wounded
 The attack on Pearl Harbor, on December 7, 1941, rocked the United States. It was so unexpected, but while it brought so much destruction, it also brought out so many heroes too. Orders did not need to be given, everyone simply jumped into action, without being told. Still, the destruction was so overwhelming, and the attack just kept coming. People were dodging bullets and bombs, as well as flying debris and suicide bombers. A heavy, choking, acrid smoke filled the air, making it very hard to breathe. There would be making deaths that day, but there would also be heroes.
The attack on Pearl Harbor, on December 7, 1941, rocked the United States. It was so unexpected, but while it brought so much destruction, it also brought out so many heroes too. Orders did not need to be given, everyone simply jumped into action, without being told. Still, the destruction was so overwhelming, and the attack just kept coming. People were dodging bullets and bombs, as well as flying debris and suicide bombers. A heavy, choking, acrid smoke filled the air, making it very hard to breathe. There would be making deaths that day, but there would also be heroes.
Lieutenant Annie G Fox was stationed at Hickam Airfield in Hawaii on December 7, 1941, and she was the chief nurse on duty that morning. When the attack began, she sprang into action to tend to the injured and dying service personnel on the base. For her outstanding performance, Fox was recommended for and awarded the Purple Heart, but she was not injured during the attack. Fox was presented the Purple Heart on October 26, 1942, at Hickam Field. Colonel William Boyd, Post Commander read the  citation which was commanded by Brigadier General W E Farthing and signed by Colonel L P Turner, Air Corps Executive Officer.
citation which was commanded by Brigadier General W E Farthing and signed by Colonel L P Turner, Air Corps Executive Officer.
Then, in 1944 in a horrible twist of fate, the rules for receiving the Purple Heart changed, and Fox no longer qualified. The recipient needed to have sustained battle wounds. Fox’s medal was rescinded. She received the Bronze Star instead. I can understand the reasons behind the change, but it seems wrong that her medal that was legitimately earned in 1941, could be taken back in 1944. It should have been grandfathered or something. Nevertheless, the Purple Heart was not returned.
Purple Heart or Bronze Star aside, Lieutenant Annie Fox showed great spirit that day. In the face of great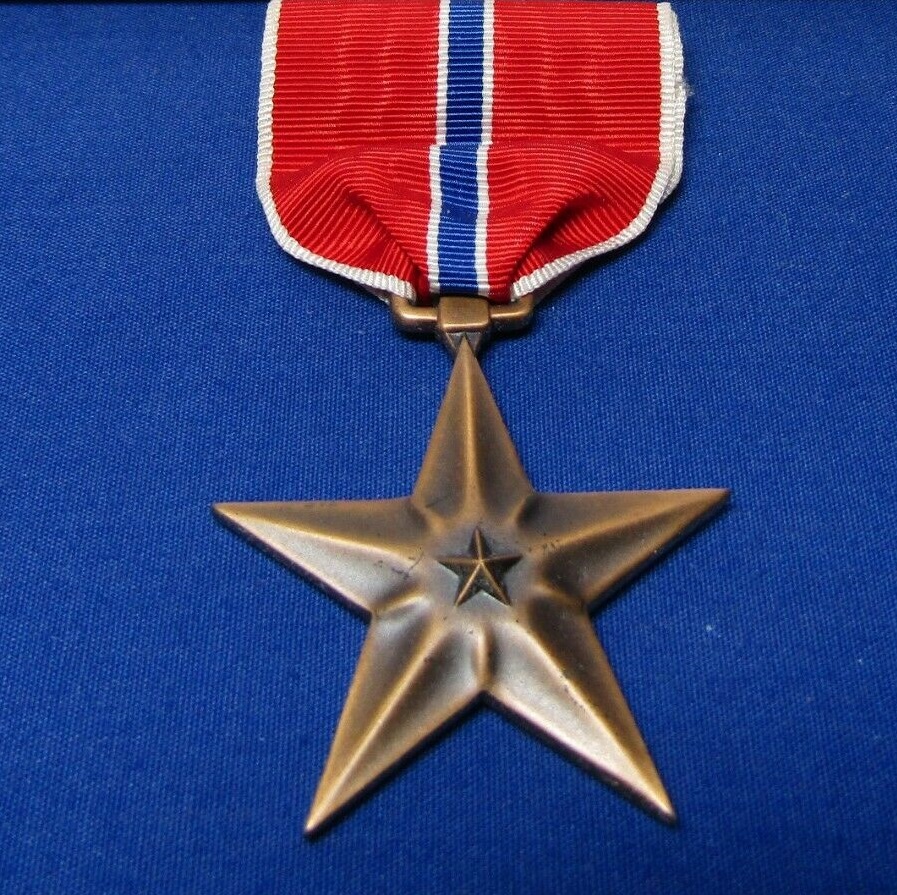  personal danger, she dodged the hail of bullets to reach many wounded people and she saved many lives. She could have been shot, bombed, breathed in poisonous gasses, or been hit by debris. It didn’t stop her. She saw the wounded, and she ran headlong into the danger, thereby saving her fellow man. Whether she was properly awarded the Purple Heart or not, she was definitely a hero.
personal danger, she dodged the hail of bullets to reach many wounded people and she saved many lives. She could have been shot, bombed, breathed in poisonous gasses, or been hit by debris. It didn’t stop her. She saw the wounded, and she ran headlong into the danger, thereby saving her fellow man. Whether she was properly awarded the Purple Heart or not, she was definitely a hero.
Annie Gayton Fox was born to Charles Fox and Deidamia (Gayton) Fox in East Pubnico, Nova Scotia, Canada, on August 4, 1893. She died at age 93 on January 20, 1987, in San Mateo County, California. Her years of service ran from July 3, 1918 through December 31, 1945. She retired as a Major in the US Army.
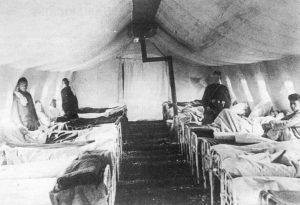
 As nursing goes, I suppose you could say that World War I changed everything. War is an ugly business, and wounded men (and women these days) are just a part of the unavoidable side effects of it. As the upheaval of World War I changed the world, so the horrors of it, changed nursing.
As nursing goes, I suppose you could say that World War I changed everything. War is an ugly business, and wounded men (and women these days) are just a part of the unavoidable side effects of it. As the upheaval of World War I changed the world, so the horrors of it, changed nursing.
From 1914 to 1918, what was dubbed “the war to end all wars” in the innocence of the times, anyway…led to the mobilization of more than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, making it one of the largest wars in history. As we know, it was hardly the war to end all wars, but it did change many of the things we had come to expect war to be. World War I was one of the deadliest conflicts in history. The death toll is staggering…estimated nine million combatants and seven million civilian deaths, as a direct result of the war. To add to that total, came the resulting genocides, as well as the 1918 influenza pandemic, which caused another 50 to 100 million deaths worldwide.
Now, just imagine being a nurse in those days. Of course, medical tents and hospitals were close to the perimeter of the fighting, to care for hurt soldiers quickly. This assured that the World War I nurses were witness to the conflict firsthand. I seriously doubt if any of them walked away from the war with less PTSD than the soldiers did. Many of them wrote about their involvement in diaries and letters that, similar to photographs from this time, offer insight into how they were personally impacted. The journals also include details about fighting, disease, and the hope that nurses and soldiers alike found in their darkest moments…if there could be any hope to be found.
It was in World War I that Germany introduced gas as a new form of aggression in 1915. It was in many ways the latest form of terrorism. To say that it was a different level of engagement seems an understatement. Gas devices became commonplace. They were worn anytime an air raid siren sounded, and some people wore them much of the time, as a precaution. The soldiers didn’t go anywhere without their gas mask. It was their life-line. Still, they were among the most feared elements of World War I.
“Sister Edith Appleton was a British nurse who served in France during World War I. She wrote about the soldiers stricken by gas and the adverse physical impacts they endured. The minimal immediate effects are tearing of the eyes, but subsequently, it causes build-up of fluid in the lungs, known as pulmonary edema, leading to death. It is estimated that as many as 85% of the 91,000 gas deaths in WWI were a result of phosgene or the related agent, diphosgene (trichloromethane chloroformate).”
Margaret Trevenen Arnold, a volunteer British Red Cross nurse in France in 1915 kept a diary of her time at Le Tréport and described “groans, and moans, and shouts, and half-dazed mutterings, and men with trephined heads suddenly sitting bolt upright… It was awful, and I really know now what [conflict] means.” These serious head injuries would most likely cause permanent brain damage for these men…if they survived at all.
Some hospital tents were eerily quiet, because the men in them were too sick to make a sound. Bandages were changed as often as every two hours, in an effort to ward off infection, and tourniquets to stop the bleeding until the soldier could be sent to surgery. Most of these field “hospitals” faced the same serious conditions…a lack of clean water and sterile surroundings. The nurses had to make due with what they had…and that often wasn’t much. Sometimes the lack of medicine became a major issue, especially when it came to anesthesia. Sometimes, the soldier had to simply force himself to remain calm, and steel himself to the inevitable pain of the surgery. These men had to place their faith in the doctors and nurses who cared for them, and they had not had time to even prepare for the need for surgery…let alone without anesthesia.
“Violet Gosset served on the Western Front from 1915 to 1919. While working at a hospital in Boulogne, France, Gosset kept notes about her experiences. She described a lack of supplies, overcrowded conditions, and scrapes that often resulted from a lack of adequate protection.”
“Helen Dare Boylston, an American nurse who served in France with the Harvard Unit medical team, had patients that spanned a wide range of age demographics. Some of the soldiers were just teenagers (“boys”), while others were in their 20s. However, Boylston recalled at least one soldier in his 60s (she called him “Dad”). Boylston saw the number of men in her care rise significantly in March 1918. At this time, she was sent…with two other nurses…to care for 500 soldiers. Boylston and her fellow nurses, including one named Ruth, quickly adapted to their conditions.”
Trench warfare was a shock to most of the soldiers. Still, most soldiers remained in good spirits. A part of nursing that might be considered a little different in the field hospitals is that the nurses are “in charge of” morale to a great degree. whether the men had Trench Foot, were sick, or wounded, they needed to have someone to lift their spirits. Who would have ever thought of nurses as morale boosters, but it was so.
Flu was widespread during World War I, even before the pandemic of 1918. After the pandemic began, things became critical. Now, nurses had to contend with treatment and prevention, in addition to other issues. One problem is that soldiers who ended up in medical tents and hospitals were often covered in mud, and flies frequently buzzed around them. Keeping germs at bay was next to impossible.
“Nurse Helen Dare Boylston was a keen observer of how soldiers reacted when they returned from the front, especially when they interacted with female nurses. She commented on the “fascinating game” of casual 
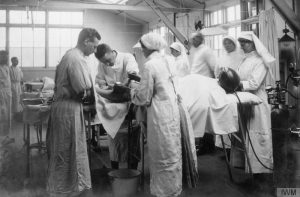 romance that commonly played out in the midst of conflict-related stress.” This was probably one of the most unusual phenomena, because nurses are told not to get emotionally involved, and yet here it was exactly what was needed. Nursing has changed over the years, but never has it been so evident as in World War I. It was as if nurses were making it up as they went along…and maybe they were.
romance that commonly played out in the midst of conflict-related stress.” This was probably one of the most unusual phenomena, because nurses are told not to get emotionally involved, and yet here it was exactly what was needed. Nursing has changed over the years, but never has it been so evident as in World War I. It was as if nurses were making it up as they went along…and maybe they were.
 For many years I was essentially unaware of the Texas Rangers. Then, with the show Walker, Texas Ranger, this elite group of law enforcement officers became a household word. Of course, the Texas Rangers have been an institution in Texan since they were unofficially created by Stephen F. Austin in a call-to-arms written in 1823. They were first headed by Captain Morris. After a decade, on August 10, 1835, Daniel Parker introduced a resolution to the Permanent Council creating a body of rangers to protect the border, something we continue to need today.
For many years I was essentially unaware of the Texas Rangers. Then, with the show Walker, Texas Ranger, this elite group of law enforcement officers became a household word. Of course, the Texas Rangers have been an institution in Texan since they were unofficially created by Stephen F. Austin in a call-to-arms written in 1823. They were first headed by Captain Morris. After a decade, on August 10, 1835, Daniel Parker introduced a resolution to the Permanent Council creating a body of rangers to protect the border, something we continue to need today.
On May 2, 1874, John B. Jones began his adventurous career as a lawman, when he was appointed as a major in the Texas Rangers. Jones was born in Fairfield District, South Carolina, in 1834. He moved to Texas with his father when he was a small boy. He went to college at Mount Zion College in South Carolina, and after graduating he returned to his home in Texas to enlist in the Confederate Army during the Civil War. Talented and ambitious, he eventually rose to the rank of adjutant general. Jones took the defeat of the Confederacy hard, and after the war, he spent some time traveling in Mexico and Brazil trying to establish a colony for other disgruntled former Confederates. After determining that the colonial schemes held little promise for success, he returned to Texas where his military experience won him his major’s commission with the Texas Rangers.
Jones commanded the Frontier Battalion, a force of about 500 men stationed along the Texas frontier from the Red River to the Rio Grande. His mission was two-fold: to keep hostile-border Indians out of Texas and control the outlaws within Texas. His first Indian fight came less than six weeks later. While patrolling near Jacksboro, Texas, with 28 men, Jones spotted a band of more than 100 Indians that he thought were hostile Kiowa, Commanche, and Apache. Displaying more courage than wisdom, Jones directed his small band to attack the larger force of Indians. In the ensuing battle, two of the Rangers were killed and two wounded, but they were lucky to escape without more serious losses. Jones, feeling quite chastened, acted with greater care in his subsequent battles with Indians. Soon, his force became highly effective in repulsing invasions.
Four years later, Jones took on one of the most notorious outlaws on the Texas frontier…a man named Sam Bass. For some months, Bass and his gang had been staging train robberies in Texas. Although most of the robberies failed to net much money because Bass and his partners were incompetent amateurs. Nevertheless, the people of Texas demanded that Bass be stopped. The Texas government turned to Jones, ordering him to  use his Rangers to run Bass down. Seizing on the drama of the chase, the press dubbed the affair the “Bass War.” For four months, Bass led Jones and his Rangers on a wild chase through Texas. In July 1878, Jones learned that Bass was planning to rob the bank in Round Rock, Texas. When Bass did hit the bank, Jones and his Rangers were waiting. Bass was badly wounded in the ensuing gun battle, and he died several days later. Oddly it was Bass who later became a legend, portrayed as good-natured Robin Hood, while Jones has largely been forgotten. Jones continued to command the Frontier Battalion until he died of natural causes in 1881 at the age of 46.
use his Rangers to run Bass down. Seizing on the drama of the chase, the press dubbed the affair the “Bass War.” For four months, Bass led Jones and his Rangers on a wild chase through Texas. In July 1878, Jones learned that Bass was planning to rob the bank in Round Rock, Texas. When Bass did hit the bank, Jones and his Rangers were waiting. Bass was badly wounded in the ensuing gun battle, and he died several days later. Oddly it was Bass who later became a legend, portrayed as good-natured Robin Hood, while Jones has largely been forgotten. Jones continued to command the Frontier Battalion until he died of natural causes in 1881 at the age of 46.
 October 7, 1780, was the beginning of the end of British rule in The Colonies. The Battle of King’s Mountain would be a battle that the British would never forget. Fewer than one thousand American Heroes, used skills and strategies that no one expected them to have to defeat Major Patrick Ferguson, who was the star of the British military might. Benjamin, James, Robert, and Samuel Knox, ancestors of my husband, Bob Schulenberg, were four of those heroes. The Knox brothers walked away from the battle without being wounded. In reality so did most of the 900 Patriots who participated in the battle. In the end, while the number of casualties reported varies from source to source, some of the most commonly reported figures are that 225 Loyalists had been killed, 163 wounded and 716 were captured, while only 28 Patriots were killed, including Colonel James Williams, and 68 wounded. The outcome of this battle was disastrous for the British, and especially for Major Patrick Ferguson, who died there.
October 7, 1780, was the beginning of the end of British rule in The Colonies. The Battle of King’s Mountain would be a battle that the British would never forget. Fewer than one thousand American Heroes, used skills and strategies that no one expected them to have to defeat Major Patrick Ferguson, who was the star of the British military might. Benjamin, James, Robert, and Samuel Knox, ancestors of my husband, Bob Schulenberg, were four of those heroes. The Knox brothers walked away from the battle without being wounded. In reality so did most of the 900 Patriots who participated in the battle. In the end, while the number of casualties reported varies from source to source, some of the most commonly reported figures are that 225 Loyalists had been killed, 163 wounded and 716 were captured, while only 28 Patriots were killed, including Colonel James Williams, and 68 wounded. The outcome of this battle was disastrous for the British, and especially for Major Patrick Ferguson, who died there.
Major Patrick Ferguson came to North Carolina in September 1780, and with the plan of recruiting troops to join the Loyalist militia to protect the flank of Lord Cornwallis’ main force. Ferguson issued a ultimatum to the rebel militias to lay down their arms or suffer the consequences. Apparently, he didn’t understand the Patriots at all…not an unusual mistake for the enemies of the United States, even today. That ultimatum led them to react alright, but not in the way Ferguson had expected. The Patriot militia led by Benjamin Cleveland, James Johnston, William Campbell, John Sevier, Joseph McDowell and Isaac Shelby rallied for an attack on Ferguson. Major Ferguson, realizing the seriousness of his error, attempted to retreat to the safety of Lord Cornwallis’ army, but never made it.
The battle took place 9 miles south of the present day town of Kings Mountain, North Carolina in rural Cherokee County, South Carolina. Because the arrival of the Patriots was almost a complete surprise, the Loyalists suffered heavy casualties. The battle lasted just one hour, after which Major Patrick Ferguson lay dead, and his men, either dead, wounded, and/or captured, but not a single one of Fergusons men had escaped. The Patriots did have to retreat quickly, so they would not be there in the event of a counterattack from Lord Cornwallis’ army, but they left Kings Mountain completely victorious. It was the beginning of the end for British rule in the United States. No longer would The Colonies be looked at as simply fledglings in need of guidance, nor would they be looked at as a small insignificant army, but rather they would be respected as a worthy opponent.
Historians agree that the Battle of Kings Mountain was the “beginning of the end” of British rule in its former colonies. In less than one hour of battle, The Overmountain Men, as they were called, not only won the day, but also undermined the British strategy for keeping America under its control. Such a defeat, as that suffered by Major Patrick Ferguson, is rare in any war. Ferguson thought that his position on Kings Mountain was one that would make an attack nearly impossible, without advance warning. The plateau of the mountain was just large enough to serve as a battleground for his command and to provide space for his camp and wagon train. There was water nearby. The slopes of the mountain would hinder the advance of the attackers. When attacked he expected that any retreat would be rendered impossible by flanking or encircling detachments, a condition he desired, because he would see to it that his men stood and fought, rather than run away. From Patrick Ferguson’s point of view, there was no better position than the one he had found. How very wrong he was.

The Knox family went on to play an illustrious and important role in American history. They were descendants of Charlemagne and the British House of Plantagenet, established by Henry II and Eleanor of Acquitaine, whose exploits were told in the movie, The Lion in Winter. They were of the same family as Richard, the Lionhearted, King John who was forced to sign the Magna Carta, and John Knox, the famous Scottish reformer, who railed against the reign of Mary, Queen of Scots. This family produced the man who would become the eleventh President of the United States of America: James Knox Polk. They were a family that my husband’s family has long been proud to be a part of.
 I have been telling you about some of the family connections I have made recently, and how surprised I have been at just who some of these people are. It isn’t always about them being famous, but rather about what amazing things they have done in their lives. So often we don’t hear what our family members have accomplished…mostly because they are too humble to really share all of their accomplishments. Recently, I made a family connection with the Noyes side of my husband, Bob Schulenberg’s family. This would be Bob’s grandmother, Nettie Noyes Knox’s side of the family. The connection was one that in all reality, I stumbled on. I had been searching for information…over a year ago, and I had copied the web addresses of several sites I thought might help, and put them into a Word document. There they sat for far too long. Finally, I found the time to check on one of them, and found the email for Paul Noyes. What an amazing find that was!!
I have been telling you about some of the family connections I have made recently, and how surprised I have been at just who some of these people are. It isn’t always about them being famous, but rather about what amazing things they have done in their lives. So often we don’t hear what our family members have accomplished…mostly because they are too humble to really share all of their accomplishments. Recently, I made a family connection with the Noyes side of my husband, Bob Schulenberg’s family. This would be Bob’s grandmother, Nettie Noyes Knox’s side of the family. The connection was one that in all reality, I stumbled on. I had been searching for information…over a year ago, and I had copied the web addresses of several sites I thought might help, and put them into a Word document. There they sat for far too long. Finally, I found the time to check on one of them, and found the email for Paul Noyes. What an amazing find that was!!
Paul has blessed me with information that I hadn’t found, and I sent him some pictures I had of Noyes family members, to add to his tree. Then he sent back more information on one of the pictures I sent him. He had no idea where that would lead…but I knew, because I had been thinking about a story about him and his family since I received his first response to my email. I love making these new connections, but some of them turn into a great cousinship and friendship too, and those are the most special ones, for sure. I had sent a picture of Eugene Noyes Jr in uniform…but Paul knew from looking at the uniform, that the uniform was from World War II. He knew this because of the 15th Army Air Forces shoulder patch on the uniform. I suppose I might have caught that too, since I had seen my dad’s 8th Army Air Forces shoulder patch, but it was simply something I didn’t notice at all.
In my defense, I am not a retired after 22 years veteran…and Paul is. Well, that got my curiosity going again. I asked Paul to tell me about his service time. True to the form I have seen with most military men and women…a humble breed…Paul told me a little bit about what he did. He spent most of his 22 year Army career was as an Army aviator. He started out as an Airborne Ranger, then served in Vietnam in Special Forces, where he was wounded. While recovering from the wounds, he was selected for flight school and served in Army Aviation special ops. I did a little research on what Special Operations does exactly, and this is the summary I came up with, “Conduct global special operations missions ranging from precision application of firepower to infiltration, aviation foreign internal defense, exfiltration, resupply and refueling of SOF operational elements.” If you’re like me, that doesn’t clarify much. Upon further research, I found that much of what Special Operations did in Vietnam was to train groups of the Vietnamese Army so they can train the remaining army members. Of course, I am probably generalizing Special Operations to a large degree, and I will have to ask Paul to tell me more about it as soon as I have a chance.
After he was wounded, Paul’s entire career changed when he was selected to become an Army Aviator. Having worked with a pilot for over 18 years now, I have had the opportunity to fly…and I use the term loosely…a small 4 seater plane. Basically what I really did was steer it, and I didn’t do that so well, because it kept climbing, and had to be brought back to level. It was an opportunity given to me with no preparation, and I really enjoyed it. I think to a degree, that is what happened with Paul too. After being wounded, he was given an opportunity to switch gears and do something he never expected to do, and he excelled at it. That is an  awesome career change, and one I look forward to hearing more about.
awesome career change, and one I look forward to hearing more about.
Of course, in a 22 year career, Paul was also building a family. He was married to his lovely wife, Elizabeth, who is an author, and after collaborating with 11 other authors on a book called “A Dozen Apologies”, she released her first book this past August, called “Imperfect Wings”. I look forward to reading both. Paul and Elizabeth have two children, daughter Shari and husband Jimmy Nardello, and their children Cameryn and Reid; and son Chris who is married to Dr Christina Noyes, and they have a son named Owen. I am really looking forward to getting to know these wonderful, new to me cousins as time goes on.
 So often, we take many of the people in our lives for granted. We just assume that they will always be there, and never consider the events in their past that…were it not for the grace of God, would have taken their lives, possibly before we even knew them. That is the case with my Uncle George. Were it not for the grace of God, he would have been killed in action in World War II, before he ever had the chance to meet and marry my Aunt Evelyn, becoming father of my cousins, and an uncle to me and the rest of the cousins. Uncle George, like my dad, my Uncle Larry, Uncle Wayne, and many other young men of that era, served his country during World War II. Many people serve in the wars our country has been involved in, and many people are injured and killed every day as a result of their service in our wars. In that way, Uncle George is not an unusual statistic, but what is unusual is that Uncle George survived…a head injury!!! He has had a plate in his head since that injury, but in every other way, he has lead a normal life.
So often, we take many of the people in our lives for granted. We just assume that they will always be there, and never consider the events in their past that…were it not for the grace of God, would have taken their lives, possibly before we even knew them. That is the case with my Uncle George. Were it not for the grace of God, he would have been killed in action in World War II, before he ever had the chance to meet and marry my Aunt Evelyn, becoming father of my cousins, and an uncle to me and the rest of the cousins. Uncle George, like my dad, my Uncle Larry, Uncle Wayne, and many other young men of that era, served his country during World War II. Many people serve in the wars our country has been involved in, and many people are injured and killed every day as a result of their service in our wars. In that way, Uncle George is not an unusual statistic, but what is unusual is that Uncle George survived…a head injury!!! He has had a plate in his head since that injury, but in every other way, he has lead a normal life.
People who don’t know about a situation, which was me concerning my Uncle George…until recently when I came across the Wyoming Wounded List where his name appears, usually assume that the person they know, and have known all their lives, was never wounded. Little did I know how very wrong I was. I knew that Uncle George has been in the Navy in World War II, but that was all I knew about his war history, and I only knew that because of a picture of my Aunt Evelyn, Uncle George, and my parents attending the Military Ball. You see, like most of the men who fought in World War II and probably many other wars too, Uncle  George never spoke of those days. It was like he either wanted to forget, or more likely that he thought he had simply done his duty and it was no big thing, because he came home after all. Many military men feel that way. They think the heroes are the ones who died for their country, but that is not the only way to be a hero. Just going into battle, makes them a hero!!
George never spoke of those days. It was like he either wanted to forget, or more likely that he thought he had simply done his duty and it was no big thing, because he came home after all. Many military men feel that way. They think the heroes are the ones who died for their country, but that is not the only way to be a hero. Just going into battle, makes them a hero!!
After learning about my Uncle George’s injuries from World War II, I feel so much more blessed to have Uncle George in my life. Thinking that, but for the grace of God, he would never have been my uncle, makes that blessing very clear to me, and I thank God for his life and for making him my uncle. I can’t imagine our family without him in it, and I know everyone else agrees with me too. Today is Uncle George’s birthday. Happy birthday Uncle George!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

