Caryn’s Thoughts

 Very early yesterday morning, a little boy named Jaxx David Harman was keeping his parents up all night. That may not seem like a strange thing to the parents of little ones, but little Jaxx had a very good reason for keeping his parents up…it was going to be his birthday, and he was excited. It wasn’t his birthday yet, and no one knew for sure if his birthday would be May 29th or May 30th. It depended on just how much of a hurry Jaxx was in. As it turned out, Jaxx wasn’t in a big hurry, and by the time he made his entrance, it was 4:15am on May 30th. Let’s hope he doesn’t make a habit of being up so late.
Very early yesterday morning, a little boy named Jaxx David Harman was keeping his parents up all night. That may not seem like a strange thing to the parents of little ones, but little Jaxx had a very good reason for keeping his parents up…it was going to be his birthday, and he was excited. It wasn’t his birthday yet, and no one knew for sure if his birthday would be May 29th or May 30th. It depended on just how much of a hurry Jaxx was in. As it turned out, Jaxx wasn’t in a big hurry, and by the time he made his entrance, it was 4:15am on May 30th. Let’s hope he doesn’t make a habit of being up so late.


Jaxx is the youngest child of my grand nephew, Jake Harman and his wife, Melanie. They have two daughters, Alice and Izabella, both of whom are very excited to have a little brother. Alice, being the oldest understands all this better than Izabella, but Izabella is quite interested anyway. Oh, I know that as little Jaxx grows up, he will most likely torment his big sisters, as most little brothers…or brothers in general…do, but they will love him anyway, because he is their brother, and nobody gets to be mad at him but them!!
I’m sure little Jaxx didn’t mean to keep his parents up all night, but I seriously doubt if it will be the last time. I 
 hope that starting out this way is not indicative of how Jaxx will be in the future, because as we all know, parents need their sleep too, especially parents of little ones. But then again, I would much rather have a baby keeping me awake than a child out on a date, and running late for curfew. I’m sure Jake and Melanie don’t even want me to think about those days yet, but as we all know, time flies quickly by, and those days will be here before they know it. Until then, Jake and Melanie, enjoy that sweet little boy. He is so precious and we are all very happy for you. Congratulations!!
hope that starting out this way is not indicative of how Jaxx will be in the future, because as we all know, parents need their sleep too, especially parents of little ones. But then again, I would much rather have a baby keeping me awake than a child out on a date, and running late for curfew. I’m sure Jake and Melanie don’t even want me to think about those days yet, but as we all know, time flies quickly by, and those days will be here before they know it. Until then, Jake and Melanie, enjoy that sweet little boy. He is so precious and we are all very happy for you. Congratulations!!

 May 30, 2002 dawned, a typically warm New York City day, but this was not a typical day at all. It had been a long, emotionally grueling 8 months and 19 days of cleanup after the September 11, 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center, the Pentagon, and the crash site in Shanksville, Pennsylvania. The majority of the lost were in the World Trade Center in New York City. Those 8 months and 19 days were filled with every possible emotion there could be…from joy when one was found alive, to grief over the lost, to anger at the attack, to hate for the Muslim attackers, to love for the survivors and the families of the lost. It was something that we all knew that we could never really wrap our heads around, and something that we knew we would never forget. It was a senseless attack that proved only that the attackers were insane and filled with hate for Americans and Christians. It was a time when America came together as one, and donated time, money, letters, and love to each other, because we were all victims of this attack, after all.
May 30, 2002 dawned, a typically warm New York City day, but this was not a typical day at all. It had been a long, emotionally grueling 8 months and 19 days of cleanup after the September 11, 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center, the Pentagon, and the crash site in Shanksville, Pennsylvania. The majority of the lost were in the World Trade Center in New York City. Those 8 months and 19 days were filled with every possible emotion there could be…from joy when one was found alive, to grief over the lost, to anger at the attack, to hate for the Muslim attackers, to love for the survivors and the families of the lost. It was something that we all knew that we could never really wrap our heads around, and something that we knew we would never forget. It was a senseless attack that proved only that the attackers were insane and filled with hate for Americans and Christians. It was a time when America came together as one, and donated time, money, letters, and love to each other, because we were all victims of this attack, after all.
On May 29, 2002, the last beam was removed from the site…marking the end of the cleanup effort that had been expected to last a year. There were many disappointments in the cleanup, because there were very few people pulled out alive after that first day, and in fact, the last survivor was pulled out 27 hours after the attack. There would be no more lives saved. People were lined up to donate blood in the hope that someone’s life could be saved, but the sad reality was that very few whole bodies were even pulled from the rubble. Most were bits and pieces, body parts, and even just fragments of bone or teeth. Authorities put the final death toll from the World Trade Center’s destruction at 2,823. Of those 2823 people, only 1,102 victims have been identified, and only 289 intact bodies were recovered.
The ceremony…if it could really be called that, because ceremony usually means a happy event…began in silence. There would be no speeches. Thousands of people stood silently in one place…Ground Zero, and no one spoke…no one spoke!! The ceremony began with the sound of a fire bell ringing for the fallen firefighters at 10:29 am ET, the same time the World Trade Center’s north tower collapsed on September 11, 2001. Thousands of people stood in silence, some with tears streaming from their eyes, as an honor guard made up of police, firefighters, and representatives of other agencies walked slowly up a ramp from the site carrying a stretcher bearing only an American flag. The flag, symbolizing the victims who were killed on September 11, but never found, was placed into a waiting ambulance. It was followed by a flatbed truck carrying the last 50 ton steel column from the site of the Trade Center ruins. The beam was part of the southeast corner of the south tower. It was hoisted onto a flatbed truck and shrouded in black cloth after its removal on May 29, 2002. Ten minutes into the ceremony, a pair of buglers…one from New York’s Police Department, the other from the New York Fire Department…played “Taps,” followed by a flyover of NYPD helicopters. Among the dead following the horrific attack, were 343 New York firefighters and an estimated 70 police officers from various departments, including 37 from New York’s Port Authority and 23 from the New York Police Department. Fewer than half of the firefighters who died were recovered. Five of them were from the Chelsea Firehouse, Engine 3 and Ladder 12. At the fire stations and police stations in New York City, dozens of family and friends watched the tribute on television. Hundreds of workers had labored around the clock since September 11 to recover the 
 bodies of those who died in the attack and to remove the 1.6 million tons of steel and concrete left behind. The debris was moved to a Staten Island landfill, but reminders of the attack remain in the area. “It’s over, but it will never be forgotten,” said FDNY Battalion Commander Richard Picciotto, who was in the north tower when it was hit. He was right. Today marks the 15th anniversary of that ceremony, and we have not forgotten.
bodies of those who died in the attack and to remove the 1.6 million tons of steel and concrete left behind. The debris was moved to a Staten Island landfill, but reminders of the attack remain in the area. “It’s over, but it will never be forgotten,” said FDNY Battalion Commander Richard Picciotto, who was in the north tower when it was hit. He was right. Today marks the 15th anniversary of that ceremony, and we have not forgotten.
 Memorial Day…the day we set aside to remember the heroes of our wars, who paid the ultimate price for the freedoms we hold dear. The men and women who were killed in the attack on Pearl Harbor come to mind, as do those lost on the beaches of Normandy, but there are so many others. From the fliers, to the foot soldiers, to the sailors…men and women, from the Revolutionary War, to the War on Terror, have set aside their goals in life, left their families at home, pushed back their fears, and done their duty to serve their country, and for so many of them, it was a one way ticket over there. They fought and died so that someone they didn’t know could be free and have the rights that so many take for granted. They looked away when they were protested, but deep down they wondered why people didn’t understand. They tried not to watch the news of death and destruction. They just did their job, until they lost their lives in a war they wished had never started.
Memorial Day…the day we set aside to remember the heroes of our wars, who paid the ultimate price for the freedoms we hold dear. The men and women who were killed in the attack on Pearl Harbor come to mind, as do those lost on the beaches of Normandy, but there are so many others. From the fliers, to the foot soldiers, to the sailors…men and women, from the Revolutionary War, to the War on Terror, have set aside their goals in life, left their families at home, pushed back their fears, and done their duty to serve their country, and for so many of them, it was a one way ticket over there. They fought and died so that someone they didn’t know could be free and have the rights that so many take for granted. They looked away when they were protested, but deep down they wondered why people didn’t understand. They tried not to watch the news of death and destruction. They just did their job, until they lost their lives in a war they wished had never started.
 Most of us knew very few soldiers who lost their lives in defense of their country, and some of us may not have known any at all, even though some of our ancestors might have been casualties of a war. I think that sometimes the families of the lost feel alone in their grief. Unless someone has been in that position, they have a difficult time really understanding the depth of the loss. People try to be understanding, imagining how they would feel if it was them, but the reality is that our imaginations are not that good. Those who have lost a loved one to war can never forget the loss or the grief they feel. Grief has no timetable, and some pain just never goes away. No pain is more horrible than losing your child, and losing them in war, seriously compounds that pain.
Most of us knew very few soldiers who lost their lives in defense of their country, and some of us may not have known any at all, even though some of our ancestors might have been casualties of a war. I think that sometimes the families of the lost feel alone in their grief. Unless someone has been in that position, they have a difficult time really understanding the depth of the loss. People try to be understanding, imagining how they would feel if it was them, but the reality is that our imaginations are not that good. Those who have lost a loved one to war can never forget the loss or the grief they feel. Grief has no timetable, and some pain just never goes away. No pain is more horrible than losing your child, and losing them in war, seriously compounds that pain.
Memorial Day, or Decoration Day as it was first called, started three years after the Civil War ended, on May 5,  1868. It was established by the head of an organization of Union veterans…the Grand Army of the Republic. Decoration Day was a time for the nation to decorate the graves of the war dead with flowers. Major General John A Logan declared that Decoration Day should be observed on May 30. It is believed that date was chosen because flowers would be in bloom all over the country. The first large observance was held that year at Arlington National Cemetery, across the Potomac River from Washington, DC. It was a day for all citizens to remember the sacrifice of the brave fallen heroes. And to let the families know that their fallen soldier would ever be forgotten. In honor of all the fallen, may you rest in peace. Thank you for your great sacrifice. Your nation is grateful.
1868. It was established by the head of an organization of Union veterans…the Grand Army of the Republic. Decoration Day was a time for the nation to decorate the graves of the war dead with flowers. Major General John A Logan declared that Decoration Day should be observed on May 30. It is believed that date was chosen because flowers would be in bloom all over the country. The first large observance was held that year at Arlington National Cemetery, across the Potomac River from Washington, DC. It was a day for all citizens to remember the sacrifice of the brave fallen heroes. And to let the families know that their fallen soldier would ever be forgotten. In honor of all the fallen, may you rest in peace. Thank you for your great sacrifice. Your nation is grateful.

 Seven days might seem like enough time when your kids come home for a visit, but when it comes time for them to leave, you find that it is definitely not enough time. Of course, deep down, you knew it wouldn’t be, you just hoped that you could cram everything you wanted to say and do into the short amount of time you had. Then, almost before the visit started, it’s time to say goodbye again. That’s how my Casper family feels every time our Washington family comes for a visit, and I’m sure that’s how they feel whenever we go to visit there too. Included in the visit is always a certain amount stress and pressure, both for them and for us, because they are trying to make time for their family…and their friends, and we are trying to spend as much time as possible with them. No one wants to share them exactly…selfish, I know, but when they are your babies, you tend to get a little bit selfish.
Seven days might seem like enough time when your kids come home for a visit, but when it comes time for them to leave, you find that it is definitely not enough time. Of course, deep down, you knew it wouldn’t be, you just hoped that you could cram everything you wanted to say and do into the short amount of time you had. Then, almost before the visit started, it’s time to say goodbye again. That’s how my Casper family feels every time our Washington family comes for a visit, and I’m sure that’s how they feel whenever we go to visit there too. Included in the visit is always a certain amount stress and pressure, both for them and for us, because they are trying to make time for their family…and their friends, and we are trying to spend as much time as possible with them. No one wants to share them exactly…selfish, I know, but when they are your babies, you tend to get a little bit selfish.
This trip home for my daughter, Amy Royce and her kids, Shai and Caalab, was to attend the graduation of my youngest grandson, Josh Petersen. The trip was wonderful, as we attended his graduation party, awards ceremony, and of 
 course, the graduation. We went out to eat, and just sat around and talked, and we even had an early birthday party for Amy. We laughed, talked, and when I was given Friday off, we even did pedicures. The kids hooked up with all their friends, and for the most part, decided that sleep was an unnecessary vice best left to old people…and apparently mornings fell into that same category. Still, they all did their best to divide their time with family and friends as fairly as possible. Nevertheless, to my “mother’s heart” it was not enough time. I found myself wishing that I could turn back time to the first day of their arrival…over and over again.
course, the graduation. We went out to eat, and just sat around and talked, and we even had an early birthday party for Amy. We laughed, talked, and when I was given Friday off, we even did pedicures. The kids hooked up with all their friends, and for the most part, decided that sleep was an unnecessary vice best left to old people…and apparently mornings fell into that same category. Still, they all did their best to divide their time with family and friends as fairly as possible. Nevertheless, to my “mother’s heart” it was not enough time. I found myself wishing that I could turn back time to the first day of their arrival…over and over again.
Try as I might, before we knew it, the last day arrived. Amy had planned a friends night to get all her friends together at once, and it went very well. I made the bold move to “horn in” on the action, even though it was supposed to be for her friends, and they graciously accepted my intrusion. My only regret was that I should have “horned in” my other daughter, Corrie and her husband, Kevin, who I thought were spending the day with their son, Josh, who went back to Bellingham with Amy, Shai, and Caalab this morning to spend his Senior 
 Trip with them. I suppose I should have realized that Josh would be attending the graduation parties of his friends, but I wasn’t thinking very clearly, because the kids were leaving and I was dreading the tearful goodbyes I knew were inevitable. Hindsight is 20/20. As I contemplate the visit that we had, mixed with the sad goodbyes, a thought came to me…”Goodbyes are always hard, but I’m very thankful that we can look forward to the next hello.”
Trip with them. I suppose I should have realized that Josh would be attending the graduation parties of his friends, but I wasn’t thinking very clearly, because the kids were leaving and I was dreading the tearful goodbyes I knew were inevitable. Hindsight is 20/20. As I contemplate the visit that we had, mixed with the sad goodbyes, a thought came to me…”Goodbyes are always hard, but I’m very thankful that we can look forward to the next hello.”

 Sometimes, the best of intentions can go horribly wrong, and when things go wrong, it becomes a disaster, and disaster is exactly what happened in Centralia, Pennsylvania when a fire was set to burn out an old landfill before the Labor Day holiday in 1962. The fire that was started on May 27, 1962, seemed like a simple solution to a big mess, but the landfill was also an old strip-mine pit, connected to a maze of abandoned underground mining tunnels full of coal. No one knows how the fire got to the coal vein below the ground, but once it did, the situation was out of control. Some called it careless trash incineration in a landfill next to an open pit mine, which ignited a coal vein, but no one expected the fire to crawl insidiously along the rich coal deposits that still laid deep in the ground. No one expected the burning coal to vent hot and poisonous gases up into town, through the basements of homes and businesses. Nevertheless, with dawn came the horror, as residents realized that the fire was not going to be extinguished, or in fact, ever burn itself out…at least not until all the interconnected coal veins in eastern Pennsylvania were finally burned out. As the underground fire worked its way under rows of homes and businesses, the threat of fires, asphyxiation, and carbon monoxide poisoning became a daily concern.
Sometimes, the best of intentions can go horribly wrong, and when things go wrong, it becomes a disaster, and disaster is exactly what happened in Centralia, Pennsylvania when a fire was set to burn out an old landfill before the Labor Day holiday in 1962. The fire that was started on May 27, 1962, seemed like a simple solution to a big mess, but the landfill was also an old strip-mine pit, connected to a maze of abandoned underground mining tunnels full of coal. No one knows how the fire got to the coal vein below the ground, but once it did, the situation was out of control. Some called it careless trash incineration in a landfill next to an open pit mine, which ignited a coal vein, but no one expected the fire to crawl insidiously along the rich coal deposits that still laid deep in the ground. No one expected the burning coal to vent hot and poisonous gases up into town, through the basements of homes and businesses. Nevertheless, with dawn came the horror, as residents realized that the fire was not going to be extinguished, or in fact, ever burn itself out…at least not until all the interconnected coal veins in eastern Pennsylvania were finally burned out. As the underground fire worked its way under rows of homes and businesses, the threat of fires, asphyxiation, and carbon monoxide poisoning became a daily concern.
Probably one of the scariest situations was when a young man, Todd Domboski fell into a hot, steaming hole created by mine fire subsidence. He survived his 45 second ordeal by grabbing onto tree roots, and screaming for help until his cousin ran to his aid, reached into the void, and hoisted him out. Many Centralia residents had worried that a calamity like the one that nearly unfolded that Valentine’s Day in 1981. Four years earlier, Domboski’s father had told a reporter, “I guess some kid will have to get killed by the gas or by falling in one of these steamy holes before anyone will call it an emergency.” Never did he imagine that it would be his kid that would fall through and almost lose his life.
After the near tragedy, signs were posted to warn visitors to the Centralia area about the dangers of death by asphyxiation or being swallowed by the ground, but the old mining town of Centralia, Pennsylvania, was once home to more than 1,000 people. People with no place else to go. Now, it’s nothing more than a smoldering ghost town that’s been burning for over half a century. Though the town was able to extinguish the fire above ground, a much bigger inferno burned underneath, and it eventually spread its way under Centralia’s town center. The fire was so widespread, destructive and unending. It’s thought that there’s enough coal underground to fuel the fire for another 250 years. In 1980, a $42 million relocation plan incentivized most of the townspeople to relocate and most of the homes were demolished, leaving only about a dozen holdouts behind. Today, Centralia exists only as an eerie grid of streets, its driveways disappearing into vacant lots. Remains of a picket fence here, a chair spindle there. Still John Lokitis and 11 others who refused to leave, the 
 occupants of a dozen scattered structures. Over the decades, the ground has opened up with sulfurous gases sometimes billowing out. The road along Highway 61 swells and cracks open. It is riddled with graffiti and hot to the touch. In the winter, snow melts in patches where the ground is warm. While a few holdouts still live there, I have to wonder what they are thinking. That is like slowly committing suicide, because you refuse to leave the past.
occupants of a dozen scattered structures. Over the decades, the ground has opened up with sulfurous gases sometimes billowing out. The road along Highway 61 swells and cracks open. It is riddled with graffiti and hot to the touch. In the winter, snow melts in patches where the ground is warm. While a few holdouts still live there, I have to wonder what they are thinking. That is like slowly committing suicide, because you refuse to leave the past.
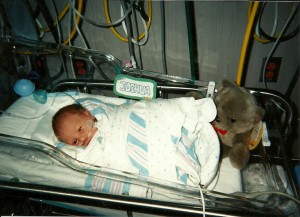
 When a child is born, you think about what they will become. Your thoughts drift to the future…that seems so distant, and you think to yourself, “The future is still so far away.” Then, much sooner than you ever thought possible, the future arrives, and your little baby is suddenly 18 years old, and graduating from high school. Then you think, “Where have the years gone?” It doesn’t matter if that child is your child or your grandchild either. The future arrives so fast. I’ve said it many times before. When you look at that precious baby, you must be aware that next week, they will be graduating from high school, and going off to make their own way in the world. In time and space, it may not be a week, but it will most certainly feel like it was.
When a child is born, you think about what they will become. Your thoughts drift to the future…that seems so distant, and you think to yourself, “The future is still so far away.” Then, much sooner than you ever thought possible, the future arrives, and your little baby is suddenly 18 years old, and graduating from high school. Then you think, “Where have the years gone?” It doesn’t matter if that child is your child or your grandchild either. The future arrives so fast. I’ve said it many times before. When you look at that precious baby, you must be aware that next week, they will be graduating from high school, and going off to make their own way in the world. In time and space, it may not be a week, but it will most certainly feel like it was.
That is where my daughter, Corrie Petersen and her husband, Kevin find themselves today as their son, Joshua 
 Petersen graduates from Kelly Walsh High School. Josh has changed so much over the years. His beginning was a little rocky, as he jumped the gun and arrived five weeks early. After spending two weeks in Denver, at Presbyterian Saint Luke’s Hospital, Josh was finally ready to come home and join the rest of his family. His rocky start over now, Josh quickly ate everything is sight, trying to make up for lost time, I think. Yes, Josh has changed in many ways, but in many other ways, he has not changed at all. He has always been a wonderful young man with a caring heart, and in that way, he will never change. He is so considerate of the feelings of others.
Petersen graduates from Kelly Walsh High School. Josh has changed so much over the years. His beginning was a little rocky, as he jumped the gun and arrived five weeks early. After spending two weeks in Denver, at Presbyterian Saint Luke’s Hospital, Josh was finally ready to come home and join the rest of his family. His rocky start over now, Josh quickly ate everything is sight, trying to make up for lost time, I think. Yes, Josh has changed in many ways, but in many other ways, he has not changed at all. He has always been a wonderful young man with a caring heart, and in that way, he will never change. He is so considerate of the feelings of others.
As the years have passed, we saw in Josh a gentleness and sincere caring for those in need of health care. When he was just six years old, he started helping take care of his grandparents, and he continued doing that until three had passed away, and the last one was in a nursing home. Josh was meticulous with their care. If you showed him how to do something, he did it exactly that way. For that reason, I was not surprised when Josh announced, “I want to be a firefighter.” I don’t think there was a shocked face in the place. Now, I know that a lot of kids say they want to be a firefighter, but Josh meant it. He even began taking Boces classes 
 toward his degree in high school. Josh is so driven, so goal oriented, and that makes me so proud of him. I have no doubt that he will be arriving at his life’s destination very quickly. The years have flown by far too fast. It seems like Josh should still be little boy, and yet here he is at the threshold of adulthood. Josh, we are so proud of your hard work and perseverance. I know that you will go far in life and in your chosen field. We are so very proud of your abilities, drive, and mostly your kind heart. Congratulations on your graduation!!
toward his degree in high school. Josh is so driven, so goal oriented, and that makes me so proud of him. I have no doubt that he will be arriving at his life’s destination very quickly. The years have flown by far too fast. It seems like Josh should still be little boy, and yet here he is at the threshold of adulthood. Josh, we are so proud of your hard work and perseverance. I know that you will go far in life and in your chosen field. We are so very proud of your abilities, drive, and mostly your kind heart. Congratulations on your graduation!!

 My niece, Cassie Iverson is a mother of 2, a wife, and a photographer. She specializes in Wyoming wilderness photography, and her landscapes are amazing. She has such a great eye for color and interest. Her photos draw you into the scene until you feel like you are standing right there next to her, and isn’t that the mark of a great photographer. Cassie has begun selling her photography at Essence Wyoming Photography on Facebook. Cassie and her husband, Chris love to take their kids, Lucas and Zoey camping on the weekends, and it also gives Cassie lots of inspiration for her photography. Sometimes they just go for photography drives into the country to give Cassie a chance to take more pictures, and to get everyone out of the house and into nature.
My niece, Cassie Iverson is a mother of 2, a wife, and a photographer. She specializes in Wyoming wilderness photography, and her landscapes are amazing. She has such a great eye for color and interest. Her photos draw you into the scene until you feel like you are standing right there next to her, and isn’t that the mark of a great photographer. Cassie has begun selling her photography at Essence Wyoming Photography on Facebook. Cassie and her husband, Chris love to take their kids, Lucas and Zoey camping on the weekends, and it also gives Cassie lots of inspiration for her photography. Sometimes they just go for photography drives into the country to give Cassie a chance to take more pictures, and to get everyone out of the house and into nature.
While photography is Cassie’s forté, her life is her family. She loves her babies with all her heart, and her 
 husband too, of course. She enjoys cooking for her family, and she is an amazing cook. She is a mom of two busy little kids, and they keep her hopping. Her oldest child, Lucas graduated from preschool a few days ago. It was an amazing accomplishment for Lucas. His journey has not been an easy one, with Down’s Syndrome, but Cassie and Chris have done an amazing job of helping him to reach his full potential. Both of their kids are very sweet.
husband too, of course. She enjoys cooking for her family, and she is an amazing cook. She is a mom of two busy little kids, and they keep her hopping. Her oldest child, Lucas graduated from preschool a few days ago. It was an amazing accomplishment for Lucas. His journey has not been an easy one, with Down’s Syndrome, but Cassie and Chris have done an amazing job of helping him to reach his full potential. Both of their kids are very sweet.
Cassie and Chris love to go camping, and they love fishing. In reality, they love animals…especially taking pictures of wild animals. They have horses, dogs, and a rare Highlander cat. Now, I didn’t really know why this was a rare cat, so I looked it up. A Highlander cat is a hybrid cat. The Highlander cat is a curl-eared variant of the Desert Lynx breed, crossed with the Jungle 
 Curl to achieve the curled ears. As Desert Lynxes, they are bobtailed or short-tailed, have spotted or marbled markings, and resemble the bobcat, however, they have no actual wild lynx or bobcat ancestry, making them completely domesticated. This cat does get to be about 14 pounds, however. Now that is quite a cat. All in all, Cassie leads a busy life, but it totally fulfills all of her dreams. Today is Cassie’s birthday. Happy birthday Cassie!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
Curl to achieve the curled ears. As Desert Lynxes, they are bobtailed or short-tailed, have spotted or marbled markings, and resemble the bobcat, however, they have no actual wild lynx or bobcat ancestry, making them completely domesticated. This cat does get to be about 14 pounds, however. Now that is quite a cat. All in all, Cassie leads a busy life, but it totally fulfills all of her dreams. Today is Cassie’s birthday. Happy birthday Cassie!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

 When the United States entered World War I, they sent men into France to join Allied forces there. Their arrival was a great relief to the exhausted Allied soldiers. Before long the American soldiers in France became known as Doughboys. This was not an unknown term, since it had been used For centuries to describe such soldiers as Horatio Nelson’s sailors and Wellington’s soldiers in Spain, for instance. Both of these groups were familiar with fried flour dumplings called doughboys, the predecessor of the modern doughnut that both we and the Doughboys of World War I came to love. The American Doughboys were the men America sent to France in the Great War, who beat Kaiser Bill and fought to make the world safe for Democracy.
When the United States entered World War I, they sent men into France to join Allied forces there. Their arrival was a great relief to the exhausted Allied soldiers. Before long the American soldiers in France became known as Doughboys. This was not an unknown term, since it had been used For centuries to describe such soldiers as Horatio Nelson’s sailors and Wellington’s soldiers in Spain, for instance. Both of these groups were familiar with fried flour dumplings called doughboys, the predecessor of the modern doughnut that both we and the Doughboys of World War I came to love. The American Doughboys were the men America sent to France in the Great War, who beat Kaiser Bill and fought to make the world safe for Democracy.
It is thought, however, that the Doughboys of World War I might have acquired the name in a slightly different way. In fact, there are a variety of theories about the origins of the nickname. One explanation is that the term dates back to the Mexican War of 1846 to 1848, when American infantrymen made long treks over dusty terrain, giving them the appearance of being covered in flour, or dough. As a variation of this account goes, the men were coated in the dust of adobe soil and as a result were called “adobes,” which morphed into “dobies” and, eventually into “doughboys.” Among other theories, according to “War Slang” by Paul Dickson, American journalist and lexicographer H.L. Mencken claimed the nickname could be traced to Continental Army soldiers who kept the piping on their uniforms white through the application of clay. When the troops got rained on the clay on their uniforms turned into “doughy blobs,” supposedly leading to the doughboy moniker.
Whatever the case may be, doughboy was just one of the nicknames given to those who fought in the Great War. For example, “poilu” meaning “hairy one” was a term for a French soldier, as a number of them had beards or mustaches, while a popular slang term for a British soldier was “Tommy,” an abbreviation of Tommy Atkins, a generic name similar to John Doe used in the Unites States on government forms. America’s last 
 World War I doughboy, Frank Buckles, died in 2011 in West Virginia at age 110. Buckles enlisted in the Army at age 16 in August 1917, four months after the United States entered the conflict, and drove military vehicles in France. One of 4.7 million Americans who served in the war, Buckles was buried at Arlington National Cemetery. It’s strange to think that my grandfather, George Byer was one of the men called doughboys, but then he was stationed in France at that time in history, so I guess that Grandpa was a doughboy.
World War I doughboy, Frank Buckles, died in 2011 in West Virginia at age 110. Buckles enlisted in the Army at age 16 in August 1917, four months after the United States entered the conflict, and drove military vehicles in France. One of 4.7 million Americans who served in the war, Buckles was buried at Arlington National Cemetery. It’s strange to think that my grandfather, George Byer was one of the men called doughboys, but then he was stationed in France at that time in history, so I guess that Grandpa was a doughboy.

 Most of the time, when we think of crime and criminals, we think of the worst evil there could be in a person, and I suppose that some criminals have more evil tendencies than others, but once in a while, someone decides to put a bit of a different twist on their crime…intending to romanticize it or give it a Robin Hood feel. In a large part, it is the media that truly romanticizes it or gives it notoriety. If the media didn’t report on every episode of the criminal’s life of crime, perhaps it would not seem so exciting to people, and maybe it wouldn’t inspire other criminals to…go for it. It all seems so exciting, at least that’s how the media plays it up.
Most of the time, when we think of crime and criminals, we think of the worst evil there could be in a person, and I suppose that some criminals have more evil tendencies than others, but once in a while, someone decides to put a bit of a different twist on their crime…intending to romanticize it or give it a Robin Hood feel. In a large part, it is the media that truly romanticizes it or gives it notoriety. If the media didn’t report on every episode of the criminal’s life of crime, perhaps it would not seem so exciting to people, and maybe it wouldn’t inspire other criminals to…go for it. It all seems so exciting, at least that’s how the media plays it up.
In reality, Bonnie and Clyde…notorious robbers and murders lived a very basic existence, and in many ways it was disgusting. Despite common popular culture depictions of Bonnie and Clyde, their life on the run was far from glamorous. They often ate sardines from the can, bathed in rivers, and drove through the night, taking shifts sleeping and driving, all in order to evade capture. They hid out in the forest, hoping not to be seen…always standing guard…always watching. Bonnie Parker met Clyde Barrow in Texas when she was 19 years old. Her husband, whom she married when she was 16, was serving time in jail for murder, and Clyde seemed exciting. Shortly after they met, Barrow was imprisoned for robbery. Bonnie visited Clyde every day, and smuggled a gun into prison to help him escape. He did escape, but was quickly recaptured in Ohio and sent back to jail. When Clyde was paroled in 1932, he immediately hooked up with Bonnie, and the couple began a life of crime together. Apparently Bonnie had a thing for bad boys…to her detriment, in the end.
The pair stole a car and committed several robberies, before Bonnie was caught by police and sent to jail for  two months. Immediately after her release in mid-1932, she hooked up with Clyde again. Over the next two years, the couple teamed with various accomplices to rob a string of banks and stores across five states…Texas, Oklahoma, Missouri, New Mexico and Louisiana. To law enforcement agents, the Barrow Gang, including Clyde’s childhood friend, Raymond Hamilton, W.D. Jones, Henry Methvin, Barrow’s brother Buck and his wife Blanche, among others, were cold-blooded criminals who didn’t hesitate to kill anyone who got in their way, especially police or sheriff’s deputies. To the public, however, Bonnie and Clyde’s reputation as dangerous outlaws was mixed with a romantic view of the couple as “Robin Hood”-like folk heroes. Their fame was increased by the fact that Bonnie was a woman, which made her an unlikely criminal, and by the fact that the couple posed for playful photographs together, which were later found by police and released to the media. Police almost captured Bonnie and Clyde in the spring of 1933, with surprise raids on their hideouts in Joplin and Platte City, Missouri. Buck Barrow was killed in the second raid, and Blanche was arrested, but Bonnie and Clyde escaped once again. In January 1934, they attacked the Eastham Prison Farm in Texas to help Hamilton break out of jail, shooting several guards with machine guns…killing one.
two months. Immediately after her release in mid-1932, she hooked up with Clyde again. Over the next two years, the couple teamed with various accomplices to rob a string of banks and stores across five states…Texas, Oklahoma, Missouri, New Mexico and Louisiana. To law enforcement agents, the Barrow Gang, including Clyde’s childhood friend, Raymond Hamilton, W.D. Jones, Henry Methvin, Barrow’s brother Buck and his wife Blanche, among others, were cold-blooded criminals who didn’t hesitate to kill anyone who got in their way, especially police or sheriff’s deputies. To the public, however, Bonnie and Clyde’s reputation as dangerous outlaws was mixed with a romantic view of the couple as “Robin Hood”-like folk heroes. Their fame was increased by the fact that Bonnie was a woman, which made her an unlikely criminal, and by the fact that the couple posed for playful photographs together, which were later found by police and released to the media. Police almost captured Bonnie and Clyde in the spring of 1933, with surprise raids on their hideouts in Joplin and Platte City, Missouri. Buck Barrow was killed in the second raid, and Blanche was arrested, but Bonnie and Clyde escaped once again. In January 1934, they attacked the Eastham Prison Farm in Texas to help Hamilton break out of jail, shooting several guards with machine guns…killing one.
Texan prison officials hired Captain Frank Hamer, a retired Texas police officer, as a special investigator to track down Bonnie and Clyde. After a three month search, Hamer traced the couple to Louisiana, where Henry Methvin’s family lived. Bonnie and Clyde appeared, the officers opened fire, killing the couple instantly in a hail of 
 bullets. All told, the Barrow Gang was believed to have been responsible for the deaths of 13 people, including nine police officers. Bonnie and Clyde are still seen by many as romantic figures, however, especially after the success of the 1967 film Bonnie and Clyde, starring Faye Dunaway and Warren Beatty. It’s really a sad thing when crime is romanticized, because people think of it as an exciting, when in fact, it is a dead end road.
bullets. All told, the Barrow Gang was believed to have been responsible for the deaths of 13 people, including nine police officers. Bonnie and Clyde are still seen by many as romantic figures, however, especially after the success of the 1967 film Bonnie and Clyde, starring Faye Dunaway and Warren Beatty. It’s really a sad thing when crime is romanticized, because people think of it as an exciting, when in fact, it is a dead end road.

 For most of her life, my sister-in-law, Brenda Schulenberg struggled with her weight. Even as a child, Brenda was heavy. She will tell you that her weight prevented her from doing many of the things that most children took for granted, such as riding a bicycle. She might have been able to do it to a degree, but not for very long or very far. As she grew into adulthood, her weight became such a problem that she couldn’t even think of riding a bicycle. Then one day, her health failed due to her weight. She knew that she had to make a change. That day was October 18, 2013…just 5½ months after her dad, Walt Schulenberg passed away. Brenda became a health nut. She learned to eat right, and she walked…slowly and with a walker at first, and later on her own. She walked further and further…often reaching 10 miles a day. The weight came off, and she felt much better. Still, one thing eluded her…riding a bicycle. Finally, the day arrived when Brenda found out that she could ride a bicycle…as long as the peddles were off, and she could reach the ground. It’s called strider riding. It is a bicycle, but the rider basically runs the bicycle down the trail, instead of riding it…and Brenda could do that.
For most of her life, my sister-in-law, Brenda Schulenberg struggled with her weight. Even as a child, Brenda was heavy. She will tell you that her weight prevented her from doing many of the things that most children took for granted, such as riding a bicycle. She might have been able to do it to a degree, but not for very long or very far. As she grew into adulthood, her weight became such a problem that she couldn’t even think of riding a bicycle. Then one day, her health failed due to her weight. She knew that she had to make a change. That day was October 18, 2013…just 5½ months after her dad, Walt Schulenberg passed away. Brenda became a health nut. She learned to eat right, and she walked…slowly and with a walker at first, and later on her own. She walked further and further…often reaching 10 miles a day. The weight came off, and she felt much better. Still, one thing eluded her…riding a bicycle. Finally, the day arrived when Brenda found out that she could ride a bicycle…as long as the peddles were off, and she could reach the ground. It’s called strider riding. It is a bicycle, but the rider basically runs the bicycle down the trail, instead of riding it…and Brenda could do that. 
After riding strider style for a time, Brenda was finally able to ride a bicycle in the normal way. She put the peddles back on her purple bicycle and off she went. Brenda became just like the postal service…”Neither snow nor rain nor heat nor gloom of night stays these couriers from the swift completion of their appointed rounds.” Ok, Brenda didn’t have appointed rounds…exactly, but she had set herself a goal of riding her bicycle every month of the year. Now, that is not an easy task, especially in the state of Wyoming, where winters can be brutal. Nevertheless, just like the postal worker, neither rain, nor sleet, nor snow, nor gloom of the very early morning will keep Brenda from riding her bicycle. She is determined to ride it, and make up for all the years that she couldn’t even ride a bicycle in the summertime, much less in the winter.
She’s a brave woman, especially when she goes out in the middle of a snow story, and pretty much turns into a 
 snow woman. She reminds me of the Campbell’s Soup commercial where the little boy is so covered with snow that only a hot bowl of soup will melt away all the snow. Maybe she’s not that bad, but she’s close. Brenda, we are proud of your determination, but I do have to wonder if the people driving by the snow woman on wheels have to rubs their eyes to make sure they are seeing what their eyes are telling them they are seeing. Today is Brenda’s birthday. Happy birthday Brenda!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
snow woman. She reminds me of the Campbell’s Soup commercial where the little boy is so covered with snow that only a hot bowl of soup will melt away all the snow. Maybe she’s not that bad, but she’s close. Brenda, we are proud of your determination, but I do have to wonder if the people driving by the snow woman on wheels have to rubs their eyes to make sure they are seeing what their eyes are telling them they are seeing. Today is Brenda’s birthday. Happy birthday Brenda!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

