World War II
 Captain Leonard Treherne “Max” Schroeder Jr looked out over the choppy water between the landing craft he was on and the shores of their destination…the beaches of Normandy, France. The beaches had been given code names, to protect the mission…Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, and Sword; the operation was code named Overlord. The beach ahead of Schroeder had been code named Utah. Along the hills behind the beach were many German bunkers, with armed German snipers hiding inside of them. Schroeder knew they were just waiting for them to step onto the beach before the snipers would open fire.
Captain Leonard Treherne “Max” Schroeder Jr looked out over the choppy water between the landing craft he was on and the shores of their destination…the beaches of Normandy, France. The beaches had been given code names, to protect the mission…Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, and Sword; the operation was code named Overlord. The beach ahead of Schroeder had been code named Utah. Along the hills behind the beach were many German bunkers, with armed German snipers hiding inside of them. Schroeder knew they were just waiting for them to step onto the beach before the snipers would open fire.
Schroeder was about to find out firsthand, just how bad this day was going to be. In fact, he was the first American soldier whose feet hit the sand on the beach at Normandy on D-Day…so, while his men were right behind him, he would experience this horrific battle at its inception. I have wondered just how they knew that he was first amid all that chaos, but it is a documented fact. Operation Overlord was pivotal in the United States’ overall success, but it was also extremely bloody, with great loss of life. While every life lost was horrific, the men who stormed the beaches of Normandy that day were willing to give their lives for a  cause that they felt was essential…and I have so much respect for each and every one of them. Captain Schroeder led his team of men onto the beach…along with thousands of others…and managed to get them to their secured location. Nevertheless, during the mission, he was shot twice by German snipers. Once the mission was accomplished and his men were where they needed to be, Captain Schroeder passed out from his injuries.
cause that they felt was essential…and I have so much respect for each and every one of them. Captain Schroeder led his team of men onto the beach…along with thousands of others…and managed to get them to their secured location. Nevertheless, during the mission, he was shot twice by German snipers. Once the mission was accomplished and his men were where they needed to be, Captain Schroeder passed out from his injuries.
Schroeder woke up at an aid station on the beach, with medics taking care of his wounds so he could be transported to an army hospital in England. While in England, he recovered and had a lot of time to read all about his role in the successful mission…in many papers. I don’t know if he realized that his had been such a pivotal role in the battle, but it had. At the time, I doubt if he thought he would ever see that beach again, but in 1994, Schroeder revisited the beach at Normandy as a guest of the French  government. It was an amazing ceremony to pay homage to his heroic efforts that helped turn the tide for the Allies in World War II. It was an honor he had given no thought to as he looked out at that beach on that long ago June 6, 1944…but, an honor that he had earned along with all the other men who fought, and the many who had died. I’m sure those who gave all, were thankful that some made it home and managed to live a long life of liberty. Captain Leonard “Max” Schroeder, who was born on July 16, 1918, in Linthicum Heights, Maryland, passed away from emphysema early on the morning of May 26, 2009, in Largo, Florida at the age of 90.
government. It was an amazing ceremony to pay homage to his heroic efforts that helped turn the tide for the Allies in World War II. It was an honor he had given no thought to as he looked out at that beach on that long ago June 6, 1944…but, an honor that he had earned along with all the other men who fought, and the many who had died. I’m sure those who gave all, were thankful that some made it home and managed to live a long life of liberty. Captain Leonard “Max” Schroeder, who was born on July 16, 1918, in Linthicum Heights, Maryland, passed away from emphysema early on the morning of May 26, 2009, in Largo, Florida at the age of 90.

 Most people, these days, have probably never heard of Marion Robert Morrison, although I’ll bet that most people have seen at least one of his movies, or at the very least a commercial advertising one of his movies on some of the old movie channels. Maybe if I said that his name was John Wayne or even The Duke (his famous nickname), more people would recognize the famous American West actor. John Wayne actually became the epitome of the American West. Wayne was born on May 26, 1907, at 224 South Second Street in Winterset, Iowa, to Clyde Leonard Morrison (1884–1937), who was the son of American Civil War veteran Marion Mitchell Morrison (1845–1915), and the former Mary “Molly” Alberta Brown (1885–1970), who was from Lancaster County, Nebraska. He weighed a whopping 13 pounds at birth. Wayne claimed his middle name was soon changed from Robert to Michael when his parents decided to name their next son Robert. That fact, if it is a fact, cannot be confirmed even with extensive research, because no such legal change was found. Wayne’s legal name remained Marion Robert Morrison his entire life, but he often went by Marion Michael Morrison…before becoming John Wayne.
Most people, these days, have probably never heard of Marion Robert Morrison, although I’ll bet that most people have seen at least one of his movies, or at the very least a commercial advertising one of his movies on some of the old movie channels. Maybe if I said that his name was John Wayne or even The Duke (his famous nickname), more people would recognize the famous American West actor. John Wayne actually became the epitome of the American West. Wayne was born on May 26, 1907, at 224 South Second Street in Winterset, Iowa, to Clyde Leonard Morrison (1884–1937), who was the son of American Civil War veteran Marion Mitchell Morrison (1845–1915), and the former Mary “Molly” Alberta Brown (1885–1970), who was from Lancaster County, Nebraska. He weighed a whopping 13 pounds at birth. Wayne claimed his middle name was soon changed from Robert to Michael when his parents decided to name their next son Robert. That fact, if it is a fact, cannot be confirmed even with extensive research, because no such legal change was found. Wayne’s legal name remained Marion Robert Morrison his entire life, but he often went by Marion Michael Morrison…before becoming John Wayne.
When he was six years old, Wayne’s family moved to Glendale, California, where he like many teens in those days, had a paper route that got him up at four in the morning to deliver newspapers. After school, he played football and made deliveries for local stores. After high school, he had big ambitions to attend the U.S. Naval Academy, but his dreams were dashed when they rejected him. Then, he accepted a full scholarship to play football at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, which is quite likely the very thing that led to his entire future, and not in football or academics.
For most football players, having a job isn’t an easy feat, because of the football and study schedules, so in the summer of 1926, Wayne’s football coach found him a job as an assistant prop man on the set of a movie directed by John Ford. Ford saw something more is the handsome young football player, and he started to use Wayne as an extra in his films. It’s strange, maybe, that I think that John Wayne became more handsome as he got older. The younger verson, while handsome, lacked the character that really defines some men. That led to larger roles, and in 1930, Ford recommended John Wayne for Fox’s epic Western, “The Big Trail.” Wayne won the part, but the movie did poorly, and Fox let his contract lapse. That didn’t deter John Wayne, who had by then been bitten by the acting bug. Over the next decade, he worked tirelessly on a number of low-budget films, to improve his acting abilities, and in the end, his old friend and mentor, John Ford gave him his big break, when he cast him in the 1939 western, “Stagecoach.” The rest is history, as John Wayne starred in more than 77 movies. Including my favorites, “Maclintock,” “True Grit,” “The Sons of Katie Elder,” and “Hell Fighters.” While John Wayne got his start in Westerns, he also did a number of military movies. It wasn’t hard to transition from a valiant cowboy or cavalry soldier to the brave WWII fighters of films like Sands of Iwo Jima (1949) and Flying Leathernecks (1951). John Wayne was deeply conservative in his politics, and he used his 1968 film, The Green Berets, to express his support of the American government’s war in Vietnam.
Unfortunately, by the late 1960s, some Americans had tired of Wayne and his simplistically masculine and patriotic characters. I simply cannot understand that at all, except that people had started to look for the increasingly sinister in movies. Sadly, western movies began rejecting the simple black-and-white moral codes championed by Wayne and replacing them with a more complex and tragic view of the American West…not a good move for the people. Nevertheless, John Wayne proved more adaptable than many expected. True Grit 
 (1969) allowed him to escape the narrow confines of his own good-guy image, but still remain basically “the good guy” in reality. Nevertheless, John Wayne was entering the final years of his life, whether he knew it or not. His final film, The Shootist (1976), proved once and for all that he was an actor who had earned the right to be called elite, when he won over even his most severe critics. At the time of the filming of “The Shootist,” John Wayne was battling lung cancer, while playing the part of a dying gunfighter whose moral codes and principles no longer fit in a changing world. Three years later, Wayne died of cancer. To this day, public polls identify him as one of the most popular actors of all time.
(1969) allowed him to escape the narrow confines of his own good-guy image, but still remain basically “the good guy” in reality. Nevertheless, John Wayne was entering the final years of his life, whether he knew it or not. His final film, The Shootist (1976), proved once and for all that he was an actor who had earned the right to be called elite, when he won over even his most severe critics. At the time of the filming of “The Shootist,” John Wayne was battling lung cancer, while playing the part of a dying gunfighter whose moral codes and principles no longer fit in a changing world. Three years later, Wayne died of cancer. To this day, public polls identify him as one of the most popular actors of all time.

 It’s almost unheard of to have a cavalry officer suddenly completely move in a different direction, and become an Army Air Force officer, but on May 15, 1942, Lieutenant Ronald Reagan, who had enlisted in the Army in 1935, was a cavalry officer at the time, applied for reassignment to the Army Air Force. Switching from the Army to the Army Air Force, while not unheard of, was an unusual event, especially in that no one really expected to be in the service for an extended period of time. For the most part, during World War II, it had been agreed upon that the soldier would be returned to the United States by February 1946. That said, it didn’t always make sense to make such a big move as switching branches of service.
It’s almost unheard of to have a cavalry officer suddenly completely move in a different direction, and become an Army Air Force officer, but on May 15, 1942, Lieutenant Ronald Reagan, who had enlisted in the Army in 1935, was a cavalry officer at the time, applied for reassignment to the Army Air Force. Switching from the Army to the Army Air Force, while not unheard of, was an unusual event, especially in that no one really expected to be in the service for an extended period of time. For the most part, during World War II, it had been agreed upon that the soldier would be returned to the United States by February 1946. That said, it didn’t always make sense to make such a big move as switching branches of service.
Then Lieutenant Ronald Reagan was, at least at that time, mostly looking to have a career in acting, and it was here that he would eventually put his thespian background to use making World War II propaganda films. Once his transfer was approved on June 9, 1942, Reagan was given a job as a public relations officer for the First Motion Picture Unit. The First Motion Picture Unit (FMPU) produced military training, morale, and propaganda films to aid the war effort. FMPU released Frank Capra’s “Why We Fight” series and a documentary of the bomber Memphis Belle, the crew of which completed a standard-setting 25 bombing missions in Europe for the first time. No other plane and crew, to that date, had managed to fly the 25 missions and make it back. War was a dangerous lifestyle for the Allied planes. The films were screened on domestic training grounds and in troop camps overseas as well as in movie theaters at home. The Memphis Belle documentary gave people hope that it could be done, and all was not lost.
Reagan did several other films, one of which, “Air Force,” which was later renamed “Beyond the Line of Duty.” That movie told the true story of the heroic feats of aviator Shorty Wheliss and his crew. Reagan narrated the film. While the documentary was originally intended simply to promote investment in war bonds, it won an 
 Academy Award in 1943 for best short subject. Reagan went on to narrate or star in three more shorts for FMPU including “For God and Country,” “Cadet Classification,” and “The Rear Gunner.” Reagan also appeared as Johnny Jones in the 1943 full-length musical film This is the Army. Of course, as we all know, Ronald Reagan’s true destiny was to become one of our greatest presidents of all time and a very brave man.
Academy Award in 1943 for best short subject. Reagan went on to narrate or star in three more shorts for FMPU including “For God and Country,” “Cadet Classification,” and “The Rear Gunner.” Reagan also appeared as Johnny Jones in the 1943 full-length musical film This is the Army. Of course, as we all know, Ronald Reagan’s true destiny was to become one of our greatest presidents of all time and a very brave man.
 Wars leave unfortunate consequences, one of the biggest being orphaned children. World War II is no exception to that rule. After the surrender of Germany, the nation was basically split into four sections…the American Zone, the Soviet Zone, the British Zone, and the French Zone. It was all part of the denazification process. The term denazification refers to the removal of the physical symbols of the Nazi regime. In 1957 the West German government re-issued World War II Iron Cross medals, among other decorations, without the swastika in the center. That was just one of the ways that the Nazi regime was removed from Germany.
Wars leave unfortunate consequences, one of the biggest being orphaned children. World War II is no exception to that rule. After the surrender of Germany, the nation was basically split into four sections…the American Zone, the Soviet Zone, the British Zone, and the French Zone. It was all part of the denazification process. The term denazification refers to the removal of the physical symbols of the Nazi regime. In 1957 the West German government re-issued World War II Iron Cross medals, among other decorations, without the swastika in the center. That was just one of the ways that the Nazi regime was removed from Germany.
Another way was the Denazified School System and the denazification of the rest of the German government…which was then reassembled without the Nazi symbolism. With the school system effectively out of commission, the children of Berlin had very little or even no structure in their lives at all. These were children whose lives had been shredded by the war, many of whom had been orphaned by the conflict or had lost at least one parent. That lead to an overall lack of adult supervisors. Children, and especially teens and preteens, roamed the streets in packs. The situation was especially difficult for the children who had lost both parents. There weren’t any real orphanages either, and so these children formed their own “families” on the streets…like street gangs. These children were known as German “wolf children” also known as “Wolfskinder,” but the reality was that they were simply the forgotten orphans of World War II.
The schools eventually reopened, but they were often in half-ruined facilities, that were underfunded and understaffed, with some schools reporting student-to-faculty ratios of 89 to 1. That kind of a classroom ratio is far too big to be able to effectively teach the students. And the re-opened schools didn’t really address the issue of these orphaned “wolf children” who were often in hiding whenever authorities were around. These children were most likely afraid of authority, because it was the authorities who got their parents killed in the first place. Many of these children were forced to flee what was then East Prussia to Lithuania at the end of World War II. They felt like the German government had failed them. These children survived hunger, cold, and the loss of their identity, and the German government had long overlooked them, so why would they trust the government now.
No one really knows just how many “wolf children” there were. That number can only be estimated. Some say there were up to 25,000 of them roaming the woods and swamps of East Prussia and Lithuania after 1945. Russians were actually forbidden from taking in these “fascist children.” These children were actually told to go to Lithuania and given the promise that there would be food there. When they arrived, they couldn’t speak the language and they had no papers, so they had no identity…no one could even know their names. Those who were taken in often had every shred of memorabilia from their past stripped from them and tossed in the trash. That was the last part of who they really were. It was the price they would pay for food, safety, and security; and it was a failure of the German government, and the four nations who were in charge of reorganizing Germany. I suppose some would disagree with me on that note, but the reality is plain to see. If these children came across kind locals, the “Vokietukai” or little Germans, in Lithuanian, as they were known, were helped with buckets of soup in front of the doors, giving the children a little nourishment. If the residents were not so kind, they would set their dogs on the children.
While the “Vokietukai” had many struggles in Lithuania, life was still better than the fate that awaited the 
 children who were too weak to make it to the Baltic states. There were thousands of these children, and they were sent to Soviet homes run by the military administration. That was the fate of approximately 4,700 German children in 1947, according to historian Ruth Leiserowitz, who has researched the fates of wolf children. Later that year, many of them were sent to the Soviet occupation zone. That zone later became the German Democratic Republic (GDR). Those poor children traveled in freight trains without any straw to sleep on…similar the Holocaust deportation years. These children were young…between 2 and 16 years of age. They arrived in East Germany after four days and four nights…really more dead than alive. There, they were put in orphanages or adopted by avid Communists. They never really escaped Communism…and that is the saddest part of all.
children who were too weak to make it to the Baltic states. There were thousands of these children, and they were sent to Soviet homes run by the military administration. That was the fate of approximately 4,700 German children in 1947, according to historian Ruth Leiserowitz, who has researched the fates of wolf children. Later that year, many of them were sent to the Soviet occupation zone. That zone later became the German Democratic Republic (GDR). Those poor children traveled in freight trains without any straw to sleep on…similar the Holocaust deportation years. These children were young…between 2 and 16 years of age. They arrived in East Germany after four days and four nights…really more dead than alive. There, they were put in orphanages or adopted by avid Communists. They never really escaped Communism…and that is the saddest part of all.

 My favorite part of war history, if a person should have a favorite part, would be World War II. It was the war my dad, Allen Spencer fought in, and maybe that is why I am so interested in it and in the B-17 Flying Fortress, from which he fought and returned home. The men and women who fought in World War II are called the Greatest Generation, and maybe because my dad was a part of that, I am partial to that part of history. I find it a bit strange that while the Vietnam Memorial Fund, Inc (VVMF) was incorporated as a non-profit organization to establish a memorial to veterans of the Vietnam War, on April 27, 1979, four years after the Fall of Saigon, but the World War II Memorial didn’t open until April 29, 2004, in Washington DC. Of course, I think it was cool that it opened on my birthday, but it really was a long overdue recognition for the 16 million US men and women who served in the war. The memorial is located on 7.4 acres on the former site of the Rainbow Pool at the National Mall between the Washington Monument and the Lincoln Memorial. The Capitol dome can be seen to the east, and Arlington Cemetery is just across the Potomac River to the west. It really is a beautiful setting and shows the proper honor to these men and women of the Greatest Generation.
My favorite part of war history, if a person should have a favorite part, would be World War II. It was the war my dad, Allen Spencer fought in, and maybe that is why I am so interested in it and in the B-17 Flying Fortress, from which he fought and returned home. The men and women who fought in World War II are called the Greatest Generation, and maybe because my dad was a part of that, I am partial to that part of history. I find it a bit strange that while the Vietnam Memorial Fund, Inc (VVMF) was incorporated as a non-profit organization to establish a memorial to veterans of the Vietnam War, on April 27, 1979, four years after the Fall of Saigon, but the World War II Memorial didn’t open until April 29, 2004, in Washington DC. Of course, I think it was cool that it opened on my birthday, but it really was a long overdue recognition for the 16 million US men and women who served in the war. The memorial is located on 7.4 acres on the former site of the Rainbow Pool at the National Mall between the Washington Monument and the Lincoln Memorial. The Capitol dome can be seen to the east, and Arlington Cemetery is just across the Potomac River to the west. It really is a beautiful setting and shows the proper honor to these men and women of the Greatest Generation.
The 16 million men and women who served in the armed forces of the US are honored at the World War II Memorial, as well as the more than 400,000 who died, and all who supported the war effort from home. The memorial was built using granite and bronze. It features fountains between arches to symbolize hostilities in Europe and the Far East. The arches are bordered by semicircles of pillars, one each for the states, territories, and the District of Columbia. Beyond the pool is a curved wall of 4,000 gold stars, one for every 100 Americans killed in the war. It also features an Announcement Stone that states that the memorial is to honor those  “Americans who took up the struggle during the Second World War and made the sacrifices to perpetuate the gift our forefathers entrusted to us: A nation conceived in liberty and justice.”
“Americans who took up the struggle during the Second World War and made the sacrifices to perpetuate the gift our forefathers entrusted to us: A nation conceived in liberty and justice.”
The project was funded with more than $164 million dollars in private donations, and an additional $16 million donated by the federal government. Former Kansas Senator Bob Dole, who was severely wounded in the war, and actor Tom Hanks were among its most vocal supporters. The really sad part is that only a fraction of the 16 million Americans who actually served in the would ever see it…my dad included. While he was alive in 2004, that was not a trip he got to take before his passing in 2007. Four million World War II veterans were still living at the time the memorial was finally opened, but more than 1,100 dying every day, according to government records. I find that to be so sad.
Roger Durbin of Berkey, Ohio, who served under General George S Patton, inspired the memorial. Durbin was at a fish fry near Toledo in February 1987, when he asked US Representative Marcy Kaptur why there was no memorial on the Mall to honor World War II veterans. It was a question that should have been asked and answered long ago. Nevertheless, Kaptur, an Ohio Democrat, introduced legislation to build one, starting a process that would stumble along through 17 years of legislative, legal, and artistic entanglements. Durbin died of pancreatic cancer in 2000, without ever actually seeing his hard work come to fruition. While he didn’t live to see his project come to life, I and so many other children of World War II veterans and lost loved ones, will be forever thankful to him for finally making sure our loved ones were properly honored. The monument was formally dedicated May 29, 2004, by US President George W Bush, but I am pleased that it actually opened on 
 my birthday in 2004. My birthday, because it was just two days after my dad’s birthday, has always been a special time that we shared. Of course, I was due and supposed to arrive on Dad’s birthday, but I’ve always said I was a little stubborn, so I held out. Nevertheless, we usually celebrated our days together, so I feel like his memorial opening on my birthday was really very cool.
my birthday in 2004. My birthday, because it was just two days after my dad’s birthday, has always been a special time that we shared. Of course, I was due and supposed to arrive on Dad’s birthday, but I’ve always said I was a little stubborn, so I held out. Nevertheless, we usually celebrated our days together, so I feel like his memorial opening on my birthday was really very cool.

 Some men are Boy Dads, which in no way means that they wouldn’t be good with girls. Some men are Girl Dads, which in no way means that they wouldn’t be good with boys. the truth is that any good dad can be a good dad to boys or to girls, but there is one thing that I think my sisters and I would all agree on with our dad, Allen Spencer. While he would have been a great dad to boys, his girls needed him to be our dad. Maybe a girl dad or a boy dad is just blessed with the gift of one or the other, because they have a particular way with one or the other.
Some men are Boy Dads, which in no way means that they wouldn’t be good with girls. Some men are Girl Dads, which in no way means that they wouldn’t be good with boys. the truth is that any good dad can be a good dad to boys or to girls, but there is one thing that I think my sisters and I would all agree on with our dad, Allen Spencer. While he would have been a great dad to boys, his girls needed him to be our dad. Maybe a girl dad or a boy dad is just blessed with the gift of one or the other, because they have a particular way with one or the other.
Our home was filled with so much love and dad understood the needs of girls…like giving up the bathroom quickly so we could get all dolled up. He understood that when camping, the fire needed to be kept going…”to keep the bears away.” There were so many other things that Dad instinctively knew about girls and our girly ways, and he always made us feel loved, special, and safe. We were his princesses, and Dad loved all his 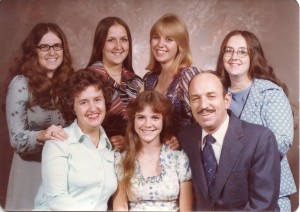 princesses and much as he loved his queen, our mom Collene Spencer. Yes, our dad was definitely a Girl Dad, but it was we, his girls, who were blessed because he was our Girl Dad.
princesses and much as he loved his queen, our mom Collene Spencer. Yes, our dad was definitely a Girl Dad, but it was we, his girls, who were blessed because he was our Girl Dad.
Dad did all the normal “dad things” that all dads do, like working hard every day to support his family, taking us on more vacations that almost any of our classmates got to go on, and I’m not bragging, just stating a fact. Dad loved to travel, and he loved this country; and he wanted his girls to be able to see as much of it as possible, because there is no greater nation on earth, except God’s chosen nation…Israel, and I think he would have loved to take us there too. For our dad, the greatest gift he could give his girls is the gift of faith in Jesus as our Savior. Faith was something he was given as a child, and I remember reading his letters home from World War II, written to his mom, Anna Spencer, in which he and his mother encouraged each other with God’s promises, given to us all in the Bible. Dad was very protective of his mom too. She was another of the women in his life who were blessed to know the love and protective nature that was always our dad, her son.


Dad went home to Heaven on December 12, 2007, and we miss him every day. There was so much more to Dad than the things he gave us or the special way we were treated, there was the love that dad gave his girls. Dad may have been blessed to be a Girl Dad, but it was really his girls who were blessed, because he was our dad. Today would have been Dad’s 98th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Dad. Have a great party with Mom and the rest of the family. We can’t wait to see you all again. We love and miss you very much.
 After years of being oppressed, starved, beaten, murdered, and used for experimentation, the Jewish people decided that it was their right to avenge their dead. The Nuremburg Trials were supposed to do all that, but so many of the Nazis had fled the country to escape the sentences they deserved, and once out of the country, it was almost impossible to get them back to face those sentences. In the late 1940s, under Juan Domingo Peron’s leadership (October 17, 1945 to July 1, 1974), the government secretly allowed entry of a number of war criminals fleeing Europe after Nazi Germany’s collapse, as part of the infamous ratlines. The number of Nazi fugitives that fled to Argentina surpassed 300, and included notorious war criminals such as Erich Priebke, Martin Bormann, Joseph Mengele, Eduard Roschmann, Josef Schwammberger, Walter Kutschmann, Otto Skorzeny and Holocaust administrator Adolf Eichmann, among others. In May 1960, Eichmann was kidnapped in Argentina by the Israeli Mossad and brought to trial in Israel. He was executed in 1962. At the time, Argentina condemned the Israeli government for abducting Eichmann, leading to a diplomatic spat between the nations.
After years of being oppressed, starved, beaten, murdered, and used for experimentation, the Jewish people decided that it was their right to avenge their dead. The Nuremburg Trials were supposed to do all that, but so many of the Nazis had fled the country to escape the sentences they deserved, and once out of the country, it was almost impossible to get them back to face those sentences. In the late 1940s, under Juan Domingo Peron’s leadership (October 17, 1945 to July 1, 1974), the government secretly allowed entry of a number of war criminals fleeing Europe after Nazi Germany’s collapse, as part of the infamous ratlines. The number of Nazi fugitives that fled to Argentina surpassed 300, and included notorious war criminals such as Erich Priebke, Martin Bormann, Joseph Mengele, Eduard Roschmann, Josef Schwammberger, Walter Kutschmann, Otto Skorzeny and Holocaust administrator Adolf Eichmann, among others. In May 1960, Eichmann was kidnapped in Argentina by the Israeli Mossad and brought to trial in Israel. He was executed in 1962. At the time, Argentina condemned the Israeli government for abducting Eichmann, leading to a diplomatic spat between the nations.
There was a financial incentive for Argentina to accept these war criminals, and they needed to provide a safe haven for them. Wealthy Germans and Argentine businessmen of German descent were willing to pay the way for escaping Nazis. The initial plan of the fleeing Nazis was to regroup, lay low for a while, and then come back with a vengeance. The Holocaust years had been very profitable for the Nazis. Nazi leaders had plundered untold millions from the Jews they murdered and some of that money accompanied them to Argentina…meaning the Argentine economy was helped by the war criminals…another incentive to help them hide out.
Some of the smarter Nazi officers and collaborators saw the writing on the wall as early as 1943 and began hiding gold, money, valuables, paintings, and more. They often moved their plunder to Switzerland. Ante Pavelic and his cabal of close advisors had several chests full of gold, jewelry, and art they had stolen from their Jewish and Serbian victims. These riches eased their passage to Argentina considerably. Disappearing, even in 1945 was not an easy matter, but if one had money, it was far more possible. The war criminals even paid off British officers to let them through Allied lines…a treasonous act for which those British officers should have  also been prosecuted and hung. Sometimes the corruption in government and military entities, even those who are supposed to be on the side of good, is absolutely astounding.
also been prosecuted and hung. Sometimes the corruption in government and military entities, even those who are supposed to be on the side of good, is absolutely astounding.
After the World War II, and the release of the surviving Jews, the Nuremburg Trials convicted these evil monsters, but many of them were gone before their sentence could be carried out. Enter the Nokmim, a group of Jewish men, also referred to as The Avengers or the Jewish Avengers. These men were a Jewish partisan militia, formed by Abba Kovner and his lieutenants Vitka Kempner and Rozka Korczak from the surviving remnants of the United Partisan Organization (Fareynikte Partizaner Organizatsye), which operated in Lithuania under Soviet command. Elements of the Nokmim collaborated with veterans of the Jewish brigade in British Palestine to form a new organization called Nakam, a group of assassins that targeted Nazi war criminals with the aim of avenging the Holocaust. The name comes from the phrase (Dam Yehudi Nakam – “Jewish Blood Will Be Avenged”) (the acronym DIN means “judgement”).
The Nakam (“vengeance”) Group was the most extremist group. They numbered around 60 Jews who were former Partisans, as well as other Jews who survived the Holocaust. This group was not about to let these men get away with all the atrocities they put their Jewish captives through, and then just walk away without punishment…not if they could help it. The group arrived in Germany after the war in order to conduct more complicated and fatal vengeance operations. Their ultimate purpose was to carry out an operation that would cause a broad international response…a warning, if you will, to anyone who might consider trying to harm Jews again, as the Nazis had. They needed to show the world that they would never be treated in such a way again. They would fight back…every time. Notables among the Hanakam group were Abba Kovner, Yitzhak Avidav, and Bezalel Michaeli. The group attempted a couple of mass poisonings, the first of the water supplies of Munich, Berlin, Weimar, Nuremberg and Hamburg, which failed when the poison had to be thrown overboard on a ship when Kovner was discovered to be carrying forges documents. The other attempt was with 3,000 loaves of bread painted with diluted arsenic, headed for 15,000 German POWs from the Langwasser internment camp near Nuremberg. The camp was under US authority. On April 23, 1946, it was reported that 2,283 German prisoners of war had fallen ill from poisoning, with 207 hospitalized and seriously ill. According to Harmatz, 300 to 400 Germans died. He said this “was nothing compared with what we really wanted to do.” A 2016 report by the Associated Press countered that the operation ultimately caused no known deaths, despite documents obtained through a Freedom of Information Act request to the National Archives and Records Administration  stating the arsenic found in the bakery was enough to kill approximately 60,000 persons. Apparently, the arsenic was spread too thin to be lethal.
stating the arsenic found in the bakery was enough to kill approximately 60,000 persons. Apparently, the arsenic was spread too thin to be lethal.
It’s hard to say just how much information is correct and how much is incorrect. I suppose it depends on who is reporting, and how accurately they want to report what they have. Propaganda in any war runs rampant, so we will likely never know. Records can and do go missing, especially when someone wants to disprove their enemies. Whether so many people died by poisoning or not, the Nokmim and the spin-off Nakam brought vengeance on many of the Nazis who would have escaped justice without them.
 Having a baby is normally a blessed event, but it is also important to be having the baby with the right person. I know that sound like something that is between the man and the woman, and it’s nobody’s business but their own, and I would agree with you on that. However, during World War II, the Nazi regime was so hated that the nations they terrorized didn’t want anything to do with them…so much so that French women having babies with German soldiers were punished by shaving their heads bald and parading them through town. This was done so that everyone would know they betrayed their country, and so they had.
Having a baby is normally a blessed event, but it is also important to be having the baby with the right person. I know that sound like something that is between the man and the woman, and it’s nobody’s business but their own, and I would agree with you on that. However, during World War II, the Nazi regime was so hated that the nations they terrorized didn’t want anything to do with them…so much so that French women having babies with German soldiers were punished by shaving their heads bald and parading them through town. This was done so that everyone would know they betrayed their country, and so they had.
The Nazi regime was set on creating “the perfect race,” in their opinion anyway. They wanted everyone to be light skinned, blond haired, and blue eyed, and those who weren’t had to prove their genetic lines. The Nazis even went so far as to set up places that women (of the right bloodlines) were sent to have their children, conceived with German soldiers. Then, the plan was that they would give their children up for adoption by a Nazi couple who was having trouble conceiving. It was Hitler’s way of preserving the “right” bloodline. Many times, if the woman changed her mind, and wanted to keep the baby, but refused to marry the soldier, their babies were taken from the by force, even if it meant taking their lives. Some of these  women were in it for the money and had no intention of keeping their babies. They were a simply a “Nazi Baby Machine.”
women were in it for the money and had no intention of keeping their babies. They were a simply a “Nazi Baby Machine.”
Once it was discovered that these women were doing this, they were marked as traitors. Often their own families disowned them. These women might not even be having babies with the Nazi soldiers, just having relations with them. The soldiers saw nothing wrong with hooking up with these women to ply them for information. It was an act of treason on the part of the women. They shouldn’t have allowed themselves to become involved with the Nazi soldiers, because they just had to know that was wrong. Treason is such a dark side of war. Still, there are many dark sides to war, and in most cases, it is the innocent and oppressed that suffer.
The French resistance brought out another dark side to the war, and it was rather brutal, but they felt like it was justified. Looking at it now, I think the beating part was the probably brutal, but maybe still have been justified. Basically, the French Resistance, when women were caught in a physical relationship with a Nazi, shaved their heads, beat the women who had been charged with collaborating with the enemy, and then paraded them around town as a form of punishment. The punishment was followed by harassing the women, with no repercussion for the beatings, head shavings, or the harassing. In France, a woman’s long hair is supposed to be seductive, so shaving their heads, was a way to make them look undesirable. The practice dates back to Biblical times. It was a common punishment for adultery. During the 20th century, it was reintroduced as a means to ridicule women who had physical relationships with the enemy or were prostitutes.  The French Resistance took a page from Bible times, and so it came to pass that during World War II, this act of humiliation was repeated on French women accused of collaborating with the German soldiers. Apart from shaving their heads, they were paraded in the streets, marked with black ink, and even stripped half-naked. At least 20,000 women have been documented to have had their heads shaved. I’m not a proponent of violence, but traitors need to be punished, and after something like that, I would think these women would think twice before getting involved with the Nazi soldiers. and any woman who hadn’t done so, would think twice before even considering such a heinous act.
The French Resistance took a page from Bible times, and so it came to pass that during World War II, this act of humiliation was repeated on French women accused of collaborating with the German soldiers. Apart from shaving their heads, they were paraded in the streets, marked with black ink, and even stripped half-naked. At least 20,000 women have been documented to have had their heads shaved. I’m not a proponent of violence, but traitors need to be punished, and after something like that, I would think these women would think twice before getting involved with the Nazi soldiers. and any woman who hadn’t done so, would think twice before even considering such a heinous act.
 World War II was coming to a close and everyone was just doing whatever they could to stay alive. Staff Sergeant Henry E “Red” Erwin Sr was the radio operator on a B-29 Superfortress bomber, piloted by Captain George A “Tony” Simeral. Formed at Dalhart, Texas, in June 1944, and deployed overseas in January 1945, this was a seasoned crew. Erwin’s unit was the 52nd Bombardment Squadron, 29th Bombardment Wing, and Erwin’s B-29 was one of the few planes in Major General Curtis E LeMay’s XXI Bomber Command to have two names. The B-29, serial number 42-65302, was called Snatch Blatch and The City of Los Angeles. On April 12, 1945, the crew was on a bombing mission over Japan. They were part of a campaign to bomb Tokyo and other major Japanese cities.
World War II was coming to a close and everyone was just doing whatever they could to stay alive. Staff Sergeant Henry E “Red” Erwin Sr was the radio operator on a B-29 Superfortress bomber, piloted by Captain George A “Tony” Simeral. Formed at Dalhart, Texas, in June 1944, and deployed overseas in January 1945, this was a seasoned crew. Erwin’s unit was the 52nd Bombardment Squadron, 29th Bombardment Wing, and Erwin’s B-29 was one of the few planes in Major General Curtis E LeMay’s XXI Bomber Command to have two names. The B-29, serial number 42-65302, was called Snatch Blatch and The City of Los Angeles. On April 12, 1945, the crew was on a bombing mission over Japan. They were part of a campaign to bomb Tokyo and other major Japanese cities.
Each of the 12 crew members on the B-29 had additional duties to perform, along with their primary jobs. Erwin’s was to drop phosphorus smoke bombs through a chute in the aircraft’s floor when the lead plane reached a designated assembly area. During the campaign, Erwin pulled the pin and released a bomb into the chute, but the fuse malfunctioned and ignited the phosphorus prematurely, burning at 1,100 degrees. The canister flew back up the chute and into Erwin’s face, blinding him, searing off one ear and obliterating his nose. Phosphorus pentoxide smoke immediately filled the aircraft. It was impossible for the pilot to see his instrument panel. At such a high heat, Erwin was afraid the bomb would burn through the metal floor into the bomb bay. Nevertheless, Erwin had a quick, fleeting chance to save the lives of his fellow crewmembers by risking severe, probably fatal, burns to his own body, and he knew he had to act. He was completely blind, and yet he picked up the flare and feeling his way, crawled around the gun turret and headed for the copilot’s window. His face and arms were covered with ignited phosphorus and his path was blocked by the navigator’s folding table, hinged to the wall but down and locked. By now the navigator was setting up to make a sighting. The table’s latches could not be released with one hand, so Erwin held the white-hot bomb between his bare right arm and  his ribcage. It only took a few seconds to raise the table, but by then, the phosphorus had burned through his flesh to the bone. His body on fire, he stumbled into the cockpit, threw the bomb out the window and collapsed between the pilot’s seats, and with that heroic act, the rest of the crew was saved.
his ribcage. It only took a few seconds to raise the table, but by then, the phosphorus had burned through his flesh to the bone. His body on fire, he stumbled into the cockpit, threw the bomb out the window and collapsed between the pilot’s seats, and with that heroic act, the rest of the crew was saved.
It was the moment of truth for Erwin, who was a modest, humble kind of guy. His thoughts on his heroic actions would have been something along the lines of, “I just did what any soldier would have done…it’s nothing special,” but the truth is, it was something very special and very heroic. Red Erwin came to the war zone as one of thousands of B-29 crewmembers placed in the North Pacific, on the Marianas islands of Guam, Saipan, and Tinian for the purpose of attacking Japan. The American taxpayer had equipped them with the largest and costliest aircraft of the war, the first large combat plane to be pressurized, enabling the crew to dispense with heated clothing and oxygen masks and to work in shirtsleeves, a fact that also put Erwin in an even more vulnerable position, because his skin was less protected than it would have been in a coat.
Erwin survived his burns. He was flown back to the United States, and after 30 months and 41 surgeries, his eyesight was restored, and he regained use of one arm. He received a disability discharge as a master sergeant in October 1947. In addition to the Medal of Honor and two Air Medals received earlier in 1945, he was also awarded the Purple Heart, the World War II Victory Medal, the American Campaign Medal, three Good Conduct Medals, the Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal with two bronze campaign stars (for participation in the Air  Offensive Japan and Western Pacific campaigns), and the Distinguished Unit Citation Emblem. He was a remarkable soldier.
Offensive Japan and Western Pacific campaigns), and the Distinguished Unit Citation Emblem. He was a remarkable soldier.
For 37 years, Erwin served as a benefits counselor at the veterans’ hospital in Birmingham, Alabama. In 1997, the Air Force created the Henry E Erwin Outstanding Enlisted Aircrew Member of the Year Award. It is presented annually to an airman, noncommissioned officer and senior noncommissioned officer in the flight engineering, loadmaster, air surveillance and related career fields. It is only the second Air Force award named for an enlisted person. Henry Erwin, despite his scars and wounds, went on to lead a typical life… marrying, raising children, and becoming a grandfather. But there was nothing “typical” about Red Erwin. “Red” Erwin died at his home on January 16, 2002, and was buried at Elmwood Cemetery in Birmingham, Alabama. His son, Hank Erwin, became an Alabama state senator.

 Some books should have a permanent copyright, and it seems like insanity to me that they don’t. As copyright laws go, a work is typically protected for 70 years after the creator’s death. That would mean that a book like Anne Frank’s diary, the copyrights would expire in 2015 because of her untimely death in a concentration camp, and the book would become public domain. It seems very wrong that her diary…her own private words…could become public domain. A diary is so private, but then I guess that when they published her diary, any semblance of privacy no longer existed.
Some books should have a permanent copyright, and it seems like insanity to me that they don’t. As copyright laws go, a work is typically protected for 70 years after the creator’s death. That would mean that a book like Anne Frank’s diary, the copyrights would expire in 2015 because of her untimely death in a concentration camp, and the book would become public domain. It seems very wrong that her diary…her own private words…could become public domain. A diary is so private, but then I guess that when they published her diary, any semblance of privacy no longer existed.
Anne Frank’s diary, the story of which abruptly ended when the family that was secretly hiding them was betrayed, and the two families they were hiding, captured, was preserved after their capture, and given to Otto Frank after he survived the Holocaust. After much soul searching, Otto Frank decided to publish his younger daughter’s story, because people needed to know the truth. It was a selfless move that must have been heartbreaking for a man who had lost everything in the Holocaust…a man whose daughters would never grow to adulthood, never marry, never have children, never grow old. The book became the only way to extend Anne’s life, and through her words to also extend the lives of her mother, sister, and the others who were in hiding. As such, it seems only fitting that the work continue as a copyrighted work beyond 2015, but the law was the law…or was it?
The Swiss foundation, that holds the copyright, made a move to extend the protection of the book. It was a bold, yet simple move. They made Anne’s father, Otto Frank co-author of the book. Of course, a move like this must hold some merit as well. Otto could not be named co-author just because he was her father. While The Diary of Anne Frank was compiled of journal entries made by Anne, it was her father who read through her journal to put together the final product. Otto admitted to having censored some of the content, leaving out 
 certain parts of her story that he decided were unsavory or too personal. It made sense. After all, this was his daughter, and she was becoming a woman, with the curiosities of that transition. His work in editing her story gave credence to naming him co-author. Otto survived World War II and didn’t pass away until 1980. That now means that the copyright could be pushed back to 2050, as he was officially deemed co-author.
certain parts of her story that he decided were unsavory or too personal. It made sense. After all, this was his daughter, and she was becoming a woman, with the curiosities of that transition. His work in editing her story gave credence to naming him co-author. Otto survived World War II and didn’t pass away until 1980. That now means that the copyright could be pushed back to 2050, as he was officially deemed co-author.

