History
 A truce in the context of war, doesn’t always mean a permanent end to the fighting. That is a fact that has often amazed me. If a war can be put “on hold” for a specific reason and a specified timeframe, why must the fighting then resume like the truce never happened? Nevertheless, resume it usually did. Such a truce happened between the German forces fighting the Russians forces in satellite regions like Lithuania and Belarus during World War I. The fighting raged in many different places at that time and continued through the winter of 1917.
A truce in the context of war, doesn’t always mean a permanent end to the fighting. That is a fact that has often amazed me. If a war can be put “on hold” for a specific reason and a specified timeframe, why must the fighting then resume like the truce never happened? Nevertheless, resume it usually did. Such a truce happened between the German forces fighting the Russians forces in satellite regions like Lithuania and Belarus during World War I. The fighting raged in many different places at that time and continued through the winter of 1917.
The intense fighting throughout the heavily forested region and had an unexpected side effect. Any time humans move into an area, the animal  population instinctively moves deeper into wilderness areas where there is less interaction with people, but when the winter is harsh and food becomes scarce, the animals can become as desperate as the humans. In that particular area at that particular time, the Russian wolves were starving. Any prey they might have been able to hunt had vacated because of the intense fighting, and so they had resorted to taking the bodies of the fallen soldiers for food. When there wasn’t enough of that, they began to actively hunt the soldiers, so now the soldiers of the Russian and the German armies had a whole new enemy, and this one could not be reasoned with.
population instinctively moves deeper into wilderness areas where there is less interaction with people, but when the winter is harsh and food becomes scarce, the animals can become as desperate as the humans. In that particular area at that particular time, the Russian wolves were starving. Any prey they might have been able to hunt had vacated because of the intense fighting, and so they had resorted to taking the bodies of the fallen soldiers for food. When there wasn’t enough of that, they began to actively hunt the soldiers, so now the soldiers of the Russian and the German armies had a whole new enemy, and this one could not be reasoned with.
The wolves had progressed from raiding villages to taking corpses to accosting groups of soldiers outright, so  the two armies mutually decided that it was necessary to call a truce so they could rid the area of the unexpected mutual enemy…roving bands of gigantic Russian wolves. They were genuinely in fear for their lives. Wolves often attack in the dark and go for the weakest link or when people are sleeping. It became obvious that this would be a fight to the end…of one or the other…man or beast. So, both armies agreed to a temporary truce and went on a joint campaign of destruction. The wolves could not be allowed to stay, for the sake of anyone in the area. The two armies slew hundreds of wolves, and then simply resumed their fight. How very strange that seems to me, but I guess it probably wasn’t up to the soldiers to walk away from the war.
the two armies mutually decided that it was necessary to call a truce so they could rid the area of the unexpected mutual enemy…roving bands of gigantic Russian wolves. They were genuinely in fear for their lives. Wolves often attack in the dark and go for the weakest link or when people are sleeping. It became obvious that this would be a fight to the end…of one or the other…man or beast. So, both armies agreed to a temporary truce and went on a joint campaign of destruction. The wolves could not be allowed to stay, for the sake of anyone in the area. The two armies slew hundreds of wolves, and then simply resumed their fight. How very strange that seems to me, but I guess it probably wasn’t up to the soldiers to walk away from the war.

 President James Buchanan was the only bachelor president of the United States, and in the absence of a first lady, his niece, Harriet Lane acted as First Lady for him. Lane was born on May 9, 1830, in Stony Batter, Pennsylvania. Her mother died when she was nine, her father when she was 11, and the orphaned girl was remanded to the custody of her mother’s brother, the future President Buchanan. He oversaw the remainder of her childhood, sending her to a prestigious private school in Washington while he was a Senator. Not only was it very unusual for a president not to have a wife, but Buchanan’s niece was only 27 years old when she was acting as first lady. For the wife of a president, that would be a big enough job, but for a young single woman, who may have never hosted a party, much less such large events, that was a big undertaking. Nevertheless, Harriet Lane was not just any young woman. During her time as First Lady, she was considered the greatest First Lady ever. Many would compare her to Jaqueline Kennedy, had they been of similar eras.
President James Buchanan was the only bachelor president of the United States, and in the absence of a first lady, his niece, Harriet Lane acted as First Lady for him. Lane was born on May 9, 1830, in Stony Batter, Pennsylvania. Her mother died when she was nine, her father when she was 11, and the orphaned girl was remanded to the custody of her mother’s brother, the future President Buchanan. He oversaw the remainder of her childhood, sending her to a prestigious private school in Washington while he was a Senator. Not only was it very unusual for a president not to have a wife, but Buchanan’s niece was only 27 years old when she was acting as first lady. For the wife of a president, that would be a big enough job, but for a young single woman, who may have never hosted a party, much less such large events, that was a big undertaking. Nevertheless, Harriet Lane was not just any young woman. During her time as First Lady, she was considered the greatest First Lady ever. Many would compare her to Jaqueline Kennedy, had they been of similar eras.
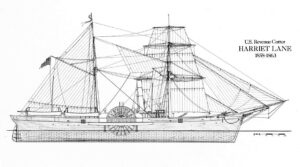
The work Harriet Lane did as First Lady also earned her the honor of having several ships named after her. In 1859, the United States Revenue Cutter Service named a revenue cutter USRC Harriet Lane. The outbreak of the Civil War, saw USRC Harriet Lane as a ship of the United States Navy and later the Confederate States Navy. The cutter was christened and entered the water for the Revenue Service in 1859 out of New York City. It saw action during the Civil War at Fort Sumter, New Orleans; Galveston, Texas; and Virginia Point. She became a ship for the Confederacy when the Confederate Navy captured her in 1863. The ship was converted to mercantile service. Then the Union forces recaptured her at the end of war. The war was not easy on USRC Harriet Lane, and so the US Navy declared the ship unfit for service and sold her. New owners out of Philadelphia renamed her Elliot Ritchie. Her crew abandoned her at sea in 1881. It was not really a very fitting end for a ship with such stately beginnings.
USRC Harriet Lane measured 177.5 feet long, 30.5 feet wide and 12 feet from the bottom of the hull to the main deck. She had a double-right-angled marine engine with two side paddles, supported by two masts. The entire ship was sheathed and fastened with copper. Her initial armaments were light guns, however after joining the West Gulf Squadron her firepower was upgraded to one four-inch rifled Parrott gun to the forecastle, one nine-inch Dahlgren gun before the first mast, two eight-inch Dahlgren Columbiads and two twenty-four-pound brass Howitzers. Her crew of 95 were also issued small arms. In August 1861, in what would likely be her most famous battle, the Harriet Lane, Monticello, and Pawnee were sent on a sortie from Hampton Roads, Virginia, to blockade runners working in the area. While off the Hatteras they also participated in the first combined arms operation of the Civil War: an amphibious landing to take Fort Hatteras and Fort Clark.
As for the real Harriet Lane, following her time as First Lady, she went to England for a while. During her time in England, Sir Fitzroy Kelly, then Prime Minister Palmerston’s attorney general, proposed marriage to her. Queen Victoria was strongly in favor of this match, as it would keep Lane in England. She was well liked in England and considered an asset. Lane considered the advantages of a number of bachelors. Her uncle cautioned Lane against “rushing precipitately into matrimonial connections.” He found most of her potential suitors “pleasant but dreadfully troublesome.” Lane eventually married Baltimore banker Henry Elliott Johnston at the age of 36. They had two sons, but between 1867 and 1885, her uncle, her husband, and her children had all died. She was alone again.
In 1895, Harriet wrote her will. She lived another eight years, during which the country’s general prosperity greatly increased the value of her estate. In 1899, she amended her will, directing that a school building be constructed on the grounds of the Washington National Cathedral property and asked that it be called the Lane-Johnston Building “to the end that the family names of my husband and myself may be associated with the bequest made in loving memory of our sons.” A codicil of 1903 increased her gift by one third, but said that 
 only half the total was to be spent on the building. The remainder was “specially to provide for the free maintenance, education and training of choirboys, primarily those in service of the Cathedral.” This bequest founded the prestigious boys’ school that today is called Saint Albans School, which opened in October 1909. Harriet Lane-Johnston died of cancer on July 3, 1903, in Narragansett, Rhode Island.
only half the total was to be spent on the building. The remainder was “specially to provide for the free maintenance, education and training of choirboys, primarily those in service of the Cathedral.” This bequest founded the prestigious boys’ school that today is called Saint Albans School, which opened in October 1909. Harriet Lane-Johnston died of cancer on July 3, 1903, in Narragansett, Rhode Island.
 As nations prepare for war, they must also prepare the weapons of warfare. These days, and really since airplanes became reliable enough to be used in war, manufacturers have been building better and better airplanes for war. The Wright brothers, Wilber and Orville made the first airplane, which they successfully flew in 1903. Planes were first used in war in 1911, but it was in World War I, 1914-1918, that their use became commonplace. Since then, we have seen an avalanche of progress is the types and capabilities of planes.
As nations prepare for war, they must also prepare the weapons of warfare. These days, and really since airplanes became reliable enough to be used in war, manufacturers have been building better and better airplanes for war. The Wright brothers, Wilber and Orville made the first airplane, which they successfully flew in 1903. Planes were first used in war in 1911, but it was in World War I, 1914-1918, that their use became commonplace. Since then, we have seen an avalanche of progress is the types and capabilities of planes.
For me, there is no greater warplane than the B-17, but I suppose I am a bit biased because my dad served on a B-17 during World War II. That mkes me very partial to the B-17. It really was a Flying Fortress, and it was that fortress that brought my dad back home. In my book, that makes it the greatest plane ever.
During World War II, the United States had the B-17, otherwise known as the Flying Fortress…among other planes, of course. There was a plane used by Britain, that would have been the similar, to a degree to the abilities to the B-17. The Lancaster was a heavy bomber “workhorse” of a plane. When compared to the B-17, it could carry a heavier payload and fly further than the B-17. The B-17 had higher flight ceiling and better defensive firepower. Speed was about even. Those things are important, but when it came to survivability, the B-17 was the better plane in that it was far easier to bail out of than the Lancaster, meaning that the crew of a plane that was going down would really hope it  was a B-17. Only 15% of shot down crewmen survived from the Lancaster, while it was around 50% for B-17s. The Lancaster bomber had only one emergency exit…at the front of the aircraft, as opposed to four (counting the bomb bays) for the B-17.
was a B-17. Only 15% of shot down crewmen survived from the Lancaster, while it was around 50% for B-17s. The Lancaster bomber had only one emergency exit…at the front of the aircraft, as opposed to four (counting the bomb bays) for the B-17.
Both of these planes were amazing weapons of war. They were just developed, designed, and built by different companies, and different countries. They served somewhat different purposes, but they were both designed to end the murderous Axis of Evil nations, of which Hitler’s Third Reich and Japan’s evil empire were a huge part. These planes were different, but both were on the side of good and not evil. I think that I am just glad they were on the same side of the war.
 In 1998, two Argentine mountaineers climbing Mount Tupungato, which is about 60 miles west-southwest of Mendoza, and about 50 miles east of Santiago, made a strange discovery emerging from the glacial ice. Upon inspection, the “discovery” turned out to be the wreckage of a Rolls-Royce Merlin aircraft engine, along with twisted pieces of metal and shreds of clothing. It didn’t take long to realize that a plane had crashed here, but when and how did that plane crash at an elevation of 15,000 feet, into the Tupungato Glacier.
In 1998, two Argentine mountaineers climbing Mount Tupungato, which is about 60 miles west-southwest of Mendoza, and about 50 miles east of Santiago, made a strange discovery emerging from the glacial ice. Upon inspection, the “discovery” turned out to be the wreckage of a Rolls-Royce Merlin aircraft engine, along with twisted pieces of metal and shreds of clothing. It didn’t take long to realize that a plane had crashed here, but when and how did that plane crash at an elevation of 15,000 feet, into the Tupungato Glacier.
The find set off an Argentine Army expedition in 2000, during which additional wreckage was found, including a propeller and wheels (one of which had an intact and still inflated tire). The expedition also noted that the wreckage was well localized, which is indicative of a head-on impact with the ground, ruling out a mid-air explosion. In addition to the plane, the expedition found human remains, including three torsos, a foot in an ankle boot, and a manicured hand.
On August 2, 1947, a plane known as the Star Dust, operated by British South American Airlines, took off from Buenos Aires, Argentina, headed for Santiago, Chile. It never made it. After 51 years, the fate of the Star Dust was finally known, but how did it happen? A recovered propeller showed that the engine had been running at  near-cruising speed at the time of the impact. The planes wheels were in a retracted state, meaning that the plane wasn’t coming in for a landing, emergency or planned. This was a controlled flight into terrain, whether planned or unplanned. It was determined that during the final portion of Star Dust’s flight, there would have been heavy clouds blocking the visibility to the ground. It is thought that because of the cloud cover and the resulting absence of visual sightings, that a large navigational error could have been made as the aircraft flew through the jet stream. This would not have been understood in 1947. High-altitude winds can blow at high speed in directions different from those of winds observed at ground level. If the airliner, which had to cross the Andes Mountain Range at 24,000 feet, had entered the jet-stream zone, which in this area normally blows from the west and south-west, resulting in the aircraft encountering a headwind, this would have significantly decreased the aircraft’s ground speed.
near-cruising speed at the time of the impact. The planes wheels were in a retracted state, meaning that the plane wasn’t coming in for a landing, emergency or planned. This was a controlled flight into terrain, whether planned or unplanned. It was determined that during the final portion of Star Dust’s flight, there would have been heavy clouds blocking the visibility to the ground. It is thought that because of the cloud cover and the resulting absence of visual sightings, that a large navigational error could have been made as the aircraft flew through the jet stream. This would not have been understood in 1947. High-altitude winds can blow at high speed in directions different from those of winds observed at ground level. If the airliner, which had to cross the Andes Mountain Range at 24,000 feet, had entered the jet-stream zone, which in this area normally blows from the west and south-west, resulting in the aircraft encountering a headwind, this would have significantly decreased the aircraft’s ground speed.
If the crew thought their airspeed was faster than it actually was, the crew may have deduced that they had already safely crossed the Andes, and so commenced their descent to Santiago, when in reality they were still a considerable distance to the east-north-east and were approaching the cloud-shrouded Tupungato Glacier at high speed. That theory is not well received by some BSAA pilots, who have expressed skepticism. They were convinced that Cook would not have started his descent without a positive indication that he had crossed the  mountains, they have suggested that strong winds may have brought down the craft in some other way. One of the pilots recalled that “we had all been warned not to enter cloud over the mountains as the turbulence and icing posed too great a threat.”
mountains, they have suggested that strong winds may have brought down the craft in some other way. One of the pilots recalled that “we had all been warned not to enter cloud over the mountains as the turbulence and icing posed too great a threat.”
A 2000 Argentine Air Force investigation cleared Captain Cook of any blame, concluding that the crash had resulted from “a heavy snowstorm” and “very cloudy weather,” as a result of which the crew “were unable to correct their positioning.” By 2002, the bodies of five of the eight British victims had been identified through DNA testing.

 Over the course of American history, several presidents have been assassinated, and several others have survived attempted assassinations. Some were quickly treated, and others were not where the would-be assassin thought they were going to be. Still, Andrew Jackson, the seventh US president better known as “Old Hickory” was, without doubt, the most amazing one. and for good reason, as one would-be assassin found out.
Over the course of American history, several presidents have been assassinated, and several others have survived attempted assassinations. Some were quickly treated, and others were not where the would-be assassin thought they were going to be. Still, Andrew Jackson, the seventh US president better known as “Old Hickory” was, without doubt, the most amazing one. and for good reason, as one would-be assassin found out.
On January 30, 1835, Richard Lawrence came up to the 67-year-old Jackson, as he left a congressional funeral and pulled a pistol on him. I’m sure he thought a 67-year-old man was going to be an easy target, but when he pulled the trigger, the gun misfired. While having his gun misfire was…inconvenient, Lawrence also found out that a 67-year-old man is not necessarily a weak, old man. A furious Jackson began beating the man viciously with his cane in retaliation. Then, while trying to dodge the cane wielded by Jackson, Lawrence managed to pull a second gun from his jacket and pull the trigger. I don’t know how, but Lawrence had to be either the unluckiest assassin, or a totally inept gunman, because the second gun also jammed. By this point, Jackson’s aides were able to wrestle Lawrence away and into custody. Jackson was unharmed. 
Jackson became convinced that the attempt was made at the behest of his political enemies, even though all evidence pointed to Lawrence being a mentally unstable lone wolf. I rather think I might agree with Jackson on this one, because politics can be a deadly career to get into. Jackson spent the rest of his presidency worried about another attack, while his vice president, Martin Van Buren, started carrying two loaded pistols with him into the Senate.
You can take away any opinion on this matter that you want to, but I have my own. I find it amazing that Jackon had the wherewithal to “pull” his cane on his would-be assassin, but how often to you see two different guns misfire in the commission of the same assassination. I see that situation as nothing but God. Jackson was the recipient of a double miracle. If either of those gun shots would have connected to their mark, he would surely have been dead. This was not a sniper shooter, but rather, a close-range shooter, and would have meant instant death. No, this man was divinely protected, and that’s all there is to it.
 While most people look back on their childhood with fond memories, most of us would say our childhood was probably typical for the era we lived in. Of course, not every childhood is perfect, and some can be absolutely horrible. President Abraham Lincoln was born on February 12, 1890, and spent his childhood years in Kentucky and Indiana. He personally summed up his childhood days on the frontier as “the short and simple annals of the poor.” While that is how Lincoln saw his childhood, he wasn’t the only one in that situation. The hardships he endured there as a child weren’t unique. Frontier life was harsh for most families in the early 1800s. Living and working on the frontier was hard work. In fact, sometimes the people worked as hard as their oxen and horses. According to Lincoln, his earliest memories were of life on the farm in Kentucky where he moved in 1811 with his parents, Thomas and Nancy, and sister, Sarah. She was four years old, and Abraham was two years old. His parents had been married five years.
While most people look back on their childhood with fond memories, most of us would say our childhood was probably typical for the era we lived in. Of course, not every childhood is perfect, and some can be absolutely horrible. President Abraham Lincoln was born on February 12, 1890, and spent his childhood years in Kentucky and Indiana. He personally summed up his childhood days on the frontier as “the short and simple annals of the poor.” While that is how Lincoln saw his childhood, he wasn’t the only one in that situation. The hardships he endured there as a child weren’t unique. Frontier life was harsh for most families in the early 1800s. Living and working on the frontier was hard work. In fact, sometimes the people worked as hard as their oxen and horses. According to Lincoln, his earliest memories were of life on the farm in Kentucky where he moved in 1811 with his parents, Thomas and Nancy, and sister, Sarah. She was four years old, and Abraham was two years old. His parents had been married five years.
At Knob Creek, in Kentucky, the Lincoln family lived in a one-room cabin with a dirt floor. The place was very similar to the place where Lincoln was born a mere nine miles way near Hodgenville. Steep, heavily wooded hills rose on each side of the home. Nevertheless, things were “looking up” on the Knob Creek farm, because while the place was leased, Lincoln’s father planted corn and pumpkins on wide fields with rich soil on the 30-acre farm. From the little dirt-floor cabin on the road from Louisville to Nashville, the Lincoln family watched as the “world passed” by. Pioneers with fully loaded wagons, peddlers, local politicians, slaves, missionaries and soldiers returning from the War of 1812.
Abraham’s dad, Thomas Lincoln, who was stern and often domineering, put his son to work before he turned seven. Of course, if you ask me, seven-year-olds can help out, provided that they aren’t mistreated in the process. Abraham filled the wood box, brought water from the creek, weeded the garden, gathered grapes for wine and jelly, picked persimmons for beer making and planted pumpkin seeds.
Lincoln didn’t have many opportunities to go to school, as was common in those days in rural Kentucky. For the most part he was self-taught. Mostly, he and his sister sporadically attended ABC schools—so-called “blab” schools in which students repeated their teacher’s oral lessons aloud. Usually barefoot, Lincoln walked to the one-room schoolhouse, “a little log room about 15 feet square, with a fireplace at one side.”
Two years later, Abraham’s mother, Nancy Lincoln died in the remote wilderness—the first of Lincoln’s many family tragedies. Nancy was a good mother, and her passing was heartbreaking for the Lincoln children. Apparently, she had consumed milk tainted when cows ate poisonous white snakeroot…although, some believed the cause of death was tuberculosis. She was just 34 years old. Eleven-year-old Sarah now became the woman of the house, and all domestic duties fell to her. The Lincoln children’s lives were worse than ever. That winter, the motherless children and their 19-year-old orphan cousin lived dismally in that place.
It didn’t take Thomas long to decide that he needed a new wife, so Thomas Lincoln traveled to Elizabethtown, Kentucky, where he proposed to widow Sarah Bush Johnston, whom he had known since childhood. She accepted, provided Lincoln paid off her debts. On December 2, 1819, Thomas and Sarah married and later returned to Little Pigeon Creek, accompanied by her three children: Elizabeth, 13; Matilda, 10; and John, 9. Thomas’s new wife brought along furniture (including a walnut bureau valued at $50), cooking utensils and comfortable bedding…astonishing luxuries for her new stepchildren. She also brought several books, including the Bible and Aesop’s Fables, which she gifted to Abe. Things were looking up again in the Lincoln household. At his wife’s insistence, Thomas Lincoln installed a cabin floor and plastered cracks between logs. Instead of cornhusks, Abraham and his sister slept on a feather bed. The cramped conditions were no match for the love Sarah brught with her, and the family thrived. To make him look “more human,” Lincoln’s stepmother dressed up the poorly clad Abraham.
On the farm, Lincoln became skillful with an ax. But Thomas didn’t see the need for the reading his son loved.  He wanted him to learn carpentry, but Abraham wasn’t interested, and the matter brought tension to the relationship. Sometimes the illiterate Thomas even reprimanded Abraham for reading instead of doing farm chores. Thankfully, Sarah Bush Lincoln persuaded her husband to allow their son to read and study. “At first, he was not easily reconciled to it,” she recalled, “but finally he too seemed willing to encourage him to a certain extent.” The bond between stepmother and stepson grew. Sarah Bush Lincoln recalled years later, “Abe was the best boy I ever saw.” I think we would a have to agree, he was not just a good boy, but a great man and a great president.
He wanted him to learn carpentry, but Abraham wasn’t interested, and the matter brought tension to the relationship. Sometimes the illiterate Thomas even reprimanded Abraham for reading instead of doing farm chores. Thankfully, Sarah Bush Lincoln persuaded her husband to allow their son to read and study. “At first, he was not easily reconciled to it,” she recalled, “but finally he too seemed willing to encourage him to a certain extent.” The bond between stepmother and stepson grew. Sarah Bush Lincoln recalled years later, “Abe was the best boy I ever saw.” I think we would a have to agree, he was not just a good boy, but a great man and a great president.
 The USCGC Blackthorn (WLB-391) was a 180-foot seagoing buoy tender for the US Coast Guard. A buoy tender is a type of vessel used to maintain and replace navigational buoys. Prior to navigational buoys, ships might run into rocks, small almost submerged islands, or coral reefs. It would be nice if every underwater danger could have a lighthouse, but that just isn’t feasible. Buoys, on the other hand, and markers serve to direct the operator of the water vessels on the safe course to take. They warn the operator of the underlying dangers in the waterways. Navigation buoys and markers are also effective navigation aid in directing the water vessel operator on the best route to use. They aid in determining the safest way through the waters.
The USCGC Blackthorn (WLB-391) was a 180-foot seagoing buoy tender for the US Coast Guard. A buoy tender is a type of vessel used to maintain and replace navigational buoys. Prior to navigational buoys, ships might run into rocks, small almost submerged islands, or coral reefs. It would be nice if every underwater danger could have a lighthouse, but that just isn’t feasible. Buoys, on the other hand, and markers serve to direct the operator of the water vessels on the safe course to take. They warn the operator of the underlying dangers in the waterways. Navigation buoys and markers are also effective navigation aid in directing the water vessel operator on the best route to use. They aid in determining the safest way through the waters.
The Blackthorn was one of 39 original 180-foot seagoing buoy tenders built between 1942-1944. All but one of the original tenders, USCGC Ironwood (WLB-297), were built in Duluth, Minnesota, which makes me wonder if my Uncle Bill Spencer, or his sisters, Laura Fredrick and Ruth Wolfe might have worked on it. Blackthorn’s preliminary design was completed by the United States Lighthouse Service and the final design was produced by Marine Iron and Shipbuilding Corporation in Duluth. On May 21, 1943, the keel was laid, the vessel was launched on July 20, 1943, and commissioned on March 27, 1944. The original cost for the hull and machinery was $876,403.
The Blackthorn was initially assigned to the Great Lakes for ice-breaking duties, but was resigned to San Pedro, California after just a few months. For several years the vessel served in San Pedro and then it was moved to the gulf coast region to serve in Mobile, Alabama. From there it was transferred to Galveston, Texas for the final years of its service until it was involved in an accident.
In 1979-1980, Blackthorn underwent a major overhaul in Tampa, Florida. The work was finished and on January 28, 1980, while leaving Tampa Bay after the completion of the overhaul, she collided with the tanker SS Capricorn near the Tampa Bay Sunshine Skyway Bridge. The Blackthorn capsized resulting in the deaths of 23 crew members. The cutter was raised for the investigation, but ultimately, instead of fixing it, Blackthorn was scuttled in the Gulf of Mexico after the investigation was complete. She is currently serving as an artificial reef for recreational diving and fishing.
 I can imagine a number of nicknames a stagecoach driver might want to have, one that no one would want to have. George Green was one of the most popular stagecoach drivers in the Sierra Mountain Range, driving for the Pioneer Stage Company between Placerville, California and Virginia City, Nevada in the 1860s. George had the nickname “Baldy” because of the sparse amount of hair he had on the top of his head. It was not the nickname “Baldy” that George would learn to hate, however. George was known for his good looks, standing about six feet tall with a large full mustache, but it was not his good looks or large mustache that earned him the nickname he hated either.
I can imagine a number of nicknames a stagecoach driver might want to have, one that no one would want to have. George Green was one of the most popular stagecoach drivers in the Sierra Mountain Range, driving for the Pioneer Stage Company between Placerville, California and Virginia City, Nevada in the 1860s. George had the nickname “Baldy” because of the sparse amount of hair he had on the top of his head. It was not the nickname “Baldy” that George would learn to hate, however. George was known for his good looks, standing about six feet tall with a large full mustache, but it was not his good looks or large mustache that earned him the nickname he hated either.
During his days as a stagecoach driver, Green drove many famous people including Ben Holladay, Horace Greeley, and Vice-President Schuyler Colfax. Nevertheless, Green was apparently not a very scary driver. On May 22, 1865, near Silver City, Nevada, three men robbed his stage of $10,000 in gold and greenbacks. I guess word must have gotten around, because more robberies followed that first one, and not only would the robbers not leave him alone, but the robberies were big news and the stories sold lots of newspapers. The Territorial Enterprise commented that Green had narrowly escaped scalping, and someone placed a sign near the robbery location saying, “Wells-Fargo Distributing Office, Baldy Green, Mgr.”
Green just couldn’t catch a break. Two years later his stage was robbed twice on successive days, and following another robbery on June 10, 1868, Virginia City’s Territorial Enterprise stated: “Baldy Green is exceedingly unlucky, as the road agents appear to have singled him out as their special man to halt and plunder, and they always come at him with shotguns.” Two more robberies occurred the same month, and you might say that the  writing was on the wall. No one came right out an accused Green of being involved, but it had come to the point that they couldn’t take the risk of keeping him on anymore. Green was fired. Whether he was guilty or not, he was the driver most likely to be robbed. While he was never given that nickname, it is rather a fitting one.
writing was on the wall. No one came right out an accused Green of being involved, but it had come to the point that they couldn’t take the risk of keeping him on anymore. Green was fired. Whether he was guilty or not, he was the driver most likely to be robbed. While he was never given that nickname, it is rather a fitting one.
Green didn’t let that stop him, however. He then went to hauling freight in Pioche, Nevada. I guess either he figured out how to stop the robberies, or freight haulers were less likely to be robbed. Either way, he managed to have more success in that trade that the stagecoach career. Later on, he even served as Justice of the Peace in Humboldt County, Nevada.
 Most people, these days, don’t necessarily know who William Cullen is, but historically speaking, he is a very important man. Born April 15, 1710, in Hamilton, Lanarkshire, the son of William Cullen…a lawyer and Elizabeth Roberton of Whistlebury. Cullen was a Scottish physician, chemist and agriculturalist, as well as a professor at the Edinburgh Medical School, but these things would not be the defining accomplishment of his life. Cullen saw a need for something, that many people knew they needed, but no one knew how to get it.
Most people, these days, don’t necessarily know who William Cullen is, but historically speaking, he is a very important man. Born April 15, 1710, in Hamilton, Lanarkshire, the son of William Cullen…a lawyer and Elizabeth Roberton of Whistlebury. Cullen was a Scottish physician, chemist and agriculturalist, as well as a professor at the Edinburgh Medical School, but these things would not be the defining accomplishment of his life. Cullen saw a need for something, that many people knew they needed, but no one knew how to get it.
Years ago, towns had an icehouse. Snow and ice were stored in a cellar in an effort to keep them frozen for use by the townspeople. Then the icehouse owner would bring ice to people, and it would basically be kept in a “cooler” so food could be kept cold for a while. It was an imperfect system, but it was all they had. Cullen could see that something better was needed. I’m sure he saw the diseases that came from spoiled food and maybe even deaths from that food. That got him thinking.
After Cullen completed his education at the University of Glasgow and the University of Edinburgh, he started his formal career. His field of study and subsequent career in medicine and after completing the studies, he started in that career, but he was also interested in working on a scientific basis to invent different things. That was when Cullen envisioned and then invented an artificial refrigerator which was used manually to save many things from getting wasted.
These days, the refrigerator is an appliance which can be found in almost every house, and it is one of the most used appliances. It comes in different shapes and in different sizes. Normally, it is made up in “the form of two compartments and one of them is insulated thermally, while the other compartment consists of a heat pump and its important function is the transfer of heat. This transfer is done to manage heat environment.” I don’t presume to understand how all that works. I just know that my food stays the temperature it needs to be to either freeze it of just keep it cold.
In 1741 he married Anne (or Anna) Johnstone, who died 1786. He was father to Robert Cullen and Henry Cullen, who became a physician. Cullen’s eldest son Robert became a Scottish judge in 1796 under the title of Lord Cullen, and later Baron Cullen, and was known for his powers of mimicry. Cullen died in Edinburgh, Scotland on February 5, 1790. He was almost 80 years of age at the time of his death.

 The world was embarking on the industrial revolution, and it was during World War I that we found out just how much of a difference that industrial revolution could make in wartime. From the introduction of airplanes to the use of tanks and railway guns on the battlefield, soldiers had to contend not only with each other but with the productions of the factory floor. Even the recent invention of the telephone made its way into battlefield units, where soldiers used it to convey orders or direct artillery fire.
The world was embarking on the industrial revolution, and it was during World War I that we found out just how much of a difference that industrial revolution could make in wartime. From the introduction of airplanes to the use of tanks and railway guns on the battlefield, soldiers had to contend not only with each other but with the productions of the factory floor. Even the recent invention of the telephone made its way into battlefield units, where soldiers used it to convey orders or direct artillery fire.
Nevertheless, there was one area where technology was not as “up to date” as it needed to be. The telephone while a great invention, was not as reliable as the commanders of Europe would have liked. I guess that anyone who has used a modern-day cellular phone can relate that. I’m sure that they could envision the need to arrange their operations, and they weren’t too sure the information was completely safe. So, they brainstormed alternatives in an attempt to improve combat communications. The leaders of World War I turned to a much older form of communication…the carrier pigeon.
Pigeons had been used for communication for many, many years. These unsung heroes of World War I, the carrier pigeons, used by both the Allied and Central Powers, helped assist their respective commanders with an accuracy and clarity unmatched by the modern technology. The National Archives holds a vast collection of messages that these feathered fighters delivered for American soldiers. Using these messages and the history of the carrier pigeon in battle, we can look at what hardship these fearless fowls endured and how their actions  saved American lives. One of the most impressive things about the war records of the carrier pigeons was how widely the birds were used. Their service as battlefield messengers is their most known use, and the pigeons found homes in every branch of service.
saved American lives. One of the most impressive things about the war records of the carrier pigeons was how widely the birds were used. Their service as battlefield messengers is their most known use, and the pigeons found homes in every branch of service.
The rudimentary airplanes of the embattled countries used pigeons to provide updates midair. Launched mid-mission, the birds would fly back to their coops and update ground commanders on what the pilots had observed. These strange update methods were born of the essential need for leaders to know what the battlefield looked like and what the enemy was doing in its own trenches. Planes flying over and pigeons bringing the information back quickly was the best way to stay ahead of the enemy. In addition, tanks carried the birds in order to relay the advance of individual units. Even after the introduction of the radio, pigeons were often the easiest way to help coordinate tank units without exposing the men to dangerous fire. Radios to be overheard. Of course, while it made the soldiers safer, the pigeons were not necessarily safer. Many of them didn’t make it back home, having been shot down and/or used for food for starving families. Still, without a radio set, the soldiers would have had to leave the relative safety of their tanks to relay or receive orders. These birds saved lives, even if it meant sacrificing their own. Their owners also saved lives by allowing their pigeons to be involved. They were a great asset to the war effort of more than one war.
The birds’ most effective use was on the front line, as they were brought forward with their armies to help update commanders and planners in the rear. When the birds were away from their home lofts, they stayed in mobile units, which were usually converted horse carriages or even double-decker buses. I’m sure it made a 
 strange sight. The mobile lofts were useful when the armies outpaced their established lines of communications or when the enemy disrupted communications lines for the telegraphs or telephones, as they often did during battle. While the other Allied powers were first to use birds, the United States did not lag far behind when we entered the fray. During the course of the war, many birds performed heroic deeds in the course of service and became heroes in their own rights.
strange sight. The mobile lofts were useful when the armies outpaced their established lines of communications or when the enemy disrupted communications lines for the telegraphs or telephones, as they often did during battle. While the other Allied powers were first to use birds, the United States did not lag far behind when we entered the fray. During the course of the war, many birds performed heroic deeds in the course of service and became heroes in their own rights.

