great britain

 Recently, my sisters, Cheryl Masterson, Caryl Reed, Alena Stevens, Allyn Hadlock, and I started a book club. Before each meeting, we read a book, on our own time, and then come together to discuss the book we read. We chose the Presidents of the United States as our topics, and each time we progress to the next president. We began at the beginning, President George Washington. We went on to John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and next will be James Monroe. One takeaway from these books has been that while our founding fathers may have had their faults, and some more than others, each tried to do what they saw as the best thing for this nation. They also knew that more than anything, we needed freedom. We could not continue to live under British rule.
Recently, my sisters, Cheryl Masterson, Caryl Reed, Alena Stevens, Allyn Hadlock, and I started a book club. Before each meeting, we read a book, on our own time, and then come together to discuss the book we read. We chose the Presidents of the United States as our topics, and each time we progress to the next president. We began at the beginning, President George Washington. We went on to John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and next will be James Monroe. One takeaway from these books has been that while our founding fathers may have had their faults, and some more than others, each tried to do what they saw as the best thing for this nation. They also knew that more than anything, we needed freedom. We could not continue to live under British rule.
We had to be free of England, and so it was that Independence Day, also known as the Fourth of July, is now a federal holiday in the United States commemorating that freedom, and the Declaration of Independence, which  was ratified by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, establishing the United States of America. The Declaration of Independence was largely written by Thomas Jefferson but was collectively the work of the Committee of Five, which also included John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Roger Sherman, and Robert Livingston. The Founding Father delegates of the Second Continental Congress declared that “the Thirteen Colonies were no longer subject (and subordinate) to the monarch of Britain, King George III, and were now united, free, and independent states.” The Congress voted to approve independence by passing the Lee Resolution on July 2 and adopted the Declaration of Independence two days later, on July 4. We were a free nation, but that did not mean that Great Britain would willingly accept that. In fact, Great Britain did not accept US independence until 1783…a full seven years after it was first declared.
was ratified by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, establishing the United States of America. The Declaration of Independence was largely written by Thomas Jefferson but was collectively the work of the Committee of Five, which also included John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Roger Sherman, and Robert Livingston. The Founding Father delegates of the Second Continental Congress declared that “the Thirteen Colonies were no longer subject (and subordinate) to the monarch of Britain, King George III, and were now united, free, and independent states.” The Congress voted to approve independence by passing the Lee Resolution on July 2 and adopted the Declaration of Independence two days later, on July 4. We were a free nation, but that did not mean that Great Britain would willingly accept that. In fact, Great Britain did not accept US independence until 1783…a full seven years after it was first declared.
Like many “start-up” countries, the United States met with heavy opposition the minute it tried to get going. The “Mother Country” didn’t want to let go. Great Britain called the United States the “Colonies” long after we 
 were actually a free nation. Even when they knew they had lost any control over the United States, they tried to get it back, and in the absence of getting their control back, they downplayed the importance of the United States. That was probably the most ridiculous part of it, because the United States became the most powerful nation in the world. While some might disagree, and while we have had our ups and downs, this nation will always stand. Today, we celebrate the nation that we love. The United States of America…the home of the free, because of the brave. Happy Independence Day to this great nation!! Let the celebration begin!!
were actually a free nation. Even when they knew they had lost any control over the United States, they tried to get it back, and in the absence of getting their control back, they downplayed the importance of the United States. That was probably the most ridiculous part of it, because the United States became the most powerful nation in the world. While some might disagree, and while we have had our ups and downs, this nation will always stand. Today, we celebrate the nation that we love. The United States of America…the home of the free, because of the brave. Happy Independence Day to this great nation!! Let the celebration begin!!

 “Who was Winston Churchill?” It’s not a question you often hear, because Winston Churchill had a presence. His features were distinct, but he was not a big man. Churchill stood 5’6½” tall and weighed 187 pounds. He was maybe 35 pounds overweight, but not in bad health, especially considering he smoked as many as ten cigars a day, and when you consider that he lived to be 90 years old, it would seem that none of the normal “risk factors” applied to Winston Churchill. He dealt with daily stress, poor eating habits, excess weight, and smoking, but outlived many people in this era or that. How people felt about Winston Churchill, depended on which side of the subject in question they were on. When he made up his mind on a matter, he rarely changed his mind, and he didn’t back down.
“Who was Winston Churchill?” It’s not a question you often hear, because Winston Churchill had a presence. His features were distinct, but he was not a big man. Churchill stood 5’6½” tall and weighed 187 pounds. He was maybe 35 pounds overweight, but not in bad health, especially considering he smoked as many as ten cigars a day, and when you consider that he lived to be 90 years old, it would seem that none of the normal “risk factors” applied to Winston Churchill. He dealt with daily stress, poor eating habits, excess weight, and smoking, but outlived many people in this era or that. How people felt about Winston Churchill, depended on which side of the subject in question they were on. When he made up his mind on a matter, he rarely changed his mind, and he didn’t back down.
He was responsible for one of the most famous speeches of the Cold War period. It was a speech in which former British Prime Minister Winston Churchill condemned the Soviet Union’s policies in Europe and declared, “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the continent.” Churchill’s Cold War speech is one of the “opening volleys” announcing the beginning of the Cold War. When he was defeated for re-election as prime minister in 1945, he was invited to Westminster College in Fulton, Missouri, which is where he gave this speech. President Harry S Truman joined Churchill on the platform and listened intently to his speech. Expressing praise for the United States, Churchill declared that the United States stood “at the pinnacle of world power.” England and the United States have long had a “friendly, but competitive relationship,” and it would soon become quite clear that a primary purpose of his talk was to argue for an even closer “special relationship” between the United States and Great Britain…the two great powers of the “English-speaking world.” But, would it be in the best interest of the United States to agree?
World War II had ended, and as in any post war situation, things were still pretty chaotic. Nevertheless, it was necessary to set policies, and to organize the losing countries so that things didn’t escalate out of control 
 again…not an easy task. The Soviet Union was well known for its expansionistic policies and was unlikely to stop trying to take over its neighbors without some kind of intervention. In addition to the “iron curtain” that had descended across Eastern Europe, Churchill spoke of “communist fifth columns” that were operating throughout western and southern Europe. Churchill compared the Soviet Union to disastrous consequences of the appeasement of Hitler prior to World War II, saying that in dealing with the Soviets there was “nothing which they admire so much as strength, and there is nothing for which they have less respect than for military weakness.” Therefore, without intervention, they would quickly get back to the same disastrous practices they used before, and the war would have to fought all over again.
again…not an easy task. The Soviet Union was well known for its expansionistic policies and was unlikely to stop trying to take over its neighbors without some kind of intervention. In addition to the “iron curtain” that had descended across Eastern Europe, Churchill spoke of “communist fifth columns” that were operating throughout western and southern Europe. Churchill compared the Soviet Union to disastrous consequences of the appeasement of Hitler prior to World War II, saying that in dealing with the Soviets there was “nothing which they admire so much as strength, and there is nothing for which they have less respect than for military weakness.” Therefore, without intervention, they would quickly get back to the same disastrous practices they used before, and the war would have to fought all over again.
The speech was well received by Truman and many other US officials. Everyone knew the truth, and somebody simply had to come right out and say it. They had decided that because the Soviet Union was determined to expand, only a tough stance on a united front would deter the Russians. Churchill’s “iron curtain” phrase immediately entered the official vocabulary of the Cold War. It was a term everyone knew, and it perfectly described the problem. Of course, agreeing with Churchill, didn’t necessarily mean that the US officials enthusiastic about Churchill’s call for a “special relationship” between the United States and Great Britain. They weren’t concerned that Great Britain would again try to have some influence over the United States, but rather they were well aware that Britain’s power was weakening, and the US had no intention of being used as pawns to help support the crumbling British empire.
Of course, the Russian leader Joseph Stalin had a very different view of the speech, saying that it was “war 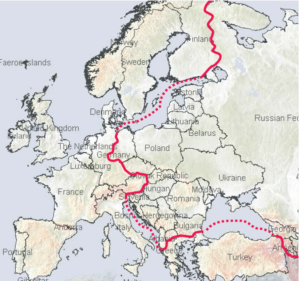
 mongering” and referred to Churchill’s comments about the “English-speaking world” as imperialist “racism.” The British, Americans, and Russians, all of whom were allies against Hitler less than a year before the speech, were now drawing the battle lines of the Cold War. It didn’t take long for the similarities between Hitler and the Soviet Union to become glaringly clear, and they had to be stopped. I don’t know why dictators feel the need to enslave other people. The “Iron Curtain” would “come down” like all other forms of tyranny must eventually do, but unfortunately, a lot of lives are lost before victory is achieved.
mongering” and referred to Churchill’s comments about the “English-speaking world” as imperialist “racism.” The British, Americans, and Russians, all of whom were allies against Hitler less than a year before the speech, were now drawing the battle lines of the Cold War. It didn’t take long for the similarities between Hitler and the Soviet Union to become glaringly clear, and they had to be stopped. I don’t know why dictators feel the need to enslave other people. The “Iron Curtain” would “come down” like all other forms of tyranny must eventually do, but unfortunately, a lot of lives are lost before victory is achieved.
 The dynamic of the world wars was probably different than most other wars…especially when it came to which units and countries were fighting side by side or against each other. When Britain declared war against Germany in August 1914, Australia was automatically also at war, because it was part of the British Empire. The New Zealand government (also under the sovereignty of the British Empire) followed without hesitation despite its geographic isolation and small population. The British Empire is for most of us, a difficult to understand group of countries that while largely independent, is also part of a larger government…the British Empire. The British Empire is a worldwide system of dependencies—colonies, protectorates, and other territories, that over a span of some three centuries was brought under the sovereignty of the crown of Great Britain and the administration of the British government. The policy of granting or recognizing significant degrees of self-government by dependencies, which was favored by the far-flung nature of the empire, led to the development by the 20th century of the notion of a “British Commonwealth” that was comprised of largely self-governing dependencies that acknowledged an increasingly symbolic British sovereignty. The term was embodied in statute in 1931. Today the Commonwealth includes former elements of the British Empire in a free association of sovereign states. Now, I don’t claim to understand the inner workings of the British Empire or the British Commonwealth, but Australia and New Zealand apparently had the option to join Britain in the war or to stand back and remain neutral. Both nations were loyal and joined Great Britain.
The dynamic of the world wars was probably different than most other wars…especially when it came to which units and countries were fighting side by side or against each other. When Britain declared war against Germany in August 1914, Australia was automatically also at war, because it was part of the British Empire. The New Zealand government (also under the sovereignty of the British Empire) followed without hesitation despite its geographic isolation and small population. The British Empire is for most of us, a difficult to understand group of countries that while largely independent, is also part of a larger government…the British Empire. The British Empire is a worldwide system of dependencies—colonies, protectorates, and other territories, that over a span of some three centuries was brought under the sovereignty of the crown of Great Britain and the administration of the British government. The policy of granting or recognizing significant degrees of self-government by dependencies, which was favored by the far-flung nature of the empire, led to the development by the 20th century of the notion of a “British Commonwealth” that was comprised of largely self-governing dependencies that acknowledged an increasingly symbolic British sovereignty. The term was embodied in statute in 1931. Today the Commonwealth includes former elements of the British Empire in a free association of sovereign states. Now, I don’t claim to understand the inner workings of the British Empire or the British Commonwealth, but Australia and New Zealand apparently had the option to join Britain in the war or to stand back and remain neutral. Both nations were loyal and joined Great Britain. 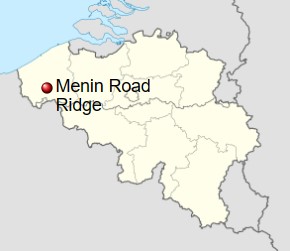
The Australian 6th Battalion was sent into warfare just two months after WWI began in August 1914. They met up with and joined the New Zealand Army, becoming the ANZAC (Australian and New Zealand Army Corps) from April 1915, while maintaining status as the Australian 6th Battalion until the unit was evacuated in December 1915. The Australian 6th Battalion fought German troops on the Western Front alongside the Allies. They were a good battalion, but for most of the time, there were no major decorations awarded…until. in September 1917, while serving in Belgium, Lieutenant Frederick Birks was awarded the only Victoria Cross ever granted within the unit. Sadly, Birks was killed in action the following day.
The Victoria Cross (VC) is “the highest and most prestigious decoration of the British honors system. It is awarded for valor ‘in the presence of the enemy’ to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously.” On September 17th, Birks’ battalion was moving parallel to a German line, with the orders to attack and capture the German line and blow them up. The men began moving toward their positions from Zillebeke on the night of September 18th, and immediately came under fire from gas shells. September 19th found the men holding their line, while the battalion prepared to attack the German line the next day. The battle that ensued became known as the Battle of Menin Road. Masked by a “light drizzle” of rain at 4am on  September 20th, the Germans sent barrages in front of and behind the battalion’s position. The battalion began their advanced at 5:40am. Birks and a corporal met the first German resistance and took two machine-gun positions, as another group of officers rushed a strong post. The Germans attacked the group with bombs, seriously wounding the corporal. Birks had to continue on alone. Birks advanced to the rear of the pillbox and forced the occupants to surrender. Birks went on to lead an attack a series of dugouts and pillboxes on the edge of Glencorse Wood, and fought against machine gun and bombs. He also assisted in the reorganization and consolidation of Australian men who had drifted away from their unit. September 21st brought more enemy shelling in response to the movement of Allied artillery. The shelling buried some men in Birks’ platoon. Birks attempted to dig the men out, “standing exposed” in the effort, another shell aimed at the C Coy post killed Birks, and four others, before he could save them. For his actions at Ypres, Birks was posthumously awarded the Victoria Cross, the announcement was made on November 8, 1917.
September 20th, the Germans sent barrages in front of and behind the battalion’s position. The battalion began their advanced at 5:40am. Birks and a corporal met the first German resistance and took two machine-gun positions, as another group of officers rushed a strong post. The Germans attacked the group with bombs, seriously wounding the corporal. Birks had to continue on alone. Birks advanced to the rear of the pillbox and forced the occupants to surrender. Birks went on to lead an attack a series of dugouts and pillboxes on the edge of Glencorse Wood, and fought against machine gun and bombs. He also assisted in the reorganization and consolidation of Australian men who had drifted away from their unit. September 21st brought more enemy shelling in response to the movement of Allied artillery. The shelling buried some men in Birks’ platoon. Birks attempted to dig the men out, “standing exposed” in the effort, another shell aimed at the C Coy post killed Birks, and four others, before he could save them. For his actions at Ypres, Birks was posthumously awarded the Victoria Cross, the announcement was made on November 8, 1917.

 The American Revolutionary War actually began on April 19, 1775, with the Battles of Lexington and Concord. At that time, it wasn’t considered a full-blown war, and attempts were still being made by July 5, 1775, to avoid that full-blown war. The Olive Branch Petition, adopted by the Second Continental Congress on July 5, 1775, and signed on July 8th, was the final attempt to avoid the full-blown war between Great Britain and the Thirteen Colonies in America, that became known as the American Revolutionary War, and ended with full independence of the United States.
The American Revolutionary War actually began on April 19, 1775, with the Battles of Lexington and Concord. At that time, it wasn’t considered a full-blown war, and attempts were still being made by July 5, 1775, to avoid that full-blown war. The Olive Branch Petition, adopted by the Second Continental Congress on July 5, 1775, and signed on July 8th, was the final attempt to avoid the full-blown war between Great Britain and the Thirteen Colonies in America, that became known as the American Revolutionary War, and ended with full independence of the United States.
It seemed that in the early days of the Revolutionary War, the main weapon was a volley of petitions and proclamations. The Second Continental Congress had already authorized the invasion of Canada more than a week earlier, but the Olive Branch Petition affirmed American loyalty to Great Britain, asking King George III to prevent further conflict. The petition was followed up with a July 6th Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms, making the success of the Olive Branch Petition unlikely in London. By August 1775, London officially declared the colonies to be in rebellion by the Proclamation of Rebellion, and the Olive Branch Petition was rejected by the British government. In fact, King George had refused to read it before declaring that the colonists were traitors.
The Second Continental Congress convened in May 1775. At that time, most and most delegates followed John Dickinson in his quest to reconcile with King George. He could not picture a world with an independent United States. I suppose there are always those people without a vision for the future. However, there was a small group of delegates, led by John Adams, who could see that war was inevitable, and that we would need to become independent of Great Britain. Nevertheless, there is a right time, so they decided that the wisest course of action was to remain quiet and wait for the opportune time to rally the people. This allowed Dickinson and his followers to pursue their own course for a reconciliation that would ultimately never happen.
Dickinson was the primary author of the Olive Branch Petition, along with Benjamin Franklin, John Jay, John Rutledge, and Thomas Johnson, all of whom also served on the drafting committee. Dickinson claimed that the colonies did not want independence, but rather, wanted more equitable trade and tax regulations. He asked that the King establish a lasting settlement between the Mother Country and the colonies “upon so firm a basis as to perpetuate its blessings, uninterrupted by any future dissensions, to succeeding generations in both countries” beginning with the repeal of the Intolerable Acts. The introductory paragraph of the letter named twelve of the thirteen colonies, all except Georgia. The letter was approved on July 5 and signed by John Hancock, President of the Second Congress, and by representatives of the named twelve colonies. It was sent to London on July 8, 1775, in the care of Richard Penn and Arthur Lee. Dickinson hoped that news of the Battles of Lexington and Concord combined with the “humble petition” would persuade the King to respond with a counterproposal or open negotiations.
Finally, Adams wrote to a friend, telling him that the petition served no purpose. Everyone knew that war was inevitable. Adams said that the colonies should have already raised a navy and taken the British officials prisoner. Unfortunately, the letter was intercepted by British officials and news of its contents reached Great Britain at about the same time as the petition itself. British advocates of a military response used Adams’ letter to claim that the petition itself was insincere, and it was rejected. The hostilities which Adams had foreseen undercut the petition, and the King had answered it before it even reached him.


With the King’s refusal to consider the petition, came the opportunity Adams and others needed to push for independence. Now the colonists viewed the King as unwilling and uninterested concerning the colonists’ grievances. The colonists finally knew that they had just two choices…complete independence or complete submission to British rule. They chose complete independence, and the rest, as we all know, is history.
 When a nation has a weapon that is so deadly to its enemy nations, those nations have no choice but to find a new way to beat that weapon. The German U-Boat was just such a weapon. Gliding along silently beneath the sea, the U-Boat put the ships of the Allied nations in constant and grave danger. That was one of the reasons that the British developed a fixation on their presence at sea. They depended on seaborne trade, and during World War I, the Germans were terrorizing that trade.
When a nation has a weapon that is so deadly to its enemy nations, those nations have no choice but to find a new way to beat that weapon. The German U-Boat was just such a weapon. Gliding along silently beneath the sea, the U-Boat put the ships of the Allied nations in constant and grave danger. That was one of the reasons that the British developed a fixation on their presence at sea. They depended on seaborne trade, and during World War I, the Germans were terrorizing that trade.
For much of Great Britain’s history, they enjoyed the luxury of having more battleships than the next two powers combined. For that reason, the Germans knew that they would have to concentrate their efforts on attacking vulnerable shipping lanes to disrupt the British war effort. They didn’t care if there were passengers on those ships. They didn’t care about loss of life or supplies. They had one plan…to dominate the seas. German submarines became a menace to the merchant navy. Something had to change, so the British came up with a plan to counter the U-boat threat. The plan involved disguising armed vessels as harmless trawlers to  lure the submarines in and then wipe them out. The answer to the U-boat were disguised vessels…decoys, known as Q-ships.
lure the submarines in and then wipe them out. The answer to the U-boat were disguised vessels…decoys, known as Q-ships.
Knowing that the U-Boats were under orders to attack just about anything. The Q-ships hid naval guns behind pivoting panels. It was the Sun Tzu tenet of “hold out baits to entice the enemy.” The Q-ships pretended to be disabled and when the U-Boats show up for the kill, the Q-ships went into action. Guns and additional crew had been concealed by hinges that could be dropped at a moment’s notice. The U-boats of World War I had limited range and carrying capacity, so the captains were nervous about wasting their torpedoes. Also, while the U-Boats of World War II were more capable of lang periods of time submerged, the U-Boats of World War I, had limited capability, so they preferred to use the submarine’s main gun to subdue ships whenever possible.
As the U-Boats came into sight of the Q-ship, the Q-ship’s crew would pretend to panic and abandon the ship to  draw the submarine in close. The U-Boats, once lured in, were at the mercy of the Q-ships. The Q-ships began to drop their depth charges as soon as the submarine tried to escape. It was a dangerous game to play and required a brave crew to pull off the ruse, and it was not always successful. Some Q-ships were lost, but because of their efforts the threat of submarines in World War I were lessened. The plan was to try the tactic again in World War II, but ships were in very short supply. The tactic of using decoy ships was much more limited but was also used by the Germans and Americans. While it wasn’t a major tactical warfare practice during the two wars, it was effective while it was used.
draw the submarine in close. The U-Boats, once lured in, were at the mercy of the Q-ships. The Q-ships began to drop their depth charges as soon as the submarine tried to escape. It was a dangerous game to play and required a brave crew to pull off the ruse, and it was not always successful. Some Q-ships were lost, but because of their efforts the threat of submarines in World War I were lessened. The plan was to try the tactic again in World War II, but ships were in very short supply. The tactic of using decoy ships was much more limited but was also used by the Germans and Americans. While it wasn’t a major tactical warfare practice during the two wars, it was effective while it was used.
 The New World (later the United States of America) was a pretty rough place in 1710. Great Britain owned a small portion of the whole of the New World, and the rest was often vied for against the French and other nations. That year, the mayor of Albany, New York, Pieter Schuyler, arranged a meeting between Queen Anne and five Indian Kings who wanted to request her aid, militarily. The Four Indian Kings or Four Kings of the New World were three Mohawk chiefs from one of the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy and a Mahican of the Algonquian peoples. Five chiefs set out on the journey, but one died in mid-Atlantic. The three Mohawk Kings were Sa Ga Yeath Qua Pieth Tow of the Bear Clan, called King of Maquas, with the Christian name Peter Brant (grandfather of Mohawk leader Joseph Brant); Ho Nee Yeath Taw No Row of the Wolf Clan, called King of Canajoharie (“Great Boiling Pot”), or John of Canajoharie; and Tee Yee Ho Ga Row, meaning “Double Life”, of the Wolf Clan, also called Hendrick Tejonihokarawa or King Hendrick. The Mahican chief was Etow Oh Koam of the Turtle Clan, mistakenly identified in his portrait as Emperor of the Six Nations. The Algonquian-speaking Mahican people were not part of the Iroquois Confederacy.
The New World (later the United States of America) was a pretty rough place in 1710. Great Britain owned a small portion of the whole of the New World, and the rest was often vied for against the French and other nations. That year, the mayor of Albany, New York, Pieter Schuyler, arranged a meeting between Queen Anne and five Indian Kings who wanted to request her aid, militarily. The Four Indian Kings or Four Kings of the New World were three Mohawk chiefs from one of the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy and a Mahican of the Algonquian peoples. Five chiefs set out on the journey, but one died in mid-Atlantic. The three Mohawk Kings were Sa Ga Yeath Qua Pieth Tow of the Bear Clan, called King of Maquas, with the Christian name Peter Brant (grandfather of Mohawk leader Joseph Brant); Ho Nee Yeath Taw No Row of the Wolf Clan, called King of Canajoharie (“Great Boiling Pot”), or John of Canajoharie; and Tee Yee Ho Ga Row, meaning “Double Life”, of the Wolf Clan, also called Hendrick Tejonihokarawa or King Hendrick. The Mahican chief was Etow Oh Koam of the Turtle Clan, mistakenly identified in his portrait as Emperor of the Six Nations. The Algonquian-speaking Mahican people were not part of the Iroquois Confederacy.
When the kings arrived in London, they were treated like diplomats. They were transported through the streets of the city in Royal carriages and received by Queen Anne at the Court of Saint James Palace. They visited the Tower of London and Saint Paul’s Cathedral as well, and they got to tour and do things all over London to honor their visit. They watched a review of the Guards in Hyde Park, visited the Banqueting House and Chapel at Whitehall, and they were taken on the Queen’s barge to Greenwich Hospital and the Woolwich Arsenal, where they heard a saluting cannonade. They listened to sermons in the city’s churches. They were guests of  honor at a dinner hosted by the Board of Trade and were privately entertained by William Penn at the Taverne du Diable at Charing Cross. They attended a performance of Powell’s Marionettes at Punch’s Theater; a presentation of Macbeth where they got to sit on the stage. I’m sure the people of the city were quite curious about these “wild men” who had come to their city. Their clothing was so different from the sophisticated garb that was normally seen gracing the royal carriages. Still, the Indians were probably wearing their finest clothing too, and in the New World, it was probably top of the line. The queen wanted to commemorate the diplomatic visit, so the Crown commissioned Jan Verelst to paint the portraits of the Four Kings. These paintings hung in Kensington Palace until 1977, when Queen Elizabeth II had them relocated to the National Archives of Canada. She unveiled them in Ottawa.
honor at a dinner hosted by the Board of Trade and were privately entertained by William Penn at the Taverne du Diable at Charing Cross. They attended a performance of Powell’s Marionettes at Punch’s Theater; a presentation of Macbeth where they got to sit on the stage. I’m sure the people of the city were quite curious about these “wild men” who had come to their city. Their clothing was so different from the sophisticated garb that was normally seen gracing the royal carriages. Still, the Indians were probably wearing their finest clothing too, and in the New World, it was probably top of the line. The queen wanted to commemorate the diplomatic visit, so the Crown commissioned Jan Verelst to paint the portraits of the Four Kings. These paintings hung in Kensington Palace until 1977, when Queen Elizabeth II had them relocated to the National Archives of Canada. She unveiled them in Ottawa.
The four kings were quite a spectacle in London, they were all described in a contemporary pamphlet as being in shape, muscular and within an inch or two of being six feet tall. Their complexions were described as being brown and their hair long and black.” Their visages are very awful and majestick, and their features regular enough, though something of the austere and sullen.” Their faces are covered in art, probably meant to inspire terror during battle. They are described as polite, they will not refuse any drink or food that is offered to them. They loved English beef more than any other kind of food offered to them. The people of London also described them as healthy. “Their health is good, as is proper for primitives; they know no gout, dropsy, gravel, or fevers.”
While I’m sure the big city was awe inspiring for the Kings, they were really there on a mission…to requesting military aid for defense against the French, and the chiefs to ask for missionaries to offset the influence of French Jesuits, who had converted numerous Mohawk to Catholicism. When they met with Queen Anne the court was mourning for the death of the Prince of Denmark, so the four Indian Kings were dressed in all black attire when they met with her. Their address to her was read, they asked for military assistance and missionaries to lead them to “true religion.” After the reading, the chiefs presented the queen with several belts of wampum to signify their meeting. In return for the gifts of the wampum, the queen gave them a set of communion plates, with the royal cipher and coat of arms, for a future Mohawk chapel. (These are now divided between the Mohawk reservations at Brantford, Ontario, and Tyendinaga, near Kingston.) The Archbishop of Canterbury gave each of the chiefs a Bible bound in Turkey-red leather. When she heard their request, Queen Anne informed the Archbishop of Canterbury, Thomas Tenison. They authorized a mission, and Mayor Schuyler  had a chapel built the next year at Fort Hunter (located near the Mohawk “Lower Castle” village) along the Mohawk River. The queen also engaged the four men in conversation through their interpreter, Peter Schuyler’s brother, John. Queen Anne was very generous to the Kings and their people, sending a gift of a silver Communion set and a reed organ. The Mohawk village known as the “Lower Castle” became mostly Christianized village in the early 18th century, unlike the “Upper Castle” at Canajoharie further upriver, where there was no mission founded until 1769, when William Johnson, British agent to the Iroquois, built the Indian Castle Church, which still stands today.
had a chapel built the next year at Fort Hunter (located near the Mohawk “Lower Castle” village) along the Mohawk River. The queen also engaged the four men in conversation through their interpreter, Peter Schuyler’s brother, John. Queen Anne was very generous to the Kings and their people, sending a gift of a silver Communion set and a reed organ. The Mohawk village known as the “Lower Castle” became mostly Christianized village in the early 18th century, unlike the “Upper Castle” at Canajoharie further upriver, where there was no mission founded until 1769, when William Johnson, British agent to the Iroquois, built the Indian Castle Church, which still stands today.
During their visit to London, the Kings were lodged at The Crown and Cushion, in King Street, Covent Garden. Here they slept on beds for the first time and became accustomed to them. Thomas Arne was their host, he was an inn keep and an upholsterer, he was very kind and considerate to his visitors. Because of this, the Indians renamed him Cataraqui in a Mohawk christening ceremony. Cataraqui was the fort that has now become the city of Kingston, Ontario. I’m sure that they really missed those beds when they returned to the New World in May of 1710.
 I think most of us have heard about the Louisiana Purchase, but I don’t know if I really ever knew the whole story. Maybe it was taught in school, but somehow I missed it. It really was one of the great surprises in diplomatic history.
I think most of us have heard about the Louisiana Purchase, but I don’t know if I really ever knew the whole story. Maybe it was taught in school, but somehow I missed it. It really was one of the great surprises in diplomatic history.
French Foreign Minister Charles Maurice de Talleyrand because he was the foreign minister to French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte, was one of the most powerful men in the world. Talleyrand had convinced Napoleon that he could create a new French Empire in North America. The French had long had a rather weak claim to the vast area west of the Mississippi River known as Louisiana Territory. The Louisiana Territory was going to be his starting place for that power in North America. In 1800, Napoleon secretly signed a treaty with Spain that officially gave France full control of the territory. Then, Napoleon began preparing the French army to occupy New Orleans and bolster French dominion. President Thomas Jefferson heard about Napoleon’s plans in 1802. It was an alarming revelation, especially in light of Napoleon’s desire for world domination. having him in control of part of North America brought him a little close for comfort. Also, Jefferson knew that the United States would need to expand  westward beyond the Mississippi, but she could never challenge the French militarily for the territory. Jefferson’s minister in France, Robert Livingston, had a lot riding on his ability to negotiate an agreement whereby Napoleon would give the United States control of New Orleans, the gateway to the Mississippi River.
westward beyond the Mississippi, but she could never challenge the French militarily for the territory. Jefferson’s minister in France, Robert Livingston, had a lot riding on his ability to negotiate an agreement whereby Napoleon would give the United States control of New Orleans, the gateway to the Mississippi River.
Livingston’s initial attempts at reaching a diplomatic agreement failed, and the situation looked bleak, but then in early 1803, Jefferson sent his young Virginia friend James Monroe to Paris to assist Livingston. By that time Napoleon’s situation in Europe had changed for the worse. He had stirred things up enough that war between France and Great Britain seemed imminent. Napoleon could no longer spare the military resources needed to secure control of Louisiana Territory. Rather than lose the territory to a British takeover, Napoleon reasoned it would be better to sell Louisiana to the Americans.
So, in the end, it wasn’t the expert negotiating skills of Livingston and Monroe, but rather Napoleon’s need to unload the territory. On this day April 11, 1803, much to Livingston’s surprise, the French minister coolly asked, “What will you give for the whole?” He was offering no the whole of New Orleans, but the whole of Louisiana Territory. Livingston and Monroe knew that for whatever reason, they were being offered “the moon” and they  should jump on the opportunity. Livingston and Monroe discussed France’s proposed cost for the territory. Several weeks later, on April 30, 1803, the American emissaries signed a treaty with France for a purchase of the vast territory for $11,250,000.
should jump on the opportunity. Livingston and Monroe discussed France’s proposed cost for the territory. Several weeks later, on April 30, 1803, the American emissaries signed a treaty with France for a purchase of the vast territory for $11,250,000.
The move was a good one for Napoleon too, because a little more than two weeks later, Great Britain declared war on France. Napoleon had to abandoned his dreams of a North American empire with the sale of the Louisiana Territory, but he also achieved a goal that he thought more important. “The sale [of Louisiana] assures forever the power of the United States,” Napoleon later wrote, “and I have given England a rival who, sooner or later, will humble her pride.”

 When we think of the weapons of warfare, we think of guns, planes, tanks, and such, but there are weapons of warfare that while seemingly far less lethal, are still deadly…in other ways. Economic warfare is something I would never have considered, even though it makes perfect sense. The Germans in World War II thought of every possible weapon, or very close to it. If a nation has no money to bankroll a war, they are very likely going to lose. That was the position that Germany wanted to put Great Britain in during World War II. They decided on an age-old plan…if you’re a criminal that is. Counterfeiting money to tank the economy.
When we think of the weapons of warfare, we think of guns, planes, tanks, and such, but there are weapons of warfare that while seemingly far less lethal, are still deadly…in other ways. Economic warfare is something I would never have considered, even though it makes perfect sense. The Germans in World War II thought of every possible weapon, or very close to it. If a nation has no money to bankroll a war, they are very likely going to lose. That was the position that Germany wanted to put Great Britain in during World War II. They decided on an age-old plan…if you’re a criminal that is. Counterfeiting money to tank the economy.
The year was 1942 and for the purpose of artificially causing inflation of the British pound, leading to the economic collapse of the competition, while simultaneously funding some of their own projects, the production of the British “White Notes” was about to start. It would not start in Britain, however. These “White Notes” would be made behind the gates of Sachsenhausen concentration camp. The Germans decided to begin counterfeiting British banknotes. These tactics were considered particularly wrong by the German soldiers themselves, basically sneaky and unprofessional. However, soon after World War II, it became common practice for different countries to counterfeit the currency of their opposition in times of war. Evil knows no bounds.
The first attempt at counterfeiting, known as Operation Andrew, failed because of disagreements between top brass inside of the Nazi Party. Friederich Walter Bernhard Krueger was placed in charge of Germany’s second attempt at counterfeiting British notes. The second operation’s codename was Bernhard because that is what Krueger was called. In preparation for the production, Bernhard assembled a team of about 140 men/prisoners. Some historians have suggested that it was as many as 300. These men were told they would receive better treatment and special perks like radio, newspapers, warm barracks, if they participated in the operation. The men had nothing to lose. All they had to do was counterfeit 400,000 British banknotes a month.
After a year of hard work, and the prisoners finally successfully counterfeited the British White Note. By 1945, conservative estimates figure 70,000,000 notes were printed by the inmates. It was a cache worth upwards of £100,000,000. In order to complete this herculean task, the team of counterfeiters studied vast quantities of authentic White Notes. They broke this massive task up into seven smaller tasks, each one seemingly more difficult than the last. “These tasks included: Discovering secret security marks, Engraving the vignette, Perfecting the paper, Creating identical ink, Solving the serial numbering system, Re-creating the signatures, dates and places of origin, and Printing the notes. The men found no fewer than 150 different security marks hidden on the White Notes. There were intentional minor defects and flaws that the Bank of England incorporated as anti-counterfeiting devices. To make things even harder, these security devices were different for each denomination. Nonetheless, in short order, the counterfeit team produced a plate for each denomination: £5, £10 £20 and £50.” The plan was coming together and soon they were ready to execute it.
The plan was to fly over and drop the counterfeit money from the planes. Once it was laundered and in the hands of the people, they could spend it and because there was no real backing for the money, the economy would tank. The operation went on for a time, but with the late February and early March 1945 advance of the Allied armies, all production of notes at Sachsenhausen ceased. The equipment and supplies were packed and transported, with the prisoners, to the Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp in Austria, arriving on 12 March. 
 They had to hide the evidence. They didn’t give up on the process, however. Shortly afterwards Krüger arranged a transfer of the equipment to the Redl-Zipf series of tunnels so production could be restarted. The order to resume production was soon rescinded, however, and the prisoners were ordered to destroy the cases of money they had with them. The equipment and any money not burned was loaded onto trucks and sunk in the Toplitz and Grundlsee lakes.
They had to hide the evidence. They didn’t give up on the process, however. Shortly afterwards Krüger arranged a transfer of the equipment to the Redl-Zipf series of tunnels so production could be restarted. The order to resume production was soon rescinded, however, and the prisoners were ordered to destroy the cases of money they had with them. The equipment and any money not burned was loaded onto trucks and sunk in the Toplitz and Grundlsee lakes.

 A military-free zone…is there such a place? Most of us don’t think so, but there is, actually. In reality, I can’t imagine fighting a war in Antarctica, but the area has actually been involved in a few disputes. Since the 1800s a number of nations, including Great Britain, Australia, Chile and Norway, have laid claim to parts of Antarctica. I think mostly the purpose for most nations is scientific research, but people have also taken trips across the frozen landscape as a way to challenge themselves. Of course, they didn’t do that in the 1800s.
A military-free zone…is there such a place? Most of us don’t think so, but there is, actually. In reality, I can’t imagine fighting a war in Antarctica, but the area has actually been involved in a few disputes. Since the 1800s a number of nations, including Great Britain, Australia, Chile and Norway, have laid claim to parts of Antarctica. I think mostly the purpose for most nations is scientific research, but people have also taken trips across the frozen landscape as a way to challenge themselves. Of course, they didn’t do that in the 1800s.
Over the years, the competing claims led to diplomatic disputes and even armed clashes. In 1948, Argentine military forces fired on British troops in an area claimed by both nations. Different nations, over the years have disputed lands and fought wars over ownership, and I guess that Antarctica was no different…even if I can’t imagine fighting over a frozen piece of land that, while it is 5,400,000 square miles of land, it is largely covered with ice and snow year round. Still, it seems to me that a continent that is that big would have plenty of room for everyone, but that did not settle the disputes.
Due to the increased number and type of incidents, together with evidence that the Soviet Union was becoming more interested in Antarctica, the United States decided to propose that the continent be made a trustee of the United Nations. This idea was rejected when none of the other nations with interests on the continent would agree to cede their claims of sovereignty to an international organization. That idea didn’t really go over too well either. By the 1950s, some officials in the United States began to press for a more active United States role in Antarctica, believing that the continent might have military potential as an area for nuclear tests. It looked like something was going to have to be done. President Dwight D Eisenhower took a different approach. US diplomats, working with their Soviet counterparts, worked out a treaty that set aside Antarctica as a military-free zone and postponed settling territorial claims for future debate. There could be “no military presence on the continent, and no testing of weapons of any sort, including nuclear weapons. Scientific ventures were allowed, and scientists would not be prohibited from traveling through any of the areas claimed by various nations.” Since the treaty did not directly tamper with issues of territorial sovereignty in Antarctica, the involved 
 parties included all nations with territorial claims on the continent. As such, the treaty marked a small but significant first step toward US-Soviet arms control and political cooperation. On December 1, 1959, twelve nations, including the United States and the Soviet Union, sign the Antarctica Treaty, which bans military activity and weapons testing on that continent. It was the first arms control agreement signed in the Cold War period. The treaty went into effect in June 1961, and its policies continue to govern Antarctica to this day.
parties included all nations with territorial claims on the continent. As such, the treaty marked a small but significant first step toward US-Soviet arms control and political cooperation. On December 1, 1959, twelve nations, including the United States and the Soviet Union, sign the Antarctica Treaty, which bans military activity and weapons testing on that continent. It was the first arms control agreement signed in the Cold War period. The treaty went into effect in June 1961, and its policies continue to govern Antarctica to this day.
 World War II was finally winding down. Germany had surrendered. Japan was still a problem, but they were losing their strength too. Hitler committed suicide on April 30, and now it was over for Germany. I fact, it was time for celebration. So on May 8, 1945, both Great Britain and the United States celebrated Victory in Europe Day. The day would come to be known as V-E Day, and cities in both nations, as well as formerly occupied cities in Western Europe, put out flags and banners, rejoicing in the defeat of the oppressive Nazi war machine.
World War II was finally winding down. Germany had surrendered. Japan was still a problem, but they were losing their strength too. Hitler committed suicide on April 30, and now it was over for Germany. I fact, it was time for celebration. So on May 8, 1945, both Great Britain and the United States celebrated Victory in Europe Day. The day would come to be known as V-E Day, and cities in both nations, as well as formerly occupied cities in Western Europe, put out flags and banners, rejoicing in the defeat of the oppressive Nazi war machine.
That was 75 years ago today that the first V-E Day was celebrated. It is hard to believe that it was 75 years ago. I wasn’t born then, of course, but over the years of researching World War II, I almost feel like those events were just yesterday. Researching World War II bought the events…good, bad, and horrific to life for me. Our men and women, as well as those of the Allies were brave and noble people. They were fighting against two oppressive regimes, both of whom had murdered their own people and the people of the nations around them. The Nazi war machine had marched through Europe, terrorizing the people around them. The Luftwaffe planes bombed many cities, taking no concern for the civilians lost. Life meant nothing to them…except for their own. Hitler was greedy for power, and wanted to bring Nazism to the whole world. Thankfully they were stopped before they could complete their reign of terror.
German troops throughout Europe finally laid down their arms on May 8, 1945 in Prague. The Soviets had lost 8,000 soldiers by the time of the surrender, but the Germans had lost considerably more. They laid down their arms too, in Copenhagen and Oslo, at Karlshorst, near Berlin, in northern Latvia, and on the Channel Island of Sark. The German surrender was almost complete in that final cease-fire. More surrender documents were signed in Berlin and in eastern Germany.
The main concern of many German soldiers was to elude the grasp of Soviet forces, to keep from being taken prisoner. About 1 million Germans attempted a mass exodus to the West when the fighting in Czechoslovakia ended, but were stopped by the Russians and taken captive. The Russians captured approximately 2 million  prisoners just before and after the German surrender. At the same time. 13,000 British soldiers were released and sent back to Great Britain. Of course, there were still pockets of confrontations into May 9th, and the Soviets lost an additional 600 soldiers in Silesia before the Germans finally surrendered. Those skirmishes pushed back the V-E Day celebration until the ninth in Moscow, with a radio broadcast salute from Stalin himself, “The age-long struggle of the Slav nations has ended in victory. Your courage has defeated the Nazis. The war is over.” It was a great day for all the people of the Allied nations, and the people of the world, with the exception of the Germans, Japanese, and the Axis nations. Good over evil.
prisoners just before and after the German surrender. At the same time. 13,000 British soldiers were released and sent back to Great Britain. Of course, there were still pockets of confrontations into May 9th, and the Soviets lost an additional 600 soldiers in Silesia before the Germans finally surrendered. Those skirmishes pushed back the V-E Day celebration until the ninth in Moscow, with a radio broadcast salute from Stalin himself, “The age-long struggle of the Slav nations has ended in victory. Your courage has defeated the Nazis. The war is over.” It was a great day for all the people of the Allied nations, and the people of the world, with the exception of the Germans, Japanese, and the Axis nations. Good over evil.

