germans
 When a nation has a weapon that is so deadly to its enemy nations, those nations have no choice but to find a new way to beat that weapon. The German U-Boat was just such a weapon. Gliding along silently beneath the sea, the U-Boat put the ships of the Allied nations in constant and grave danger. That was one of the reasons that the British developed a fixation on their presence at sea. They depended on seaborne trade, and during World War I, the Germans were terrorizing that trade.
When a nation has a weapon that is so deadly to its enemy nations, those nations have no choice but to find a new way to beat that weapon. The German U-Boat was just such a weapon. Gliding along silently beneath the sea, the U-Boat put the ships of the Allied nations in constant and grave danger. That was one of the reasons that the British developed a fixation on their presence at sea. They depended on seaborne trade, and during World War I, the Germans were terrorizing that trade.
For much of Great Britain’s history, they enjoyed the luxury of having more battleships than the next two powers combined. For that reason, the Germans knew that they would have to concentrate their efforts on attacking vulnerable shipping lanes to disrupt the British war effort. They didn’t care if there were passengers on those ships. They didn’t care about loss of life or supplies. They had one plan…to dominate the seas. German submarines became a menace to the merchant navy. Something had to change, so the British came up with a plan to counter the U-boat threat. The plan involved disguising armed vessels as harmless trawlers to  lure the submarines in and then wipe them out. The answer to the U-boat were disguised vessels…decoys, known as Q-ships.
lure the submarines in and then wipe them out. The answer to the U-boat were disguised vessels…decoys, known as Q-ships.
Knowing that the U-Boats were under orders to attack just about anything. The Q-ships hid naval guns behind pivoting panels. It was the Sun Tzu tenet of “hold out baits to entice the enemy.” The Q-ships pretended to be disabled and when the U-Boats show up for the kill, the Q-ships went into action. Guns and additional crew had been concealed by hinges that could be dropped at a moment’s notice. The U-boats of World War I had limited range and carrying capacity, so the captains were nervous about wasting their torpedoes. Also, while the U-Boats of World War II were more capable of lang periods of time submerged, the U-Boats of World War I, had limited capability, so they preferred to use the submarine’s main gun to subdue ships whenever possible.
As the U-Boats came into sight of the Q-ship, the Q-ship’s crew would pretend to panic and abandon the ship to  draw the submarine in close. The U-Boats, once lured in, were at the mercy of the Q-ships. The Q-ships began to drop their depth charges as soon as the submarine tried to escape. It was a dangerous game to play and required a brave crew to pull off the ruse, and it was not always successful. Some Q-ships were lost, but because of their efforts the threat of submarines in World War I were lessened. The plan was to try the tactic again in World War II, but ships were in very short supply. The tactic of using decoy ships was much more limited but was also used by the Germans and Americans. While it wasn’t a major tactical warfare practice during the two wars, it was effective while it was used.
draw the submarine in close. The U-Boats, once lured in, were at the mercy of the Q-ships. The Q-ships began to drop their depth charges as soon as the submarine tried to escape. It was a dangerous game to play and required a brave crew to pull off the ruse, and it was not always successful. Some Q-ships were lost, but because of their efforts the threat of submarines in World War I were lessened. The plan was to try the tactic again in World War II, but ships were in very short supply. The tactic of using decoy ships was much more limited but was also used by the Germans and Americans. While it wasn’t a major tactical warfare practice during the two wars, it was effective while it was used.
 In the Battle of Trafalgar, on October 21, 1805, the British Royal Navy took on the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815), and soundly defeated them. As the French and Spanish Navies came into sight, Admiral Horatio Nelson raised one set of signal flags. His orders were simple and direct, “England expects every man to do his duty.” His men knew exactly what he meant and what was expected of them…fight, and if necessary, die for their country!! Without hesitation, Nelson’s ships closed in on and destroyed their enemy. The victory of this battle has been called the greatest naval victory in history, and for the remainder of the century, the British really had control over the oceans and the world. In the years following that victory, the British grew lackadaisical about keeping a strong military force, and 111 years later, that issue would be evident for the British Royal Navy when they went up against the Germans in the Battle of Jutland.
In the Battle of Trafalgar, on October 21, 1805, the British Royal Navy took on the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815), and soundly defeated them. As the French and Spanish Navies came into sight, Admiral Horatio Nelson raised one set of signal flags. His orders were simple and direct, “England expects every man to do his duty.” His men knew exactly what he meant and what was expected of them…fight, and if necessary, die for their country!! Without hesitation, Nelson’s ships closed in on and destroyed their enemy. The victory of this battle has been called the greatest naval victory in history, and for the remainder of the century, the British really had control over the oceans and the world. In the years following that victory, the British grew lackadaisical about keeping a strong military force, and 111 years later, that issue would be evident for the British Royal Navy when they went up against the Germans in the Battle of Jutland.
Apparently not understanding that things were no longer what they used to be, a British naval force commanded by Vice Admiral David Beatty confronted a squadron of German ships, led by Admiral Franz von Hipper, approximately 75 miles off the Danish coast, just before 4:00 on the afternoon of May 31, 1916. In what was later called the greatest naval battle of World War I, the two squadrons opened fire on each other simultaneously, beginning the opening phase of the Battle of Jutland.
Following the Battle of Dogger Bank in January 1915, the German navy knew that they were, at the very least, numerically inferior to the British Royal Navy, so the Germans chose not to engage them in a major battle for more than a year. During that time, they began pursuing a new strategy for their naval warfare…namely, its lethal U-boat submarines. Biding his time, Vice Admiral Reinhard Scheer waited until May 1916, when the majority of the British Grand Fleet was anchored far away, at Scapa Flow, off the northern coast of Scotland. Then Sheer, the commander of the German High Seas Fleet, believed the time was right to resume attacks on the British coastline. The unique coding system of the U-boats made it very difficult for the British to know what was coming. Scheer ordered 19 U-boat submarines to position themselves for a raid on the North Sea coastal city of Sunderland while using air reconnaissance crafts to keep an eye on the British fleet’s movement  from Scapa Flow. The first planned raid was scrapped because of bad weather, and Scheer instead ordering his fleet, consisting of 24 battleships, five battle cruisers, 11 light cruisers, and 63 destroyers, to head north, to the Skagerrak, a waterway located between Norway and northern Denmark, off the Jutland Peninsula, where they could attack Allied shipping interests…hoping to punch a hole in the stringent British blockade.
from Scapa Flow. The first planned raid was scrapped because of bad weather, and Scheer instead ordering his fleet, consisting of 24 battleships, five battle cruisers, 11 light cruisers, and 63 destroyers, to head north, to the Skagerrak, a waterway located between Norway and northern Denmark, off the Jutland Peninsula, where they could attack Allied shipping interests…hoping to punch a hole in the stringent British blockade.
Truly, the only thing that saved the British Grand Fleet that night was that unbeknownst to Scheer, a newly created intelligence unit located within an old building of the British Admiralty, known as Room 40, had cracked the German codes and warned the British Grand Fleet’s commander, Admiral John Rushworth Jellicoe, of Scheer’s intentions. So, the night before the planned attack…May 30, 1916, a British fleet of 28 battleships, nine battle cruisers, 34 light cruisers, and 80 destroyers set out from Scapa Flow, bound for positions off the Skagerrak.
Then, on May 31, 1916, at 2:20pm, Beatty, leading a British squadron, spotted Hipper’s warships. The squadrons quickly maneuvered south to get a better position, and shots were fired at about 3:48 that afternoon. They fought for 55 minutes, the British losing two British battle cruisers, Indefatigable and Queen Mary. Over 2,000 sailors lost their lives in the battle. At 4:43pm, Hipper’s squadron was joined by the remainder of the German fleet, commanded by Scheer. The British were out gunned, and Beatty was forced to fight a delaying action for the next hour, until Jellicoe could arrive with the rest of the Grand Fleet.
Once both entire fleets were there, they faced off. It was a huge battle of naval strategy between the four commanders, and particularly between Jellicoe and Scheer. As the fleets continued to engage each other throughout the late evening and the early morning of June 1, Jellicoe maneuvered 96 of the British ships into a V-shape surrounding 59 German ships. Hipper’s flagship, Lutzow, was disabled by 24 direct hits, but was still able to sink the British battle cruiser Invincible, before it sank too. Just after 6:30 on the evening of June 1, Scheer’s fleet executed a previously planned withdrawal under cover of darkness to their base at the German port of Wilhelmshaven, ending the battle and cheating the British of the major win they had envisioned.
The Battle of Jutland…or the Battle of the Skagerrak, as it was known to the Germans, involved a total of 100,000 men aboard 250 ships over the course of 72 hours. The Germans, claimed vistory, and the British had to agree…at first anyway. The German navy lost 11 ships, including a battleship and a battle cruiser, and 3,058 men lost their lives. The British losses were heavier, with 14 ships sunk, including three battle cruisers, and 6,784 lives lost. The only thing that made the British losses seem less was that ten more German ships had suffered heavy damage, and by June 2, 1916, only 10 of the German ships that had been involved in the battle were ready to leave port again. Jellicoe, on the other hand, could have put 23 British ships to sea. On July 4, 1916, Scheer reported to the German high command that further fleet action was not an option, and that  submarine warfare was Germany’s best hope for victory at sea. Despite the missed opportunities and heavy losses, the Battle of Jutland had left British naval superiority on the North Sea intact, but if they had been better prepared, they might have held a place of domination over the Germans then. When a nation decides to sit back and ride on its reputation, rather than continue a practice of a strong military force, that nation can find itself in a tough spot when the enemy attacks. The British could have had a very different outcome, but maybe better aim or the favor of God held the German High Seas Fleet at bay. They made no further attempts to break the Allied blockade or cross the Grand Fleet for the rest of World War I.
submarine warfare was Germany’s best hope for victory at sea. Despite the missed opportunities and heavy losses, the Battle of Jutland had left British naval superiority on the North Sea intact, but if they had been better prepared, they might have held a place of domination over the Germans then. When a nation decides to sit back and ride on its reputation, rather than continue a practice of a strong military force, that nation can find itself in a tough spot when the enemy attacks. The British could have had a very different outcome, but maybe better aim or the favor of God held the German High Seas Fleet at bay. They made no further attempts to break the Allied blockade or cross the Grand Fleet for the rest of World War I.
 A truce in the context of war, doesn’t always mean a permanent end to the fighting. That is a fact that has often amazed me. If a war can be put “on hold” for a specific reason and a specified timeframe, why must the fighting then resume like the truce never happened? Nevertheless, resume it usually did. Such a truce happened between the German forces fighting the Russians forces in satellite regions like Lithuania and Belarus during World War I. The fighting raged in many different places at that time and continued through the winter of 1917.
A truce in the context of war, doesn’t always mean a permanent end to the fighting. That is a fact that has often amazed me. If a war can be put “on hold” for a specific reason and a specified timeframe, why must the fighting then resume like the truce never happened? Nevertheless, resume it usually did. Such a truce happened between the German forces fighting the Russians forces in satellite regions like Lithuania and Belarus during World War I. The fighting raged in many different places at that time and continued through the winter of 1917.
The intense fighting throughout the heavily forested region and had an unexpected side effect. Any time humans move into an area, the animal  population instinctively moves deeper into wilderness areas where there is less interaction with people, but when the winter is harsh and food becomes scarce, the animals can become as desperate as the humans. In that particular area at that particular time, the Russian wolves were starving. Any prey they might have been able to hunt had vacated because of the intense fighting, and so they had resorted to taking the bodies of the fallen soldiers for food. When there wasn’t enough of that, they began to actively hunt the soldiers, so now the soldiers of the Russian and the German armies had a whole new enemy, and this one could not be reasoned with.
population instinctively moves deeper into wilderness areas where there is less interaction with people, but when the winter is harsh and food becomes scarce, the animals can become as desperate as the humans. In that particular area at that particular time, the Russian wolves were starving. Any prey they might have been able to hunt had vacated because of the intense fighting, and so they had resorted to taking the bodies of the fallen soldiers for food. When there wasn’t enough of that, they began to actively hunt the soldiers, so now the soldiers of the Russian and the German armies had a whole new enemy, and this one could not be reasoned with.
The wolves had progressed from raiding villages to taking corpses to accosting groups of soldiers outright, so  the two armies mutually decided that it was necessary to call a truce so they could rid the area of the unexpected mutual enemy…roving bands of gigantic Russian wolves. They were genuinely in fear for their lives. Wolves often attack in the dark and go for the weakest link or when people are sleeping. It became obvious that this would be a fight to the end…of one or the other…man or beast. So, both armies agreed to a temporary truce and went on a joint campaign of destruction. The wolves could not be allowed to stay, for the sake of anyone in the area. The two armies slew hundreds of wolves, and then simply resumed their fight. How very strange that seems to me, but I guess it probably wasn’t up to the soldiers to walk away from the war.
the two armies mutually decided that it was necessary to call a truce so they could rid the area of the unexpected mutual enemy…roving bands of gigantic Russian wolves. They were genuinely in fear for their lives. Wolves often attack in the dark and go for the weakest link or when people are sleeping. It became obvious that this would be a fight to the end…of one or the other…man or beast. So, both armies agreed to a temporary truce and went on a joint campaign of destruction. The wolves could not be allowed to stay, for the sake of anyone in the area. The two armies slew hundreds of wolves, and then simply resumed their fight. How very strange that seems to me, but I guess it probably wasn’t up to the soldiers to walk away from the war.
 Through the years, Russia, also known as the Soviet Union and the USSR, has been sometimes ally and sometimes enemy of the United States. World War I and World War II found the Soviet Union once again on the side of good as a part of the Allied Forces. The main countries in the Allied powers of World War I were France, the British Empire and the Russian Empire. The main Allied powers of World War II were France, Great Britain, the United States, China, and the Soviet Union. So in these two wars anyway, the United States and Russia were on the same side. The three principal partners in the Axis alliance in World War II were Germany, Italy, and Japan. They were joined by Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania and Thailand, who also signed the Tri-Partite Pact as member states.
Through the years, Russia, also known as the Soviet Union and the USSR, has been sometimes ally and sometimes enemy of the United States. World War I and World War II found the Soviet Union once again on the side of good as a part of the Allied Forces. The main countries in the Allied powers of World War I were France, the British Empire and the Russian Empire. The main Allied powers of World War II were France, Great Britain, the United States, China, and the Soviet Union. So in these two wars anyway, the United States and Russia were on the same side. The three principal partners in the Axis alliance in World War II were Germany, Italy, and Japan. They were joined by Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania and Thailand, who also signed the Tri-Partite Pact as member states.
On May 12, 1942, Soviet forces under the command of Marshal Semyon Timoshenko attacked the German 6th  Army from a vulnerable point established during the winter counter-offensive. After a promising start, the offensive was stopped on May 15th by massive airstrikes. There were a number of critical Soviet errors by several staff officers and by Joseph Stalin, who failed to accurately estimate the 6th Army’s potential and overestimated their own newly raised forces, facilitated a German pincer attack on May 17th which cut off three Soviet field armies from the rest of the front by May 22nd. The Soviet Army was hemmed into a narrow area, and the 250,000-strong Soviet force inside the pocket was exterminated from all sides by German armored, artillery, and machine gun firepower, as well as 7,700 tons of air-dropped bombs. After six days of encirclement by the German Army, the Soviet resistance ended as their troops were killed or taken prisoner. It was a devastating loss for the Soviets.
Army from a vulnerable point established during the winter counter-offensive. After a promising start, the offensive was stopped on May 15th by massive airstrikes. There were a number of critical Soviet errors by several staff officers and by Joseph Stalin, who failed to accurately estimate the 6th Army’s potential and overestimated their own newly raised forces, facilitated a German pincer attack on May 17th which cut off three Soviet field armies from the rest of the front by May 22nd. The Soviet Army was hemmed into a narrow area, and the 250,000-strong Soviet force inside the pocket was exterminated from all sides by German armored, artillery, and machine gun firepower, as well as 7,700 tons of air-dropped bombs. After six days of encirclement by the German Army, the Soviet resistance ended as their troops were killed or taken prisoner. It was a devastating loss for the Soviets.
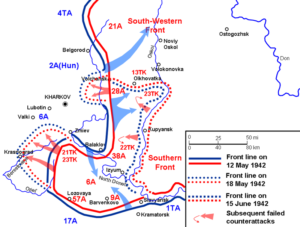
The Counter-offensive of the Second Battle of Kharkov, was called Operation Fredericus, and was launched by the Axis forces in the region around Kharkov against the Red Army Izium bridgehead offensive, and was conducted from May 12 to May 28, 1942, on the Eastern Front during World War II. The objective was to  eliminate the Izium bridgehead over Seversky Donets, also known as the “Barvenkovo bulge,” which was one of the Soviet offensive’s staging areas. A winter counter-offensive drove German troops away from Moscow, but depleted the Red Army’s reserves. The Kharkov offensive was next Soviet attempt to expand their strategic initiative, although it failed to secure a significant element of surprise. The battle ended up being an overwhelming German victory, with 280,000 Soviet casualties compared to just 20,000 for the Germans and their allies. The German Army Group South pressed its advantage, encircling the Soviet 28th Army on June 13 in Operation Wilhelm and pushing back the 38th and 9th Armies on June 22.
eliminate the Izium bridgehead over Seversky Donets, also known as the “Barvenkovo bulge,” which was one of the Soviet offensive’s staging areas. A winter counter-offensive drove German troops away from Moscow, but depleted the Red Army’s reserves. The Kharkov offensive was next Soviet attempt to expand their strategic initiative, although it failed to secure a significant element of surprise. The battle ended up being an overwhelming German victory, with 280,000 Soviet casualties compared to just 20,000 for the Germans and their allies. The German Army Group South pressed its advantage, encircling the Soviet 28th Army on June 13 in Operation Wilhelm and pushing back the 38th and 9th Armies on June 22.

 Many people know that April 20th is Hitler’s birthday, not that most of us would celebrate that fact. Nevertheless, for the Allies in World War II, at least on April 20, 1945, that day meant something. Not because it was Hitler’s birthday…no, it was because the Allies had a plan. The Germans had been in control in much of Italy, and their advancement had to be stopped. As always, there were multiple campaigns planned on any given day in the war. One planned attack, called Operation Corncob, was to send Allied bombers into Italy to begin a three-day attack on the bridges over the rivers Adige and Brenta to cut off the German lines of possible retreat on the peninsula. They knew that Hitler would be otherwise occupied, it being his birthday and all…and so he was.
Many people know that April 20th is Hitler’s birthday, not that most of us would celebrate that fact. Nevertheless, for the Allies in World War II, at least on April 20, 1945, that day meant something. Not because it was Hitler’s birthday…no, it was because the Allies had a plan. The Germans had been in control in much of Italy, and their advancement had to be stopped. As always, there were multiple campaigns planned on any given day in the war. One planned attack, called Operation Corncob, was to send Allied bombers into Italy to begin a three-day attack on the bridges over the rivers Adige and Brenta to cut off the German lines of possible retreat on the peninsula. They knew that Hitler would be otherwise occupied, it being his birthday and all…and so he was.
Hitler was actually occupied for more reasons than just his birthday, as Soviet artillery had begun shelling Berlin at 11am on his 56th birthday. Preparations were being made to evacuate Hitler and his staff to Obersalzberg to make a final stand in the Bavarian mountains, but Hitler refused to leave his bunker. So, Hermann Göring and Heinrich Himmler left the bunker for the last time. Operation Herring had begun the day before, with American aircraft dropping Italian paratroopers over Northern Italy, and with Operation Corncob came the other half of the attack, which was to remove the bridges and thereby halt the expected retreat of the German forces. I doubt if Hitler knew anything about these attacks, I’m sure his mind was on his upcoming suicide, a death which some say didn’t really take place, and a fact which we will never know for sure.
The Allied attacks of April 1945 on the Italian front, were intended to end the Italian campaign and the war in Italy, and to decisively break through the German Gothic Line, the defensive line along the Apennines and the River Po plain to the Adriatic Sea and swiftly drive north to occupy Northern Italy and get to the Austrian and Yugoslav borders as quickly as possible. Unfortunately, German strongpoints, as well as bridge, road, levee and dike blasting, and any occasional determined resistance in the Po Valley plain slowed the planned sweep down. Allied planners decided that dropping paratroops into some key areas and locales south of the River Po might help wreak havoc in the German rear area, attack German communications, and vehicle columns, further disrupting the German retreat, and prevent German engineers from blowing up key structures before Allied spearheads could exploit them. Lieutenant General Sir Richard McCreery, commander of the Commonwealth 8th Army, had a number of Italian paratroopers at hand for the task.
Meanwhile, Adolf Hitler celebrated his 56th birthday with a traditional parade and full celebration, while a 
 Gestapo reign of terror took the lives by hanging of 20 Russian prisoners of war and 20 Jewish children, at least nine of which were under the age of 12. All of the victims had been taken from Auschwitz to Neuengamme, the place of execution, for the purpose of medical experimentation. Hitler and his Third Reich didn’t fully understand it then, but they were finished, and the end was coming quickly.
Gestapo reign of terror took the lives by hanging of 20 Russian prisoners of war and 20 Jewish children, at least nine of which were under the age of 12. All of the victims had been taken from Auschwitz to Neuengamme, the place of execution, for the purpose of medical experimentation. Hitler and his Third Reich didn’t fully understand it then, but they were finished, and the end was coming quickly.
 On January 31, 1917, at the height of World War I, Germany announced that they would renew the use of unrestricted submarine warfare in the Atlantic Ocean. The German torpedo-armed submarines, known as U-Boats, prepared to attack any and all ships operating in the Atlantic, including civilian passenger carriers, which were said to have been sighted in war-zone waters. They were prepared to attack without a second thought, whether they were innocent civilians or not. Unleashing the U-Boats was almost like unleashing terrorists, because the U-Boats were an invisible enemy. Yes, the could be seen, but beneath the surface of the water, they could easily hide in the murky darkness, unleashing their torpedoes to go streaking through the water. The first sign of danger was when the doomed ship watchmen saw the dreaded white streak coming at them through the water. There was no time to take evasive action. The ship could not move that fast, and it could not turn on a dime. They were sitting ducks.
On January 31, 1917, at the height of World War I, Germany announced that they would renew the use of unrestricted submarine warfare in the Atlantic Ocean. The German torpedo-armed submarines, known as U-Boats, prepared to attack any and all ships operating in the Atlantic, including civilian passenger carriers, which were said to have been sighted in war-zone waters. They were prepared to attack without a second thought, whether they were innocent civilians or not. Unleashing the U-Boats was almost like unleashing terrorists, because the U-Boats were an invisible enemy. Yes, the could be seen, but beneath the surface of the water, they could easily hide in the murky darkness, unleashing their torpedoes to go streaking through the water. The first sign of danger was when the doomed ship watchmen saw the dreaded white streak coming at them through the water. There was no time to take evasive action. The ship could not move that fast, and it could not turn on a dime. They were sitting ducks.
The vast majority of people of the United States favored neutrality when it came to World War I. So when the war erupted in 1914, President Woodrow Wilson pledged the stay neutral. The problem was that Britain was one of America’s closest trading partners. That created serious tension between the United States and Germany, when Germany attempted a blockade of the British isles. Several US ships traveling to Britain were damaged or sunk by German mines and, in February 1915, Germany announced unrestricted warfare against all ships, neutral or otherwise, that entered the war zone around Britain. One month later, Germany announced that a German cruiser had sunk the William P. Frye, a private American merchant vessel that was transporting grain to England when it disappeared. President Wilson was outraged, but the German government apologized, calling the attack an unfortunate mistake. That didn’t stop their reign of terror, however. In November they sank an Italian liner without warning, killing 272 people, including 27 Americans. Public opinion concerning the war, and the stand of the United States in it began to change. It was time for the United States to get into World War I.
The Germans were far in advance of other nations when it came to submarines. The U-boat was 214 feet long, carried 35 men and 12 torpedoes, and could travel underwater for two hours at a time. In the first few years of World War I, the U-boats took a terrible toll on Allied shipping. In early May 1915, several New York newspapers had to publish a warning by the German embassy in Washington that Americans traveling on British or Allied ships in war zones did so at their own risk. The announcement was placed on the same page as an advertisement for the imminent sailing of the British-owned Lusitania ocean liner from New York to Liverpool. I’m sure they had hoped that people would heed the warning, but many people boarding the Lusitania either didn’t take notice of the warning or they didn’t see it. On May 7, the Lusitania was torpedoed without warning just off the coast of Ireland. Of the 1,959 passengers, 1,198 were killed, including 128 Americans. The Germans had proven once again that they were ruthless and conniving. Following the sinking of the Lusitania The German government accused the Lusitania was carrying munitions. The US demanded an end to German attacks on unarmed passenger and merchant ships, and full repayment for the loss.
Following the sinking of the Lusitania the German government accused the Lusitania was carrying munitions. The US demanded an end to German attacks on unarmed passenger and merchant ships, and full repayment for the loss. Germany countered with a pledge to see to the safety of passengers before sinking unarmed vessels in August 1915. All that changed by January 1917, when Germany, determined to win its war of attrition against the Allies, announced the resumption of unrestricted warfare. Three days later, the United States broke off diplomatic relations with Germany, who, just hours later sunk the American liner Housatonic. None of the 25 Americans on board were killed and they were picked up by a British steamer.
On February 22, Congress passed a $250 million arms-appropriations bill intended to ready the United States for war. British authorities gave the US ambassador to Britain a copy of what has become known as the “Zimmermann Note,” a coded message from German Foreign Secretary Arthur Zimmermann to Count Johann von Bernstorff, the German ambassador to Mexico. In the telegram, intercepted and deciphered by British intelligence, Zimmermann stated that, in the event of war with the United States, Mexico should be asked to  enter the conflict as a German ally. In return, Germany would promise to restore to Mexico the lost territories of Texas, New Mexico and Arizona. On March 1, the outraged US State Department published the note and America was galvanized against Germany once and for all. In late March, Germany sank four more US merchant ships. President Wilson appeared before Congress and called for a declaration of war against Germany on April 2nd. On April 4th, the Senate voted 82 to six to declare war against Germany. Two days later, the House of Representatives endorsed the declaration by a vote of 373 to 50 and America formally entered World War I. They were after that invisible enemy, and they were determined to find it and destroy it.
enter the conflict as a German ally. In return, Germany would promise to restore to Mexico the lost territories of Texas, New Mexico and Arizona. On March 1, the outraged US State Department published the note and America was galvanized against Germany once and for all. In late March, Germany sank four more US merchant ships. President Wilson appeared before Congress and called for a declaration of war against Germany on April 2nd. On April 4th, the Senate voted 82 to six to declare war against Germany. Two days later, the House of Representatives endorsed the declaration by a vote of 373 to 50 and America formally entered World War I. They were after that invisible enemy, and they were determined to find it and destroy it.

 As the Third Reich was losing its war against the world, German General Friedrich Paulus, who was commander in chief of the German 6th Army at Stalingrad, urgently requests permission from Adolf Hitler to surrender his position there. Paulus knew they had no chance, but Hitler refused. Of course, we all know that Hitler was insane. He would make his men fight to the death when there was no hope of winning the battle.
As the Third Reich was losing its war against the world, German General Friedrich Paulus, who was commander in chief of the German 6th Army at Stalingrad, urgently requests permission from Adolf Hitler to surrender his position there. Paulus knew they had no chance, but Hitler refused. Of course, we all know that Hitler was insane. He would make his men fight to the death when there was no hope of winning the battle.
Stalingrad was a prized strategic area, and the battle to take the city began in the summer of 1942. German forces assaulted the city, which was a major industrial center, but they had misjudged the Soviets. Despite repeated attempts and having pushed the Soviets almost to the Volga River in mid-October, as well as encircling Stalingrad, the 6th Army, under Paulus, and part of the 4th Panzer Army could not break past the adamantine defense of the Soviet 62nd Army. As their resources diminished. The Germans suffered diminishing resources, partisan guerilla attacks, and the cruelty of the Russian winter, all of which began to take their toll on the Germans. The Soviets made their move on November 19, launching a counteroffensive that began with a massive artillery bombardment of the German position. The assault began when the Soviets attacked the weakest link in the German force-inexperienced Romanian troops. Soviet soldiers took 65,000 soldiers prisoner that day. Then, the Soviets in a bold strategic move, encircled the enemy and launched pincer movements from north and south simultaneously, just as the Germans were encircling Stalingrad. It was at this point that the Germans should have withdrawn, and Paulus requested permission to withdraw, but Hitler wouldn’t allow it. He told his armies to hold out until they could be reinforced. Fresh troops would not arrive until December, and by then it was too late. The Soviet position was too strong, and the Germans were exhausted. They were out of options.
By January 24, the Soviets had overrun Paulus’ last airfield. His position was indefensible and surrender was the only hope for survival. Paulus urgently requested, “Let us surrender!!” Still, Hitler wouldn’t hear of it: “The 6th Army will hold its positions to the last man and the last round.” Paulus held out until January 31, when he finally surrendered. Of more than 280,000 men under Paulus’ command, half were already dead or dying, 
 about 35,000 had been evacuated from the front, and the remaining 91,000 were hauled off to Soviet POW camps. Paulus eventually sold out to the Soviets altogether, joining the National Committee for Free Germany and urging German troops to surrender. Testifying at Nuremberg for the Soviets, he was released and spent the rest of his life in East Germany. Hitler was crazy, and his officers knew it, but there was little they could do about it.
about 35,000 had been evacuated from the front, and the remaining 91,000 were hauled off to Soviet POW camps. Paulus eventually sold out to the Soviets altogether, joining the National Committee for Free Germany and urging German troops to surrender. Testifying at Nuremberg for the Soviets, he was released and spent the rest of his life in East Germany. Hitler was crazy, and his officers knew it, but there was little they could do about it.
 The many atrocities of the Nazi soldiers are well known, but somehow, every time I read about another one, I am very shocked again. I suppose that the prisoners of war were treated better than the Jews or the political prisoners, but I don’t think it was enough better to really take notice of. The Third Reich was an equal opportunity murder machine. Somehow they felt certain that they could get away with anything they wanted to do.
The many atrocities of the Nazi soldiers are well known, but somehow, every time I read about another one, I am very shocked again. I suppose that the prisoners of war were treated better than the Jews or the political prisoners, but I don’t think it was enough better to really take notice of. The Third Reich was an equal opportunity murder machine. Somehow they felt certain that they could get away with anything they wanted to do.
During the Battle of the Bulge, which was a major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II. It took place from December 16, 1944 to January 25, 1945. The battle was launched through the densely forested Ardennes region of Wallonia in eastern Belgium, northeast France, and Luxembourg, towards the end of the war in Europe. The war was winding down, and the Germans knew they were losing. It was during this time that they began trying to get rid of the evidence.
The Malmedy massacre was the result of their attempt to hide what they were doing. I was a war crime committed by members of Kampfgruppe Peiper, which is a part of the SS Division Leibstandarte, a German Waffen-SS unit led by Joachim Peiper, at Baugnez crossroads near Malmedy, Belgium, on December 17, 1944.  In all, 84 American prisoners of war were massacred by their German captors. The Germans assembled the prisoners in a field and mowed them down with machine guns. Afterward, they walked through the field and any of the prisoners who were still alive were killed by close-range shots to the head.
In all, 84 American prisoners of war were massacred by their German captors. The Germans assembled the prisoners in a field and mowed them down with machine guns. Afterward, they walked through the field and any of the prisoners who were still alive were killed by close-range shots to the head.
The term Malmedy massacre has also been generally associated with the series of massacres committed by the same unit on the same day and following days. These men were intent on getting rid of the evidence of their crimes. With these men living, they could tell the world how they had been treated. They felt that the if the men were dead, then Germany could get out of the war crimes. Nevertheless, they killed these men in vain, because the killings were the subject of the Malmedy massacre trial, which was part of the Dachau Trials of 1946.
 I am always amazed at the lengths nations will go to try to have a better weapon with which to war against their enemies. Some of the weapons were horrifically great successes, while others only succeeded in being amusingly unsuccessful. It seems that the Germans were famous for trying to come up with unusual ideas for weaponry. In fact, World War II seemed to be full of bizarre weapons.
I am always amazed at the lengths nations will go to try to have a better weapon with which to war against their enemies. Some of the weapons were horrifically great successes, while others only succeeded in being amusingly unsuccessful. It seems that the Germans were famous for trying to come up with unusual ideas for weaponry. In fact, World War II seemed to be full of bizarre weapons.
Wars always present opportunities for technological development, but Germany seemed to be particularly motivated to pour considerable resources into weapons projects. The level of success, varied with the weapons. That is not unusual, as weapons go, but I think that when you look some of the bizarre weapon designs that Germany came up with really seemed like a recipe for calamity to me. The weapons they came up with had varying degrees of success. The Germans developed the V-2 rocket, which both rained destruction on the United Kingdom and jumpstarted the space race. On the other hand, they also tried to build a “sun gun,” an orbital heat ray that was supposed to use reflected sunlight to torch cities.
The V-3 cannon project falls in the middle of the spectrum of weaponry. In the end, it never threatened the Allied powers, but if it had been given more production time, it very well could have. The V-3 was an extremely long artillery piece, over 430 feet in length. It was designed to fire projectiles up to a distance of 100 miles away. The V-3 cannon was built to bombard British cities from mainland Europe, bypassing the need for planes or the V-2. These enormous guns had been in development since World War I, on both sides of the conflict, but to this point these weapons hadn’t been deployed in combat. The problem was that the size of an explosion needed to propel a projectile over such a distance was so large that it would quickly destroy any gun barrel. They just couldn’t get that part fixed.
At the outbreak of World War II, the Germans rediscovered the plans for the V-3 and began to research them  again. In 1943, Hitler restarted the V-3 project under his Armaments and War Procurement Minister, Albert Speer. The first goal was to solve the explosion problem. It was decided that the V-3 would use several small explosions that would propel the projectile along the barrel. Even with that change, the barrel was so large and unwieldy that it couldn’t be aimed. It had to be built already aiming at the intended target, and the target had to be the size of a city. That is a tall order.
again. In 1943, Hitler restarted the V-3 project under his Armaments and War Procurement Minister, Albert Speer. The first goal was to solve the explosion problem. It was decided that the V-3 would use several small explosions that would propel the projectile along the barrel. Even with that change, the barrel was so large and unwieldy that it couldn’t be aimed. It had to be built already aiming at the intended target, and the target had to be the size of a city. That is a tall order.
The Germans made plans to build 50 V-3 cannons on the French coastline, but RAF bombings delayed the project. When the Allies retook France in 1944, the V-3 project was again abandoned. The Allies didn’t learn of the V-3 project until after World War II had ended. Winston Churchill said that “if the guns had been completed, they could have devastated England more than any other German weapon.” Thankfully the Allies retook France in time to avoid such a disaster.
 In the Soviet Union’s Catherine Palace, located near Saint Petersburg, is rumored to have been a beautiful chamber decorated in amber panels backed with gold leaf and mirrors. The elaborately designed hall was a gift to Peter the Great from Germany. Constructed in the 18th century in Prussia, the room was dismantled and eventually disappeared during World War II. In the days before World War II started, Hitler had worked an “alliance agreement” with Stalin. Hitler really had no intention of keeping the agreement, but rather wanted to take control of Poland without Soviet interference. That didn’t make the Soviet Union safe either. When Germany made their move, the Soviets did not have enough time to prepare.
In the Soviet Union’s Catherine Palace, located near Saint Petersburg, is rumored to have been a beautiful chamber decorated in amber panels backed with gold leaf and mirrors. The elaborately designed hall was a gift to Peter the Great from Germany. Constructed in the 18th century in Prussia, the room was dismantled and eventually disappeared during World War II. In the days before World War II started, Hitler had worked an “alliance agreement” with Stalin. Hitler really had no intention of keeping the agreement, but rather wanted to take control of Poland without Soviet interference. That didn’t make the Soviet Union safe either. When Germany made their move, the Soviets did not have enough time to prepare.
It was 1941, when the Germans advanced. The job of removing the panels to safety would take time…time they didn’t have. The panels were quickly taken by the Germans and transported to Konigsberg, East Prussia. They were confiscating anything of value. Initially, the Amber Room was placed on public display at the Konigsberg Castle, but was hidden in anticipation of the 1945 Soviet advance. Before its loss, it was considered an “Eighth Wonder of the World.”
In 1701, the Amber Room was intended for the Charlottenburg Palace, in Berlin, Prussia, but was eventually installed at the Berlin City Palace. Designed by German baroque sculptor Andreas Schlüter and Danish amber craftsman Gottfried Wolfram, who worked on the room until 1707, at which time the work was continued by amber masters Gottfried Turau and Ernst Schacht from Danzig (Gdansk). The masterpiece remained in Berlin until 1716, when it was given by the Prussian King Frederick William I to his ally Tsar Peter the Great of the Russian Empire. In Russia, the beautiful room was installed in the Catherine Palace. In the castle, the room was further expanded and several renovations where performed, making it an even more stunning chamber than it had been before. In the end, it covered more than 590 square feet and contained over 13,000 pounds of amber.
When the Army Group North of Nazi Germany took possession of the Amber Room during World War II, it was taken to Königsberg for reconstruction and display. Like many stolen treasures, the Germans hid the Amber Rooms panels, and its eventual fate and current whereabouts, if it has survived, remain a mystery. While most  experts believed it was obliterated during the intense shelling that destroyed the Konigsberg Castle, I don’t believe that is true, because surely some evidence of that much amber would have been found after a bombing, but none was ever found at the site.
experts believed it was obliterated during the intense shelling that destroyed the Konigsberg Castle, I don’t believe that is true, because surely some evidence of that much amber would have been found after a bombing, but none was ever found at the site.
Persistent rumors about the current location of the Amber Room have never panned out, and after years of searching, it was decided in 1979, to create a reconstructed Amber Room at the Catherine Palace. After decades of work by Russian craftsmen and donations from Germany, the reconstructed Amber Room was finally inaugurated in 2003.

