History
 As long has there have been road trips with children, there have been bored children, asking, “When do we get there?” They don’t understand that one of the best parts of a road trip is the time spent on the road. The destination is the end of the adventure, not necessarily the adventure itself. Invariably, after the ten time that those precious little ones ask that dreaded question, tempers begin to flare. These days, cars come with built in DVD players to occupy the kids on the road trip, but back when I was a kid, those things didn’t exist.
As long has there have been road trips with children, there have been bored children, asking, “When do we get there?” They don’t understand that one of the best parts of a road trip is the time spent on the road. The destination is the end of the adventure, not necessarily the adventure itself. Invariably, after the ten time that those precious little ones ask that dreaded question, tempers begin to flare. These days, cars come with built in DVD players to occupy the kids on the road trip, but back when I was a kid, those things didn’t exist.
Somewhere along the way, someone…probably a frustrated parent…came up with the idea of allowing the kids to participate in the trip by giving them a steering wheel of their own, so they could help their parents drive. I do know that in January of 1955, a  man named Jack Fletcher of West Covina, California installed a plastic windshield and three miniature steering wheels in the back seat of his car to entertain his children, Janie, Johnny and Ricky, who were 3 years, 21 months, and 21 months respectively. Apparently, it was a good idea, at least for those children, because, the idea has hung around ever since. In fact, for Christmas, we got our great granddaughter a version that can sit on the floor in front of her, or even on her highchair tray. Now she can “help” her daddy drive too. As children get older, I’m sure that the novelty of a steering wheel wore off, but if you
man named Jack Fletcher of West Covina, California installed a plastic windshield and three miniature steering wheels in the back seat of his car to entertain his children, Janie, Johnny and Ricky, who were 3 years, 21 months, and 21 months respectively. Apparently, it was a good idea, at least for those children, because, the idea has hung around ever since. In fact, for Christmas, we got our great granddaughter a version that can sit on the floor in front of her, or even on her highchair tray. Now she can “help” her daddy drive too. As children get older, I’m sure that the novelty of a steering wheel wore off, but if you  got a year or so of peace in the car, it’s worth the effort.
got a year or so of peace in the car, it’s worth the effort.
Of course, when I was a kid, there were mo car seats, and it wasn’t illegal to drive with your child on your lap. Many a child, me and my sisters included, learned to steer the car while seated on our daddy’s lap. It was great fun, and a memory we will always have. I suppose that today’s drivers, police officers, and child safety advocates would cringe at the thought of a child on the lap of the driver, and maybe it wasn’t the safest way to do things, but I don’t recall hearing about dozens of children dying in that manner either, so maybe the parents of yesteryear weren’t so careless after all. All I know, is that we had a great time on those road trips.
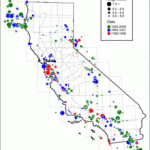 Earthquakes can happen anywhere, but there are areas that are more prone to earthquakes than other areas. When we think about that, we think of Alaska, California, or Japan, all of which experience daily earthquakes. Of course, there are many other places that get a lot of earthquakes. One such place is in Italy. The area around Sicily and Calabria are known as la terra ballerina, “the dancing land,” for the periodic seismic activity that strikes the region. I would have thought that with 12,000 earthquakes a year in Alaska, or 10,000 earthquakes a year in California, or 1,500 earthquakes in Japan, that any of these places would be called “the dancing land” before the area of Sicily and Calabria, which doesn’t have nearly as many.
Earthquakes can happen anywhere, but there are areas that are more prone to earthquakes than other areas. When we think about that, we think of Alaska, California, or Japan, all of which experience daily earthquakes. Of course, there are many other places that get a lot of earthquakes. One such place is in Italy. The area around Sicily and Calabria are known as la terra ballerina, “the dancing land,” for the periodic seismic activity that strikes the region. I would have thought that with 12,000 earthquakes a year in Alaska, or 10,000 earthquakes a year in California, or 1,500 earthquakes in Japan, that any of these places would be called “the dancing land” before the area of Sicily and Calabria, which doesn’t have nearly as many.
Nevertheless, the name was given and it stuck. While it may not have as many, the ones that hit there seem to be especially devastating. In 1693, 60,000 people were killed in southern Sicily by an earthquake, and in 1783 most of the Tyrrenian coast of Calabria was leveled by a massive earthquake that  killed 50,000. The quake of 1908 was particularly costly in terms of human life because it struck at at dawn, catching most people at home in bed rather than in the relative safety of the streets or fields. The December 28, 1908 earthquake which struck at 5:20am was the most destructive earthquake in recorded European history strikes the Straits of Messina in southern Italy. The cities of Messina in Sicily and Reggio di Calabria on the Italian mainland were leveled by the devastating quake. The earthquake and tsunami it caused killed an estimated 100,000 people. The main shock registered an estimated 7.5 magnitude on the Richter scale. It caused a devastating tsunami with 40-foot waves that washed over coastal towns and cities. The two major cities on either side of the Messina Straits–Messina and Reggio di Calabria, had about 90 percent of their buildings destroyed. The quake cut telegraph lines and damaged railway lines, seriously slowing down the relief efforts. To make matters worse, many of the remaining buildings were destroyed by hundreds of smaller
killed 50,000. The quake of 1908 was particularly costly in terms of human life because it struck at at dawn, catching most people at home in bed rather than in the relative safety of the streets or fields. The December 28, 1908 earthquake which struck at 5:20am was the most destructive earthquake in recorded European history strikes the Straits of Messina in southern Italy. The cities of Messina in Sicily and Reggio di Calabria on the Italian mainland were leveled by the devastating quake. The earthquake and tsunami it caused killed an estimated 100,000 people. The main shock registered an estimated 7.5 magnitude on the Richter scale. It caused a devastating tsunami with 40-foot waves that washed over coastal towns and cities. The two major cities on either side of the Messina Straits–Messina and Reggio di Calabria, had about 90 percent of their buildings destroyed. The quake cut telegraph lines and damaged railway lines, seriously slowing down the relief efforts. To make matters worse, many of the remaining buildings were destroyed by hundreds of smaller 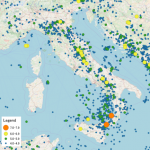 tremors over subsequent days. These tremors injured or killed rescuers. On December 30, King Victor Emmanuel III arrived aboard the battleship Napoli to inspect the devastation.
tremors over subsequent days. These tremors injured or killed rescuers. On December 30, King Victor Emmanuel III arrived aboard the battleship Napoli to inspect the devastation.
To make matters worse, a steady rain fell on the ruined cities, forcing the dazed and injured survivors, clad only in their nightclothes, to take shelter in caves, grottoes, and impromptu shacks built out of materials salvaged from the collapsed buildings. Veteran sailors could barely recognize the shoreline because long stretches of the coast had sunk several feet into the Messina Strait. The devastation was horrific. After all that, I can see why it is called la terra ballerina, “the dancing land.”
 There is a tradition in England and a few other nations like Canada and Ireland, that takes place the day after Christmas, called Boxing Day. It is an odd name for a holiday, but I think the purpose of the holiday far outweighs the name of the holiday. People might argue the original purpose of the holiday, but the most straightforward answer as to what it is about would be that, “We are a little greedy here in the England and Ireland in wanting a more extended holiday. It is not enough for us to have only Christmas Day celebrations, we have added to this another event called Boxing Day.” That might be one part of the picture, but the full answer is not that simple. But firstly, it has nothing to do with the sport of boxing.
There is a tradition in England and a few other nations like Canada and Ireland, that takes place the day after Christmas, called Boxing Day. It is an odd name for a holiday, but I think the purpose of the holiday far outweighs the name of the holiday. People might argue the original purpose of the holiday, but the most straightforward answer as to what it is about would be that, “We are a little greedy here in the England and Ireland in wanting a more extended holiday. It is not enough for us to have only Christmas Day celebrations, we have added to this another event called Boxing Day.” That might be one part of the picture, but the full answer is not that simple. But firstly, it has nothing to do with the sport of boxing.
Boxing Day is a national Bank Holiday. It is a day to spend with family and friends and to eat up all the leftovers of Christmas Day, but there is more to it than that. The origins of the day are filled with history and tradition. People have long disputed the origins of the name Boxing Day. The name is actually a reference to holiday gifts. A “Christmas Box” in Britain is a name for a Christmas present. Boxing Day was traditionally a day off for the servants and the day when they received a “Christmas Box” from the master. The servants would also go home on Boxing Day to give “Christmas Boxes” to their families.
Traditionally, a box to collect money for the poor was placed in churches on Christmas day. The boxes were  opened the next day…Boxing Day. The name refers to a nautical tradition. Great sailing ships when setting sail would have a sealed box containing money on board for good luck. Were the voyage a success, the box was given to a priest, opened at Christmas and the contents then given to the poor. Boxing Day is the 26th December is a national holiday in England and Ireland.
opened the next day…Boxing Day. The name refers to a nautical tradition. Great sailing ships when setting sail would have a sealed box containing money on board for good luck. Were the voyage a success, the box was given to a priest, opened at Christmas and the contents then given to the poor. Boxing Day is the 26th December is a national holiday in England and Ireland.
Boxing Day is a time to spend with family or friends, but usually not those seen on Christmas Day itself. In recent times, the day has begun to include many sports. Horse racing is particularly popular with meets all over the country. Many top football teams also play on Boxing Day. Boxing Day is a time when the British show their eccentric side by taking part in all kinds of silly activities. Bizarre traditions include swimming the icy cold English Channel, fun runs, and charity events. Until 2004, Boxing Day hunts were a traditional part of the day, but the ban on fox hunting has put an end to this in its usual sense. Hunters will still gather dressed resplendently in red hunting coats to the sound of the hunting horn. But, since it is now forbidden to chase the fox with dogs, they now follow artificially laid trails.
Another “sport” to emerge in recent years is shopping. Sadly, what was once a day of relaxation and family time sees the start of the sales. Sales used to start in January, post-New Year, but the desire to grab a bargain and for shops to off-load stock means many now begin on Boxing Day. This tradition makes me especially sad, because it is like Black Friday. By moving Black Friday shopping to Thanksgiving, and now post Christmas sales to Boxing Day, have soured many people to shopping on these days, and the whole purpose is defeated.

In Ireland, Boxing Day is also known as “Saint Stephen’s Day” named after the Saint stoned to death for believing in Jesus. In Ireland on Boxing, there was once a barbaric act carried out by the so-called “Wren Boys.” These boys would dress up and go out, and stone wren birds to death then carry their catch around the town knocking on doors and asking for money, the stoning representing what had happened to Saint Stephen. This terrible tradition has now stopped, thank goodness, but the Wrens Boys still dress up. Now, instead they parade around town and collect money for charity. I’m thankful that such a barbaric tradition, has now taken on a new look, and is now used for good.
 When most people think of Christmas, their minds think of Santa Clause, turkey dinners, and weeks of preparatory shopping, and yes those things are a part of Christmas for most people, but there is a far more important reason for the Christmas season…the birth of our Saviour, Jesus Christ, the Lord. Yes, I am aware that we don’t know the exact date of our Saviour’s birth, and many are quite certain that it was nowhere near December 25th, and in reality, not in winter. To most Christians, however, those minor details don’t matter, because we are talking about our Lord. It’s ok to celebrate Jesus anytime.
When most people think of Christmas, their minds think of Santa Clause, turkey dinners, and weeks of preparatory shopping, and yes those things are a part of Christmas for most people, but there is a far more important reason for the Christmas season…the birth of our Saviour, Jesus Christ, the Lord. Yes, I am aware that we don’t know the exact date of our Saviour’s birth, and many are quite certain that it was nowhere near December 25th, and in reality, not in winter. To most Christians, however, those minor details don’t matter, because we are talking about our Lord. It’s ok to celebrate Jesus anytime.
Most Christians think of gift giving as being symbolic of the greatest gift ever given…Jesus who came to earth to save us from our sin filled world by dying on the cross so that we would be able to go Heaven. Of course, no gift we could ever give could measure up to the gift Jesus gave us, but we can celebrate Jesus by having a giving spirit. After all, that is what Jesus was all about. I don’t mean presents, but rather the ultimate gift, the greatest love ever given…”For God so loved the world that He gave His only begotten Son, that whoever believes in Him should not perish but have everlasting life.” John 3:16. What great gift could there ever be than to give His life so that we could live, and what greater reason could there ever be to celebrate Jesus. The date error, if there is one, makes no difference…just God’s love.

Christmas means different things to different people, of course, but I think that the most important thing is to make sure that we don’t lose sight of the real reason for the season…the birth of the Saviour of the world. Before Jesus came,we had no hope. We were lost, and going to Hell. After Jesus lived, died, and rose again, everything changed and hope returned. For Christians, there is nothing more important. Jesus is our advocate with the Father. He is the the true meaning o grace. His git to us…salvation, was not something we could ever earn. we were lost and all hope was gone. Then Jesus was born, and we had a reason to celebrate again. Happy birthday Jesus, and Merry Christmas everyone.
 It was 1914, and World War I was in the 5th month of a 51 month offensive. The war effort was in a bit of a transition period, following the stalemate of the Race to the Sea and the indecisive result of the First Battle of Ypres. As leadership on both sides reconsidered their strategies, hostilities entered a bit of a lull. The men were hoping for a break in the action for Christmas that year, but they had to wait for their orders. When the orders came down, it was not to be a Christmas truce, but rather a Christmas strike. As the first men to go forth prepared to make the first advances, some men were killed, and some returned. It was the way of war. The leadership wanted to take advantage of the possibility that the enemy might not expect a Christmas attack. One of the younger men…17 years old to be exact, couldn’t help himself. He began to sing Silent Night.His superiors ordered it to be quiet. They feared that the enemy was waiting in the darkness.
It was 1914, and World War I was in the 5th month of a 51 month offensive. The war effort was in a bit of a transition period, following the stalemate of the Race to the Sea and the indecisive result of the First Battle of Ypres. As leadership on both sides reconsidered their strategies, hostilities entered a bit of a lull. The men were hoping for a break in the action for Christmas that year, but they had to wait for their orders. When the orders came down, it was not to be a Christmas truce, but rather a Christmas strike. As the first men to go forth prepared to make the first advances, some men were killed, and some returned. It was the way of war. The leadership wanted to take advantage of the possibility that the enemy might not expect a Christmas attack. One of the younger men…17 years old to be exact, couldn’t help himself. He began to sing Silent Night.His superiors ordered it to be quiet. They feared that the enemy was waiting in the darkness.
Then, a miracle occurred. In the week leading up to the 25th of December, French, German, and British soldiers crossed trenches to exchange seasonal greetings…and to talk. In some areas, men from both sides ventured into what was called no man’s land, because to go there was to risk death. Nevertheless, on that Christmas Eve and Christmas Day, things seemed different. The soldiers took a chance and stepped forward, hoping to convince their enemies that they only wanted to bury their dead, and hoping that it would be  agreeable to stop the fighting for one hour to bury the dead. As they buried their dead, with heavy hearts, someone suggested that they take Christmas Day off. This was totally against their orders, and they knew that at some point they were going to have to go back and follow their orders. They were going to have to become enemies again. Still, for now…for this day, they mingled and exchange food and souvenirs. There were joint burial ceremonies and prisoner swaps. Men played games of football with one another, giving one of the most memorable images of the truce. Peaceful behavior was not ubiquitous, however, and fighting continued in some sectors, while in others the sides settled on little more than arrangements to recover bodies. Several meetings ended in carol-singing. Someone commented, “How many times in a life do you actually meet your enemy face to face.” It was almost strange to them, because these “enemies” were not the monsters they expected them to be. These were simply men, just like they were. I’m sure the men were in shock. it’s hard to have your total view of your enemy change so drastically and then have to follow your orders, pickup your weapons, and shoot at the same men again. The Christmas truce (German: Weihnachtsfrieden; French: Trêve de Noël) was a series of widespread but unofficial ceasefires along the Western Front of World War I around Christmas 1914.
agreeable to stop the fighting for one hour to bury the dead. As they buried their dead, with heavy hearts, someone suggested that they take Christmas Day off. This was totally against their orders, and they knew that at some point they were going to have to go back and follow their orders. They were going to have to become enemies again. Still, for now…for this day, they mingled and exchange food and souvenirs. There were joint burial ceremonies and prisoner swaps. Men played games of football with one another, giving one of the most memorable images of the truce. Peaceful behavior was not ubiquitous, however, and fighting continued in some sectors, while in others the sides settled on little more than arrangements to recover bodies. Several meetings ended in carol-singing. Someone commented, “How many times in a life do you actually meet your enemy face to face.” It was almost strange to them, because these “enemies” were not the monsters they expected them to be. These were simply men, just like they were. I’m sure the men were in shock. it’s hard to have your total view of your enemy change so drastically and then have to follow your orders, pickup your weapons, and shoot at the same men again. The Christmas truce (German: Weihnachtsfrieden; French: Trêve de Noël) was a series of widespread but unofficial ceasefires along the Western Front of World War I around Christmas 1914.
The Christmas Truces of 1914, while wonderful for the men, were not to be a Christmas tradition in World War I. The following year, a few units arranged ceasefires but the truces were not nearly as widespread as in 1914.  This was, in part, due to strongly worded orders from the high commands of both sides prohibiting truces. It was evident that while the mini-mutiny of 1914 was tolerated and the men were not punished, that this would not be tolerated in the future. It really didn’t matter, because the Soldiers were no longer amenable to truce by 1916. The war had become increasingly bitter after devastating human losses suffered during the battles of the Somme and Verdun, and the use of poison gas. While a Christmas truce would be nice in theory, bitter and angry feelings on both sides of a war make it an impractical idea. Still, in 1914, the miracle of the Christmas Truce was a wonderful treat for the men on all sides of a bitter war.
This was, in part, due to strongly worded orders from the high commands of both sides prohibiting truces. It was evident that while the mini-mutiny of 1914 was tolerated and the men were not punished, that this would not be tolerated in the future. It really didn’t matter, because the Soldiers were no longer amenable to truce by 1916. The war had become increasingly bitter after devastating human losses suffered during the battles of the Somme and Verdun, and the use of poison gas. While a Christmas truce would be nice in theory, bitter and angry feelings on both sides of a war make it an impractical idea. Still, in 1914, the miracle of the Christmas Truce was a wonderful treat for the men on all sides of a bitter war.
 When disaster strikes, and homes are in ruin, people try to come together to help return a sense of normalcy to the people affected by the disaster. Disasters happen quickly, and the devastation is often heavy. It is a difficult thing to help people heal. While one disaster or event is often the same as another in terms of damage, something we somehow don’t connect to that same kind of devastation, is war. I’m not sure why, but when I think of war,I picture a battle held in the middle of a vast desert, with no civilization in sight. of course, when I really think about it, I now that is not reality, but rather my mind trying to fit war into a box of civility. In reality, there is nothing civil about war. Gun shots, bombs, and land mines aren’t picky about who they hit. Soldier or civilian…all are fair game in a war. And towns…well, there is often little to nothing left after a bomb hits.
When disaster strikes, and homes are in ruin, people try to come together to help return a sense of normalcy to the people affected by the disaster. Disasters happen quickly, and the devastation is often heavy. It is a difficult thing to help people heal. While one disaster or event is often the same as another in terms of damage, something we somehow don’t connect to that same kind of devastation, is war. I’m not sure why, but when I think of war,I picture a battle held in the middle of a vast desert, with no civilization in sight. of course, when I really think about it, I now that is not reality, but rather my mind trying to fit war into a box of civility. In reality, there is nothing civil about war. Gun shots, bombs, and land mines aren’t picky about who they hit. Soldier or civilian…all are fair game in a war. And towns…well, there is often little to nothing left after a bomb hits.
During World War II, London was often the targets of the German Luftwaffe, and the bombs they dropped, devastated many parts of London. From September 7, 1940, London was systematically bombed by the Luftwaffe for 56 out of the following 57 days and nights, in what was called “The Blitz.” Most notable was a large daylight attack against London on September 15th. Of course, these weren’t the only bombings, and the people of London didn’t know when or if it was safe to be out of the bomb shelters. Life in London had taken on eerie gloom,as people continued to seek refuge in the bomb shelters, because that was the only safe place to be. The biggest problem was that the bomb shelters were also gloomy, boring, and generally depressing. The children probably suffered the most, because kids don’t really understand all this hatred and killing. Their world had been turned upside down…and they didn’t know why.
By the end of 1940, 24,000 civilians had been killed in the Blitz and hundreds of thousands made homeless. In November, German bombers had obliterated Coventry city center and there had been particularly fierce raids on Manchester and Liverpool in the days leading up to Christmas. The public were now mourning the loss of their loved ones on the home front and in combat, as well as praying for the 41,000 British soldiers captured on the continent, but it was the children, in my mind, who suffered the most. Their childlike innocence was completely destroyed, along with their homes. Their parents, and other adults made the decision to change their little world, even if it was only for a short time. They didn’t have much, but they put together whatever they could to lift the spirits of these scared children. Christmas parties were held for the children and the shelter walls were decorated with paper chains and decorations, while amateur singing nights, discussion groups, and sewing circles were held regularly.
In order to avoid the bombs, many families spent some of the holidays in air-raid shelters and other places of refuge. They decked out their temporary homes with makeshift decorations…and very short Christmas trees because of the height of the shelters. Even if gas or electricity was available, Christmas dinner would have still been an amazing feat, because turkey was so expensive. Most people made do with other cuts of meat, which were still expensive. A family of four’s weekly meat ration probably wouldn’t even cover the cost of a small chicken. One alternative was home-raised chickens or rabbits, much to the shock of young children who often regarded them as pets. Home-grown vegetables and chutneys would have also made the table. Rations were  scrimped and saved including ham, bacon, butter, suet, and margarine. The tea and sugar rations were increased in the week before Christmas. Very little fruit was imported and nuts were very costly. Consequently, cooks had to improvise Christmas cakes and puddings devoid of dried fruit and marzipan, using instead sponge or other unlikely ingredients. Alcohol was available but, horribly expensive. And there would be no after-dinner French cheeses or brandy due to the German occupation. It was a poor Christmas party in comparison to those in the past, but it served to remind all the people that Christmas is more about the blessings in life, than it is about the things we are given.
scrimped and saved including ham, bacon, butter, suet, and margarine. The tea and sugar rations were increased in the week before Christmas. Very little fruit was imported and nuts were very costly. Consequently, cooks had to improvise Christmas cakes and puddings devoid of dried fruit and marzipan, using instead sponge or other unlikely ingredients. Alcohol was available but, horribly expensive. And there would be no after-dinner French cheeses or brandy due to the German occupation. It was a poor Christmas party in comparison to those in the past, but it served to remind all the people that Christmas is more about the blessings in life, than it is about the things we are given.

 Two days ago, I wrote a story in celebration of my Uncle George Wave Hushman’s 92nd birthday. Little did I now that it would also be the day of his home-going, but it was. It is a rather rare thing, except in infant deaths, for someone to be born and die on the same day, but that is what my Uncle George did. He was born on December 20, 1926 in Rock River, Wyoming, and went home to Heaven on December 20, 2018 in Mills, Wyoming…exactly 92 years later.
Two days ago, I wrote a story in celebration of my Uncle George Wave Hushman’s 92nd birthday. Little did I now that it would also be the day of his home-going, but it was. It is a rather rare thing, except in infant deaths, for someone to be born and die on the same day, but that is what my Uncle George did. He was born on December 20, 1926 in Rock River, Wyoming, and went home to Heaven on December 20, 2018 in Mills, Wyoming…exactly 92 years later.
Uncle George led an unusual life, so I guess I shouldn’t be surprised that his home-going would be just as unusual. He lost his mother when he was just eleven years old. I’m not sure how long after her passing, before he was sent to the Wyoming State Children’s Home in Casper, Wyoming, but during those years, his guardian was listed as Ethel S. Kittle. Uncle George didn’t know much about his family for most of his life, but his dad, also named George Wave Hushman was in the Navy, stationed in the Philippines when he was killed in action on November 21, 1943…Uncle George was just 17 years old. To his knowledge, that left him very much alone in this world, except for his friend James Wesley Saint John ‘Wes” and Wes’ family, who had unofficially adopted him as a part of their family. Wes, who was three years older than Uncle George was lost at sea on September 9, 1943. While Uncle George didn’t know his father well, he did know his friend, and I find it unusual that he enlisted in the Navy too, but he did. His Draft Card listed his next of kin as WE Saint John. He mustered out on May 31, 1944, and was later listed among the wounded. I am grateful that he was one of those who made it home from the war. Uncle George, was first assigned to LCI(L) 23…Landing Craft Infantry (L)23. He later mustered out on USS Gurke (DD-783), a Gearing-class destroyer.
By 1946, Uncle George was released from the Navy, and was living in Mills, Wyoming, and falling in love with my aunt, Evelyn Byer, whom he married on September 1, 1947. He had found the love of his life, and he only wanted to be with her for the rest of his life…missing her terribly after she passed away on May 4, 2015. Aunt 
 Evelyn and Uncle George would be blessed with five children, George Hushman, Susie Young, Shelly Campbell, Shannon Limmer, and Greg Hushman. They were also blessed with many grandchildren, great grand children, and great great grandchildren. Uncle George was also blessed to be able to reunite with his half siblings over the years, although their passings brought him a feeling of losing them twice. Now that they are together again in Heaven, Uncle George will never have to be away from his beloved Evelyn, or the other loved ones who had gone before him. Rest in peace Uncle George. We love and miss you very much.
Evelyn and Uncle George would be blessed with five children, George Hushman, Susie Young, Shelly Campbell, Shannon Limmer, and Greg Hushman. They were also blessed with many grandchildren, great grand children, and great great grandchildren. Uncle George was also blessed to be able to reunite with his half siblings over the years, although their passings brought him a feeling of losing them twice. Now that they are together again in Heaven, Uncle George will never have to be away from his beloved Evelyn, or the other loved ones who had gone before him. Rest in peace Uncle George. We love and miss you very much.
 The September 6, 1620 trip to the new world, in which 102 passengers, who had been dubbed Pilgrims by William Bradford, one of the passengers who would become the first governor of Plymouth Colony, was a crowded, grueling trip on the Mayflower to a new life in the New World. The trip was filled with hardship, and sometimes even loss. Nevertheless, the pilgrims knew it had to be taken. The situation actually began in 1606, when a group of reform-minded Puritans in Nottinghamshire, England, founded their own church, that was separate from the state-sanctioned Church of England. This was truly the reason why “Freedom of Religion” is such an important part of our constitution. Many people dispute that fact that our nation was formed on religious principles, but it was, from the very core of the move here.
The September 6, 1620 trip to the new world, in which 102 passengers, who had been dubbed Pilgrims by William Bradford, one of the passengers who would become the first governor of Plymouth Colony, was a crowded, grueling trip on the Mayflower to a new life in the New World. The trip was filled with hardship, and sometimes even loss. Nevertheless, the pilgrims knew it had to be taken. The situation actually began in 1606, when a group of reform-minded Puritans in Nottinghamshire, England, founded their own church, that was separate from the state-sanctioned Church of England. This was truly the reason why “Freedom of Religion” is such an important part of our constitution. Many people dispute that fact that our nation was formed on religious principles, but it was, from the very core of the move here.
On November 11, 1620, the Mayflower anchored at what is now Provincetown Harbor, Cape Cod. Of course, it was mandatory that they scout out the new land to make sure it  was safe before bringing the women and children there. Before going ashore, 41 male passengers…heads of families, single men and three male servants…signed the famous Mayflower Compact, agreeing to submit to a government chosen by common consent and to obey all laws made for the good of the colony. Over the next month, several small scouting groups were sent ashore to collect firewood and scout out a good place to build a settlement.
was safe before bringing the women and children there. Before going ashore, 41 male passengers…heads of families, single men and three male servants…signed the famous Mayflower Compact, agreeing to submit to a government chosen by common consent and to obey all laws made for the good of the colony. Over the next month, several small scouting groups were sent ashore to collect firewood and scout out a good place to build a settlement.
Around December 10, one of these groups found a harbor they liked on the western side of Cape Cod Bay. They returned to the Mayflower to tell the other passengers, but bad weather prevented them from docking until December 18. After exploring the region, the settlers chose a cleared area previously occupied by members of a local Native American tribe, the Wampanoag. The travel weary pilgrims finally prepared to begin their new settlement, Plymouth Colony. The Wampanoag tribe had abandoned the village several years earlier, after an outbreak of European disease. That winter of 1620-1621 was brutal, as the Pilgrims struggled to build their settlement, find food and ward off sickness. They were less than highly successful, because by spring, 50 of the original 102 Mayflower passengers were dead. The remaining settlers made contact with returning  members of the Wampanoag tribe, and in March they signed a peace treaty with a tribal chief, Massasoit. Aided by the Wampanoag, especially the English-speaking Squanto, the Pilgrims were able to plant crops…especially corn and beans…that were vital to their survival. The Mayflower and its crew left Plymouth to return to England on April 5, 1621.
members of the Wampanoag tribe, and in March they signed a peace treaty with a tribal chief, Massasoit. Aided by the Wampanoag, especially the English-speaking Squanto, the Pilgrims were able to plant crops…especially corn and beans…that were vital to their survival. The Mayflower and its crew left Plymouth to return to England on April 5, 1621.
Over the next several decades, more and more settlers made the trip across the Atlantic to Plymouth, which gradually grew into a prosperous shipbuilding and fishing center. In 1691, Plymouth was incorporated into the new Massachusetts Bay Association, ending its history as an independent colony. And the rest, as they say, is history.
 While most of the economy in Southeast Texas depended on agriculture, cattle ranching, and the lumber business in the 19th century, things were about to change. The presence of oil was known, but untapped until 1901 when the oil industry would change the landscape of the region. Uses for oil date back many years. In the 1500s, the Spanish used oil from seeps near Sabine Pass for caulking their ships, and to the north, settlers near Nacogdoches used seeping oil for lubricants before 1800. There were numerous discoveries in east and central Texas in the later 1800s, especially at Corsicana in 1896. Attempts were made to drill wells at Spindletop 1893 and 1896 and at Sour Lake in 1896, but they had no successful oil production along the Gulf Coast until the Lucas Gusher came in on Spindletop Hill on January 10, 1901.
While most of the economy in Southeast Texas depended on agriculture, cattle ranching, and the lumber business in the 19th century, things were about to change. The presence of oil was known, but untapped until 1901 when the oil industry would change the landscape of the region. Uses for oil date back many years. In the 1500s, the Spanish used oil from seeps near Sabine Pass for caulking their ships, and to the north, settlers near Nacogdoches used seeping oil for lubricants before 1800. There were numerous discoveries in east and central Texas in the later 1800s, especially at Corsicana in 1896. Attempts were made to drill wells at Spindletop 1893 and 1896 and at Sour Lake in 1896, but they had no successful oil production along the Gulf Coast until the Lucas Gusher came in on Spindletop Hill on January 10, 1901.
Spindletop Hill was a salt dome oil field, that was located in the southern portion of Beaumont, Texas. People had long suspected that oil might be under the hill as the area had been known for its sulfur springs and  bubbling gas seepages that would ignite if lit. Then in August, 1892, several men including George W. O’Brien, George W. Carroll, and Pattillo Higgins formed the Gladys City Oil, Gas, and Manufacturing Company to do exploratory drilling on Spindletop Hill.
bubbling gas seepages that would ignite if lit. Then in August, 1892, several men including George W. O’Brien, George W. Carroll, and Pattillo Higgins formed the Gladys City Oil, Gas, and Manufacturing Company to do exploratory drilling on Spindletop Hill.
By September 1901, there were at least six successful wells on Gladys City Company lands. Wild speculation drove land prices around Spindletop to incredible heights. One man who had been trying to sell his tract there for $150 for three years sold his land for $20,000; the buyer promptly sold to another investor within fifteen minutes for $50,000. One well, representing an initial investment of under $10,000, was sold for $1,250,000. Legal entanglements and multimillion-dollar deals became almost commonplace. An estimated $235 million had been invested in oil that year in Texas; while some had made fortunes, others lost everything.
Following the success of the oil industry at Spindletop Hill, many people, including my grandparents, Allen and  Anna Spencer would make their way to Texas in search of a better life. They would settle on the oilfields near Ranger, Texas. They didn’t find any oil fields, so their income came from his work for other people in the oilfields. These days people working in the oilfield business make good money, but as near as I can tell oilfield workers averaged about 90 cents an hour in 1919, which would be about $11.74 an hour today. That’s pretty poor wages, especially for the oilfield, but I suppose people didn’t realize how valuable they really were. Needless to say, the oilfield was not the place my grandfather would choose to make his living, and eventually they returned to Wisconsin where he went to work for the railroad.
Anna Spencer would make their way to Texas in search of a better life. They would settle on the oilfields near Ranger, Texas. They didn’t find any oil fields, so their income came from his work for other people in the oilfields. These days people working in the oilfield business make good money, but as near as I can tell oilfield workers averaged about 90 cents an hour in 1919, which would be about $11.74 an hour today. That’s pretty poor wages, especially for the oilfield, but I suppose people didn’t realize how valuable they really were. Needless to say, the oilfield was not the place my grandfather would choose to make his living, and eventually they returned to Wisconsin where he went to work for the railroad.

 Following the Crash of 1929, which occurred on October 29, 1929, people quickly found that the jobs they thought were secure, were not only not secure, they were gone. That day became known as Black Tuesday. It was the day the stock market took a huge hit, as investors traded some 16 million shares on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors. The Great Depression followed the crash of 1929…banks failed, businesses closed, city streets were desolate, families lost their homes, and unemployment in rose to nearly 25%. The crash was the culmination of many years of economic instability. In the middle part of the United States, the depression occurred during the drought season. The farmers quickly lost their lands, because their crops died out, and many became migrant workers. They traveled around the country, hoping to find work for all members of the family in exchange for a meal or a place to sleep. Husbands and fathers traveled great distances from their homes in search of any work that they could find. There was no work…anywhere. Times were just about the worst they could possibly be.
Following the Crash of 1929, which occurred on October 29, 1929, people quickly found that the jobs they thought were secure, were not only not secure, they were gone. That day became known as Black Tuesday. It was the day the stock market took a huge hit, as investors traded some 16 million shares on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors. The Great Depression followed the crash of 1929…banks failed, businesses closed, city streets were desolate, families lost their homes, and unemployment in rose to nearly 25%. The crash was the culmination of many years of economic instability. In the middle part of the United States, the depression occurred during the drought season. The farmers quickly lost their lands, because their crops died out, and many became migrant workers. They traveled around the country, hoping to find work for all members of the family in exchange for a meal or a place to sleep. Husbands and fathers traveled great distances from their homes in search of any work that they could find. There was no work…anywhere. Times were just about the worst they could possibly be.

Architects, bankers, engineers and educators suddenly found themselves standing in long unemployment lines, competing for menial, basic jobs with pay that was barely enough to put food on their tables. Men who had defined themselves by taking care of their families, being the breadwinner, struggled with the emotional depression that came with the economic depression. As men traveled farther and farther away from home looking for jobs, they are forced to find lodging in public housing or shelters, waking up to begin job hunting again the next morning. Husbands and fathers who had previously earned enough money to feed and clothe their families were forced to stand in bread lines to receive free food so their families would not starve.
People became so desperate for work. As men went from town to town, they were met with billboard signs telling them to keep going, because there was no work in the town. Men with families even got their children involved, carrying signs asking why no one would hire their dad. Then men started wearing their resume on cardboard placards that they wore as they walked along. It seemed incredulous to the men who had been in higher paid jobs, that they could no longer find work…even with their qualifications. Signs like one saying, “I know 3 trades, I speak 3 languages, fought for 3 years, have 3 children and no work for 3 months. But I only 
 want one job,” appeared everywhere. Times couldn’t possibly get worse. While there’s no consensus about the exact end of the Great Depression among economic historians, the unemployment rate remained high for the rest of the 1930s, even as the banking crisis eased up. One major event, however, shifted the focus of the country away from the Great Depression. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, millions of men and women would join the work force as the US entered World War II.
want one job,” appeared everywhere. Times couldn’t possibly get worse. While there’s no consensus about the exact end of the Great Depression among economic historians, the unemployment rate remained high for the rest of the 1930s, even as the banking crisis eased up. One major event, however, shifted the focus of the country away from the Great Depression. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, millions of men and women would join the work force as the US entered World War II.

