Hawaii

 We have all heard about the importance of thinking ahead. It’s important in many situations, but unfortunately, it isn’t always appreciated. One case of forward thinking that rather backfired is the case of Robert G Heft. Heft, who went by Bob, was in high school in 1958, when his history teacher, Stanley Pratt, asked his class to make anything they wanted and bring it in for a show-and-tell. Heft took a little bit different approach than his classmates, and it rather backfired. While most of his classmates designed a conventional approach for their class project, Heft decided to do something a little more ambitious.
We have all heard about the importance of thinking ahead. It’s important in many situations, but unfortunately, it isn’t always appreciated. One case of forward thinking that rather backfired is the case of Robert G Heft. Heft, who went by Bob, was in high school in 1958, when his history teacher, Stanley Pratt, asked his class to make anything they wanted and bring it in for a show-and-tell. Heft took a little bit different approach than his classmates, and it rather backfired. While most of his classmates designed a conventional approach for their class project, Heft decided to do something a little more ambitious.
It was a noble effort, and definitely forward thinking, but when Heft brought his flag to school, his teacher was not impressed. Years later, Heft recalled, “He told me, ‘Why you got too many stars? You don’t even know how  many states we have.'” Heft received a B- for his project. Nevertheless, he was offered an opportunity to enhance his grade by persuading the US government to adopt his flag design. Despite the slim chances, Heft was determined. He initiated a campaign, writing letters and placing calls to the White House, urging the president to consider his flag.
many states we have.'” Heft received a B- for his project. Nevertheless, he was offered an opportunity to enhance his grade by persuading the US government to adopt his flag design. Despite the slim chances, Heft was determined. He initiated a campaign, writing letters and placing calls to the White House, urging the president to consider his flag.
Two years after Alaska and Hawaii were admitted as states, Heft was surprised with a call from President Dwight D Eisenhower, informing him that his design had been selected for the new 50-star flag. On July 4, 1960, Heft was honored with an invitation from President Eisenhower to attend a flag-raising ceremony at the US Capitol in Washington DC. Even Heft’s history teacher was impressed, saying, “I guess if it’s good enough for Washington, it’s good enough for me. I hereby change the grade to an A.” Well, that took a fair amount of decency on the part of the teacher. He could have let it go, but he didn’t.
Since that time, Heft’s banner has established a new record as the longest-serving U.S. flag. Heft pursued a career as a professor at Northwest State Community College in Archbold, Ohio, and held the position of mayor in Napoleon, Ohio. He gained recognition as a motivational speaker and made 14 visits to the White House. Anticipating future changes, Heft also crafted a 51-star American flag in the event that Washington DC, or Puerto Rico achieves statehood. His 51-star flag design features six alternating rows of stars with nine and 
 eight stars each.
eight stars each.
Heft, born in Saginaw, Michigan on January 19, 1942. He left Michigan following his parents’ separation when he was around a year old. He returned upon retiring from his professorship at Northwest State Community College in Archbold, Ohio. Robert G Heft, who passed away on December 12, 2009, at a hospital in Saginaw, Michigan, at the age of 67, will always be remembered as the student who created the 50-star American flag design.
 The Cold War, and the Soviet Union’s sudden announcement on August 30, 1961, to end a three-year moratorium on nuclear testing, brought about a shift in US policy, and a number of to nuclear test operations. One, known as Operation Fishbowl was a series of high-altitude nuclear tests in 1962 that were carried out by the United States as a part of the larger Operation Dominic nuclear test program. Flight-test vehicles were designed and manufactured by Avco Corporation. The test planned for the first half of 1962, called Bluegill, Starfish and Urraca were originally planned for the first half of 1962, but the first test attempt was delayed until June. Planning was complex, but necessary.
The Cold War, and the Soviet Union’s sudden announcement on August 30, 1961, to end a three-year moratorium on nuclear testing, brought about a shift in US policy, and a number of to nuclear test operations. One, known as Operation Fishbowl was a series of high-altitude nuclear tests in 1962 that were carried out by the United States as a part of the larger Operation Dominic nuclear test program. Flight-test vehicles were designed and manufactured by Avco Corporation. The test planned for the first half of 1962, called Bluegill, Starfish and Urraca were originally planned for the first half of 1962, but the first test attempt was delayed until June. Planning was complex, but necessary.
The launch sites were planned from Johnston Island in the Pacific Ocean north of the equator. The island was the chosen launch site, rather than the other locations in the Pacific Proving Grounds. However, the testing was not without push back. Even as early as 1958, Lewis Strauss, t hen chairman of the United States Atomic Energy Commission, opposed doing any high-altitude tests at locations that had been used for earlier Pacific nuclear tests. The motivation for concern was the fear of the flash from the nighttime high-altitude detonations might blind civilians who were living on nearby islands. Still, Johnston Island was a remote location. It was more distant from populated areas than the other potential test locations. Nevertheless, in order to protect residents of the Hawaiian Islands from flash blindness or permanent retinal injury from the bright nuclear flash, the nuclear missiles of Operation Fishbowl were launched toward the southwest of Johnston Island. The detonation part of the test would be farther from Hawaii.
hen chairman of the United States Atomic Energy Commission, opposed doing any high-altitude tests at locations that had been used for earlier Pacific nuclear tests. The motivation for concern was the fear of the flash from the nighttime high-altitude detonations might blind civilians who were living on nearby islands. Still, Johnston Island was a remote location. It was more distant from populated areas than the other potential test locations. Nevertheless, in order to protect residents of the Hawaiian Islands from flash blindness or permanent retinal injury from the bright nuclear flash, the nuclear missiles of Operation Fishbowl were launched toward the southwest of Johnston Island. The detonation part of the test would be farther from Hawaii.
The Urraca test involved about a 1 megaton yield at very high altitude of just over 621 miles. With the damage caused to satellites by the Starfish Prime detonation, the proposed Urraca test was always controversial. Because they couldn’t put the fears to rest, the Urraca test was finally canceled, and an extensive re-evaluation of the Operation Fishbowl plan as a whole was made during the 82-day operations pause after the Bluegill Prime disaster of July 25, 1962. When prime was added to a test, it indicated that the main test had failed, so when Bluegill Prime failed, it was the second test fail for that test series, which in this case (Bluegill Double Prime), ended in disaster when the Thor suffered a stuck valve preventing the flow of LOX to the combustion chamber. The engine lost thrust and unburned RP-1 spilled down into the hot thrust chamber, igniting and starting a fire around the base of the missile. Bluegill would go on to have two more tests, before they finally achieved success.

A test named Kingfish was added during the early stages of Operation Fishbowl planning. Two low-yield tests, Checkmate and Tightrope, were also added during the project, so the final number of tests in Operation Fishbowl was five. Tightrope was the last atmospheric nuclear test conducted by the United States, as the Limited Test Ban Treaty came into effect shortly thereafter. A total of Seven rockets carrying scientific instrumentation were launched from Johnston Island in support of the Tightrope test, which was the final atmospheric test conducted by the United States. I suppose testing is necessary, and I don’t know where else or how else it could be done, but the whole thing seems crazy to me. I do think that in light of this and other nuclear test disasters, care should be taken to better protect human life.

 I would never have considered that an earthquake in Chili could affect Hawaii, which is 6,593 miles away, but on May 23, 1960, that seemingly huge distance suddenly became very small. When a 9.5 magnitude earthquake hit Chili on May 22, 1960, thousands of people lost their lives, and a giant tsunami was triggered. By the next day, that tsunami had traveled across the Pacific Ocean and killed an additional 61 people in Hilo, Hawaii. That distance and the amount of devastation seems incredible to me.
I would never have considered that an earthquake in Chili could affect Hawaii, which is 6,593 miles away, but on May 23, 1960, that seemingly huge distance suddenly became very small. When a 9.5 magnitude earthquake hit Chili on May 22, 1960, thousands of people lost their lives, and a giant tsunami was triggered. By the next day, that tsunami had traveled across the Pacific Ocean and killed an additional 61 people in Hilo, Hawaii. That distance and the amount of devastation seems incredible to me.
The earthquake, which involved a severe plate shift, caused a large displacement of water just off the coast of southern Chile at 3:11pm. The resulting wave, traveling at speeds in excess of 400 miles per hour, moved west and north. The damage to the west coast of the United States was estimated at $1 million, but there were no deaths there.
In 1948, the Pacific Tsunami Warning System was established in response to another deadly tsunami. It worked properly and warnings were issued to Hawaiians six hours before the deadly wave was expected to arrive. Unfortunately, some people ignored the warnings, as always seems to happen. Some other people actually headed to the coast in order to view the wave…like the warning was actually an announcement of a coming attraction. The tsunami arrived only a minute after it was predicted, and it absolutely destroyed Hilo Bay on the island of Hawaii.
People really don’t fully understand just how much destructive power water has, until they see it in action. When the waves hit Hilo Bay, they were thirty-five-feet high. They were so strong that they bent parking meters to the ground and wiped away most of the buildings. When the wave hit a 10-ton tractor, it was swept out to sea like it was made of Styrofoam. you would think that boulders would be sturdy enough to hold back the waves, but the 20-ton boulders that made up the seawall were easily moved 500 feet. The 61 people who lost their lives were in Hilo…the hardest hit area of the island chain.
With all of that destruction, you might be inclined to think that the waves would have lost power, and to a degree, I suppose they did. Nevertheless, the tsunami continued to race further west across the Pacific. Even given a ten-thousand-mile distance from the earthquake’s epicenter, Japan still wasn’t able to provide enough warning time to get the people out of harm’s way. The wave hit Japan at about 6:00pm, more than a full day after the earthquake. The tsunami struck the Japanese islands of Honshu and Hokkaido. The wave’s power was still enough to crushing 180 people, and to leave 50,000 more homeless. In Japan, it caused $400 million in 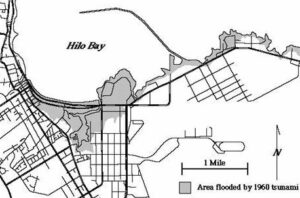
 damages. With everything destroyed by this one earthquake and the subsequent tsunami, you would think that people would finally learn to stay away from the shore during a tsunami warning, but every year people lose their lives because they decided to cross paths with waves…be it from tsunamis, hurricanes, and other floods. Water is a force to be reckoned with. It should be considered very dangerous.
damages. With everything destroyed by this one earthquake and the subsequent tsunami, you would think that people would finally learn to stay away from the shore during a tsunami warning, but every year people lose their lives because they decided to cross paths with waves…be it from tsunamis, hurricanes, and other floods. Water is a force to be reckoned with. It should be considered very dangerous.
 The attack on Pearl Harbor, on December 7, 1941, rocked the United States. It was so unexpected, but while it brought so much destruction, it also brought out so many heroes too. Orders did not need to be given, everyone simply jumped into action, without being told. Still, the destruction was so overwhelming, and the attack just kept coming. People were dodging bullets and bombs, as well as flying debris and suicide bombers. A heavy, choking, acrid smoke filled the air, making it very hard to breathe. There would be making deaths that day, but there would also be heroes.
The attack on Pearl Harbor, on December 7, 1941, rocked the United States. It was so unexpected, but while it brought so much destruction, it also brought out so many heroes too. Orders did not need to be given, everyone simply jumped into action, without being told. Still, the destruction was so overwhelming, and the attack just kept coming. People were dodging bullets and bombs, as well as flying debris and suicide bombers. A heavy, choking, acrid smoke filled the air, making it very hard to breathe. There would be making deaths that day, but there would also be heroes.
Lieutenant Annie G Fox was stationed at Hickam Airfield in Hawaii on December 7, 1941, and she was the chief nurse on duty that morning. When the attack began, she sprang into action to tend to the injured and dying service personnel on the base. For her outstanding performance, Fox was recommended for and awarded the Purple Heart, but she was not injured during the attack. Fox was presented the Purple Heart on October 26, 1942, at Hickam Field. Colonel William Boyd, Post Commander read the  citation which was commanded by Brigadier General W E Farthing and signed by Colonel L P Turner, Air Corps Executive Officer.
citation which was commanded by Brigadier General W E Farthing and signed by Colonel L P Turner, Air Corps Executive Officer.
Then, in 1944 in a horrible twist of fate, the rules for receiving the Purple Heart changed, and Fox no longer qualified. The recipient needed to have sustained battle wounds. Fox’s medal was rescinded. She received the Bronze Star instead. I can understand the reasons behind the change, but it seems wrong that her medal that was legitimately earned in 1941, could be taken back in 1944. It should have been grandfathered or something. Nevertheless, the Purple Heart was not returned.
Purple Heart or Bronze Star aside, Lieutenant Annie Fox showed great spirit that day. In the face of great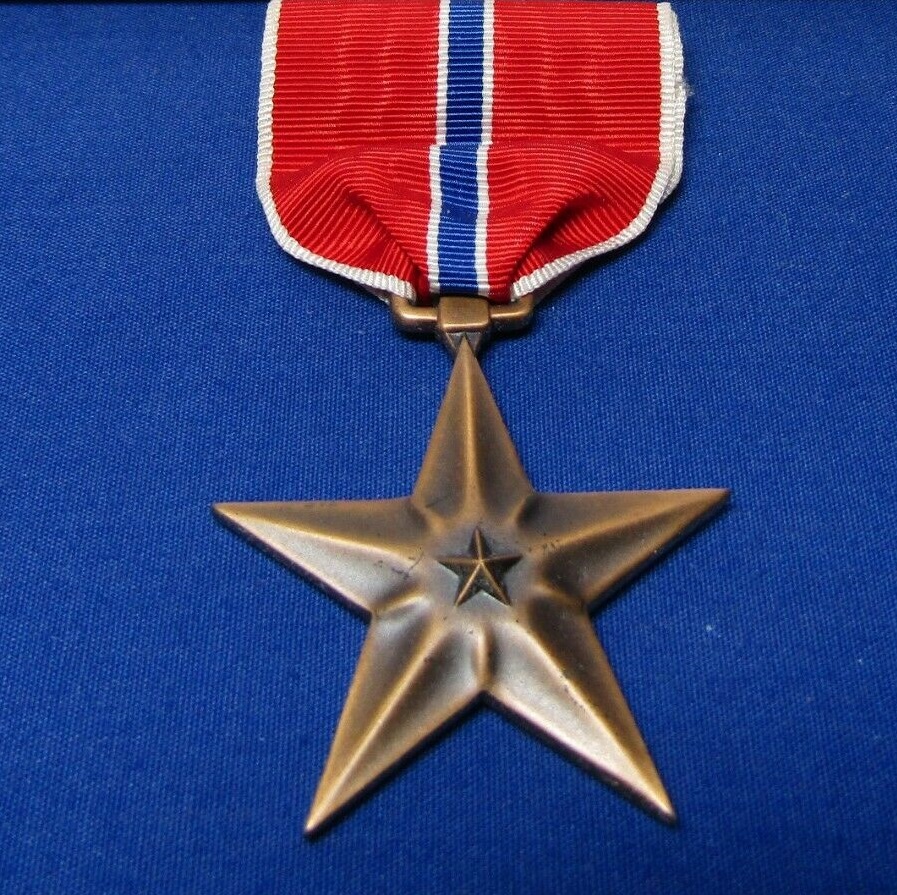  personal danger, she dodged the hail of bullets to reach many wounded people and she saved many lives. She could have been shot, bombed, breathed in poisonous gasses, or been hit by debris. It didn’t stop her. She saw the wounded, and she ran headlong into the danger, thereby saving her fellow man. Whether she was properly awarded the Purple Heart or not, she was definitely a hero.
personal danger, she dodged the hail of bullets to reach many wounded people and she saved many lives. She could have been shot, bombed, breathed in poisonous gasses, or been hit by debris. It didn’t stop her. She saw the wounded, and she ran headlong into the danger, thereby saving her fellow man. Whether she was properly awarded the Purple Heart or not, she was definitely a hero.
Annie Gayton Fox was born to Charles Fox and Deidamia (Gayton) Fox in East Pubnico, Nova Scotia, Canada, on August 4, 1893. She died at age 93 on January 20, 1987, in San Mateo County, California. Her years of service ran from July 3, 1918 through December 31, 1945. She retired as a Major in the US Army.
 Pan American World Airways Flight 845/26, a Boeing 377 Stratocruiser, Clipper United States, N1032V departed from Seattle-Tacoma Airport (SeaTac) on March 26, 1955 at 8:15am…a Saturday morning, destined for Sydney, Australia, with stops at Portland, Oregon and Honolulu, Hawaii. Following its stop in Portland (PDX), the plane took off at 10:21am, with a crew of 8 and 15 passengers on board. It looked to be an easy flight to Hawaii, with plenty of onboard staff to make the trip enjoyable for the passengers. The plane was piloted by Captain Herman Joslyn, with First Officer Angus Gustavus Hendrick Jr; Second Officer Michael Kerwick; Flight Engineer Donald Read Fowler; and Assistant Flight Engineer Stuart Bachman. In the passenger cabin were Purser Natalie Parker, Stewardess Elizabeth Thompson, and Steward James Peppin.
Pan American World Airways Flight 845/26, a Boeing 377 Stratocruiser, Clipper United States, N1032V departed from Seattle-Tacoma Airport (SeaTac) on March 26, 1955 at 8:15am…a Saturday morning, destined for Sydney, Australia, with stops at Portland, Oregon and Honolulu, Hawaii. Following its stop in Portland (PDX), the plane took off at 10:21am, with a crew of 8 and 15 passengers on board. It looked to be an easy flight to Hawaii, with plenty of onboard staff to make the trip enjoyable for the passengers. The plane was piloted by Captain Herman Joslyn, with First Officer Angus Gustavus Hendrick Jr; Second Officer Michael Kerwick; Flight Engineer Donald Read Fowler; and Assistant Flight Engineer Stuart Bachman. In the passenger cabin were Purser Natalie Parker, Stewardess Elizabeth Thompson, and Steward James Peppin.
The flight was proceeding as normal, until it hit 10,000 feet, at which point a severe vibration lasting 5 to 8 seconds began. The Number 3 engine, which is on the right side, on the inside, suddenly ripped away from the starboard wing. The damage to the wing caused severe shaking. At the same time, the nose pitched down and the airspeed increased rapidly. Captain Joslyn immediately reduced engine power slow the plane down some, but they were losing altitude rapidly, quickly dropping by 5,000 feet. The damage cause by the engine ripping away included damage to the engines’ electrical system, and the flight engineer was not able to increase power on the remaining three engines. Without the added power on the remaining engines, the Stratocruiser was too heavy at this early stage in the flight to maintain its altitude. She still had too much fuel onboard to compensate. The Stratocruiser was doomed, and there was nowhere to land.
The flight crew ditched the Stratocruiser into the north Pacific Ocean at 11:12am, approximately 35 miles west of the Oregon coastline. The conditions were ideal for ditching, with smooth seas and little wind, but it was a hard impact. As the plane hit the water, seats were torn loose, and several occupants were injured. Nevertheless, no one was killed and evacuation began immediately with the inflation of all three life rafts. The water temperature was 47° F, so getting out of the water was essential. Soon after the crash, a North American Aviation F-86F Sabre flown by Captain W L Parks, 142nd Fighter Interceptor Group, Oregon Air National Guard, located the scene of the ditching. When he saw the smoke flares that had been released, he was able to see the two life rafts tied together. A Lockheed Constellation also rushed to the scene from the south. After confirming that Air Force rescue aircraft were on the way, Captain Parks returned to Portland, because he was low on fuel.
Among the injured was the airliner’s purser, Natalie Parker, who had been assisting passengers with their life vests and seat belts when the airliner hit the water. Because she was standing in the aisle, she was thrown forward, knocking down five rows of seats as she hit them. She was badly bruised and suffering from shock. Nevertheless, Parker assisted the passengers in abandoning the sinking Stratocruiser. When everyone was off, she enter the water and saw that some of the injured had begun to drift away. In an amazing act of bravery and duty, and suffering from shock, Parker swam out and towed the only seriously injured passenger to the nearest raft, some 200 feet away. The Stratocruiser floated for an amazing 20 minutes before sinking. While all survived the impact, four of the 23 persons on board, passengers John Peterson, David Darrow, First Officer Hendrick, and Flight Engineer Fowler, died of injuries and exposure. The survivors were rescued after two hours by the crew of USS Bayfield (APA-33), a United States Navy attack transport.
During the Civil Aeronautics Board hearings into the accident, Vice Chairman Joseph P. Adams commended Natalie Parker, the flight’s purser, “. . . all of us feel inspired that a fellow citizen, or just a fellow human being, can rise to such an occasion in the manner in which you did. It is most commendable, Miss Parker.” The exact cause of the loss of the Stratocruiser was not fully determined, because the engine and propeller were not recovered. Th investigation assumed that the most likely cause was a fracture of a propeller blade resulting in a severely unbalanced condition, causing the violent separation of the engine from the wing. This was the fifth time that a Boeing 377 Stratocruiser had lost an engine following the failure of a hollow-steel Hamilton Standard 2J17 propeller blade. Further complicating the matter, was the flight engineer’s attempt to increase the propeller rpm on the three engines simultaneously. That caused an electrical overload occurred which opened the master circuit breaker. This prevented any engine power increase, effectively bringing down the Stratocruiser.
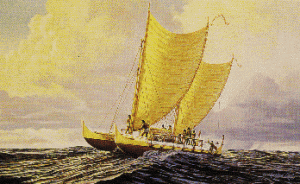
 As the world first began to be settled, the Hawaiian Islands were discovered, and in approximately 400AD Polynesians from the Marquesas Islands traveled the 2000 miles distance to Hawaii’s Big Island in canoes. To get to Hawaii, they navigated by the sun and stars, reading the winds, currents, and seabirds’ flight. The Polynesians sailed across the open ocean in great double-hulled canoes. The Polynesians brought with them items essential to their survival, including pigs, dogs, and chickens; the roots of kalo (a root vegetable and one of the most complex carbohydrates on the planet) and sweet potato; the seeds and saplings of coconut, banana, sugar cane, and other edible and medicinal plants. Polynesians were well-established on the islands when Polynesians from the Society Islands arrived in Hawaii. These newcomers became the new rulers of Hawaii. After a time of voyaging back and forth between the Society Islands and the Hawaiian Archipelago, contact with southern Polynesia ceased. During the 400 years of isolation that followed, a unique Hawaiian culture developed. That is similar to what happened when the pilgrims came to the new world…present-day United States. Once away from the culture one comes from, new ideas and new skills begin to form.
As the world first began to be settled, the Hawaiian Islands were discovered, and in approximately 400AD Polynesians from the Marquesas Islands traveled the 2000 miles distance to Hawaii’s Big Island in canoes. To get to Hawaii, they navigated by the sun and stars, reading the winds, currents, and seabirds’ flight. The Polynesians sailed across the open ocean in great double-hulled canoes. The Polynesians brought with them items essential to their survival, including pigs, dogs, and chickens; the roots of kalo (a root vegetable and one of the most complex carbohydrates on the planet) and sweet potato; the seeds and saplings of coconut, banana, sugar cane, and other edible and medicinal plants. Polynesians were well-established on the islands when Polynesians from the Society Islands arrived in Hawaii. These newcomers became the new rulers of Hawaii. After a time of voyaging back and forth between the Society Islands and the Hawaiian Archipelago, contact with southern Polynesia ceased. During the 400 years of isolation that followed, a unique Hawaiian culture developed. That is similar to what happened when the pilgrims came to the new world…present-day United States. Once away from the culture one comes from, new ideas and new skills begin to form.
The Hawaiian people were highly skilled farmers and fishermen, who lived in small communities ruled by chieftains who battled one another for territory. The new Hawaiian culture was a highly stratified society with strictly maintained classes of people. The chiefs headed the social pyramid and ruled over the land. The highest class, the Kahuna (professionals) were highly regarded and sometimes feared, they were experts on religious ritual or specialists in canoe-building, herbal medicine, and healing. The middle class, the maka`ainana (commoners) farmed, fished, built walls, houses, and fishponds…and paid taxes to the paramount chiefs and his chiefs. Kauwa, the lowest class, were outcasts or slaves. I can’t say that the class society was fair, because it really wasn’t, but many societies of that era were ruled in that way, and in reality, this class society still exists…maybe with slight differences, but it still exists.
In many ways, the culture was quite oppressive, especially to women. A system of laws known as Kanawai enforced Hawaii’s social order. Certain people, places, things, and times were considered sacred. Being near them was kapu, or forbidden except to a very privileged few. Women ate apart from men and were restricted from eating pork, coconuts, bananas, or a variety of other foods. Kapu regulated fishing, planting, and the harvesting of other resources, thus ensuring their conservation. Any breaking of kapu disturbed the stability of society, and the punishment for breaking this law was usually death.
Still, even with the strict laws, village life was rich and interesting. Hawaiians fished in coastal waters and collected shellfish, seaweed, and salt along the shore. They raised pigs, dogs, and chickens and harvested sweet potatoes, kalo, and other crops. Men pounded kalo into poi, which is the staple food of Hawaiians, while women beat the inner bark of wauke (paper mulberry) into kapa (bark cloth). The sounds of taro pounding and 
 kapa beating were rhythmical signatures of Hawaiian village life. That changed dramatically after Captain James Cook arrived in 1778 and introduced the rest of the world to Hawaii. Cook, who named the islands after the Earl of Sandwich, returned a year later and was killed in a confrontation with Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay, on Hawaii’s Big Island. Still his impact on the state of Hawaii remains.
kapa beating were rhythmical signatures of Hawaiian village life. That changed dramatically after Captain James Cook arrived in 1778 and introduced the rest of the world to Hawaii. Cook, who named the islands after the Earl of Sandwich, returned a year later and was killed in a confrontation with Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay, on Hawaii’s Big Island. Still his impact on the state of Hawaii remains.
 Most of us have learned of the event that brought the United States into World War II…the attack on Pearl Harbor. The United States was caught totally unaware, even though the signs were there, and even some chatter was heard. Nevertheless, our ships were sitting in the harbor, with many of the men not on board, and our planes were sitting on the tarmac. The plan the Japanese had was to wipe out the US military machine, so that the United States was virtually out of the war. The mistake the made was that they misjudged the United States. Nevertheless, on December 7, 1941, the attack on Pearl Harbor was a battle the United States lost.
Most of us have learned of the event that brought the United States into World War II…the attack on Pearl Harbor. The United States was caught totally unaware, even though the signs were there, and even some chatter was heard. Nevertheless, our ships were sitting in the harbor, with many of the men not on board, and our planes were sitting on the tarmac. The plan the Japanese had was to wipe out the US military machine, so that the United States was virtually out of the war. The mistake the made was that they misjudged the United States. Nevertheless, on December 7, 1941, the attack on Pearl Harbor was a battle the United States lost.
There were heroes on that day, however. The people who worked to save what lives they could, and put out the fires caused by the attack. And there were two heroes I had never heard about. I’m not sure why I hadn’t, but the fact remains that I hadn’t. Kenneth Taylor and George Welch were pilots stationed at Pearl Harbor on that fateful day. Taylor was a second lieutenant in the US Army Air Corps’ 47th Pursuit Squadron. He received his first posting to Wheeler Army Airfield in Honolulu, Hawaii in April 1941. His commanding officer, General Gordon Austin, chose Taylor and another pilot, George Welch, as his flight commanders shortly after they arrived in Hawaii. A week before the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, the 47th Pursuit Squadron was temporarily moved to the auxiliary airstrip at Haleiwa Field, located some 11 miles from Wheeler, for gunnery practice…a move that made their response to the attack possible.
Saturday, December 6, 1941, found Taylor and Welch spending the evening at a dance held at the officers’ club at Wheeler Field. After the dance, the two pilots joined an all-night poker game. After that, the account of the story gets a little fuzzy. Some said that the two pilots had finally gone to sleep, and were awoken only around 7:51am, when Japanese fighter planes and dive bombers attacked Wheeler, but others said that the poker game was just wrapping up, and they were contemplating a morning swim when the attack began. Whatever the case may be, Taylor and Welch were stunned to hear low-flying planes, explosions, and machine-gun fire above them. Information was scarce in all the chaos, but they learned that two-thirds of the planes at the main bases of Hickham and Wheeler Fields had been destroyed or damaged so badly that they were unable to fly. The two men rush to Haleiwa Field to get their planes. They had no orders, but Taylor called Haleiwa and  commanded the ground crew to prepare their Curtiss P-40 Tomahawks for takeoff, while Welch ran to get Taylor’s new Buick. The men were still wearing their tuxedo pants from the night before, but that didn’t stop them. The two pilots drove the 11 miles to Haleiwa, reaching speeds of 100 miles per hour along the way.
commanded the ground crew to prepare their Curtiss P-40 Tomahawks for takeoff, while Welch ran to get Taylor’s new Buick. The men were still wearing their tuxedo pants from the night before, but that didn’t stop them. The two pilots drove the 11 miles to Haleiwa, reaching speeds of 100 miles per hour along the way.
When they reached the field, Welch and Taylor jumped into their P-40s, which by that time had been fueled but not fully armed. That didn’t stop them. They took off and immediately attracted Japanese fire. Welch and Taylor were facing off virtually alone against some 200 to 300 enemy aircraft. When they ran out of ammunition, they returned to Wheeler to reload. The senior officers ordered the pilots to stay on the ground, but then
the second wave of Japanese raiders flew in, scattering the crowd. Taylor and Welch took off again, in the midst of a swarm of enemy planes. Though Welch’s machine guns were disconnected, he fired his .30-caliber guns, destroying two Japanese planes on the first attack run. On the second, with his plane heavily damaged by gunfire, he shot down two more enemy aircraft. A bullet pierced the canopy of Taylor’s plane, hitting his arm and sending shrapnel into his leg, but he managed to shoot down at least two Japanese planes, and perhaps more. In the end, Taylor was officially credited with two kills, and Welch with four.
Welch and Taylor were among only five Air Force pilots who managed to get their planes off the ground and engage the Japanese that morning. The total loss in aircraft at Pearl Harbor were estimated at 188 planes destroyed and 159 damaged. The Japanese lost just 29 planes. Both men were awarded the Distinguished Service Cross medals, becoming the first to be awarded that distinction in World War II. Welch was nominated for the Medal of Honor, the military’s highest award, but was reportedly denied because his superiors maintained he had taken off without proper authorization. For his injuries, Taylor received the Purple Heart.
After Pearl Harbor, George Welch flew nearly 350 missions in the Pacific Theater during World War II, shooting down 12 more planes and winning many other decorations. After he contracted malaria in 1943, his wartime career came to an end. While in the hospital in Sydney, Australia, he met his wife. After the war, Welch became a test pilot for North American Aviation. There are some claims that he became the first pilot to break the Mach-1 barrier with an unauthorized flight over the California desert in 1947, several weeks before Chuck Yeager’s famous flight. Unfortunately, Welch was killed in 1954 while ejecting from his disintegrating F-100 Super Sabre fighter jet during a test flight.

After Pearl Harbor, Ken Taylor was transferred to the South Pacific, where he flew out of Guadalcanal and was credited with downing another Japanese aircraft. Unfortunately, his combat career was cut short after someone fell on top of him in a trench during an air raid on the base, breaking his leg. He became a commander in the Alaska Air National Guard and retired as a brigadier general after 27 years of active duty. Taylor was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, the Legion of Merit, the Air Medal, and a number of other decorations. In his post military career, he worked as an insurance underwriter. Taylor died in Tucson, Arizona in 2006, at the age of 86.

 My husband’s Uncle Butch Schulenberg is such a sweet man. Bob and I went up to Forsyth, Montana a couple of years ago, and Uncle Butch was so gracious and kind to show me so many pictures of himself and his family. They were pictures we had never seen before, and it was such a treat to receive them, along with the stories that went along with them. Uncle Butch is my father-in-law, Walt Schulenberg’s half-brother by their dad’s second marriage, and to me, he is such a precious part of the family. His is loving and kind, and he is a man of integrity and honor.
My husband’s Uncle Butch Schulenberg is such a sweet man. Bob and I went up to Forsyth, Montana a couple of years ago, and Uncle Butch was so gracious and kind to show me so many pictures of himself and his family. They were pictures we had never seen before, and it was such a treat to receive them, along with the stories that went along with them. Uncle Butch is my father-in-law, Walt Schulenberg’s half-brother by their dad’s second marriage, and to me, he is such a precious part of the family. His is loving and kind, and he is a man of integrity and honor.
Uncle Butch, like many of the young men of his era served honorably in the Army after high school, and was one of the lucky guys who got to be stationed in Hawaii part of that time. He did find out that not all of Hawaii is a tropical paradise, when he got to go up to one of the high peaks that are between 10,000 and 13,000 feet, and are the only places where Hawaii gets snow every year. Butch tells me that it was absolutely freezing while they were up there. Yikes!! I had no idea. Still, knowing Butch as I have come to, I know that the views he had while he was in Hawaii were spectacular, and some that he cherishes still today. Butch loves the outdoors, and takes lots of walks near his home. He probably has the best view in Forsyth, Montana, especially if, like Butch, you love taking pictures of sunrises and sunsets. His home overlooks the Yellowstone River, and the sun sets on the horizon behind the river view…making for a spectacular image.
Butch married Charlys Stull on June 25, 1966 and their marriage was blessed with three children, Tadd, Andi Kay, and Heath. They also have seven grandchildren. Their marriage has been blessed with many wonderful years, and is still going strong. They love to travel around, and especially to go visit their children and grandchildren. Butch is also a very strong supporter of the local school teams, and knows the players 
 personally. Forsyth is a small town, so most people know each other, and Butch is well known as an encourager of the teams. What a wonderful way to be known. Of course, I know just how they feel, because Butch is that way with everyone, and I have been privileged to receive his words of praise many times over my writing…something that blesses me more than he could possibly know. Today is Uncle Butch’s 80th birthday. Happy birthday Uncle Butch!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
personally. Forsyth is a small town, so most people know each other, and Butch is well known as an encourager of the teams. What a wonderful way to be known. Of course, I know just how they feel, because Butch is that way with everyone, and I have been privileged to receive his words of praise many times over my writing…something that blesses me more than he could possibly know. Today is Uncle Butch’s 80th birthday. Happy birthday Uncle Butch!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

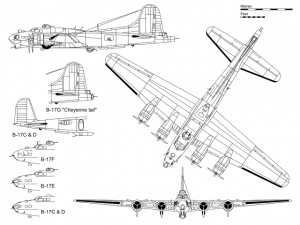 In World War II, my dad, Allen Spencer was the Flight Engineer and top turret gunner on a B-17. The B-17 was an amazing plane. Strategic bombing missions actually began at the tail end of World War I, And the big world powers knew that they needed to develop bomber fleets that could handle this new kind of bombing mission, because if they did not, they would be vulnerable to the evil nations who did develop such bombers. During the month of August 1934, in anticipation of rising tensions in the Pacific, the US Army Air Corps proposed a new multi-engine bomber that would replace the outdated Martin B-10. They put out the challenge and Boeing decided to get into the competition. The plan for this bomber was to provide reinforcement to bases in Hawaii, Alaska, and Panama.
In World War II, my dad, Allen Spencer was the Flight Engineer and top turret gunner on a B-17. The B-17 was an amazing plane. Strategic bombing missions actually began at the tail end of World War I, And the big world powers knew that they needed to develop bomber fleets that could handle this new kind of bombing mission, because if they did not, they would be vulnerable to the evil nations who did develop such bombers. During the month of August 1934, in anticipation of rising tensions in the Pacific, the US Army Air Corps proposed a new multi-engine bomber that would replace the outdated Martin B-10. They put out the challenge and Boeing decided to get into the competition. The plan for this bomber was to provide reinforcement to bases in Hawaii, Alaska, and Panama.
Enter the B-17 Flying Fortress. Boeing competed against both Martin and Douglas for the contract to build 200 units of such a bomber, but failed to deliver, as the first B-17 Flying Fortress crashed. Nevertheless, the Air Corps loved the design so much that they ordered 13 units for further evaluation and analysis. After a string of tests, it was introduced in 1938. The B-17 was now the prime bomber for all kinds of bombing raids. The prototype B-17 Bomber was built at the company’s own expense and was a fusion of the features of Boeing XB-15 and Boeing 247 Transport Aircraft. Initially, it could carry a payload of 4850 pounds along with 5x .30-inch machine guns. The 4x Hornet Radial Engines could produce 750 HP at 2100 meters. It was a tremendous machine. A reporter from the Seattle Times would nickname it The Flying Fortress…a name that stuck, even if he didn’t know how very accurate he was.
As World War II heated up, the attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into it, and the B-17 Flying 
 Fortress became a staple, used in every single World War II combat zone and by the time production ended in 1945. Boeing along with Douglas and Vega had built 12,731 bombers. When the US 8th Airforce arrived in England in 1942, their sole mission was to destroy Germany’s ability to wage war. They would use any means necessary, from carpet bombing to precision bombing. On August 17th, 1942, eighteen B-17s launched a bombing raid over Nazi-held territory in Europe, hitting railway networks and strategic points. The Luftwaffe was unprepared and didn’t know how to best attack the new planes, but it didn’t take long to improve their tactics. The B-17s suffered losses too. On September 6th, 1943, 400 bombers were sent out to attack a ball-bearing plant, 45 didn’t return. October 4th, 60 out of 291 B-17s sent to the same location were lost. January 11th, 1944, 600 B-17s were sent to various industries. Bad weather kept all but 238 of them on base. Still, 60 were lost. These losses were quite costly when you consider that a single B-17 Flying Fortress would cost $238,329 in 1945. The Luftwaffe quickly perfected their attacks on the B-17 Flying Fortress. Head on proved more fruitful and therefore the Americans developed the term “Bandits at 12 O’clock High” for oncoming Luftwaffe fighters.
Fortress became a staple, used in every single World War II combat zone and by the time production ended in 1945. Boeing along with Douglas and Vega had built 12,731 bombers. When the US 8th Airforce arrived in England in 1942, their sole mission was to destroy Germany’s ability to wage war. They would use any means necessary, from carpet bombing to precision bombing. On August 17th, 1942, eighteen B-17s launched a bombing raid over Nazi-held territory in Europe, hitting railway networks and strategic points. The Luftwaffe was unprepared and didn’t know how to best attack the new planes, but it didn’t take long to improve their tactics. The B-17s suffered losses too. On September 6th, 1943, 400 bombers were sent out to attack a ball-bearing plant, 45 didn’t return. October 4th, 60 out of 291 B-17s sent to the same location were lost. January 11th, 1944, 600 B-17s were sent to various industries. Bad weather kept all but 238 of them on base. Still, 60 were lost. These losses were quite costly when you consider that a single B-17 Flying Fortress would cost $238,329 in 1945. The Luftwaffe quickly perfected their attacks on the B-17 Flying Fortress. Head on proved more fruitful and therefore the Americans developed the term “Bandits at 12 O’clock High” for oncoming Luftwaffe fighters.
Various models of the B-17 Flying Fortress were produced, but the B-17G was the one that was most liked. Almost 9000 B-17Gs were produced, the most of any of the models, because of their superior specs. A B-17G weighed 65,000 pounds and could cruise at a speed of 150 miles per hour, peaking at 287 miles per hour. It could attain a service ceiling of 35,600 feet, and carry a 9600 pounds payload. The four Wright R-1820 Cyclone engines could produce 1200 horse power each! It was one rugged machine. One particular B-17 Bomber 
 survived a bombing mission over Cologne, Germany, and flew back to safety with 180 flak holes and only 2 out of 4 engines in operation. The veteran never forgot, and 75 years later wrote a thank you letter to Boeing. He was thankful to be alive. My dad always felt that way too. Any amount of damage that happens to a plane can mean the difference between crashing and making it home. The B-17 was truly a flying fortress, and on of the best planes to be in. The chances of coming home were better than most.
survived a bombing mission over Cologne, Germany, and flew back to safety with 180 flak holes and only 2 out of 4 engines in operation. The veteran never forgot, and 75 years later wrote a thank you letter to Boeing. He was thankful to be alive. My dad always felt that way too. Any amount of damage that happens to a plane can mean the difference between crashing and making it home. The B-17 was truly a flying fortress, and on of the best planes to be in. The chances of coming home were better than most.

 The Swamp Ghost began its very short career on December 6, 1941, one day before the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor. The Swamp Ghost started out as B-17 Flying Fortress, 41-2446 (which is not a tail number, and indicated that the plane was a new purchase) and under that number it was delivered to the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). Eleven days later, the bomber departed California for Hickam Field in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The plane and her crew were based at Wheeler Field in Wahiawa for a very short time, and flew patrol missions for the Navy until February 1942, when the Japanese Troops invaded Rabaul on New Britain and established a base. Of course, this was a threat to the rest of New Guinea and Australia. In response to the invasion, 41-2446 was ordered to Garbutt Field, Townsville, in Queensland, Australia. Swamp Ghost’s crew included Pilot Captain Frederick C. “Fred” Eaton, Co-Pilot Captain Henry M. “Hotfoot” Harlow, Navigator 1st Lieutenant George B. Munroe Jr, Bombardier Sergeant J.J. Trelia, Flight Engineer Technical Sergeant Clarence A. LeMieux, Radio Operator/Gunner Sergeant Howard A. Sorensen, Waist Gunner Sergeant William E. Schwartz, Waist Gunner Technical Sergeant Russell Crawford, and Tail Gunner Staff Sergeant John V. Hall. The only crew change would be Sergeant Richard Oliver, who replaced Bombardier Trelia after he became ill.
The Swamp Ghost began its very short career on December 6, 1941, one day before the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor. The Swamp Ghost started out as B-17 Flying Fortress, 41-2446 (which is not a tail number, and indicated that the plane was a new purchase) and under that number it was delivered to the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). Eleven days later, the bomber departed California for Hickam Field in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The plane and her crew were based at Wheeler Field in Wahiawa for a very short time, and flew patrol missions for the Navy until February 1942, when the Japanese Troops invaded Rabaul on New Britain and established a base. Of course, this was a threat to the rest of New Guinea and Australia. In response to the invasion, 41-2446 was ordered to Garbutt Field, Townsville, in Queensland, Australia. Swamp Ghost’s crew included Pilot Captain Frederick C. “Fred” Eaton, Co-Pilot Captain Henry M. “Hotfoot” Harlow, Navigator 1st Lieutenant George B. Munroe Jr, Bombardier Sergeant J.J. Trelia, Flight Engineer Technical Sergeant Clarence A. LeMieux, Radio Operator/Gunner Sergeant Howard A. Sorensen, Waist Gunner Sergeant William E. Schwartz, Waist Gunner Technical Sergeant Russell Crawford, and Tail Gunner Staff Sergeant John V. Hall. The only crew change would be Sergeant Richard Oliver, who replaced Bombardier Trelia after he became ill.
Because of the B-17’s long flying range, the Japanese control of Wake Island and Guam, and the Vichy government’s armistice with the Nazi government, 41-2446 island hopped nearly 5,700 detour miles to get to Townsville. They didn’t want to take a chance on running into enemy fighters, if they could help it. On February 22, 1942, nine B-17Es of the 19th Bombing Group were scheduled to take off for Rabaul. Unfortunately, this mission seemed doomed from the start, as nothing would go quite as planned. Out of the nine aircraft, four had to completely abort the mission due to mechanical problems. To further complicate matters, bad weather conditions made it difficult to see up in the air for those who were able to takeoff. Finally, poor visibility separated the five remaining in flight.
I would like to say that was all the problems they ran into, but there’s more. When 41-2446 was to drop its payload, the bomb bay malfunctioned. The crew had to go around for a second pass, where they managed a clear drop over their target. The Japanese were working hard to make this mission fail too. Japanese fire was intense and a flak round managed to punch a hole through the starboard wing of 41-2556. Fortunately for the crew, the wing didn’t detonate. While the crew hoped to make it to Fort Moresby, they were low on fuel. The dog-fight, had seen to that. They would have to land in New Guinea.
Captain Fred Eaton thought he was setting down the bomber in a wheat field, however, they actually landed wheels-up in the middle of Agaiambo swamp. The only good news in this horrific failure of a mission was that the crew was unscathed, except for one with minor cuts and scrapes. Now, they still had to get out of the swamp. It took two days of hacking their way through the razor-sharp kunai grass for the men to reach dry land. They ran into some locals who were chopping wood. The locals took them, horribly bitten by mosquitos and infected with malaria, to their village. After a night of rest, they traveled downriver in canoes, where they were handed over to an Australian magistrate, and eventually arrived at Port Moresby on April 1…thirty six days after their crash. After a week in the hospital, the men returned to combat, but their plane did not. After 41-2446’s crash, Captain Fred Eaton flew 60 more missions. Whenever these missions would take him over the crash site, he would circle it and tell his new crewmembers the story of what happened. I suppose it was therapeutic to re-live the amazing escape from the Agaiambo swamp. This was where the plane’s legend was born. After Eaton returned home, 41-2446 slipped from the public eye for nearly three decades.
Then, in 1972, some Australian soldiers happened upon the crash. After spotting the wreckage from a helicopter, they landed on the aircraft’s wing and found the plane semi-submerged, and strangely intact. The machine guns were in place, and even the coffee thermoses were intact. They nicknamed the plane, Swamp Ghost, and the name stuck. Thanks to warbird collector Charles Darby who included dozens of photographs in his book, Pacific Aircraft Wrecks, word spread in 1979 . Once the fad of recovering World War II aircraft really took off. Trekkers hiked into the site and began stripping the aircraft for keepsakes and sellable items. Despite the stripping, the aircraft structure itself remained remarkably intact, until it was removed from the swamp.
Alfred Hagen, a pilot and commercial builder from Pennsylvania, set his sights on Swamp Ghost and wanted to take it free it from the disintegration of the swamp. In November 2005, he obtained an export permit for the 
 B-17 for $100,000. For four weeks they labored over the aircraft, dismantling it in order to ship it out of the country. The controversy over its removal halted the cargo before it could be shipped to the United States. Eventually, it was cleared for import and by February 2010 it arrived at the Pacific Aviation Museum at Pearl Harbor for display.
B-17 for $100,000. For four weeks they labored over the aircraft, dismantling it in order to ship it out of the country. The controversy over its removal halted the cargo before it could be shipped to the United States. Eventually, it was cleared for import and by February 2010 it arrived at the Pacific Aviation Museum at Pearl Harbor for display.

