Family
 Heroes come from all walks of life, and you really never know who will become a hero and who won’t. In fact, I don’t think a hero even knows that the heroic in inside him, until the heroic is needed. Often the heroic comes from being faced with a situation that would require your life to save that of another. Such was the case for Maximilian Kolbe in 1941.
Heroes come from all walks of life, and you really never know who will become a hero and who won’t. In fact, I don’t think a hero even knows that the heroic in inside him, until the heroic is needed. Often the heroic comes from being faced with a situation that would require your life to save that of another. Such was the case for Maximilian Kolbe in 1941.
The Catholics didn’t really agree with the Jewish beliefs, and the Jews felt the same way about the Catholics beliefs, so when Hitler began rounding up the Jews, many Catholics and other religions, were quick to turn them over…it might have been to save their own lives, but they were handing them over to be killed, nevertheless…and they knew it. The non-Jews could pretend that everything was fine and the Jewish people who were taken, would be returned when things settled down, and maybe at first they truly thought that, but as time went by the truth was coming out. They now had a choice to make…a moral choice.
Kolbe was a Catholic priest during World War II. He saw what was going on with the Jewish people, when Hitler started rounding them up. Kolbe could read between the lines, as many people could in those horrific days, and he decided to help Jewish people escape the Nazis. Being a Catholic priest, he likely had more room that other  people might have had. He started harboring Jewish people and hiding them from the Nazis, keeping them safe from the public and any harm that might be afflicted upon them. As with many people who harbored Jews, Kolbe was soon caught, and was sent to Auschwitz for sheltering Jewish people.
people might have had. He started harboring Jewish people and hiding them from the Nazis, keeping them safe from the public and any harm that might be afflicted upon them. As with many people who harbored Jews, Kolbe was soon caught, and was sent to Auschwitz for sheltering Jewish people.
Auschwitz was one of the worst of Hitler’s torture chamber death camps, and it certainly proved to be just that for Kolbe. During his time at the horrid concentration camp, a prisoner escaped from the camp and as punishment, ten innocent prisoners had to starve to death in a hollow, concrete tube. One of the elected people started to cry and exclaimed that they had a wife and kids, so Kolbe spoke up and took his place so the man could be with this family. The prisoners were kept in the tube for the next two weeks. Most of them were already in a weakened and starved state, and so the prisoners inside the tube slowly began to die. Of the ten prisoners, Kolbe and  three other men managed to survive the torturous tube. One would think that if they survived the tube, they would be considered strong enough to bring out and put back to work, but the remaining prisoners were brought out of the tube and killed by being injected with Carbolic Acid. When it was his turn to receive the injection, Kolbe didn’t fight like the rest of the men, but instead, he gave his arm to the prison guard and never once made a fuss over it. One might think that Kolbe was just done with the whole mess, and maybe that was true, but it would have made no difference for him to fight. The guards had decided, and his fighting the injection would make no difference. Maximilian Kolbe died on August 14, 1941. He was 47 years old.
three other men managed to survive the torturous tube. One would think that if they survived the tube, they would be considered strong enough to bring out and put back to work, but the remaining prisoners were brought out of the tube and killed by being injected with Carbolic Acid. When it was his turn to receive the injection, Kolbe didn’t fight like the rest of the men, but instead, he gave his arm to the prison guard and never once made a fuss over it. One might think that Kolbe was just done with the whole mess, and maybe that was true, but it would have made no difference for him to fight. The guards had decided, and his fighting the injection would make no difference. Maximilian Kolbe died on August 14, 1941. He was 47 years old.
 It’s hard to picture a dentist as being a hero, but US Army Medic Ben Salomon, who was a dentist before he was drafted in to the US Army as a private in 1940, as World War II was in its early stages. Salomon was assigned, not to the medical units, but rather, to the infantry. It was in the infantry during rifle and pistol qualifications that Salomon was rated an Expert Marksman. He also had medical knowledge that could be used during battlefield surgery. Salomon was assigned to a unit as their medic. Being a medic in wartime means that you are doing the noble thing, a task which is not often recognized as anything special. I think was have all seen the television show, MASH, in which the position of Army Doctor is viewed as mostly safe, far from the front lines, and given to a little bit of hanky panky. It doesn’t often paint a picture of heroic actions, although, sometimes the doctors are heroic (Nevertheless, I don’t mean to say that all military doctors are like the doctors on MASH, who are, after all, playing a part.) Medics serve and protect like every other serviceman, but they sometimes see a lot more of war’s ugly side. These unit medics might saw torn apart friends, horrific injuries, and a lot of deaths. The men they served with every day were their friends, and while the medic was usually behind the unit in a tent, caring for the wounded, these were not strangers to them. They were friends and comrades in arms.
It’s hard to picture a dentist as being a hero, but US Army Medic Ben Salomon, who was a dentist before he was drafted in to the US Army as a private in 1940, as World War II was in its early stages. Salomon was assigned, not to the medical units, but rather, to the infantry. It was in the infantry during rifle and pistol qualifications that Salomon was rated an Expert Marksman. He also had medical knowledge that could be used during battlefield surgery. Salomon was assigned to a unit as their medic. Being a medic in wartime means that you are doing the noble thing, a task which is not often recognized as anything special. I think was have all seen the television show, MASH, in which the position of Army Doctor is viewed as mostly safe, far from the front lines, and given to a little bit of hanky panky. It doesn’t often paint a picture of heroic actions, although, sometimes the doctors are heroic (Nevertheless, I don’t mean to say that all military doctors are like the doctors on MASH, who are, after all, playing a part.) Medics serve and protect like every other serviceman, but they sometimes see a lot more of war’s ugly side. These unit medics might saw torn apart friends, horrific injuries, and a lot of deaths. The men they served with every day were their friends, and while the medic was usually behind the unit in a tent, caring for the wounded, these were not strangers to them. They were friends and comrades in arms.
Just one month after Salomon’s promotion to captain, he experienced his first battle. Salomon volunteered to replace the 2nd Battalion, 105th Infantry Regiment’s field surgeon, who had been wounded. The unit was sent to Saipan to fight the Japanese forces. Little did Salomon know that this would be his only battle. When the unit landed in Saipan, they found immediately themselves in one of the most intense fights in the Pacific arena. Apparently this little island had been determined to be vital…no matter which side you were on. The Japanese army was not willing to concede the island and the US Army was adamant that they needed to take it. By the time Salomon’s unit arrived, the Japanese had taken the approach of advance and attack to their own deaths.
The tents for the field surgeons were located 50 yards behind the front, and it was there that Salomon worked to triage the severely wounded men. On July 6, 1944, the Japanese reached the trenches and Salomon’s position. Then on July 7th, the Japanese made it over the trenches and went straight to the medical tents. Inside, Salomon was treating wounded soldiers. He looked up and saw a Japanese soldier storm into the tent and bayonet one of the wounded and unarmed soldiers. Solomon acted instinctively. He grabbed an M1 rifle which was on a table close by and fired, killing the enemy soldier. For a medic, who never expected to need to fire his weapon, that situation must have come as a bit of a shock, but that soldier was not to be the only one Salomon killed that day. He turned back to the wounded soldiers, and then he saw two more enemy soldiers burst into the tent. There wasn’t much room in the tents, and they weren’t designed for hand to hand combat, but the tent soon became the battlefield, nevertheless. Salomon began swinging the rifle and clubbed the first soldier, then jamming the second with the butt of the weapon. Then, he shot one and bayoneted the other.
Immediately, four more Japanese soldiers made their way into the medical tent and tried to catch Salomon by surprise. One of the soldiers had a knife that Salomon kicked out of his hand before firing his rifle, killing one soldier and using his bayonet to kill another. By now, Salomon was out of bullets, so he picked up the knife and engaged with the two remaining enemy fighters. He killed one using the knife before head-butting the other, who was then shot by one of the patients in the tent. After dispatching the enemy soldiers, Salomon ordered his colleagues to evacuate the wounded. He would stay behind to hold off the enemy to give them the extra time they needed. As Captain Salomon loaded his rifle, the 30 wounded soldiers and orderlies in the tent started to retreat. The decision to stay and fight while the wounded were evacuated saved many lives, but Salomon was now in a battle that he had no hope of winning, much less living through. Ben Salomon made his last stand. He commandeered a heavy machine gun and was last seen firing at oncoming Japanese troops.
When the American troops were finally able to return to the area, they found Salomon’s body slumped over the machine gun, surrounded by the bodies of 98 Japanese soldiers. He had been shot 76 times and had 24  bayonet wounds on his body. Yes, Captain Salomon had died in the battle, but not before he killed 98 enemy soldiers, and the wounded soldiers and the medics with him had all managed to escape. Salomon was a serious force to be reckoned with, as the Japanese found out that day.
bayonet wounds on his body. Yes, Captain Salomon had died in the battle, but not before he killed 98 enemy soldiers, and the wounded soldiers and the medics with him had all managed to escape. Salomon was a serious force to be reckoned with, as the Japanese found out that day.
Medical personnel were considered ineligible for the Medal of Honor at that time, due to the terms of the Geneva Convention, so the request that he be awarded the medal was denied. After numerous other attempts over the years, Salomon’s bravery was finally recognized with the Medal of Honor in 2002, 58 years after his death.
 Underground mining, as we all know is dangerous. It was even more dangerous in the 1800s, when the equipment used was much more primitive. Still, many mining companies have switched to open pit mining to avoid the possibility of a cave in. One of the most dangerous forms of underground mining was and still is coal mining. The distinct possibility of a build up of methane gas makes underground coal mining a deadly venture for many miners. Aside from breathing the deadly gas and coal dust, causing death, either instantaneously or later in life…from black lung, the danger of an explosion was always present.
Underground mining, as we all know is dangerous. It was even more dangerous in the 1800s, when the equipment used was much more primitive. Still, many mining companies have switched to open pit mining to avoid the possibility of a cave in. One of the most dangerous forms of underground mining was and still is coal mining. The distinct possibility of a build up of methane gas makes underground coal mining a deadly venture for many miners. Aside from breathing the deadly gas and coal dust, causing death, either instantaneously or later in life…from black lung, the danger of an explosion was always present.
One of the most dangerous parts of underground mining, was the miner’s inability to see, or rather the lanterns used to solve the problem of the miner’s inability to see. It’s pretty difficult to maneuver around in a mine, much less find ore, if you can’t see, and caves don’t generally have built in lights. Miners these days have battery powered lights on their hard hats, but those things didn’t exist in the 1800s. Most generally the miners carried a lantern, filled with heavy vegetable oil and using a wick that was unprotected, thus allowing it to ignite the methane or other flammable gasses, called firedamp or minedamp, lurking undetected in the mine.
The problem needed to be solved, and so several inventors began looking into just how to do that. Probably the best one, at that time, was the Davy lamp. It is a safety lamp designed specifically for use in flammable atmospheres. It was invented in 1815 by Sir Humphry Davy. They didn’t have light bulbs or batteries that could be used in the mines back then. The Davy Lamp consists of a wick lamp with the flame enclosed inside a mesh screen. The mesh screen kept the flame from escaping, thereby reducing the danger of explosions. The Davy Lamp also provided a test for the presence of gases. If flammable gas mixtures were present, the flame of the Davy lamp burned higher with a blue tinge. The lamps were equipped with a metal gauge to measure the height of the flame. When the lamp was placed close to the ground, it could detect gases, such as carbon dioxide, that are more dense than air and so could collect in depressions in the mine. If the lamp determined that the mine air was oxygen-poor (asphyxiant gas), the lamp flame would be extinguished, using a black damp or chokedamp. A methane-air flame is extinguished at about 17% oxygen content…which will still support life, so the lamp gave an early indication of a dangerous atmosphere, allowing the miners to get out before they died of asphyxiation.
Apparently, Davy’s invention was preceded by that of William Reid Clanny, an Irish doctor at Bishopwearmouth, who had read a paper to the Royal Society in May 1813. The Clanny lamp was more cumbersome, but it was successfully tested at Herrington Mill, and he won medals, from the Royal Society of Arts. Another lamp version was the lamp designed by engine-wright George Stephenson. His “Geordie Lamp” drew air in via tiny holes, through which the flames of the lamp could not pass. If you ask me, the metal plate, only allowing small pin points of light would not be a very illuminating. A month before Davy presented his design to the Royal Society, 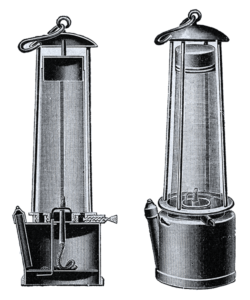 Stephenson supposedly demonstrated his own lamp to two witnesses by taking it down Killingworth Colliery and holding it in front of a fissure from which firedamp was issuing. Unfortunately for Stephenson, Davy beat him to the necessary people.
Stephenson supposedly demonstrated his own lamp to two witnesses by taking it down Killingworth Colliery and holding it in front of a fissure from which firedamp was issuing. Unfortunately for Stephenson, Davy beat him to the necessary people.
The first trial of a Davy lamp with a wire sieve was at Hebburn Colliery on January 9, 1816. Because of its success, Davy was awarded the society’s Rumford Medal. Davy’s lamp differed from Stephenson’s in that the flame was surrounded by a screen of gauze, whereas Stephenson’s prototype lamp had a perforated plate contained in a glass cylinder, which was a design mentioned in Davy’s Royal Society paper, as an alternative to his preferred solution. For his invention Davy was given £2,000 worth of silver. Stephenson, on the other hand, was accused of stealing the idea from Davy. His “Geordie Lamp” had not been demonstrated by Stephenson until after Davy had presented his paper at the Royal Society. While Stephenson was exonerated, Davy went to his grave insisting that he had tried to steal his idea.

 My uncle, Jim Wolfe was a favorite uncle to my sisters, Cheryl Masterson, Caryl Reed, Alena Stevens, Allyn Hadlock, and me. Uncle Jim had a great sense of humor, and a deep sense of family. He loved kids and he was good to all kids. In fact, Uncle Jim was good to everyone. He was the best kind of person. Uncle Jim has a soft heart. Whatever we wanted when we were around Uncle Jim…if he had any say in it, we could have it, or do it! I’m not sure how my parents, Al and Collene Spencer, felt about all that “spoiling,” but I’m sure they were ok with it, because after all, it was only temporary. He just liked to make us happy.
My uncle, Jim Wolfe was a favorite uncle to my sisters, Cheryl Masterson, Caryl Reed, Alena Stevens, Allyn Hadlock, and me. Uncle Jim had a great sense of humor, and a deep sense of family. He loved kids and he was good to all kids. In fact, Uncle Jim was good to everyone. He was the best kind of person. Uncle Jim has a soft heart. Whatever we wanted when we were around Uncle Jim…if he had any say in it, we could have it, or do it! I’m not sure how my parents, Al and Collene Spencer, felt about all that “spoiling,” but I’m sure they were ok with it, because after all, it was only temporary. He just liked to make us happy.
My uncle Jim was a storyteller among storytellers. The best of the best. When Uncle Jim started telling his stories, we all sat around him wide-eyed with wonder. We never knew if his stories were going to be from real life and which ones were going to be tall tales…at least not until the end, when he would tell us the punch line. Then we would all laugh and say, “Oh! Uncle Jim!” He loved to get a little rise out of us, and it really tickled his funny bone. And speaking of tickling, Uncle Jim was a tickler from way back. He used to chase us around and tickle us, if we started bugging him…so naturally, we always started bugging him. Then we would try to get away. Hahahaha!! Not that that ever happened. Uncle Jim had the kindest heart and he was always a lot of fun!
Uncle Jim would help anyone who needed help, if it was within his power…neighbors, friends, and even complete strangers. He was generous, and would always lend a helping hand where he could. He loved his family fiercely and loyally. No one better hurt his wife or kids, in any way. He defended them in word and deed. He was faithful to them in every way. When he decided to buy some land out in Washington, where he would build his final home, he bought enough so that each of his kids could have their own place nearby. He never wanted any of them to not have a home, so he made sure of it. The land he purchased was on he top of a mountain with some of the most beautiful views on the way up. He did his very best for all of his family, and I don’t know anyone who didn’t love Uncle Jim. In his later years, when his care for Alzheimer’s Disease required that he be in a nursing home, Uncle Jim still kept his character. He loved putting a smile on the faces of all the 
 nursing staff, and anyone else who might be there visiting. He could often be found getting into “mischief” behind the nurses station desk, not that he ever hurt anything, he was just “visiting,” after all. My sisters and I love him still! Just thinking about him make us smile. Uncle Jim went to Heaven in 2013 to join his wife, my Aunt Ruth, and other family members who have gone before him. I know they are having a great time, and we are so glad to know where he is, and one day we will be together with him, and all our family again. Today would have been Uncle Jim’s 100th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Uncle Jim. We love and miss you very much.
nursing staff, and anyone else who might be there visiting. He could often be found getting into “mischief” behind the nurses station desk, not that he ever hurt anything, he was just “visiting,” after all. My sisters and I love him still! Just thinking about him make us smile. Uncle Jim went to Heaven in 2013 to join his wife, my Aunt Ruth, and other family members who have gone before him. I know they are having a great time, and we are so glad to know where he is, and one day we will be together with him, and all our family again. Today would have been Uncle Jim’s 100th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Uncle Jim. We love and miss you very much.
 War is an ugly business, and the men and women who fight in wars are subjected to great stress and anxiety. These days, most of us recognize the term, PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder). We also recognize that a person doesn’t have to be in a war situation to have PTSD. Any traumatic event can trigger PTSD, and the symptoms of this disorder can be devastating. In fact, PTSD can result in things like suicide, attacks on others, institutionalization, or isolation.
War is an ugly business, and the men and women who fight in wars are subjected to great stress and anxiety. These days, most of us recognize the term, PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder). We also recognize that a person doesn’t have to be in a war situation to have PTSD. Any traumatic event can trigger PTSD, and the symptoms of this disorder can be devastating. In fact, PTSD can result in things like suicide, attacks on others, institutionalization, or isolation.
During World War II, PTSD (then known as Shell Shock) first came to the attention of the military leaders. On October 4, 1944, General Dwight D Eisenhower distributed to his combat units a report by the US Surgeon General that revealed the hazards of prolonged exposure to combat. The then General’s report read, “[T]he danger of being killed or maimed imposes a strain so great that it causes men to break down. One look at the shrunken, apathetic faces of psychiatric patients…sobbing, trembling, referring shudderingly to ‘them shells’ and to buddies mutilated or dead, is enough to convince most observers of this fact.” General Eisenhower had been on the battlefield, and so, knew firsthand of the “attacks” on the minds and emotions of these poor soldiers.

After evaluation of many cases of “Shell Shock” in the hospital wards, the American commanders came to the conclusion that the average soldier could last about 200 days in combat before suffering serious psychiatric damage. They looked into the fact that British commanders used a rotation method, pulling soldiers out of combat every 12 days for a four-day rest period, thereby enabling British soldiers to put in 400 days of combat before being deleteriously affected. The Surgeon General’s report went on to lament the fact that a “wound or injury is regarded, not as a misfortune, but a blessing.” Now, when a wound is considered a blessing, you know that things have taken a serious turn for the worst in the area of morale. That basically means that the soldiers will do just about anything to get off the battlefield. For them, death isn’t far from being acceptable either. General Eisenhower and the military leaders of that era could see that the war was clearly taking a toll on more than just men’s bodies. The far greater toll was on their minds and emotions.
 While I can see that the idea of a rotation, or a limited period of exposure to the battlefield could sound like a viable solution, in reality is is only a partial solution, and one that probably won’t really work. While the time spent on the battlefield can cause fatigue, both mentally and physically, it only takes one event to change the mental status of a person. Even a strong person is going to be effected by the horrific death of a comrade at the hands of a land mine. Yes, their own wounds would get them off the battlefield, but that will not take away the pictures of blood and death they have see on the battlefield. To take the soldiers off the battlefield after 200 days is a noble effort, but it is not likely to solve the problem of Shell Shock in the way that they had hoped. I guess that main thing is that they knew about it and were trying to fix it.
While I can see that the idea of a rotation, or a limited period of exposure to the battlefield could sound like a viable solution, in reality is is only a partial solution, and one that probably won’t really work. While the time spent on the battlefield can cause fatigue, both mentally and physically, it only takes one event to change the mental status of a person. Even a strong person is going to be effected by the horrific death of a comrade at the hands of a land mine. Yes, their own wounds would get them off the battlefield, but that will not take away the pictures of blood and death they have see on the battlefield. To take the soldiers off the battlefield after 200 days is a noble effort, but it is not likely to solve the problem of Shell Shock in the way that they had hoped. I guess that main thing is that they knew about it and were trying to fix it.

 In the state of New York, just north of Buffalo, the Niagara Falls provide a beautiful border between the United States and Canada. It’s not the first time that water has been part of a border, but not many include a beautiful falls in the mix. Niagara Falls are considered one of the most well-known and breathtaking landmarks in North America. Having seen them for myself, I can attest to that. Tourists have come from all over the world to see this natural wonder as the power of the water has been on display for over 200 years.
In the state of New York, just north of Buffalo, the Niagara Falls provide a beautiful border between the United States and Canada. It’s not the first time that water has been part of a border, but not many include a beautiful falls in the mix. Niagara Falls are considered one of the most well-known and breathtaking landmarks in North America. Having seen them for myself, I can attest to that. Tourists have come from all over the world to see this natural wonder as the power of the water has been on display for over 200 years.
The falls have always been beautiful, but they also have a dark side…and it might have been darker than anyone knew. In 1969, the waters that pounded through the Niagara Falls were stopped before they could get to the area, allowing the bedrock to be exposed and the water to be no more than a little stream. Seeing the Falls like this, for the first time in history, allowed researchers to see a part of this landscape that had been permanently hidden by water. What was found at the bottom of the dried out Falls brought visitors and researchers alike to their knees. Some things were never meant to be found.
The state government and the local community knew that the falls needed some major repairs, if the area was going to continue to have the major tourism business that it had enjoyed for so many years, but they were really not prepared for part of what they found when the water was basically stopped. Niagara Falls is actually made up of three waterfalls, that share a common cliff, making them combined in reality. The American Falls is known for being the most self-destructive one of the three. The water that was going over was eroding it over time. The locals were worried that the America Falls would eventually erode away the cliff, and the tourism trade would end.
What they weren’t really thinking about when the falls were stopped, was what was beneath the falls. Every year, a number of people decide to try some new stunt to gain attention, by going over the falls in a barrel, or some other such vehicle. It’s a crazy idea, and most don’t survive their stunt. That said, one might expect to find lots of bones beneath the falls, when the engineers and workers were standing at the bottom of the Falls, their faces showed total disbelief. “In addition to the massive talus rock and the never before seen geography of the bedrock, there was a far more sinister sight. As the water drew back and dried up so the workers could continue with the plan, they looked down and saw a bones and other remains at their feet. These were not animal remains, either, but human. Everyone at the scene was shocked, but they were also very curious.”
Before them, the engineers found the remains of two individuals, a man and a woman. It was impossible to find out who the remains belonged to, due to the fact that the remains were under water for so long, and the DNA testing and such that we have now were not available then. The whole grisly discovery, remained a mystery, but rumors circulated as to who the people could be. Most assumed that the man might have jumped, but they didn’t think the woman would have. The thing that was even more strange than finding two bodies beneath the falls, was that there were not more bodies of more crazy thrill seekers, because the base of the Falls has had around 5,000 bodies found at its base from 1850 to 2011. Authorities state that between 20 and 40 people a year end their lives right there at the Falls. This statistic is the reason why finding only two bodies in 1969 was so confusing. There should have been more bodies.
Another known, unknown found at the base of the falls were the many coins thrown in as people “made a wish” and tossed in their “lucky” wishing coin. As the engineers looked around, trying to find information on the mystery couple, they also found that there were millions upon millions of coins. While everyone as shocked at both findings, the main mission of the blockage of the water was to fix the falls and get them back on track. Despite the remains and coins that had been found, the point of the mission was to get water going again.
Incredibly, despite all the money and time that was spent on this project, after the talus was dried up in American Falls, the lead engineers made the final decision to leave the talus as is, because they realized that 
 the talus was actually supporting the cliff face behind it. To change it could cause the cliff to cave in. Instead they decided to focus on the project of giving the American Falls the revamp it needed. The team of engineers and construction workers came up with a plan to use bolts, anchors, and cables to stabilize the Falls, so that the falls and tourism could get back on track.
the talus was actually supporting the cliff face behind it. To change it could cause the cliff to cave in. Instead they decided to focus on the project of giving the American Falls the revamp it needed. The team of engineers and construction workers came up with a plan to use bolts, anchors, and cables to stabilize the Falls, so that the falls and tourism could get back on track.
 The German Kradmelder, motorcycle dispatch rider in English, could be used at any time in history, but in this case, they were used during World War II, specifically on the Eastern Front. The Eastern Front of World War II was a theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Poland and other Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from June 22, 1941 to May 9, 1945. The Soviet Union called it the Great Patriotic War, but everyone else called it the Eastern Front.
The German Kradmelder, motorcycle dispatch rider in English, could be used at any time in history, but in this case, they were used during World War II, specifically on the Eastern Front. The Eastern Front of World War II was a theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Poland and other Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from June 22, 1941 to May 9, 1945. The Soviet Union called it the Great Patriotic War, but everyone else called it the Eastern Front.
Dispatch riders were used by armed forces to get information from headquarters to the military units. They often didn’t have radios, and depending on the message, they might not have trusted the airwaves with some of the top secret messages. The Nazi Regime never really cared about its soldiers or its people, so the Kradmelder were sent out in the heat of summer or the frigid temperatures of winter. They were expendable, and that was all there was to it. Nevertheless, they played a vital role at a time when telecommunications were limited and insecure. They were also used to deliver carrier pigeons. The pigeons were used to send information back to headquarters, concerning the current situations on the front.
This type of dispatch was essential, but riding on an exposed vehicle in the Russian Winter, was brutal, and even deadly sometimes. During the winter the riders had better have protective clothing, or they could freeze to death.  The Kradfahrer (motorcycle rider) might wear a sentry’s fur-lined overcoat, heavy mittens, the fur-lined cap of the reversible winter suit, which is no doubt being worn beneath the overcoat, and a gas-mask for face protection…with the air filter canister removed from the gas-mask. Special extra eyepiece lens were issued for cold weather to prevent fogging by creating an airspace between the two lens.
The Kradfahrer (motorcycle rider) might wear a sentry’s fur-lined overcoat, heavy mittens, the fur-lined cap of the reversible winter suit, which is no doubt being worn beneath the overcoat, and a gas-mask for face protection…with the air filter canister removed from the gas-mask. Special extra eyepiece lens were issued for cold weather to prevent fogging by creating an airspace between the two lens.
In the summer, the German Kradmelder might wear his rubberized coat (Kradmantel) wrapped and buttoned around his legs to keep dirt and dust off his uniform. Personally, I can’t imagine wearing a rubberized coat in the summer simply to keep the dust off of a uniform. The rider would surly be melting from the heat, but the regime would require that the uniform be neat and clean at all times…even if it was soaked in sweat!! During World War II, the German military was the largest employers of motorcycles. On June 22, 1941 Germany launched its Operation Barbarossa, the 3-million-man invasion of the Soviet Union. The Kradmelder served a variety of functions including chauffeur service for officers, delivering dispatches, hot meals, as scouting patrols, as point vehicles taking the brunt of battle, sometimes as specially equipped tank destroyers. As with all motorcyclists, there was a kinship among these soldiers who called themselves “Kradmelder.” They bravely rode exposed without the armor plating of the Panzers Tanks and without the safety of hundreds of foot soldiers beside them. They were moving targets and sniper magnets. They never knew when they would encounter mine fields, artillery fire, and strafing aircraft, but they bravely went, because Hitler’s orders must be carried out…even if they died trying.
 Besides the known enemy, there was another enemy…the Russian weather. As Autumn approached, the roads had turned into nearly impassable bogs, the fields over which the motorcycles traveled turning in to “seas of jelly three feet more deep.” If that weren’t bad enough, Winter brought falling temperatures, often down to -40° Fahrenheit, causing engine oil and exposed soldiers froze solid. The “lucky” German Kradmelder benefited from special heating systems grafted onto their bikes, including foot and hand warmers. Still there were those who did not have these things, and even these things didn’t totally protect the rider. By the end of World War II, many if not most of the motorcycles, along with their riders, simply never returned home.
Besides the known enemy, there was another enemy…the Russian weather. As Autumn approached, the roads had turned into nearly impassable bogs, the fields over which the motorcycles traveled turning in to “seas of jelly three feet more deep.” If that weren’t bad enough, Winter brought falling temperatures, often down to -40° Fahrenheit, causing engine oil and exposed soldiers froze solid. The “lucky” German Kradmelder benefited from special heating systems grafted onto their bikes, including foot and hand warmers. Still there were those who did not have these things, and even these things didn’t totally protect the rider. By the end of World War II, many if not most of the motorcycles, along with their riders, simply never returned home.
 Harvey Ball was a commercial artist from Worcester, Massachusetts. You may not know him, but everyone knows what he created…the smiley face. Harvey Ross Ball was born on July 10, 1921 the third of six children to Ernest G Ball and Christine “Kitty” Ross Ball. Ball’s artistic skills presented early. As a student at Worcester South High School, he decided to become an apprentice to a local sign painter. Later he attended the Worcester Art Museum School, where he studied fine arts, however, it was not in the fine arts that Ball’s fame emerged. He is recognized as the designer of a popular smiley graphic picture, which became an enduring and notable international icon.
Harvey Ball was a commercial artist from Worcester, Massachusetts. You may not know him, but everyone knows what he created…the smiley face. Harvey Ross Ball was born on July 10, 1921 the third of six children to Ernest G Ball and Christine “Kitty” Ross Ball. Ball’s artistic skills presented early. As a student at Worcester South High School, he decided to become an apprentice to a local sign painter. Later he attended the Worcester Art Museum School, where he studied fine arts, however, it was not in the fine arts that Ball’s fame emerged. He is recognized as the designer of a popular smiley graphic picture, which became an enduring and notable international icon.
Ball worked for a local advertising firm after World War II. Then he decided to start his own business, which he called Harvey Ball Advertising, in 1959. He designed the smiley in 1963. The State Mutual Life Assurance Company of Worcester, Massachusetts, now known Hanover Insurance, had purchased Guarantee Mutual Company of Ohio. After the merger, employee morale was pretty  low. The company decided to try to boost morale, so they asked Ball to come up with an image that would help. What he created was a smiley face, with one eye bigger than the other. The creation took Ball ten minutes, and the executives liked it immediately. They paid Ball a mere $45 for his creation.
low. The company decided to try to boost morale, so they asked Ball to come up with an image that would help. What he created was a smiley face, with one eye bigger than the other. The creation took Ball ten minutes, and the executives liked it immediately. They paid Ball a mere $45 for his creation.
The smiley face became part of the company’s friendship campaign, and State Mutual handed out 100 smiley pins to employees. The aim was to get employees to smile while using the phone and doing other tasks. The buttons became popular, with orders being taken in lots of 10,000. More than 50 million smiley face buttons had been sold by 1971, and the smiley has been described as an international icon. As for Ball, well…he never applied for a trademark or copyright of the smiley and that $45 was all he ever got for his trouble. I don’t suppose that did much for his morale. Nevertheless, State Mutual didn’t make any money from the design either. According to Ball’s son, Charles, his father never regretted not registering the copyright. Charles Ball said, “he was not a money-driven guy, he used to say, ‘Hey, I can only eat one steak at a time, drive one car at a time.'”

Ball had a heart for children, and founded the World Smile Foundation in 1999, a non-profit charitable trust that supports children’s causes. Then, he came up with World Smile Day. It was a great idea, I think. How nice it is to celebrate a day dedicated to putting a smile on your face and sharing that great smile with others. The first World Smile Day was celebrated in 1999. It’s been held annually on the first Friday of October since then. After Harvey died in 2001, the “Harvey Ball World Smile Foundation” was created to honor his name and memory. The slogan of the Smile Foundation is “improving this world, one smile at a time.” The Foundation continues to be the official sponsor of World Smile Day each year. We should all consider that slogan.

 When most of us think of going to the lake, we envision the cool blue water of a lake, most likely somewhere near our city of residence, but if we were to live in Australia, while we might picture a lake near our home, we might not necessarily picture cool blue water. That would be because Australia has more than ten pink lakes. Yes, I said pink. One well known pink lake, is located in Western Australia’s Goldfields-Esperance region.
When most of us think of going to the lake, we envision the cool blue water of a lake, most likely somewhere near our city of residence, but if we were to live in Australia, while we might picture a lake near our home, we might not necessarily picture cool blue water. That would be because Australia has more than ten pink lakes. Yes, I said pink. One well known pink lake, is located in Western Australia’s Goldfields-Esperance region.
Pink lakes are salt lakes, and their color can vary due to the salt content in them at any given time. Pink Lake has lost much of its pink color due to a reduced amount of salt in it right now. The lake’s waters were visibly pink in years past, but it has not been rosy since 2017. The concentration of salt in the lake is essential to the pink color and, if the salt conditions alter, Pink Lake could turn pink again. The lake is located approximately 2 miles south of Esperance, in Western Australia.
Pink lakes are rare, and there aren’t that many of them in the world, and Australia seems to have the lion’s share of them. There are some in California and the Great Salt Lake has pink hues as well. A pink lake is a lake that has a red or pink color. This is often caused by the presence of algae that produces carotenoids, such as Dunaliella salina. Dunaliella salina is a type of halophile green micro-algae especially found in sea salt fields. Dunaliella salina is known for its antioxidant activity because of its ability to create large amount of carotenoids. It is actually used in cosmetics and dietary supplements. Few organisms can survive like Dunaliella salina thrives in such highly saline conditions as salt evaporation ponds.

 There are also rose rivers and rose beaches, in which the same compounds exist. It’s very complicated the dynamics of why a river turns rose. The pond color may be affected by external modifications and climate circumstances. The Pink Lake of Esperance has lost its blue color owing to modifications in the salinity resulting from human activities. Whatever the cause of these pink lakes, rivers, and beaches, they are a very unique phenomena, and one that I wouldn’t mind visiting.
There are also rose rivers and rose beaches, in which the same compounds exist. It’s very complicated the dynamics of why a river turns rose. The pond color may be affected by external modifications and climate circumstances. The Pink Lake of Esperance has lost its blue color owing to modifications in the salinity resulting from human activities. Whatever the cause of these pink lakes, rivers, and beaches, they are a very unique phenomena, and one that I wouldn’t mind visiting.
 Since I am not a fishing fanatic, and in fact, I find the sport…boring, sorry folks, but I do, I’m sure it seems odd for me to write a fish story. Nevertheless, there was a time when I found a certain fish really fascinating. My husband, Bob Schulenberg and I were on a Caribbean cruise for our 25th anniversary, and we loved walking the upper deck of the ship. We often stood looking over the edge looking for dolphin, but it was not dolphin that really made an impact on us, although we did see dolphin. The fish that really caught our eye was the Flying Fish.
Since I am not a fishing fanatic, and in fact, I find the sport…boring, sorry folks, but I do, I’m sure it seems odd for me to write a fish story. Nevertheless, there was a time when I found a certain fish really fascinating. My husband, Bob Schulenberg and I were on a Caribbean cruise for our 25th anniversary, and we loved walking the upper deck of the ship. We often stood looking over the edge looking for dolphin, but it was not dolphin that really made an impact on us, although we did see dolphin. The fish that really caught our eye was the Flying Fish.
Flying fish, also known as Exocoetid is a marine fish in the order Beloniformes class Actinopterygii, known in simple terms as flying fish or flying cod. They are “ray-finned fish with highly modified pectoral fins.” While they are called Flying Fish, the  name is a bit misleading in that they aren’t capable of powered flight. Their fins can’t act as wings. Instead they propel themselves out of the water at speeds of more than 35 miles an hour. Once in the air, their rigid “wings” allow them to glide for up to 650 feet. The wing-like pectoral fins are primarily for gliding. Then, while swimming, the fish hold the fins flat at their sides. Their streamlined bodies reduce drag when the fish are “flying.” However it works, the Flying Fish is a unique and very interesting thing to see…especially when you had no idea that such a thing existed. Another interesting characteristic of the flying fish is its “unevenly forked tail, which has a top lobe that’s shorter than the bottom lobe.” While the Flying Fish looked small from the deck of the ship, they can actually be up to 18 inches long. Nevertheless, they average Flying Fish is 7 to 12 inches.
name is a bit misleading in that they aren’t capable of powered flight. Their fins can’t act as wings. Instead they propel themselves out of the water at speeds of more than 35 miles an hour. Once in the air, their rigid “wings” allow them to glide for up to 650 feet. The wing-like pectoral fins are primarily for gliding. Then, while swimming, the fish hold the fins flat at their sides. Their streamlined bodies reduce drag when the fish are “flying.” However it works, the Flying Fish is a unique and very interesting thing to see…especially when you had no idea that such a thing existed. Another interesting characteristic of the flying fish is its “unevenly forked tail, which has a top lobe that’s shorter than the bottom lobe.” While the Flying Fish looked small from the deck of the ship, they can actually be up to 18 inches long. Nevertheless, they average Flying Fish is 7 to 12 inches.
Another thing I didn’t know is that there are approximately 40 species of flying fish. They are tropical fish and  can be seen off both the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of the United States. They are also found in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans. most flying fish live in open oceans, but some live on the outskirts of coral reefs.
can be seen off both the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of the United States. They are also found in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans. most flying fish live in open oceans, but some live on the outskirts of coral reefs.
I don’t claim to know all the fish in the sea, but I had no idea that such a thing existed. At first we thought they were birds. We couldn’t figure out how these “little birds” could be flying around so far out to sea, then we found out that they were actually fish. I’ll never forget how cool it was to watch them. It was a highlight of the cruise…very strange for a non-fisherman, I know.

