prisoners of war

 When we think of Prisoners of War during the world wars, we usually think of the prisoners as being men, but there were women too…nurses. At that time, women couldn’t be in combat positions, and if they wanted to serve their country, it had to be as nurses or medics. One group of United States Army Nurse Corps and United States Navy Nurse Corps nurses, were stationed in the Philippines at the outset of the Pacific War, were later dubbed the Angels of Bataan (also including the the nurses of the island of Corregidor), were also called the Angels of Bataan and Corregidor and the Battling Belles of Bataan. The 78 nurses served during the Battle of the Philippines (1941–42). When Bataan and Corregidor fell, 11 Navy nurses, 66 army nurses, and 1 nurse-anesthetist were captured and imprisoned in and around Manila. These loyal, patriotic women continued to serve as a nursing unit while prisoners of war, taking care of their fellow prisoners, even if it meant punishment for their actions.
When we think of Prisoners of War during the world wars, we usually think of the prisoners as being men, but there were women too…nurses. At that time, women couldn’t be in combat positions, and if they wanted to serve their country, it had to be as nurses or medics. One group of United States Army Nurse Corps and United States Navy Nurse Corps nurses, were stationed in the Philippines at the outset of the Pacific War, were later dubbed the Angels of Bataan (also including the the nurses of the island of Corregidor), were also called the Angels of Bataan and Corregidor and the Battling Belles of Bataan. The 78 nurses served during the Battle of the Philippines (1941–42). When Bataan and Corregidor fell, 11 Navy nurses, 66 army nurses, and 1 nurse-anesthetist were captured and imprisoned in and around Manila. These loyal, patriotic women continued to serve as a nursing unit while prisoners of war, taking care of their fellow prisoners, even if it meant punishment for their actions.
After the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Japanese immediately went after the Philippines and the military personnel based there, including the nurses. In late December 1941, many of the nurses were assigned to a pair of battlefield hospitals on Bataan named Hospital #1 and Hospital #2. These hospitals included the first open-air wards since the Civil War. Tropical diseases, including malaria and dysentery, were widespread among both hospital patient and staff. Just prior to the fall of Bataan on April 9, 1942, the nurses serving there were ordered to the island fortress of Corregidor by General Wainwright (commander of the forces in the Philippines after MacArthur was ordered to Australia). Wainwright tried to save as many people as he could by moving them to the safer island of Corregidor. In the end it made no difference, because Corregidor was captured too.
During their occupation of the Philippines, the Japanese commandeered the campus of the University of Santo Tomas and converted it to be the Santo Tomas Internment Camp. In addition to its civilian population, Santo Tomas became the initial internment camp for both the army and navy nurses, with the army nurses remaining there until their liberation, while the soldiers were taken on the Bataan Death March. While there, the nurses continued to take care of anyone they were allowed to. Under the supervision of Captain Maude C Davison, a 57 year old nurse, with 20 years of service experience, the nurses continued to do their jobs. Davison took command of the nurses, maintained a regular schedule of nursing duty, and insisted that all nurses wear their khaki blouses and skirts while on duty.
The number of internees at Santo Tomas Internment Center in February 1942 amounted to approximately 4,670 people, of whom 3,200 Americans. Of those 3,200 Americans, 78 were nurses. The Americans, anticipating the war, had sent many wives and children of American men employed in the Philippines to the states before December 8, 1941. A few people had been sent to the Philippines from China to escape the war in that country. Some had arrived only days before the Japanese attack. The prisoners were crowded 30 to 50 people per small classrooms in university buildings. The allotment of space for each individual was 16 to 22 square feet. Bathrooms were scarce. Twelve hundred men living in the main building had 13 toilets and 12 showers. Lines were normal for toilets and meals. Internees with money were able to buy food and built huts, “shanties,” of bamboo and palm fronds in open ground where they could take refuge during the day, although the Japanese insisted that all internees sleep in their assigned rooms at night. Soon there were several hundred shanties and their owners constituted a “camp aristocracy.” The Japanese attempted to enforce a ban on sex, marriage, and displays of affection among the internees. They often complained to the Executive Committee about “inappropriate” relations between men and women in the shanties.
The conditions at Santo Tomas were horrific. The biggest problem for the internees was sanitation, followed closely by starvation. The Sanitation and Health Committee had more than 600 internee men working for it. Their tasks included building more toilets and showers, laundry, dishwashing, and cooking facilities, disposal of garbage, and controlling the flies, mosquitoes, and rats that infested the compound. Then, in January 1944, control of the Santo Tomas Internment Camp changed from Japanese civil authorities to the Imperial Japanese Army, with whom it remained until the camp was liberated. Food, which had been scarce before, was reduced to only 960 calories per person per day by November 1944, and then to 700 calories per person per day by  January 1945. At the time the nurses were finally released, it was found that they had lost, on average, 30% of their body weight during internment, and subsequently experienced a degree of service-connected disability “virtually the same as the male ex-POW’s of the Pacific Theater.” Davison’s body weight dropped from 156 pounds to 80 pounds.
January 1945. At the time the nurses were finally released, it was found that they had lost, on average, 30% of their body weight during internment, and subsequently experienced a degree of service-connected disability “virtually the same as the male ex-POW’s of the Pacific Theater.” Davison’s body weight dropped from 156 pounds to 80 pounds.
Finally, General Douglas MacArthur, emboldened by the success of the Raid at Cabanatuan, ordered Major General Vernon D Mudge to make an aggressive raid on Santo Tomas in the Battle of Manila in 1945. The internees at Santo Tomas, including the nurses, were liberated on February 3, 1945, by a “flying column” of the 1st Cavalry.
 In many of the wars there have been in our world, one thing seems to be a constant…the atrocities against prisoners of war, and even the citizens of the evil nations we are fighting against. World War II probably saw some of the worst atrocities, during the Holocaust. It was during that time that prison camps like Auschwitz-Birkenau, Buchenwald, Chelmno, Dachau, and Terezin, just to name a few, were used either for the murder of Jews and anyone else Hitler felt was not of the standard of people he thought they should be, or the prisoners they held were used as forced labor.
In many of the wars there have been in our world, one thing seems to be a constant…the atrocities against prisoners of war, and even the citizens of the evil nations we are fighting against. World War II probably saw some of the worst atrocities, during the Holocaust. It was during that time that prison camps like Auschwitz-Birkenau, Buchenwald, Chelmno, Dachau, and Terezin, just to name a few, were used either for the murder of Jews and anyone else Hitler felt was not of the standard of people he thought they should be, or the prisoners they held were used as forced labor.
Buchenwald was not an Annihilation camp, but that doesn’t mean that it was a easy existence. The Germans were not good to their prisoners. Prisoners from all over Europe and the Soviet Union…Jews, Poles and other Slavs, the mentally ill and physically-disabled from birth defects, religious and political prisoners, Roma and Sinti, Freemasons, Jehovah’s Witnesses (then called Bible Students), criminals, homosexuals, and prisoners of war, worked primarily as forced labor in local armaments factories. It seems as if there were no groups who were exempt. If they didn’t fit into Hitler’s mold, they were contained in the camps, or killed. Buchenwald concentration camp (German: Konzentrationslager, which in English, literally means beech forest) was a German Nazi concentration camp established on the Ettersberg (Etter Mountain) near Weimar, Germany, in July 1937. It was one of the first and the largest of the concentration camps on German soil, following Dachau’s opening just over four years earlier.
On April 11, 1945, four soldiers in the Sixth Armored Division of the US Third Army, commanded by General  George S Patton, liberated the Buchenwald concentration camp. Just before the Americans arrived, the camp had already been taken over by the Communist prisoners who had killed some of the guards and forced the rest to flee into the nearby woods. They knew the end was near for them anyway, and there seemed no further reason to stand and fight. I suppose that the fact that the guards had deserted their posts, made it possible for just four soldiers to take over and liberate the camp. On the morning of April 12, 1945, soldiers of the 80th Infantry Division arrived in the nearby town of Weimar and found it deserted except for some of the liberated prisoners roaming around. The townspeople were cowering in fear inside their homes…bomb-damaged from the February 9, 1945 air raid that was to precede the liberation process. I would think that if any of them were a part of the concentration camp, there would be reason to fear the prisoners in town, because they had a reason to kill them, after all they had been through in German custody.
George S Patton, liberated the Buchenwald concentration camp. Just before the Americans arrived, the camp had already been taken over by the Communist prisoners who had killed some of the guards and forced the rest to flee into the nearby woods. They knew the end was near for them anyway, and there seemed no further reason to stand and fight. I suppose that the fact that the guards had deserted their posts, made it possible for just four soldiers to take over and liberate the camp. On the morning of April 12, 1945, soldiers of the 80th Infantry Division arrived in the nearby town of Weimar and found it deserted except for some of the liberated prisoners roaming around. The townspeople were cowering in fear inside their homes…bomb-damaged from the February 9, 1945 air raid that was to precede the liberation process. I would think that if any of them were a part of the concentration camp, there would be reason to fear the prisoners in town, because they had a reason to kill them, after all they had been through in German custody.
Recently, I found out that General George S Patton was my 8th cousin twice removed, on my grandmother, Hattie Pattan Byer’s side. I had always suspected a relationship there, with my grandmother’s maiden name being Pattan, but I didn’t expect it in the way it came about, since it is from my grandmother Elizabeth Shuck, who married my grandfather David Pattan, and not from the Pattan side outright. I have always liked General  Patton, and I think it is really awesome that he is related to my family. In my opinion, he was an amazing general. He served as a commissioned officer in the United States Army for 36 years. He served in three major conflicts (Mexican Punitive Expedition, World War I and World War II) during his military career. He was awarded with the Distinguished Service Cross with one oak leaf cluster, the Army Distinguished Service Medal with two oak leaf clusters, the Navy Distinguished Service Medal, the Silver Star with one oak leaf cluster, the Legion of Merit, the Bronze Star Medal, the Purple Heart, the Silver Lifesaving Medal, the Mexican Border Service Medal, the World War I Victory Medal with four bronze campaign stars, the American Defense Service Medal, the European-African-Middle Eastern Campaign Medal with one silver and two bronze campaign star, the World War II Victory Medal, and posthumously…the Army of Occupation Medal with Germany clasp. That’s quite a war record. I’m sure the prisoners that he liberated felt that he very much earned them for his war skills.
Patton, and I think it is really awesome that he is related to my family. In my opinion, he was an amazing general. He served as a commissioned officer in the United States Army for 36 years. He served in three major conflicts (Mexican Punitive Expedition, World War I and World War II) during his military career. He was awarded with the Distinguished Service Cross with one oak leaf cluster, the Army Distinguished Service Medal with two oak leaf clusters, the Navy Distinguished Service Medal, the Silver Star with one oak leaf cluster, the Legion of Merit, the Bronze Star Medal, the Purple Heart, the Silver Lifesaving Medal, the Mexican Border Service Medal, the World War I Victory Medal with four bronze campaign stars, the American Defense Service Medal, the European-African-Middle Eastern Campaign Medal with one silver and two bronze campaign star, the World War II Victory Medal, and posthumously…the Army of Occupation Medal with Germany clasp. That’s quite a war record. I’m sure the prisoners that he liberated felt that he very much earned them for his war skills.
 For as long as there have been wars, there have been prisoners of war. Obviously, part of the reason was to take those soldiers out of the fighting. If you are fighting against less enemy combatants, you have a better change of winning. It was a simply a part of war. Both sided took prisoners, and both sides knew that the other side was going to take prisoners. It was not the fact that prisoners were taken, but rather the way they were treated that made this part of war ugly sometimes.
For as long as there have been wars, there have been prisoners of war. Obviously, part of the reason was to take those soldiers out of the fighting. If you are fighting against less enemy combatants, you have a better change of winning. It was a simply a part of war. Both sided took prisoners, and both sides knew that the other side was going to take prisoners. It was not the fact that prisoners were taken, but rather the way they were treated that made this part of war ugly sometimes.
I’m sure that if there was work to do, it made sense to use the prisoners of war 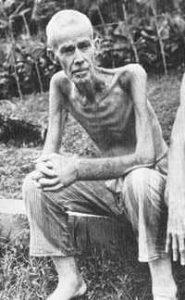 as, basically slave labor…make them earn their keep, so to speak, but often they were beaten, starved, overworked to the point of exhaustion, and basically treated like they were sub-human. Some nations were worse than others. And sometimes, the prisoners of war, weren’t even combatants, but civilians taken hostage for a variety of reasons…most of which had nothing to do with them being a danger in battle. Of course, from about the time of the Vietnam war, it became harder to tell if someone was a “combatant” or not. When children were sent out to interact with soldiers…bombs strapped to their chest…soldiers had to learn to be less than hospitable to the little ones too.
as, basically slave labor…make them earn their keep, so to speak, but often they were beaten, starved, overworked to the point of exhaustion, and basically treated like they were sub-human. Some nations were worse than others. And sometimes, the prisoners of war, weren’t even combatants, but civilians taken hostage for a variety of reasons…most of which had nothing to do with them being a danger in battle. Of course, from about the time of the Vietnam war, it became harder to tell if someone was a “combatant” or not. When children were sent out to interact with soldiers…bombs strapped to their chest…soldiers had to learn to be less than hospitable to the little ones too.
I understand the need for prisoners of war, when the war is still going on, but what is appalling is the treatment of the prisoners sometimes, and the refusal to give the prisoners back at the end of the conflict. Vietnam was also one of the times when prisoners were held long after the war. I know that sometimes the reasons for holding prisoners is that the opposing government refuses to abide by the conditions of the  surrender of the losing side. Still, sometimes, the prisoners were held, for no legitimate reason, and for far longer than was reasonable. After World War II, the western Allies released their final prisoners in 1948, but many German POWs in the USSR were held for several more years. Most were used as slave labor in copper or coal mines, and anywhere between 400,000, and up to one million eventually died while in Russian custody. Some 20,000 former soldiers were still in Soviet hands at the time of Joseph Stalin’s death in 1953, and the last 10,000 didn’t get their freedom until 1955 and 1956 a full decade after the war had ended. That seems completely unconscionable to me, but then I’m not part of an evil nation.
surrender of the losing side. Still, sometimes, the prisoners were held, for no legitimate reason, and for far longer than was reasonable. After World War II, the western Allies released their final prisoners in 1948, but many German POWs in the USSR were held for several more years. Most were used as slave labor in copper or coal mines, and anywhere between 400,000, and up to one million eventually died while in Russian custody. Some 20,000 former soldiers were still in Soviet hands at the time of Joseph Stalin’s death in 1953, and the last 10,000 didn’t get their freedom until 1955 and 1956 a full decade after the war had ended. That seems completely unconscionable to me, but then I’m not part of an evil nation.

