
 These days, we all know what mass transit is. It’s about taking a trip on a plane, train, ship, or even a bus. Certainly, trains existed prior to 1832, but they were not designed for cross-town travel back then. On November 14, 1832, all that changed when the New York and Harlem Railroad in New York City introduced the nation’s first horse-drawn streetcar. The streetcar service was launched on the Bowery and Fourth Avenue in Manhattan, spanning from Prince to 14th Street, and with that, it became the city’s inaugural mass transit system. The fare for a ride was set at 12.5 cents.
These days, we all know what mass transit is. It’s about taking a trip on a plane, train, ship, or even a bus. Certainly, trains existed prior to 1832, but they were not designed for cross-town travel back then. On November 14, 1832, all that changed when the New York and Harlem Railroad in New York City introduced the nation’s first horse-drawn streetcar. The streetcar service was launched on the Bowery and Fourth Avenue in Manhattan, spanning from Prince to 14th Street, and with that, it became the city’s inaugural mass transit system. The fare for a ride was set at 12.5 cents.
The streetcar was named “John Mason” after the President of Chemical Bank, a prosperous New York businessman and railroad co-founder who financed its creation. It was essentially a horse-drawn bus with seating for about a dozen passengers. However, as reported by the New York Herald, this did not deter people from crowding in, “People are packed into streetcars like sardines in a box, with perspiration for oil. The seats being more than filled, the passengers are placed in rows down the middle, where they hang on by the straps, like smoked hams in a corner grocery.” No one thought about the problems, and in fact dangers of overcrowding, and as it turns out those dangers did not materialize anyway, so the ride, overcrowding and all, was a beloved pastime.
Horse-drawn carriages had always existed in New York City, but the omnibus was different because it ran along a designated route and was a more affordable option. “Omni” meant the bus carried everyone and anyone. The ride was cushioned with steel springs, but wheels were solid metal and wood. I can imagine the rough ride its passengers must have experienced, and the amount of effort needed by the draft animals to pull the oversize coaches along New York City’s cobblestone, unfinished, and litter-strewn streets. While riding was a trick sometimes, getting off was just as strange. To signal their desire to disembark from the large stagecoach, passengers would pull on a leather strap connected to the driver’s ankle. Imagine how annoying that constant pulling on the ankle must have been for the driver. I suppose he got used to it, but to me it seems like it would be a huge annoyance.
The next step took over 50 years, but in 1883, New York saw its first steam-powered streetcar, which replaced 
 the horse-drawn omnibus. From there, change was rapid. By 1909, electric trolleys were introduced to the city. Even the local baseball team got in on the streetcar craze. Baseball historians tell of the Brooklyn Dodgers, originally the “Trolley Dodgers,” who earned their name because the borough’s baseball team fans quite often had to navigate through busy streetcar traffic.
the horse-drawn omnibus. From there, change was rapid. By 1909, electric trolleys were introduced to the city. Even the local baseball team got in on the streetcar craze. Baseball historians tell of the Brooklyn Dodgers, originally the “Trolley Dodgers,” who earned their name because the borough’s baseball team fans quite often had to navigate through busy streetcar traffic.

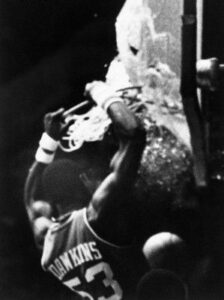 It became an almost commonplace practice for a while, but it really wasn’t a safe practice or an acceptable practice. A backboard shattering, also referred to as backboard breaking or smashing, is an accident or deliberate stunt in basketball. It happens when a player slam dunks with enough force to break the tempered glass backboard, which may also result in the hoop detaching. This event typically leads to game cancellations or delays, a foul against the player responsible, potential serious injuries, and significant cleanup and replacement costs. The act of shattering a backboard is hazardous, as it propels small shards of glass over the players, sideline press, referees, and spectators. Nevertheless, On November 13, 1979, during a game at the Municipal Auditorium in Kansas City, Philadelphia 76ers center Darryl Dawkins soared over Kansas City Kings forward Bill Robinzine and executed a slam dunk that shattered the fiberglass backboard. Witnesses described the noise as resembling a bomb detonating on the court. Glass shards scattered everywhere, cutting Robinzine’s arms and legs and embedding in Dr. J’s Afro. Dawkins later remarked, “It wasn’t really safe, but it was a Darryl Dawkins thing to do.” It also wasn’t the first time it happened. Chuck Connors, who would later gain fame as an actor in “The Rifleman,” was the first NBA player to shatter a backboard, not with a dunk but with a set shot. While playing for the Boston Celtics in 1946, during pregame warmups, Connors’ shot hit the front of the rim. The backboard shattered because an arena worker had neglected to install a protective piece between the rim and the backboard. I can only imagine his shock.
It became an almost commonplace practice for a while, but it really wasn’t a safe practice or an acceptable practice. A backboard shattering, also referred to as backboard breaking or smashing, is an accident or deliberate stunt in basketball. It happens when a player slam dunks with enough force to break the tempered glass backboard, which may also result in the hoop detaching. This event typically leads to game cancellations or delays, a foul against the player responsible, potential serious injuries, and significant cleanup and replacement costs. The act of shattering a backboard is hazardous, as it propels small shards of glass over the players, sideline press, referees, and spectators. Nevertheless, On November 13, 1979, during a game at the Municipal Auditorium in Kansas City, Philadelphia 76ers center Darryl Dawkins soared over Kansas City Kings forward Bill Robinzine and executed a slam dunk that shattered the fiberglass backboard. Witnesses described the noise as resembling a bomb detonating on the court. Glass shards scattered everywhere, cutting Robinzine’s arms and legs and embedding in Dr. J’s Afro. Dawkins later remarked, “It wasn’t really safe, but it was a Darryl Dawkins thing to do.” It also wasn’t the first time it happened. Chuck Connors, who would later gain fame as an actor in “The Rifleman,” was the first NBA player to shatter a backboard, not with a dunk but with a set shot. While playing for the Boston Celtics in 1946, during pregame warmups, Connors’ shot hit the front of the rim. The backboard shattered because an arena worker had neglected to install a protective piece between the rim and the backboard. I can only imagine his shock.
When 6’10”, 260-pound Dawkins joined the 76ers in 1975, he was the first NBA player drafted directly from high school. His nickname, reportedly bestowed on him by Stevie Wonder, was “Chocolate Thunder.” His aim was to become the league’s most entertaining player. His slam dunks, huge crowd-pleasers, and he named them all: “the In-Your-Face Disgrace, Look Out Below, Turbo Sexophonic Delight, Rim-Wrecker, Go-Rilla, Spine Chiller Supreme, Cover Your Head, Yo Mama, and his personal favorite, the Get-Out-of-the-Waying, Backboard-Swaying, Game-Delaying, If-You-Ain’t-Grooving-You-Best-Get-Moving Dunk.” His notorious Kansas City backboard shattering dunk was aptly named “the Chocolate-Thunder-Flying, Robinzine-Crying, Teeth-Shaking, Glass-Breaking, Rump-Roasting, Bun-Toasting, Wham-Bam Glass-Breaker-I-Am Jam.”
Apparently, he liked this showiness, because a few weeks later, Dawkins shattered another backboard, this time at the Philadelphia Spectrum. Following this incident, NBA Commissioner Larry O’Brien summoned the young player to his office and issued a stern warning: for each backboard Dawkins broke, he would face a $5,000 fine and suspension. While the dramatic dunks were generating publicity for the NBA, which was then facing difficulties, they also led to lengthy game delays as janitors cleaned up the broken glass, not to mention the inherent danger. Consequently, the league decided to equip every arena with shatterproof backboards and breakaway rims. If you can’t stop the players from this risky behavior, you make it impossible to perform.
Darryl Dawkins’ iconic backboard-shattering dunks are some of the most memorable moments from an 
 especially exuberant era in NBA history. I don’t think there is one person who hasn’t see a replay or two. He continued his basketball career in Italy, where he broke several backboards that were not Dawkins-proof and later coached the Pennsylvania Valley Dawgs in the United States Basketball League. Dawkins was born in Orlando, Florida, on January 11, 1957, to Harriet James and Frank Dawkins. His grandmother Amanda Celestine Jones was fond of the young Darryl and personally raised him. Dawkins passed away in 2015, at the age of 58
especially exuberant era in NBA history. I don’t think there is one person who hasn’t see a replay or two. He continued his basketball career in Italy, where he broke several backboards that were not Dawkins-proof and later coached the Pennsylvania Valley Dawgs in the United States Basketball League. Dawkins was born in Orlando, Florida, on January 11, 1957, to Harriet James and Frank Dawkins. His grandmother Amanda Celestine Jones was fond of the young Darryl and personally raised him. Dawkins passed away in 2015, at the age of 58
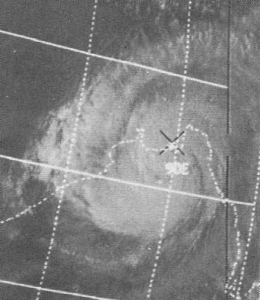 When weather gets ugly, and things end up in really bad shape, the blame often falls on the disaster crew trying to help. The 1970 Bhola cyclone, which was also referred to as the Great Cyclone of 1970, was a catastrophic tropical cyclone that hit East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Bengal in India on November 12, 1970. It was also a prime example of the blame game. The 1970 Bhola Cyclone was the deadliest tropical cyclone on record and one of the most lethal natural disasters in history. The death toll from the storm was at least 300,000, with estimates reaching up to 500,000, largely due to the storm surge that inundated the low-lying islands of the Ganges Delta. Bhola was the most intense and the sixth cyclonic storm of the 1970 North Indian Ocean cyclone season.
When weather gets ugly, and things end up in really bad shape, the blame often falls on the disaster crew trying to help. The 1970 Bhola cyclone, which was also referred to as the Great Cyclone of 1970, was a catastrophic tropical cyclone that hit East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Bengal in India on November 12, 1970. It was also a prime example of the blame game. The 1970 Bhola Cyclone was the deadliest tropical cyclone on record and one of the most lethal natural disasters in history. The death toll from the storm was at least 300,000, with estimates reaching up to 500,000, largely due to the storm surge that inundated the low-lying islands of the Ganges Delta. Bhola was the most intense and the sixth cyclonic storm of the 1970 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. 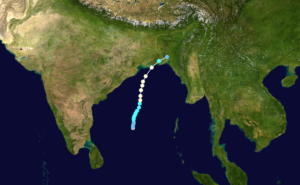
A cyclone developed over the central Bay of Bengal on November 8th and moved northwards, gaining strength along the way. It peaked with winds of 115 mph on November 10 and struck the coast of East Pakistan the next afternoon. The resulting storm surge demolished numerous offshore islands, wiping out villages and decimating crops across the area. In Tazumuddin, the upazila (sub-district) hardest hit, the storm claimed the lives of more than 45% of its 167,000 residents. The death toll was just shocking.
 The Pakistani administration, under the leadership of General Yahya Khan, faced criticism for its slow response to relief efforts after the storm from both East Pakistani political figures and international media. Of course, the media doesn’t always understand the logistics concerned in such a rescue effort. This inadequate and biased response from the government of West Pakistan contributed to growing disenchantment among the people of East Pakistan, which enabled the opposition Awami League to secure a decisive victory in the provincial elections the following month and also led to the Bangladesh Liberation War seven months later. This was most likely a clear showing of weather making history.
The Pakistani administration, under the leadership of General Yahya Khan, faced criticism for its slow response to relief efforts after the storm from both East Pakistani political figures and international media. Of course, the media doesn’t always understand the logistics concerned in such a rescue effort. This inadequate and biased response from the government of West Pakistan contributed to growing disenchantment among the people of East Pakistan, which enabled the opposition Awami League to secure a decisive victory in the provincial elections the following month and also led to the Bangladesh Liberation War seven months later. This was most likely a clear showing of weather making history.
 The name was originally Armistice Day, but now is known as Remembrance Day in the Commonwealth of England and Veterans Day in the United States. It is observed annually on November 11th. This day marks the armistice signed at Compiègne, France, between the Allies of World War I and Germany at 5:45am, leading to the end of hostilities on the Western Front, effective from 11:00am…the “eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month” in 1918. Despite this, Thomas R Gowenlock, a US First Division intelligence officer, reported that shelling continued throughout the day, ceasing only at nightfall. The armistice, initially set for 36 days, required several extensions until the formal peace agreement with the Treaty of Versailles was signed the following year. In celebration of the day, “Legally, two minutes of silence is recommended to be observed at 2:11pm Eastern Standard Time.”
The name was originally Armistice Day, but now is known as Remembrance Day in the Commonwealth of England and Veterans Day in the United States. It is observed annually on November 11th. This day marks the armistice signed at Compiègne, France, between the Allies of World War I and Germany at 5:45am, leading to the end of hostilities on the Western Front, effective from 11:00am…the “eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month” in 1918. Despite this, Thomas R Gowenlock, a US First Division intelligence officer, reported that shelling continued throughout the day, ceasing only at nightfall. The armistice, initially set for 36 days, required several extensions until the formal peace agreement with the Treaty of Versailles was signed the following year. In celebration of the day, “Legally, two minutes of silence is recommended to be observed at 2:11pm Eastern Standard Time.”

Originally set for November 11th annually, Veterans Day was shifted to the fourth Monday of October starting in 1971, due to the Uniform Monday Holiday Act. This change occurred on October 25, 1971; October 23, 1972; October 22, 1973; October 28, 1974; October 27, 1975; October 25, 1976, and October 24, 1977. However, in 1978, the observance was returned to its original date of November 11th, mainly because its date had significance too. Although the official holiday is still on November 11th, if it falls on a weekend, federal employees and various organizations observe the holiday on the adjacent Friday or Monday.
Veterans Day, the federal holiday in the United States, is observed annually on November 11th to honor military veterans from the United States Armed Forces. Veterans Day is distinct from Memorial Day, a US public holiday in May: Veterans Day commemorates the service of all US veterans, while Memorial Day specifically honors those who have died while in military service. Another military holiday that also occurs in May, Armed Forces Day, honors those currently serving in the US military. Additionally, Women Veterans Day is recognized by a growing number of US states that specifically honor women who have served in the US military.

While the holiday is commonly printed as Veteran’s Day or Veterans’ Day in calendars and advertisements, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs website states that the attributive (no apostrophe) rather than the possessive case is the official spelling “because it is not a day that ‘belongs’ to veterans, it is a day for honoring all veterans.” I find that very informative, because I have always struggled with where that apostrophe was supposed to go…silly as that may sound. I like that it is actually no apostrophe to honor all veterans. So, to our veterans, Happy Veterans Day!!

 Ok, so you bought a car. You already know, I’m sure, that there are many things your car will need. You just hope that it will be…eventually. With the introduction of the automobile, came the need for parts…lots of parts. On of the parts that might seem insignificant…until it rains anyway, is the windshield wipers. Nevertheless, after those first cars were invented, and the rain, snow, and sleet moved in, the windshield wiper became very important. Enter Mary Anderson. Mary was a woman from Birmingham, Alabama, who came up with her “window cleaning device for electric cars and other vehicles to remove snow, ice or sleet from the window.” The product was very unique, and the patent office awarded US Patent Number 743,801 to Mary for her work. Upon receiving her patent, Anderson attempted to sell it to a Canadian manufacturer, but the firm declined, stating the device lacked prac9tical value and was not monetarily worthwhile. Despite mechanical windshield wipers becoming standard in passenger vehicles by approximately 1913, Anderson did not profit from her invention.
Ok, so you bought a car. You already know, I’m sure, that there are many things your car will need. You just hope that it will be…eventually. With the introduction of the automobile, came the need for parts…lots of parts. On of the parts that might seem insignificant…until it rains anyway, is the windshield wipers. Nevertheless, after those first cars were invented, and the rain, snow, and sleet moved in, the windshield wiper became very important. Enter Mary Anderson. Mary was a woman from Birmingham, Alabama, who came up with her “window cleaning device for electric cars and other vehicles to remove snow, ice or sleet from the window.” The product was very unique, and the patent office awarded US Patent Number 743,801 to Mary for her work. Upon receiving her patent, Anderson attempted to sell it to a Canadian manufacturer, but the firm declined, stating the device lacked prac9tical value and was not monetarily worthwhile. Despite mechanical windshield wipers becoming standard in passenger vehicles by approximately 1913, Anderson did not profit from her invention.
As the story goes, “on a freezing, wet winter day around the turn of the century, Mary Anderson was riding a streetcar on a visit to New York City when she noticed that the driver could hardly see through his sleet-encrusted front windshield. Although the trolley’s front window was designed for bad-weather visibility—it was split into parts so that the driver could open it, moving the snow- or rain-covered section out of his line of vision—in fact the multi-pane windshield system worked very poorly. It exposed the driver’s uncovered face (not to mention all the passengers sitting in the front of the trolley) to the inclement weather, and did not improve his ability to see where he was going in any case.”
Mary Anderson’s invention solved this problem for everyone. With a simple flip of a switch, the wipers kick in, and our windshields are clean and dry. Yes, they wear out sometimes, and many people would say that they 
 don’t last as long as they should, but try to do much driving in the rain or snow without them. Many parts, some much more expensive don’t last long either. It’s better to have a set of almost worn-out wiper blades than to have none at all. Many people would have expected an automobile invention to come from a man, but not in this case. So the next time you use your wiper blades, you can thank Mary.
don’t last as long as they should, but try to do much driving in the rain or snow without them. Many parts, some much more expensive don’t last long either. It’s better to have a set of almost worn-out wiper blades than to have none at all. Many people would have expected an automobile invention to come from a man, but not in this case. So the next time you use your wiper blades, you can thank Mary.

 Our uncle, Butch Schulenberg is a man who cares deeply about the things he loves. He is a family man, who is always there for his wife and kids…going above and beyond for them in everything from their health to their kids’ school activities. These past few years, he has been caring for his wife of 58 years, Charlys, who suffered a burn a while back, but is doing quite well under Butch’s care and that of their grandson, Christian Schulenberg, a CNA at the Forsyth Nursing Home, who lives with them. Having Christain there gives them extra help, when he isn’t working. I am so thankful that Charlys is doing well. She is so sweet, and we want to keep her with us for a long time. Butch has been an excellent caregiver.
Our uncle, Butch Schulenberg is a man who cares deeply about the things he loves. He is a family man, who is always there for his wife and kids…going above and beyond for them in everything from their health to their kids’ school activities. These past few years, he has been caring for his wife of 58 years, Charlys, who suffered a burn a while back, but is doing quite well under Butch’s care and that of their grandson, Christian Schulenberg, a CNA at the Forsyth Nursing Home, who lives with them. Having Christain there gives them extra help, when he isn’t working. I am so thankful that Charlys is doing well. She is so sweet, and we want to keep her with us for a long time. Butch has been an excellent caregiver.
Uncle Butch is a sports fan, from his own days as a football player, I’m sure. He is what would be called a booster. He supports every sport his grandchildren play in, as well as every sport of his hometown, Forsyth,  Montana. He may not be able to get to every game, but he knows who won and by how much. He is an encouragement to the teams…win or lose. Of course, he wants them to win, but in sports, there is just as much importance in sportsmanship as there is in victory. A poor winner is as bad as a poor loser. Sports is about being the best team they can be and knowing that not every game will be won. Nevertheless, every player in the small town of Forsyth, Montana knows that Butch Schulenberg supports their hard work.
Montana. He may not be able to get to every game, but he knows who won and by how much. He is an encouragement to the teams…win or lose. Of course, he wants them to win, but in sports, there is just as much importance in sportsmanship as there is in victory. A poor winner is as bad as a poor loser. Sports is about being the best team they can be and knowing that not every game will be won. Nevertheless, every player in the small town of Forsyth, Montana knows that Butch Schulenberg supports their hard work.
In the summer months, when school is out, Butch can usually be found in his yard growing the sweetest little flower garden. He loves yard work, and while the place he lives has a crew that maintains the grounds, they know that Butch Schulenberg will likely be mowing his area of the lawn. He loves to take pictures of his flowers so we can all enjoy them, and he also loves to take pictures of the beautiful sunsets over the Yellowstone River near their home. They live high up 
 above the river on a bit of a bluff, and the view down to the river is spectacular, sunset or not. Whenever they can, they like to visit their kids, Andi Kay, Tadd, and Heath at their homes, or have the kids come for visits. Their grandchildren are the collective apple of their eye. They love them unconditionally and support them in all they do. People just couldn’t be more blessed than having people like Butch and Charlys as their parents and grandparents. Today is Uncle Butch’s 84th birthday. Happy birthday Uncle Butch!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
above the river on a bit of a bluff, and the view down to the river is spectacular, sunset or not. Whenever they can, they like to visit their kids, Andi Kay, Tadd, and Heath at their homes, or have the kids come for visits. Their grandchildren are the collective apple of their eye. They love them unconditionally and support them in all they do. People just couldn’t be more blessed than having people like Butch and Charlys as their parents and grandparents. Today is Uncle Butch’s 84th birthday. Happy birthday Uncle Butch!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

 Aunt Ruth Wolfe grew up on a farm surrounded by horses…her absolute favorite animal. The country girl lifestyle suited her. During World War II, while her brother, my father Allen Spencer, served in the Army Air Forces, she worked the farm with her mother brother, Bill. She took on the farm work and also worked as a welder in the shipyards, becoming one of the Worl War II’s well known “Rosie the Riveters.” Later, married to my Uncle Jim Wolfe, they lived in the country near Casper, Wyoming…gardening, canning, and raising farm animals. Aunt Ruth was a capable woman, achieving anything she set her
Aunt Ruth Wolfe grew up on a farm surrounded by horses…her absolute favorite animal. The country girl lifestyle suited her. During World War II, while her brother, my father Allen Spencer, served in the Army Air Forces, she worked the farm with her mother brother, Bill. She took on the farm work and also worked as a welder in the shipyards, becoming one of the Worl War II’s well known “Rosie the Riveters.” Later, married to my Uncle Jim Wolfe, they lived in the country near Casper, Wyoming…gardening, canning, and raising farm animals. Aunt Ruth was a capable woman, achieving anything she set her  mind to. Her talents were many, ranging from the hard work of farming and canning to playing musical instruments and painting.
mind to. Her talents were many, ranging from the hard work of farming and canning to playing musical instruments and painting.
One of the most unexpected decisions Aunt Ruth and Uncle Jim made was moving to Vallejo, California. It’s surprising that someone who loved country living would choose a city. Vallejo, a suburb of San Francisco, is a sharp contrast to Casper, Wyoming, and Holyoke, Minnesota, where Aunt Ruth grew up. Perhaps they just wanted a change, which I get since my family transitioned from rural to urban living in Casper. Still, I can see the draw of city life and California’s milder climate probably better suited my aunt and uncle.
After living in California for a while, the country life drew them back to the mountains of Washington state. The move to the mountains didn’t surprise me much; country living seemed to be in my aunt and uncle’s blood, as much a part of their being, as their DNA. Once they settled in eastern Washington, they stayed put. They purchased a mountaintop 
 and built three cabins: one for themselves, one for their daughter Shirley and her husband Shorty Cameron, and one for their son Terry and his family. For Aunt Ruth and Uncle Jim, this was their final abode. Having visited their mountaintop, I understand its allure, but since moving back to town, I’ve realized I wouldn’t want to live in the countryside or on a mountaintop permanently. Nonetheless, it was their safe haven. Today would have marked Aunt Ruth’s 99th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Aunt Ruth. We love and miss you very much.
and built three cabins: one for themselves, one for their daughter Shirley and her husband Shorty Cameron, and one for their son Terry and his family. For Aunt Ruth and Uncle Jim, this was their final abode. Having visited their mountaintop, I understand its allure, but since moving back to town, I’ve realized I wouldn’t want to live in the countryside or on a mountaintop permanently. Nonetheless, it was their safe haven. Today would have marked Aunt Ruth’s 99th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Aunt Ruth. We love and miss you very much.

 As a toddler, my aunt, Evelyn Hushman was learning how to properly address her adult relatives. Each time she referred to an aunt or uncle by their first name, her parents would remind her, “You must say Uncle Ted or Aunt Gladys.” This instruction was likely repeated often, as it’s challenging for a toddler to understand why they must use a different title when everyone else uses the person’s first name. It’s a perplexing period for a young child who is just starting to understand social norms.
As a toddler, my aunt, Evelyn Hushman was learning how to properly address her adult relatives. Each time she referred to an aunt or uncle by their first name, her parents would remind her, “You must say Uncle Ted or Aunt Gladys.” This instruction was likely repeated often, as it’s challenging for a toddler to understand why they must use a different title when everyone else uses the person’s first name. It’s a perplexing period for a young child who is just starting to understand social norms.
These days, at least in our family, many of the aunts and uncles go by just their first names, and while some people might think that odd, I am just as comfortable being Caryn as I am Aunt Caryn. We don’t consider it to be any kind of a show of disrespect. But in times past, and in many families today, if the person is an aunt or uncle, you must address them as Aunt this or Uncle that. We do draw the line at grandma and grandpa, and my grandchildren know that while Gma, G, or G-mamma is ok, Caryn is not. I suppose that could be confusing to  little kids too, but that is the way it is. Another place where we draw the line is Mommy and Daddy, or Mom and Dad. But for the aunts and uncles we are a little more casual.
little kids too, but that is the way it is. Another place where we draw the line is Mommy and Daddy, or Mom and Dad. But for the aunts and uncles we are a little more casual.
Aunt Evelyn was an incredibly social person with a close-knit circle of friends who formed a club. This group consisted of eight girls and eight boys, and their parents would rotate hosting parties for them. They were the envy of all the siblings, who longed to be old enough to join in. When it was my grandmother’s turn, she organized the gathering at the North Casper Clubhouse for a Taffy Pulling Party. A few parents were present, but the event was primarily for the sixteen club members, with younger children excluded, though they did receive some taffy afterwards. The party was a resounding success, leaving my grandmother delighted with the outcome. It’s likely that the younger siblings aspired to have such friendships when they grew up, but Aunt Evelyn’s club was truly one of a kind.
My Aunt Evelyn was the oldest among my mother’s siblings. She and my mother often went on double dates 
 during the time my parents were dating. Aunt Evelyn and Uncle George had been married for about five years then. Despite the eight-year age difference, the sisters shared a close friendship. My father and Uncle George were also friends, making double dating a natural choice for them. They joined a bowling league together, turning their double dates into a cherished weekly tradition that lasted for years and years. They were nights that my sisters and I fondly recall. Today would have been Aunt Evelyn’s 96th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Aunt Evelyn. We love and miss you very much.
during the time my parents were dating. Aunt Evelyn and Uncle George had been married for about five years then. Despite the eight-year age difference, the sisters shared a close friendship. My father and Uncle George were also friends, making double dating a natural choice for them. They joined a bowling league together, turning their double dates into a cherished weekly tradition that lasted for years and years. They were nights that my sisters and I fondly recall. Today would have been Aunt Evelyn’s 96th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Aunt Evelyn. We love and miss you very much.

 My great grandnephew, Asa Balcerzak is a sweet little three-year-old, who is all boy. He likes trucks, motorcycles, and Grandpa Dave Balcerzak’s hot rod, but he also has a softer side…at least when it comes to kittens and other pets. I think Asa is very much his daddy, Keifer’s boy, but he also loves his mommy, Katie and sister, Reece very much too. Recently, his family made a trip to the Corn Maze in town. It was a big family thing, with lots of extra family members there too. There were rides and games, lots of things to see and do, and one big chair for picture taking.
My great grandnephew, Asa Balcerzak is a sweet little three-year-old, who is all boy. He likes trucks, motorcycles, and Grandpa Dave Balcerzak’s hot rod, but he also has a softer side…at least when it comes to kittens and other pets. I think Asa is very much his daddy, Keifer’s boy, but he also loves his mommy, Katie and sister, Reece very much too. Recently, his family made a trip to the Corn Maze in town. It was a big family thing, with lots of extra family members there too. There were rides and games, lots of things to see and do, and one big chair for picture taking.
Like many little kids these days, Asa likes the two wheeled bikes. When I was a kid, three might have been the age to receive a tricycle, but these kids can and do ride two wheelers, 
 and even drive motorized cars, without running into everything in sight. I guess that with technology, comes the advancement of their abilities too. These kids know how to work a tablet, phone, and probably a computer too. Sometimes I am just amazed. The computer stuff doesn’t really shock me too much, because Asa’s dad is a computer programmer by trade, so why should his kid be different.
and even drive motorized cars, without running into everything in sight. I guess that with technology, comes the advancement of their abilities too. These kids know how to work a tablet, phone, and probably a computer too. Sometimes I am just amazed. The computer stuff doesn’t really shock me too much, because Asa’s dad is a computer programmer by trade, so why should his kid be different.
Asa has a great smile. I always think that when he smiles, his whole face smiles. Not everyone is that way, but Asa and his sister definitely are two of those people. Reese is so proud of her little brother, and they are so sweet together. I’m sure there are fights. All siblings fight sometimes, but they get along very well. I think Reece was very excited to get a baby 
 brother. She was all smiles. I’m sure she wanted him to play right away, but that had to wait. Now, playtime is here, and they love having a sibling…even though their interests are quite different. Reece is a girly girl, and Asa is definitely all boy. Nevertheless, she watches out for her little brother, and I’m sure he will watch out for her when he is a little older.
brother. She was all smiles. I’m sure she wanted him to play right away, but that had to wait. Now, playtime is here, and they love having a sibling…even though their interests are quite different. Reece is a girly girl, and Asa is definitely all boy. Nevertheless, she watches out for her little brother, and I’m sure he will watch out for her when he is a little older.
It’s hard to believe that Asa is three years old already. It seems like he was just born yesterday, but her we are at the milestone between toddler and little boy. It’s amazing…they are a baby and then a toddler, and suddenly…they are a little boy. Before we know it he will be a grown man. For now though, he is a little boy. Today is Asa’s 3rd birthday. Happy birthday Asa!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

 Our uncle, Eddie Hein, was always a man you could count on. He was hard working and always willing to help someone in need. He would even travel to help. When my in-laws, Walt and Joann Schulenberg, were building their house in Homa Hills, Eddie came down from Forsyth, Montana to Casper, Wyoming to help lay the cinder blocks. It was a big job, and while the whole family helped out, we didn’t really know how to lay brick. My father-in-law and his brother, Eddie did. I suppose we would have finished the house one way or the other, but it would have taken a lot longer.
Our uncle, Eddie Hein, was always a man you could count on. He was hard working and always willing to help someone in need. He would even travel to help. When my in-laws, Walt and Joann Schulenberg, were building their house in Homa Hills, Eddie came down from Forsyth, Montana to Casper, Wyoming to help lay the cinder blocks. It was a big job, and while the whole family helped out, we didn’t really know how to lay brick. My father-in-law and his brother, Eddie did. I suppose we would have finished the house one way or the other, but it would have taken a lot longer.
Eddie was that way with everyone. If people called, he did his best to help. I’m certain that when he passed 
 away, on October 16, 2019, the loss to the town of Forsyth was deeply felt. I know it was deeply felt in our family…not because of what Eddie might do for us, but for who he was. Eddie wasn’t just the guy who could get the job done, he was kind and caring, a friend to all who knew him, and a wonderful family man. He was very close to his children, Larry Hein and Kim Arani, his grandkids, Dalton Hein and Destiny Wallace, and of course, his loving wife, Pearl, of 52 years at the time of his passing. His family always knew that they were his priority.
away, on October 16, 2019, the loss to the town of Forsyth was deeply felt. I know it was deeply felt in our family…not because of what Eddie might do for us, but for who he was. Eddie wasn’t just the guy who could get the job done, he was kind and caring, a friend to all who knew him, and a wonderful family man. He was very close to his children, Larry Hein and Kim Arani, his grandkids, Dalton Hein and Destiny Wallace, and of course, his loving wife, Pearl, of 52 years at the time of his passing. His family always knew that they were his priority.
Eddie worked at Peabody coal mine in Colstrip, Montana until his retirement. He was well respected and loved by bosses and coworkers alike. They always knew that if Eddie Hein was on the job, he would give it his full 
 attention and full effort. He worked hard, and very much earned his retirement. Anyone who worked in mining can attest to that for sure. After his retirement, Eddie and Pearl loved to relax at their home in Forsyth, visit their daughter Kim and her husband Michael, in Texas, and I’m sure Eddie pitched in at Larry’s shop too. Unfortunately, all that was cut short by a stroke, and later the heart attack that took Eddie’s life in 2019. That was such a sad day for all of us. Today would have been Eddie’s 81st birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Eddie. We love and miss you very much.
attention and full effort. He worked hard, and very much earned his retirement. Anyone who worked in mining can attest to that for sure. After his retirement, Eddie and Pearl loved to relax at their home in Forsyth, visit their daughter Kim and her husband Michael, in Texas, and I’m sure Eddie pitched in at Larry’s shop too. Unfortunately, all that was cut short by a stroke, and later the heart attack that took Eddie’s life in 2019. That was such a sad day for all of us. Today would have been Eddie’s 81st birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Eddie. We love and miss you very much.

