World War II
 My great grandparents, Carl and Henriette (Hensel) Schumacher immigrated to the United States from Germany, in 1884 and 1882 respectively. It was an amazing time for them. The United States was a whole new world, and for those who came, the land of opportunity. By 1886, they were married and ready to start a family. My grandmother, Anna Schumacher was born in 1887, followed by siblings Albert, Mary (who died before she was 3), Mina, Fred, Bertha, and Elsa, who was born in 1902.
My great grandparents, Carl and Henriette (Hensel) Schumacher immigrated to the United States from Germany, in 1884 and 1882 respectively. It was an amazing time for them. The United States was a whole new world, and for those who came, the land of opportunity. By 1886, they were married and ready to start a family. My grandmother, Anna Schumacher was born in 1887, followed by siblings Albert, Mary (who died before she was 3), Mina, Fred, Bertha, and Elsa, who was born in 1902.
By 1914, World War I broke out, following the assassination of Franz Ferdinand. The government of the United States was understandably nervous about the German immigrants now living in in America. It didn’t matter that many of these people had been living in the united States for a long time, and some had become citizens, married, and had families. The government was still nervous, and I can understand how that could be, because we have the same problem these days with the Muslim nations. Still, when I think about the fact that these were my sweet, kind, and loving, totally Lutheran great grandparents, I find it hard to believe that anyone could be nervous about them. Apparently, I was right, because to my knowledge, they were never detained in any of the internment camps, nor were they even threatened with it.
Nevertheless, there were German nationals, and even naturalized citizens who faced possible detention during 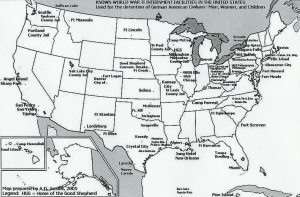 World War I and World War II. By World War II, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt declared Presidential Proclamation 2526, the legal basis for internment under the authority of the Alien and Sedition Acts. With the United States’ entry into World War I, the German nationals were automatically classified as “enemy aliens.” Two of the four main World War I-era internment camps were located in Hot Springs, North Carolina and Fort Oglethorpe, Georgia. Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer wrote that “All aliens interned by the government are regarded as enemies, and their property is treated accordingly.”
World War I and World War II. By World War II, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt declared Presidential Proclamation 2526, the legal basis for internment under the authority of the Alien and Sedition Acts. With the United States’ entry into World War I, the German nationals were automatically classified as “enemy aliens.” Two of the four main World War I-era internment camps were located in Hot Springs, North Carolina and Fort Oglethorpe, Georgia. Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer wrote that “All aliens interned by the government are regarded as enemies, and their property is treated accordingly.”
By the time of World War II, the United States had a large population of ethnic Germans. Among residents of the United States in 1940, more than 1.2 million persons had been born in Germany, 5 million had two native-German parents, and 6 million had one native-German parent. Many more had distant German ancestry. With that many people of German ancestry, it seems impossible that they could have detained all of them. Nevertheless, at least 11,000 ethnic Germans, overwhelmingly German nationals were detained during World War II in the United States. The government examined the cases of German nationals individually, and detained relatively few in internment camps run by the Department of Justice, as per its responsibilities under the Alien and Sedition Acts. To a much lesser extent, some ethnic German United States citizens were classified as suspect after due process and also detained. There were also a small proportion of Italian nationals  and Italian Americans who were interned in relation to their total population in the United States. The United States had allowed immigrants from both Germany and Italy to become naturalized citizens, which many had done by then. It was much less likely for those people to be detained, if they had already become citizens. In the early 21st century, Congress considered legislation to study treatment of European Americans during World War II, but it did not pass the House of Representatives. Activists and historians have identified certain injustices against these groups. I suppose that some injustices were done, but those were times of war and strong measures were needed.
and Italian Americans who were interned in relation to their total population in the United States. The United States had allowed immigrants from both Germany and Italy to become naturalized citizens, which many had done by then. It was much less likely for those people to be detained, if they had already become citizens. In the early 21st century, Congress considered legislation to study treatment of European Americans during World War II, but it did not pass the House of Representatives. Activists and historians have identified certain injustices against these groups. I suppose that some injustices were done, but those were times of war and strong measures were needed.
 It has been 74 years since 17,740 Americans gave their lives to liberate the people of the Netherlands (often called Holland) from the Germans during World War II, and the people of Holland have never forgotten that sacrifice. For 74 years now, the people of the small village of Margraten, Netherlands have taken care of the graves of the lost at the Margraten American Cemetery. On Memorial Day, they come, every year, bringing Memorial Day bouquets for men and women they never knew, but whose 8,300 headstones the people of the Netherlands have adopted as their own. Of the 17,740 who were originally buried there, 9,440 were later moved to various paces in he United States by their families. “What would cause a nation recovering from losses and trauma of their own to adopt the sons and daughters of another nation?” asked Chotin, the only American descendant to speak on that Sunday 4 years ago. “And what would keep that commitment alive for all of these years, when the memory of that war has begun to fade? It is a unique occurrence in the history of civilization.”
It has been 74 years since 17,740 Americans gave their lives to liberate the people of the Netherlands (often called Holland) from the Germans during World War II, and the people of Holland have never forgotten that sacrifice. For 74 years now, the people of the small village of Margraten, Netherlands have taken care of the graves of the lost at the Margraten American Cemetery. On Memorial Day, they come, every year, bringing Memorial Day bouquets for men and women they never knew, but whose 8,300 headstones the people of the Netherlands have adopted as their own. Of the 17,740 who were originally buried there, 9,440 were later moved to various paces in he United States by their families. “What would cause a nation recovering from losses and trauma of their own to adopt the sons and daughters of another nation?” asked Chotin, the only American descendant to speak on that Sunday 4 years ago. “And what would keep that commitment alive for all of these years, when the memory of that war has begun to fade? It is a unique occurrence in the history of civilization.”
The people of Margraten immediately embraced the Americans, who had come to their aid when they needed it most. The town’s mayor invited the company’s commanders to sleep in his home, while the enlisted men slept in the schools. The protection against rain and buzz bombs was welcomed. Later, villagers hosted U.S. troops when the men were given rest-and-recuperation breaks from trying to breach the German frontier defenses, known as the Siegfried Line. “After four dark years of occupation, suddenly [the Dutch] people were free from the Nazis, and they could go back to their normal lives and enjoy all the freedoms they were used to. They knew they had to thank the American allies for that,” explained Frenk Lahaye, an associate at the cemetery.
By November 1944, two months after the village’s 1,500 residents had been freed from Nazi occupation by the U.S. 30th Infantry Division the town’s people were filled with gratitude, but the war wasn’t over. In late 1944  and early 1945, thousands of American soldiers would be killed in nearby battles trying to pierce the German defense lines. The area was filled with Booby-traps and heavy artillery fire. All that combined with a ferocious winter, dealt major setbacks to the Allies, who had already suffered losses trying to capture strategic Dutch bridges crossing into Germany during the ill-fated Operation Market Garden.
and early 1945, thousands of American soldiers would be killed in nearby battles trying to pierce the German defense lines. The area was filled with Booby-traps and heavy artillery fire. All that combined with a ferocious winter, dealt major setbacks to the Allies, who had already suffered losses trying to capture strategic Dutch bridges crossing into Germany during the ill-fated Operation Market Garden.
Now, the U.S. military needed a place to bury its fallen. The Americans ultimately picked a fruit orchard just outside Margraten. On the first day of digging, the sight of so many bodies made the men in the 611th Quartermaster Graves Registration Company ill. The bodies arrived in a procession of trucks and trailers. Death hung in the air over the whole village of Margraten. The sight of so much death caused a few of the people helping with the burials to become ill. They suddenly made a break for the latrines. The first burial at Margraten took place on November 10, 1944. Laid to rest in Plot A, Row 1, Grave 1: John David Singer Jr, a 25-year-old infantryman, whose remains would later be repatriated and buried in Denton, Maryland, about 72 miles east of Washington. Between late 1944 and spring 1945, up to 500 bodies arrived each day, so many that the mayor went door to door asking villagers for help with the digging. Over the next two years, about 17,740 American soldiers would be buried here, though the number of graves would shrink as thousands of families asked for their loved ones’ remains to be sent home, until 8,300 remained, and still, the graves are cared for by the town’s people, as if the dead were their own loved one. Not only that, but they have taken it upon themselves to research the deceased, and learn of their lives as a way of showing honor to these fallen heroes.
On May 29, 1945, the day before the cemetery’s first Memorial Day commemoration, 20 trucks from the 611th  collected flowers from 60 different Dutch villages. Nearly 200 Dutch men, women and children spent all night arranging flowers and wreaths by the dirt-covered graves, which bore makeshift wooden crosses and Stars of David. By 8am, the road leading into Margraten was jammed with Dutch people coming on foot, bicycle, carriages, horseback and by car. Silent film footage shot that day shows some of the men wearing top hats as they carried wreaths. A nun and two young girls laid flowers at a grave, then prayed. Solemn-faced children watched as cannons blasted salutes. The Dutch, Shomon wrote, “were perceptibly stirred, wept in bowed reverence.” All they do for these heroes is because they have vowed never to forget.
collected flowers from 60 different Dutch villages. Nearly 200 Dutch men, women and children spent all night arranging flowers and wreaths by the dirt-covered graves, which bore makeshift wooden crosses and Stars of David. By 8am, the road leading into Margraten was jammed with Dutch people coming on foot, bicycle, carriages, horseback and by car. Silent film footage shot that day shows some of the men wearing top hats as they carried wreaths. A nun and two young girls laid flowers at a grave, then prayed. Solemn-faced children watched as cannons blasted salutes. The Dutch, Shomon wrote, “were perceptibly stirred, wept in bowed reverence.” All they do for these heroes is because they have vowed never to forget.
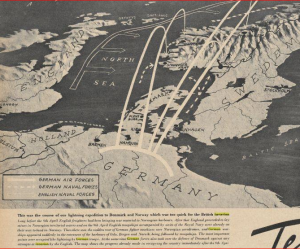 During World War II, it seems that there were a number of missed warnings about coming actions. Perhaps, if these warnings had been heeded, parts of the war, and indeed the length of it might have been different. One such event occurred when two German officers who were flying after consuming too much alcohol, became lost in the inky black night sky, when suddenly their plane began to nosedive. Maybe they thought, as their doomed plane plunged toward the ground, “Please let this be German soil we’re hurtling towards.” No matter what their thoughts were, they were definitely not headed for a crash landing in Germany, but rather they crashed in Holland.
During World War II, it seems that there were a number of missed warnings about coming actions. Perhaps, if these warnings had been heeded, parts of the war, and indeed the length of it might have been different. One such event occurred when two German officers who were flying after consuming too much alcohol, became lost in the inky black night sky, when suddenly their plane began to nosedive. Maybe they thought, as their doomed plane plunged toward the ground, “Please let this be German soil we’re hurtling towards.” No matter what their thoughts were, they were definitely not headed for a crash landing in Germany, but rather they crashed in Holland.
The crash landing in Holland was a big problem for the officers, because they were carrying battle plans for Hitler’s coming invasion of Holland. The plans, which involved exotic strategies like flamethrowers, and using gliders to silently deliver troops behind enemy lines, all seemed so unlikely that the  Dutch commanders refused to believe it. Just weeks later, it all unfolded exactly as the plan had foretold. Germany occupied Holland. It seems incredible but almost every daring German offensive was known well beforehand. Yet, in every case, those in power refused to see what was right in front of them. Hitler could have been stopped long before he was, if these botched early warnings had been taken seriously. In another such example, a German deserter was captured by the Russians. He gave up the plans to Hitler’s “Operation Barbarossa.” Yet, the Russian commanders found the 1,800 mile wide offensive too unlikely to believe. Then, just weeks later, they were caught off guard by the largest invasion in history.
Dutch commanders refused to believe it. Just weeks later, it all unfolded exactly as the plan had foretold. Germany occupied Holland. It seems incredible but almost every daring German offensive was known well beforehand. Yet, in every case, those in power refused to see what was right in front of them. Hitler could have been stopped long before he was, if these botched early warnings had been taken seriously. In another such example, a German deserter was captured by the Russians. He gave up the plans to Hitler’s “Operation Barbarossa.” Yet, the Russian commanders found the 1,800 mile wide offensive too unlikely to believe. Then, just weeks later, they were caught off guard by the largest invasion in history.
But, perhaps the most chilling warning of all came far earlier: before the war had even started. The warning came from an analyst dispatched to Hitler’s Germany in 1938. In 1939 he delivered a sobering prediction: the worst conflict in history was about to begin. He reported: “War is coming to Europe, but not until September at the earliest.” On September 1, 1939, Hitler launched his attack on Poland. World  War II had begun. That analyst belonged to a group that soon became part of the largest underground news and research network in the world. One that would go on to predict large world shifts with shocking accuracy: As early as 1987, this network predicted the fall of the Soviet Union. In 1989, they called the crash of the Japanese “miracle.” In the early 90s, they spoke out about the threat of radical Islamic terrorism. In the mid 2000s, they predicted the 2008 financial meltdown. They also predicted Donald Trump’s improbable win in the 2016 Presidential race, which in my opinion was their best prediction. Sadly, this underground news and research group, was not taken seriously in the warnings they gave, and the world paid the consequences for those missed warnings.
War II had begun. That analyst belonged to a group that soon became part of the largest underground news and research network in the world. One that would go on to predict large world shifts with shocking accuracy: As early as 1987, this network predicted the fall of the Soviet Union. In 1989, they called the crash of the Japanese “miracle.” In the early 90s, they spoke out about the threat of radical Islamic terrorism. In the mid 2000s, they predicted the 2008 financial meltdown. They also predicted Donald Trump’s improbable win in the 2016 Presidential race, which in my opinion was their best prediction. Sadly, this underground news and research group, was not taken seriously in the warnings they gave, and the world paid the consequences for those missed warnings.
 Recently, I found out that I am related to Audie Murphy, who was one of the most decorated American combat soldiers in World War II. As it turns out, he is my 7th cousin 3 times removed, on my dad’s side of the family. We share the same grandfather, Thomas Fuller, who is my 9th great grandfather, and Audie’s 7th great grandfather. Audie became an actor in 1948 and 1969, during which time he was beloved by many people, including my parents. I think they would have been very excited to find out that he was actually related to them, but then I guess they already know it by now. While his acting was impressive, it was his military career that always impressed my parents.
Recently, I found out that I am related to Audie Murphy, who was one of the most decorated American combat soldiers in World War II. As it turns out, he is my 7th cousin 3 times removed, on my dad’s side of the family. We share the same grandfather, Thomas Fuller, who is my 9th great grandfather, and Audie’s 7th great grandfather. Audie became an actor in 1948 and 1969, during which time he was beloved by many people, including my parents. I think they would have been very excited to find out that he was actually related to them, but then I guess they already know it by now. While his acting was impressive, it was his military career that always impressed my parents.
Audie Leon Murphy, was born on June 20, 1925 to Josie Bell Killian and Emmett Berry Murphy in Kingston, Texas. He was born into a large family of sharecroppers. Before long, his father abandoned them, and then his mother died when he was a teenager. Murphy left school in fifth grade to pick cotton and find other work to help support his family. He was a skilled rifleman, and hunting became a necessity for putting food on the table.
After the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor in 1941, Murphy’s decided that he wanted to help, but he was too young. His older sister helped him to falsify documentation about his birthdate in order to meet the minimum-age requirement for enlisting in the military, because he was only 16 at the time. He was turned down by the Navy and the Marine Corps, so he enlisted in the Army. He first saw action in the 1943 Allied invasion of Sicily. Then, in 1944 he participated in the Battle of Anzio, the liberation of Rome, and the invasion of southern France. Murphy fought at Montélimar and led his men on a successful assault at the L’Omet quarry near Cleurie in northeastern France in October. He received every military combat award for valor available from the U.S. Army, as well as French and Belgian awards for heroism. Murphy received the Medal of Honor for valor that he demonstrated at the age of 19 for single-handedly holding off an entire company of German soldiers for an  hour at the Colmar Pocket in France in January 1945, then leading a successful counterattack while wounded and out of ammunition.
hour at the Colmar Pocket in France in January 1945, then leading a successful counterattack while wounded and out of ammunition.
After his acting career ended, Murphy, like many actors without work, experienced money problems, but still, he refused offers to appear in alcohol and cigarette commercials, because he did not want to set a bad example. He never let Hollywood take away his high moral standards. Murphy died in a plane crash in Virginia in 1971, shortly before his 46th birthday. Such a sad ending to an amazing life. He was interred with full military honors at Arlington National Cemetery. His grave is one of the most visited sites in the cemetery.
 In March or 1941, the United States was largely considered neutral, so we could provide the countries, who were fighting Adolf Hitler, with war material. It was during this period of time, that the United Kingdom, an old enemy of the United States, since the United States fought against them for our independence, needed our help. Of course, we were allies by that time, and so the thought of a loan to the UK was not out o the question. The UK had been fighting against Adolf Hitler’s Germany army for a while by then, and funds were dwindling. The US loaned $4.33 billion to Britain in 1945, while Canada loaned US$1.19 billion in 1946, at a rate of 2% annual interest. It was a good deal, but in the end, the amount paid back was nearly double the amounts loaned in 1945 and 1946.
In March or 1941, the United States was largely considered neutral, so we could provide the countries, who were fighting Adolf Hitler, with war material. It was during this period of time, that the United Kingdom, an old enemy of the United States, since the United States fought against them for our independence, needed our help. Of course, we were allies by that time, and so the thought of a loan to the UK was not out o the question. The UK had been fighting against Adolf Hitler’s Germany army for a while by then, and funds were dwindling. The US loaned $4.33 billion to Britain in 1945, while Canada loaned US$1.19 billion in 1946, at a rate of 2% annual interest. It was a good deal, but in the end, the amount paid back was nearly double the amounts loaned in 1945 and 1946.
The United States was pulled into World War II shortly after, when Japan attacked Pearl Harbor. That marked to end of the program to provide military materials, because the United States was no longer considered neutral. At this point, the United States was very much needed in a very different way, and could not be neutral and be an effective help, but they also had a score to settle, and it could not be handled on the sidelines. The United States had hoped to sit this one out, but that was not to be. The Axis of Evil was winning against the Allied Nations, and they needed help, but it was the boldness of the attack on Pearl Harbor that finally awoke the sleeping giant that was the United States. The United States victory over Japan in the Battle of Midway was the turning point of the war in the Pacific. Then Germany invaded the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union defeated Germany at Stalingrad, marking the turning point of the war in Eastern Europe. As we all know, in the end the Allies were victorious in World War II.
There are still World War I debts owed to and by Britain. Since a moratorium on all debts from that conflict was agreed at the height of the Great Depression, no repayments have been made to or received from other nations since 1934. Despite the favorable rates there were six years in which Britain deferred payment because of economic or political crises. Britain settled its World War II debts to the United States and Canada when it paid the final  two installments in 2006. The payments of $83.25 million to the US and US$22.7 million to Canada are the last of 50 installments since 1950. Upon the final payments, the UK will have paid back a total of $7.5 billion to the US and US$2 billion to Canada. “This week we finally honor in full our commitments to the United States and Canada for the support they gave us 60 years ago,” said Treasury Minister Ed Balls at the time of those final payments. “It was vital support which helped Britain defeat Nazi Germany and secure peace and prosperity in the post-war period. We honor our commitments to them now as they honored their commitments to us all those years ago,” he added.
two installments in 2006. The payments of $83.25 million to the US and US$22.7 million to Canada are the last of 50 installments since 1950. Upon the final payments, the UK will have paid back a total of $7.5 billion to the US and US$2 billion to Canada. “This week we finally honor in full our commitments to the United States and Canada for the support they gave us 60 years ago,” said Treasury Minister Ed Balls at the time of those final payments. “It was vital support which helped Britain defeat Nazi Germany and secure peace and prosperity in the post-war period. We honor our commitments to them now as they honored their commitments to us all those years ago,” he added.

 A number of years ago, I requested my dad, Staff Sergeant Allen Lewis Spencer’s military records from the National Personnel Records Center (NPRC) in Saint Louis, Missouri, only to be told that the records had been destroyed by a fire in 1973. I hadn’t heard about this before, and so really knew nothing about the details, except that I would never be able to find any more records of my dad’s military service during World War II, other than the ones we had, which was comparatively little. I wondered how it could be that the only military records for all those men were stored in one building, with no back up records. I know computers were not used as often, but there were things like microfiche back then. Nevertheless, the records were lost…and the loss felt devastating to me.
A number of years ago, I requested my dad, Staff Sergeant Allen Lewis Spencer’s military records from the National Personnel Records Center (NPRC) in Saint Louis, Missouri, only to be told that the records had been destroyed by a fire in 1973. I hadn’t heard about this before, and so really knew nothing about the details, except that I would never be able to find any more records of my dad’s military service during World War II, other than the ones we had, which was comparatively little. I wondered how it could be that the only military records for all those men were stored in one building, with no back up records. I know computers were not used as often, but there were things like microfiche back then. Nevertheless, the records were lost…and the loss felt devastating to me.
When I heard about the fire that destroyed my dad’s records, it all seemed like the distant past, but in reality, it was during my high school years. Then, it just seemed like a bad dream…a nightmare really. I couldn’t believe that there was no way to get copies of those records. My dad’s pictures, one of which was signed by the pilot of Dad’s B-17, on which Dad was a top turret gunner. Those pictures and the few records are all we have of his war years, and to this day, that makes me sad.
The fire broke out on July 13, 1973 and quickly engulfed the top floor of the National Personnel Records Center (NPRC). In less 15 minutes from the time the fire was reported, the first firefighters arrived at the sixth floor of the building, only to be forced to retreat as their masks began to melt on their faces. The fire was that hot!! There was just no way to successfully save the documents that were stored there. The fire burned out of control for more than 22 hours…even with 42 fire districts attempting to extinguish the flames. It was not until five days later that it was finally completely out. Besides the burning of records, the tremendous heat of the fire warped shelves while water damage caused some surviving documents to carry mold.

About 73% to 80% of the approximately 22 million individual Official Military Personnel Files stored in the building were destroyed. The records lost were those of former members of the U.S. Army, the Army Air Force, and the Air Force who served between 1912 and 1963. My dad joined the Army Air Force on March 19, 1943 and was discharged October 3, 1945. Many of the documents lost were from those years. They were gone, and there was no way to get them back. The National Personnel Records Center staff continues to work to preserve the damaged records that ere saved. There were about 6.5 million records recovered since the fire.

 Despite having a domineering father, who was never pleased with anything he did, Edsel Ford, the son of the founder of Ford Motors is mainly remembered for the Edsel, a failed 1958-60 car model. In reality, he was one of the masterminds of the Allied victory in World War II. Against the wishes of his father, Edsel Ford telephones William Knudsen of the U.S. Office of Production Management on June 12, 1940, to confirm Ford Motor Company’s acceptance of Knudsen’s proposal to manufacture 9,000 Rolls-Royce-designed engines to be used in British and United States airplanes. In all, they would build, 9,000 B-24 Liberator bombers, 278,000 Jeeps, 93,000 military trucks, 12,000 armored cars, 3,000 tanks, and 27,000 tank engines, but it was not without a few stumbling blocks. Edsel and Charles Sorensen, Ford’s production chief, had apparently gotten the go-ahead from Henry Ford by June 12, when Edsel telephoned Knudsen to confirm that Ford would produce 9,000 Rolls-Royce Merlin airplane engines (6,000 for the RAF and 3,000 for the U.S. Army). However, as soon as the British press announced the deal, Henry Ford personally and publicly canceled it, telling a reporter: “We are not doing business with the British government or any other government.”
Despite having a domineering father, who was never pleased with anything he did, Edsel Ford, the son of the founder of Ford Motors is mainly remembered for the Edsel, a failed 1958-60 car model. In reality, he was one of the masterminds of the Allied victory in World War II. Against the wishes of his father, Edsel Ford telephones William Knudsen of the U.S. Office of Production Management on June 12, 1940, to confirm Ford Motor Company’s acceptance of Knudsen’s proposal to manufacture 9,000 Rolls-Royce-designed engines to be used in British and United States airplanes. In all, they would build, 9,000 B-24 Liberator bombers, 278,000 Jeeps, 93,000 military trucks, 12,000 armored cars, 3,000 tanks, and 27,000 tank engines, but it was not without a few stumbling blocks. Edsel and Charles Sorensen, Ford’s production chief, had apparently gotten the go-ahead from Henry Ford by June 12, when Edsel telephoned Knudsen to confirm that Ford would produce 9,000 Rolls-Royce Merlin airplane engines (6,000 for the RAF and 3,000 for the U.S. Army). However, as soon as the British press announced the deal, Henry Ford personally and publicly canceled it, telling a reporter: “We are not doing business with the British government or any other government.”
Unlike other automakers, Ford had already built a successful airplane in the 1920s called the Tri-Motor. That fact made them the logical choice when the war effort needed more planes. In two meetings in late May and early June 1940, Knudsen and Edsel Ford agreed that Ford would manufacture the new fleet of aircraft for the RAF on an expedited basis. The one significant obstacle was Edsel’s father Henry Ford, who still retained complete control over the company he founded, even though he had turned the figurehead control over to his son. Henry Ford was well known for his opposition to the possible U.S. entry into World War II, so it would be up to Edsel to convince him that it was necessary.
According to Douglas Brinkley’s biography of Ford, “Wheels for the World,” Henry Ford had in effect already accepted a contract from the German government. The Ford subsidiary Ford-Werke in Cologne was doing business with the Third Reich at the time, which Ford’s critics took as proof that he was concealing a pro-German bias behind his claims to be a man of peace. Nevertheless, as U.S. entry into the war became more of 
 a certainty, Ford reversed his position, and the company opened a large new government-sponsored facility at Willow Run, Michigan in May of 1941, for the purposes of manufacturing the B-24E Liberator bombers for the Allied war effort. Ford Motor plants also produced a great deal of other war materiel during World War II, including a variety of engines, trucks, jeeps, tanks and tank destroyers. The production needs met by Ford Motor Company during World War II were instrumental in the Allied victory in that war.
a certainty, Ford reversed his position, and the company opened a large new government-sponsored facility at Willow Run, Michigan in May of 1941, for the purposes of manufacturing the B-24E Liberator bombers for the Allied war effort. Ford Motor plants also produced a great deal of other war materiel during World War II, including a variety of engines, trucks, jeeps, tanks and tank destroyers. The production needs met by Ford Motor Company during World War II were instrumental in the Allied victory in that war.
 When a mistake is made in the air, it usually results in a disaster. Air disasters often involve the pilot, a mechanic, or an old part. Of course, some of the worst disasters were caused when an air traffic controller sent two planes to the same place at the same altitude. The resulting mid-air collision killed everyone on board. Mistakes are never good, but in the air they are especially devastating.
When a mistake is made in the air, it usually results in a disaster. Air disasters often involve the pilot, a mechanic, or an old part. Of course, some of the worst disasters were caused when an air traffic controller sent two planes to the same place at the same altitude. The resulting mid-air collision killed everyone on board. Mistakes are never good, but in the air they are especially devastating.
War is no different, in fact mistakes in war can be really disastrous. Gunners shooting at the enemy planes are often so focused that when the enemy flies past their own squadron, they can end up shooting down their own squadron members with friendly fire. 
The strange thing is that sometimes, a would be disaster ends up becoming one of the greatest miracles. Such was the case during World War II. The Americans planed a bombing run, and it was going to be a big bombing run. The orders had been issued. The problem…one squadron accidentally showed up thousands of feet lower down than the other one. In many cases, this would not have bee such a big problem, but both squadrons ended up a the drop site at the same time. The scheduled bombing began, and no one would really realize what was about to happen until it was too late.
Neither of the squadrons saw each other, until the bombs had been dropped. Miraculously, none of the lower planes were hit by the higher planes. It was a miracle of epic proportions. In addition, the Germans thought  that the Allies had come up with an ingenious bombing strategy to bomb an area twice as much. After that bombing event, the Germans were scared that the Allies had this level of skill. It seemed completely impossible that they could plan a bomb run in which the lower planes flew in sync enough to allow the upper planes to drop their bombs in between the lower planes, while the lower planes were also dropping their bombs. It was impossible, and yet it happened. The impossible was achieved without one bit of planning. There is simply no other word for it. It was a miracle. God took a potential disaster and turned it into one of the greatest feats of warfare.
that the Allies had come up with an ingenious bombing strategy to bomb an area twice as much. After that bombing event, the Germans were scared that the Allies had this level of skill. It seemed completely impossible that they could plan a bomb run in which the lower planes flew in sync enough to allow the upper planes to drop their bombs in between the lower planes, while the lower planes were also dropping their bombs. It was impossible, and yet it happened. The impossible was achieved without one bit of planning. There is simply no other word for it. It was a miracle. God took a potential disaster and turned it into one of the greatest feats of warfare.

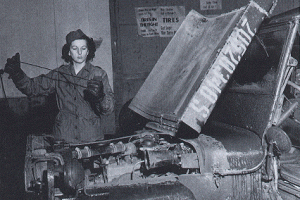 World War II saw many changes in how women were viewed in the normally male-dominated world. With so many men off fighting the war, the women stepped up to do the jobs of riveters in the shipyards, and they stepped up in many other occupations too. If there are no men to do the jobs, someone had to keep the country running, and the United States found out that women were up for the task. I don’t suppose that everyone thought that women could do it, but they simply had no choice. World War II was the largest and most violent armed conflict in the history of mankind. This war taught us, not only about the profession of arms, but also about military preparedness, global strategy, and combined operations in the coalition war against fascism.
World War II saw many changes in how women were viewed in the normally male-dominated world. With so many men off fighting the war, the women stepped up to do the jobs of riveters in the shipyards, and they stepped up in many other occupations too. If there are no men to do the jobs, someone had to keep the country running, and the United States found out that women were up for the task. I don’t suppose that everyone thought that women could do it, but they simply had no choice. World War II was the largest and most violent armed conflict in the history of mankind. This war taught us, not only about the profession of arms, but also about military preparedness, global strategy, and combined operations in the coalition war against fascism.
Prior 1942, the only way for women to be involved in the service was as an Army Nurse, in the Army Nurse Corps, but early in 1941 Congresswoman Edith Nourse Rogers of Massachusetts met with General George C. Marshall, the Army’s Chief of Staff, and told him that she intended to introduce a bill to establish an Army women’s corps, separate and distinct from the existing Army Nurse Corps. Congress approved that bill on May 14, 1942, and the Women’s Army Auxiliary Corps (WAAC) was born. The WAAC bill became law on May 15, 1942. Congressional opposition to the bill centered around southern congressmen. With women in the armed services, one representative asked, “Who will then do the cooking, the washing, the mending, the humble homey tasks to which every woman has devoted herself; who will nurture the children?” These days he would have been run out of Congress for having backward ideas but it was a different time, and one that some women of today truly miss…especially young mothers.
After a long and bitter debate which filled ninety-eight columns in the Congressional Record, the bill finally passed the House 249 to 86. The Senate approved the bill 38 to 27 on May 14. When President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed the bill into law the next day, he set a recruitment goal of 25,000 for the first year. WAAC recruitment topped that goal by November of 1942, at which point Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson authorized WAAC enrollment at 150,000, the original ceiling set by Congress. The day the bill became law, Stimson appointed Oveta Culp Hobby as Director of the WAAC. As chief of the Women’s Interest Section in the Public Relations Bureau at the War Department, Hobby had helped shepherd the WAAC bill through Congress. She had impressed both the media and the public when she testified in favor of the WAAC bill in January. In the words of the Washington Times Herald, “Mrs. Hobby has proved that a competent, efficient woman who works longer days than the sun does not need to look like the popular idea of a competent, efficient woman.” Women would go on to not only become competent and efficient, but requested…sometimes above the men!!
So, what led to the Army’s decision to enlist women during World War II? The answer is simple. The “unfathomable” became reality, as the Army struggled to fulfill wartime quotas from an ever-shrinking pool of candidates. By mid-1943, the Army was simply running out of eligible white men to enlist. The Army could scarcely spare those men already in the service for non-combatant duties. General Dwight D. Eisenhower remarked: “The simple headquarters of a Grant or Lee were gone forever. An Army of filing clerks, stenographers, office managers, telephone operators, and chauffeurs had become essential, and it was scarcely 
 less than criminal to recruit these from needed manpower when great numbers of highly qualified women were available.” While women played a vital role in the success of World War II, their admission into combat roles would not come for many years, and many weren’t sure it was a good idea when it did. The WAC, as a branch of the service, was disbanded in 1978 and all female units were integrated with male units.
less than criminal to recruit these from needed manpower when great numbers of highly qualified women were available.” While women played a vital role in the success of World War II, their admission into combat roles would not come for many years, and many weren’t sure it was a good idea when it did. The WAC, as a branch of the service, was disbanded in 1978 and all female units were integrated with male units.

 My dad was the top turret gunner and flight engineer on a B-17G Fortress Heavy Bomber during World War II. That was something that my family always knew. Dad didn’t talk much about it, but we were always very proud of him. What we didn’t know about all of that was that my dad was on the toughest plane ever built. At the time of his service, this little known fact probably wouldn’t have brought much comfort to his parents or siblings, but now, all these years later, it somehow brings a good measure of comfort to my dad’s daughter…me. My dad made it home from the war, of course. I know that there were times that his plane sustained damage, but it always brought the crew home.
My dad was the top turret gunner and flight engineer on a B-17G Fortress Heavy Bomber during World War II. That was something that my family always knew. Dad didn’t talk much about it, but we were always very proud of him. What we didn’t know about all of that was that my dad was on the toughest plane ever built. At the time of his service, this little known fact probably wouldn’t have brought much comfort to his parents or siblings, but now, all these years later, it somehow brings a good measure of comfort to my dad’s daughter…me. My dad made it home from the war, of course. I know that there were times that his plane sustained damage, but it always brought the crew home.
The testing of the B-17 Bomber, as is the case with most planes was rigorous. Is this great trial, the B-17 Flying Fortress put up one of most impressive displays, proving not only an effective carrier of firepower in which the plane delivered over a 3rd of the ordnance dropped by the allies in Europe and much of the ordnance dropped in the Pacific, but an astoundingly tough plane. Pilots and crews soon learned that the B-17s, which flew tens of thousands of missions under heavy anti-aircraft and fighter-plane pressure, could take extraordinary damage and still get home.
During the war years, the B-17s proved time and time again just what a wonderful plane they were. While they may not have brought their entire crew home every time they returned, they came home with part of them even with parts of the nose, propellers, and wings missing…and even with a tail that was hanging on by a thread. Of course, if the wing was torn completely off or the plane took a hit that ripped it in half, it did go down, but that is to be expected, as was the case with B-17G-15-BO “Wee Willie,” 322d BS, 91st BG, after direct flak hit on her 128th mission.
Still, the condition in which some of these planes came home would have shocked the builder altogether, if you ask me. I have looked at the pictures of these damaged planes, and I don’t know how they stayed in flight. The 
 “All American,” with the 97th Bomber Group, made without a doubt, the most astonishing return. The plane had a huge gash in it’s tail section from a collision with an enemy fighter, whose wing sliced almost completely through the fuselage. The tail gunner was trapped at the rear of the plane because the floor connecting his section to the rest of the plane was gone. The plane was piloted by Lieutenant Kendrick Bragg, who flew 90 minutes back to base with the tail barely hanging on. One crew member said that the tail wagged like a dog’s tail. The pilot, proceeded to drop his bombs, and then made a U-turn taking the plane in a wide turn over 70 miles, so as not to stress the tail. When the plane landed and came to a complete stop, the tail finally broke off. Now that is one tough plane!!
“All American,” with the 97th Bomber Group, made without a doubt, the most astonishing return. The plane had a huge gash in it’s tail section from a collision with an enemy fighter, whose wing sliced almost completely through the fuselage. The tail gunner was trapped at the rear of the plane because the floor connecting his section to the rest of the plane was gone. The plane was piloted by Lieutenant Kendrick Bragg, who flew 90 minutes back to base with the tail barely hanging on. One crew member said that the tail wagged like a dog’s tail. The pilot, proceeded to drop his bombs, and then made a U-turn taking the plane in a wide turn over 70 miles, so as not to stress the tail. When the plane landed and came to a complete stop, the tail finally broke off. Now that is one tough plane!!

