In 1967, von Braun was inducted into the National Academy of Engineering and in 1975, he received the National Medal of Science. Von Braun died on June 16, 1977 of pancreatic cancer in Alexandria, Virginia at age 65. He was buried at the Ivy Hill Cemetery. His gravestone quotes Psalm 19:1: “The heavens declare the glory of God; and the firmament sheweth his handywork” (KJV).
 Every time I learn anything about Adolf Hitler, I am stunned that so much evil could exist in one man. World War II technically started when Adolf Hitler invaded Poland. Hitler told his men that “it did not matter who was right or wrong, that in fighting a war, coming out triumphant is the only thing that counted.” He urged his men to have no sympathy for their opponent. On September 1, 1939, Hitler ordered the invasion of Poland, by ordering the attack of defenseless civilians. In this way, they put the citizens in a state of shock. The sky was dark and there were dead bodies everywhere. Once Germany invaded Poland, it opened a door to allow the Soviets to also invade Poland. Of course, this was not exactly what either country wanted.
Every time I learn anything about Adolf Hitler, I am stunned that so much evil could exist in one man. World War II technically started when Adolf Hitler invaded Poland. Hitler told his men that “it did not matter who was right or wrong, that in fighting a war, coming out triumphant is the only thing that counted.” He urged his men to have no sympathy for their opponent. On September 1, 1939, Hitler ordered the invasion of Poland, by ordering the attack of defenseless civilians. In this way, they put the citizens in a state of shock. The sky was dark and there were dead bodies everywhere. Once Germany invaded Poland, it opened a door to allow the Soviets to also invade Poland. Of course, this was not exactly what either country wanted.
Before the end of the month, on September 29, 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union agree to divide control of occupied Poland roughly along the Bug River, with the Germans taking everything west, and the Soviets taking everything east. The people of Poland were given away like slaves. In addition, as a follow-up to the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, which was also known as the Hitler-Stalin Pact, a non-aggression treaty was created between the two huge military powers of Germany and the USSR. The German foreign minister, Joachim von Ribbentrop met with his Soviet counterpart, VM Molotov, to sign the German-Soviet Boundary and Friendship Treaty. Of course, the “friendship” did not extend to the Polish people.
As in normal in any contract, there was “fine print” in this agreement too. The fine print of the original non-aggression pact had promised the Soviets a slice of eastern Poland. It was to be a small part, simply a matter of agreeing where to draw the lines. Joseph Stalin, Soviet premier and dictator, personally drew the line that partitioned Poland. He originally wanted it drawn at the River Vistula, just west of Warsaw. In the end, he agreed to pull it back east of the capital and Lublin, giving Germany control of most of Poland’s most heavily populated and industrialized regions. In exchange, Stalin wanted Lvov, and its rich oil wells, and Lithuania, which sits atop East Prussia. Germany was fine with that, because now they had 22 million Poles, “slaves of the Greater German Empire,” at its disposal…and Russia had a western buffer zone.
On this same day, the Soviet Union also signed a Treaty of Mutual Assistance with the Baltic nation of Estonia, giving Stalin the right to occupy Estonian naval and air bases. What was thought to be a buffer zone, seems more like a land grab to me. A similar treaty would later be signed with Latvia. These nations really didn’t seem to realize what they were getting into. Eventually, Soviet tanks rolled across these borders, in the name of “mutual assistance,” placing the Baltic States under the rule of the USSR for decades to come. These so called treaties were once again merely the realization of more fine print from the Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact, giving Stalin more border states as buffer zones, and protecting Russian territory where the Bolshevik ideology had not been enthusiastically embraced from intrusion by its western neighbor, namely its non-aggression partner Germany. The highly vulnerable Baltic nations had no say in any of these arrangements. They were merely annexed…by force in a huge Soviet land grab.
 On September 23, 1989, one of the worst days for accidents on the German Autobahn, five huge pileups involving 256 cars with a large number of series injuries, occurred due to heavy fog in the area. The Autobahn in Germany has no speed limits, and cars often travel as fast as 140 miles per hour, which in foggy conditions, is a recipe for disaster. Most of us would think that driving at the speeds seen on the Autobahn would be catastrophic. Here in the United States, where most such highways have a speed limit of 80 miles per hour, travelling at 140 miles per hour would seem more like something you might need a pilot’s license for, rather that a driver’s license.
On September 23, 1989, one of the worst days for accidents on the German Autobahn, five huge pileups involving 256 cars with a large number of series injuries, occurred due to heavy fog in the area. The Autobahn in Germany has no speed limits, and cars often travel as fast as 140 miles per hour, which in foggy conditions, is a recipe for disaster. Most of us would think that driving at the speeds seen on the Autobahn would be catastrophic. Here in the United States, where most such highways have a speed limit of 80 miles per hour, travelling at 140 miles per hour would seem more like something you might need a pilot’s license for, rather that a driver’s license.
Given the speeds on the Autobahn, one might expect it to be one of the most dangerous roads in the world, but their assumption would be very wrong. In reality, the Autobahn is statistically safer than any interstate or other such highway in the world. That seems strange given the speeds seem there. Of course, not all of the Autobahn is speed limit free. The German Autobahnen are widely known for having no federally mandated speed limit for some classes of vehicles, with classes of vehicles being the operative word. There are limits posted, and enforced, in areas that are urbanized, substandard, accident-prone, or under construction. On speed-unrestricted stretches, an advisory speed limit of 81 miles per hour applies. While driving faster is not illegal, as such in the absence of a speed limit, it can cause an increased liability in the case of a collision…which the mandatory auto insurance has to cover. Courts have ruled that an “ideal driver” who is exempt from absolute liability for “inevitable” tort under the law would not exceed the suggested speed limit.

The Autobahn was conceived in the 1920s, and with Hitler’s embrace of the system in 1933, construction was scheduled and began 1936. It was a bold idea to put into motion, and probably the only Hitler back idea that is still in operation today. Of course, Hitler didn’t have many “good” ideas in his lifetime, so this one was an exceptional feat, and obviously not an idea of his making. Nevertheless, the very safe Autobahn continues to be utilized by all of Germany today. It is not accident free, as we have seen by the awful accident of September 23, 1989, but these tragedies seem to be few and far between.
 World War II took it’s toll on many people. The soldiers, families at home, and probably unknown to the people of the Allied nations…the German people. When we think of the Nazis, we think of an entire country so filled with hate for the Jewish people…as well as any nationality that was different that the Nazi white people. The reality is that while there were a relatively small number of Hitler’s puppets to actually embraced the thinking and the hatred of Hitler; there were also a great many of the German people who were not Nazis, nor did they agree with anything that Hitler did or believed. They were good and decent people, who valued life, and just wanted to work hard, and live their lives in peace and happiness.
World War II took it’s toll on many people. The soldiers, families at home, and probably unknown to the people of the Allied nations…the German people. When we think of the Nazis, we think of an entire country so filled with hate for the Jewish people…as well as any nationality that was different that the Nazi white people. The reality is that while there were a relatively small number of Hitler’s puppets to actually embraced the thinking and the hatred of Hitler; there were also a great many of the German people who were not Nazis, nor did they agree with anything that Hitler did or believed. They were good and decent people, who valued life, and just wanted to work hard, and live their lives in peace and happiness.

These post-war German citizens were faced with a new and strange kind of post-war reality. The country suffered from collective PTSD. Said one German citizen, “We were a broken, defeated, extinguished people in 1045. 60 million human beings suffered from PTDS. And Knowing that not only did you lose…but also that you were on the wrong side. On the wrong side of morality, of humanity, of history. We were the bad guys. There was no pride. Just the knowledge that we were at rock bottom, and rightfully so.”
As American and Allies, it is hard for us to accept their feelings of remorse. I’m sure that the Jews, Gypsies, and other persecuted races had an even harder time feeling bad for the German people…at least, not unless they were some of the German citizens who escaped from Germany along with other refugees, or those who helped their Jewish or Gypsy counterparts to escape or to survive. One of those sympathizers who lived, warned his children and grandchildren, saying, “Don’t forget, but don’t tell anyone about this.” He was so ashamed and so angry, still, 40, 50 years  later. He said that the Nazis had taken the best years of his life, saying, “We must look out for them, it can happen again. Beware, pay attention to politics! Speak up! We couldn’t stop them, maybe you can, next time.” The man hammered these things into his grandchild’s brain, over and over and over. He knew the dangers of complacency where politics is concerned. He knew that if they take your guns you are helpless. He knew that if evil people get in office, the danger grows exponentially. He had seen it…first hand. It is a lesson many people today need to learn. It could happen again, if we aren’t vigilant.
later. He said that the Nazis had taken the best years of his life, saying, “We must look out for them, it can happen again. Beware, pay attention to politics! Speak up! We couldn’t stop them, maybe you can, next time.” The man hammered these things into his grandchild’s brain, over and over and over. He knew the dangers of complacency where politics is concerned. He knew that if they take your guns you are helpless. He knew that if evil people get in office, the danger grows exponentially. He had seen it…first hand. It is a lesson many people today need to learn. It could happen again, if we aren’t vigilant.
 Almost immediately after he gained power in Germany, Adolf Hitler began making plans to control the world. He never was and never would be happy with just being the dictator of Germany. By May of 1940, Hitler had a plan in place to seize control. On 10 May 1940, Germany invaded Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and Belgium under the operational plan Fall Gelb, or Case Yellow. The Battle of Belgium or Belgian Campaign, often referred to within Belgium as the 18 Days’ Campaign. The Allied armies tried to halt the German Army in Belgium, thinking it to be the main German thrust. After the French had fully committed the best of the Allied armies to Belgium between 10 and 12 May, the Germans enacted the second phase of their operation. It was an unexpected move, and since the Allies were unprepared, the Germans advanced toward the English Channel. The German Army reached the Channel after five days, encircling the Allied armies. The Germans gradually reduced the pocket of Allied forces, forcing them
Almost immediately after he gained power in Germany, Adolf Hitler began making plans to control the world. He never was and never would be happy with just being the dictator of Germany. By May of 1940, Hitler had a plan in place to seize control. On 10 May 1940, Germany invaded Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and Belgium under the operational plan Fall Gelb, or Case Yellow. The Battle of Belgium or Belgian Campaign, often referred to within Belgium as the 18 Days’ Campaign. The Allied armies tried to halt the German Army in Belgium, thinking it to be the main German thrust. After the French had fully committed the best of the Allied armies to Belgium between 10 and 12 May, the Germans enacted the second phase of their operation. It was an unexpected move, and since the Allies were unprepared, the Germans advanced toward the English Channel. The German Army reached the Channel after five days, encircling the Allied armies. The Germans gradually reduced the pocket of Allied forces, forcing them  back to the sea. The Belgian Army surrendered on 28 May 1940, ending the Battle of Belgium.
back to the sea. The Belgian Army surrendered on 28 May 1940, ending the Battle of Belgium.
The first tank battle of the war occurred during the Battle of Belgium. It was called the Battle of Hannut. It was the largest tank battle in history at the time, but was later surpassed by the battles of the North African Campaign and the Eastern Front. The battle also included the Battle of Fort Eben-Emael, the first strategic airborne operation using paratroopers ever attempted. It would seem that there were a lot of firsts that happened during the 18 days of the Battle of Belgium.
Strangely, the official German historic account stated that in the 18 days of bitter fighting, the Belgian Army  were tough opponents and spoke of the “extraordinary bravery” of its soldiers. That surprises me, because the Germans hated to appear weaker than their opponents. Nevertheless, in the end, the Belgium forces were no match for the Germans, and the Belgian collapse forced the Allied withdrawal from continental Europe. The British Royal Navy were forced to evacuate Belgian ports during Operation Dynamo, allowing the British Expeditionary Force, along with many Belgian and French soldiers, to escape capture and continue military operations. France reached its own armistice with Germany in June 1940. Belgium continued to be occupied by the Germans until the autumn of 1944, when it was finally liberated by the Western Allies.
were tough opponents and spoke of the “extraordinary bravery” of its soldiers. That surprises me, because the Germans hated to appear weaker than their opponents. Nevertheless, in the end, the Belgium forces were no match for the Germans, and the Belgian collapse forced the Allied withdrawal from continental Europe. The British Royal Navy were forced to evacuate Belgian ports during Operation Dynamo, allowing the British Expeditionary Force, along with many Belgian and French soldiers, to escape capture and continue military operations. France reached its own armistice with Germany in June 1940. Belgium continued to be occupied by the Germans until the autumn of 1944, when it was finally liberated by the Western Allies.
 When we think of heroes during the Nazi years, we think mostly of men, but there were a few women who were real heroes too. One such woman, Sophia Magdalena Scholl, who was born on May 9, 1921, was a German student, who was also a serious anti-Nazi political activist. She was active within the White Rose non-violent resistance group in Nazi Germany. Scholl was the fourth of six children born to Magdalena (Müller) and liberal politician and ardent Nazi critic Robert Scholl. Her father was the mayor of her hometown of Forchtenberg am Kocher in the Free People’s State of Württemberg, at the time of her birth.
When we think of heroes during the Nazi years, we think mostly of men, but there were a few women who were real heroes too. One such woman, Sophia Magdalena Scholl, who was born on May 9, 1921, was a German student, who was also a serious anti-Nazi political activist. She was active within the White Rose non-violent resistance group in Nazi Germany. Scholl was the fourth of six children born to Magdalena (Müller) and liberal politician and ardent Nazi critic Robert Scholl. Her father was the mayor of her hometown of Forchtenberg am Kocher in the Free People’s State of Württemberg, at the time of her birth.
Scholl was brought up in the Lutheran church. She entered junior or grade school at the age of seven, and was considered an intelligent child who learned easily. Her childhood was a happy and carefree one. In 1930, the family moved to Ludwigsburg and then two years later to Ulm where her father had a business consulting office. These were definitely the best years of her life.
In 1932, after Scholl started attending a secondary school for girls, at the age of twelve, she chose to join the Bund Deutscher Mädel (League of German Girls), as did most of her classmates. It was as common as joining the girl scouts was in the United States. Her initial enthusiasm gradually gave way to criticism. She was aware of the dissenting political views of her father, friends, and some teachers. Even her own brother Hans, who once eagerly participated in the Hitler Youth program, became entirely disillusioned with the Nazi Party. Sophia was quickly learning of the horrors of Hitler and his Nazi regime. Political attitude had become an essential criterion in her choice of friends. The arrest of her brothers and friends in 1937 for participating in the German Youth Movement left a strong impression on her.
In 1943, with the Nazi movement in full swing, Sophia and her brother, Hans were at the University of Munich distributing anti-war leaflets when they were arrested and charged with high treason. Of course, handing out  anti-war leaflets in the United States would never be considered cause for a high treason conviction, but then Sophia and her brother did not live in the United States. In the People’s Court before Judge Roland Freisler on 22 February 1943, Scholl was recorded as saying these words, “Somebody, after all, had to make a start. What we wrote and said is also believed by many others. They just don’t dare express themselves as we did.” There was no testimony allowed for the defendants; this was their only defense. The brother and sister were subsequently convicted of the high treason charges, and as a result, were executed by guillotine on February 22, 1943. Since the 1970s, Scholl has been extensively commemorated for her anti-Nazi resistance work.
anti-war leaflets in the United States would never be considered cause for a high treason conviction, but then Sophia and her brother did not live in the United States. In the People’s Court before Judge Roland Freisler on 22 February 1943, Scholl was recorded as saying these words, “Somebody, after all, had to make a start. What we wrote and said is also believed by many others. They just don’t dare express themselves as we did.” There was no testimony allowed for the defendants; this was their only defense. The brother and sister were subsequently convicted of the high treason charges, and as a result, were executed by guillotine on February 22, 1943. Since the 1970s, Scholl has been extensively commemorated for her anti-Nazi resistance work.
 There was, during the Second World War, a somewhat strange and almost morbid plan that was concocted to dupe the Germans into believing that the Allies were going to invade Greece in 1943, when in fact, they were going to invade Sicily, some 500 miles away. The success of the mission really depended on the element of surprise, and in the end, the Allies needed something that would be believable to the Germans.
There was, during the Second World War, a somewhat strange and almost morbid plan that was concocted to dupe the Germans into believing that the Allies were going to invade Greece in 1943, when in fact, they were going to invade Sicily, some 500 miles away. The success of the mission really depended on the element of surprise, and in the end, the Allies needed something that would be believable to the Germans.
The thing that made the operation morbid was that in the end, they would use a dead body to bring about their deception. In their plan a body was dumped in the sea, to be discovered by Axis forces, carrying fake secret documents suggesting the invasion would be staged in Greece. They were a bit shocked when their plan worked, but work it did. The German troops were diverted to Greece, and Operation Mincemeat became a huge success, but even after it was over, it remained a source of secrecy, confusion, and conspiracy theory. The biggest source of confusion being…just who was this man who was found floating in the ocean, and how did he really die? For most people, the operation remains a mystery to this day, but one man believes that he now knows the true identity of the man found floating in the ocean.
In the 1956 film called “The Man Who Never Was,” one historian claims to have finally established beyond any reasonable doubt the identity of the person who played the part of the dead man, He believes he was a homeless Welshman named Glyndwr Michael. The body, which was given the identity of a fake Royal Marine, Major William Martin, was dropped into the sea off Spain in 1943. Winston Churchill had remarked that “Anyone but a bloody fool would know it was Sicily”, but after the tides carried Major Martin’s body into the clutches of Nazi agents, Hitler and his High Command became convinced Greece was the target. “You can forget about Sicily. We know it’s in Greece,” proclaimed General Alfred Jodl, head of the German supreme command operations staff.
“Mincemeat swallowed, rod, line and sinker” was the message sent to Churchill after the Allies learned the plot had worked. In recent years, there have been repeated claims that Mincemeat’s chief planner, Lieutenant Commander Ewen Montagu, was so intent on deceiving the Germans that he stole the body of a crew member from HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy aircraft carrier which exploded off the Scottish coast in March 1943, and lied to the dead man’s relatives. In 2003, a documentary based on 14 years of research by former police officer Colin 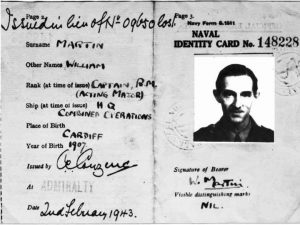 Gibbon claimed that ‘Major Martin’ was Dasher sailor Tom Martin. Then in 2004, official sanction appeared to be given to another candidate, Tom Martin’s crewmate John Melville. At a memorial service on board the current HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy patrol vessel, off the coast of Cyprus, Lieutenant Commander Mark Hill named Mr Melville as Major Martin, describing him as “a man who most certainly was”. Mr Melville’s daughter, Isobel Mackay, later told The Scotsman newspaper: “I feel very honored if my father saved 30,000 Allied lives.” I don’t suppose that we will ever know who the man really was, without exhuming his body, and that hardly seems right. Whoever he was, his family can rest assured that he saved many lives that day.
Gibbon claimed that ‘Major Martin’ was Dasher sailor Tom Martin. Then in 2004, official sanction appeared to be given to another candidate, Tom Martin’s crewmate John Melville. At a memorial service on board the current HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy patrol vessel, off the coast of Cyprus, Lieutenant Commander Mark Hill named Mr Melville as Major Martin, describing him as “a man who most certainly was”. Mr Melville’s daughter, Isobel Mackay, later told The Scotsman newspaper: “I feel very honored if my father saved 30,000 Allied lives.” I don’t suppose that we will ever know who the man really was, without exhuming his body, and that hardly seems right. Whoever he was, his family can rest assured that he saved many lives that day.

