History
 In the movies about the old west, you often see a gun fight. If someone got shot, the procedure to get the bullet out, was…well, painful. When we think of an operation, we think of a person being under anesthesia, and completely asleep during the entire procedure. In reality, prior to March 30, 1842, people who had to have an operation, had better have a strong constitution, because the best a doctor could do for them was to have them bite down on a stick. Now, this didn’t reduce the pain, but I suppose it lessened the noise level of the scream that the doctor knew was coming. I’m sure that surgery was seriously the last resort, and even often delayed longer than it should have been, simply because of the pain involved.
In the movies about the old west, you often see a gun fight. If someone got shot, the procedure to get the bullet out, was…well, painful. When we think of an operation, we think of a person being under anesthesia, and completely asleep during the entire procedure. In reality, prior to March 30, 1842, people who had to have an operation, had better have a strong constitution, because the best a doctor could do for them was to have them bite down on a stick. Now, this didn’t reduce the pain, but I suppose it lessened the noise level of the scream that the doctor knew was coming. I’m sure that surgery was seriously the last resort, and even often delayed longer than it should have been, simply because of the pain involved.
Enter, Dr Crawford Williamson Long, an American surgeon and pharmacist. Long was a bright child, graduating from the local academy at 14 years old, and continuing on to the University of Georgia in Athens. In 1835, he received his Masters Degree. Then, he began studying at Transylvania College in the fall of 1836 in Lexington, Kentucky. Long studied under Benjamin Dudley, a revered surgeon. He observed and participated in many surgeries and noted the effects of operating without anesthesia. Long transferred to the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia after spending only a year at Transylvania College, and was introduced to some of the most cutting edge medical technology of the time. He received his MD degree at the University of Pennsylvania in 1839.
After an 18 month internship in New York, Dr Long returned to Georgia. He took over a rural medical practice in Jefferson, Georgia in 1841. After observing the same physiological effects with Diethyl Ether that Humphry Davy had described for nitrous oxide in 1800, he used Ether for the first time on March 30, 1842 to remove a tumor from the neck of a patient, James M. Venable. He administered Sulfuric Ether on a towel and simply had the patient inhale. He performed many other surgeries using this technique over the next few years. Then, he introduced the technique to his obstetrics practice as well. Long subsequently removed a second tumor from Venable and used Ether as an anesthetic in amputations and childbirth. While Long’s use of Ether continued for quite a while, he didn’t immediately publish his findings. The results of these trials were eventually published in 1849 in The Southern Medical and Surgical Journal. It was a major advancement in surgical procedures.
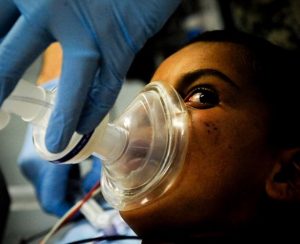 General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation. Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. Of course, Ether is no longer used, because of the dangerous side effects, but many other types of anesthesia have been developed since Ether was used. I can’t imagine just how awful it would be to have surgery without anesthesia, and I for one am glad that it was developed. My shoulder surgery would have been horrible, if it had to be done without my arm being completely numb with a newer form of medicine that kept it numb, and me comfortable all that day.
General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation. Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. Of course, Ether is no longer used, because of the dangerous side effects, but many other types of anesthesia have been developed since Ether was used. I can’t imagine just how awful it would be to have surgery without anesthesia, and I for one am glad that it was developed. My shoulder surgery would have been horrible, if it had to be done without my arm being completely numb with a newer form of medicine that kept it numb, and me comfortable all that day.

 Over the centuries, tornadoes have managed to wreak havoc on various areas of the world, not to mention the thousands of lives they have taken. With advancements in the early warning systems and on weather conditions, the deaths have decreased, but in 1920, no such systems existed. It was March 28, 1920…Palm Sunday, when at least 37 tornadoes, 31 of which were significant, raged across the Midwest and Deep South states. The tornadoes left more than 380 dead, as well as at least 1,215 injured. Many communities and outlying farmers alike were caught off guard as the storms moved to the northeast at speeds that reached over 60 miles per hour. Georgia saw most of the fatalities with over 200 deaths. Indiana had 56 deaths and Ohio had 55, while the other states saw fewer fatalities. Without ways to monitor the tornadoes, very little is known about many of the specific tornadoes that occurred.
Over the centuries, tornadoes have managed to wreak havoc on various areas of the world, not to mention the thousands of lives they have taken. With advancements in the early warning systems and on weather conditions, the deaths have decreased, but in 1920, no such systems existed. It was March 28, 1920…Palm Sunday, when at least 37 tornadoes, 31 of which were significant, raged across the Midwest and Deep South states. The tornadoes left more than 380 dead, as well as at least 1,215 injured. Many communities and outlying farmers alike were caught off guard as the storms moved to the northeast at speeds that reached over 60 miles per hour. Georgia saw most of the fatalities with over 200 deaths. Indiana had 56 deaths and Ohio had 55, while the other states saw fewer fatalities. Without ways to monitor the tornadoes, very little is known about many of the specific tornadoes that occurred.
Early in the morning of March 28th, severe thunderstorms began developing in Missouri, moving quickly to the northeast towards Chicago, Illinois. The first tornado injured five people 35 miles southeast of Springfield, Missouri, in Douglas County. This first tornado was a warning of things to come as the morning went on and the atmosphere began to destabilize, due to the abundance of sunshine that preceded the cold front in the warm sector, which covered the lower Great Lakes region extending southward, well past the Ohio River Valley. According to meteorologist and weather historian Charles Merlin Umpenhour, the climatic conditions on Palm Sunday 1920 were favorable for all the atmospheric ingredients to come together that were needed to create the classic setup for long-track tornadoes. The forecasting…or communications technology and public awareness about Severe Weather was nearly nonexistent in 1920. That technology would not begin for another 33 years, when the US Weather Bureau implemented its Public Watch.
The residents of the Great Lakes region and Ohio Valley areas, had as their only source of weather information, the rather vague forecasts that were issued in the local newspaper the day before or by word of mouth. The use of the word “tornado” was strictly prohibited in public weather forecasting until the 1950s because of the fear and panic it might cause. This policy would come under fire in the years to come especially after the Tri-State Tornado in 1925 that stands today as the deadliest tornado in American history…as it should have. It would be insane not to let the people know of such deadly weather, simply because someone might get scared. That really is the point of it. To “scare” people into action!! It saves lives.
Weather forecasters and the public alike in the Chicago, Dayton, Fort Wayne, Lansing, South Bend, and Toledo areas were unaware of the likelihood of a significant tornado outbreak that would follow a beautiful Palm Sunday afternoon. The weather maps in use in March 1920 showed a rather large and deep cyclone over northern Iowa, and they knew it would be moving across central Lower Michigan by nightfall with a cold front right behind it. Meteorologists knew rain showers, and very likely thundershowers, were a good possibility, but were unaware that the helicity (which is a property of a moving fluid which represents the potential for helical flow…or a flow which follows the pattern of a corkscrew to evolve. Helicity is proportional to the strength of the 
 flow, the amount of vertical wind shear, and the amount of turning in the flow known as a vorticity), the lifted index, and upper level winds which were being guided by a strong jet stream with a probable negative tilt. When all that is put together, it creates conditions that are favorable for the development of tornadoes, and thereby, a seriously dangerous situation. Had the people known all that in 1920, perhaps most of the lives lost, could have been saved.
flow, the amount of vertical wind shear, and the amount of turning in the flow known as a vorticity), the lifted index, and upper level winds which were being guided by a strong jet stream with a probable negative tilt. When all that is put together, it creates conditions that are favorable for the development of tornadoes, and thereby, a seriously dangerous situation. Had the people known all that in 1920, perhaps most of the lives lost, could have been saved.
 Most people in the United States consider driving a car a right, but in reality it is a privilege, and must be earned. At 15 a child may obtain a permit to drive with a licensed driver by taking a written exam. Then in a year, or at age 16, they have to take a written and driving test to get a license. The driving test can be waived if they have completed driver’s education. The exams are pretty basic, and in this country, most people pass the test on the first try, and if not on the first try, most pass on the second try. The first driving test was administered in 1899 Chicago and New York City. Massachusetts and Missouri were the first US states to require a license for driving a motor vehicle in 1903. Pennsylvania’s 1909 licensing laws were the first to give an age restriction “18 years of age” and the first state to allow 16 year olds to drive, if they were accompanied by a licensed driver, was Connecticut in 1921. I’m sure that prior to these times most people didn’t have one of the new fangled automobiles, so a license was not needed.
Most people in the United States consider driving a car a right, but in reality it is a privilege, and must be earned. At 15 a child may obtain a permit to drive with a licensed driver by taking a written exam. Then in a year, or at age 16, they have to take a written and driving test to get a license. The driving test can be waived if they have completed driver’s education. The exams are pretty basic, and in this country, most people pass the test on the first try, and if not on the first try, most pass on the second try. The first driving test was administered in 1899 Chicago and New York City. Massachusetts and Missouri were the first US states to require a license for driving a motor vehicle in 1903. Pennsylvania’s 1909 licensing laws were the first to give an age restriction “18 years of age” and the first state to allow 16 year olds to drive, if they were accompanied by a licensed driver, was Connecticut in 1921. I’m sure that prior to these times most people didn’t have one of the new fangled automobiles, so a license was not needed.
The United Kingdom made the move to require testing on March 24, 1934, and the requirements were a little different than in the United States. The test must be taken in order to receive a full license, and also to add full entitlements to an existing license. The test varies, depending on the class of vehicle that is to be driven, and is administered by the Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency or DVSA, in Great Britain and the Driver and Vehicle Agency, or DVA in Ireland. Those parts of the program seem to be just like here in the United States, but from there on out, there is a pretty big difference. In the United Kingdom, the minimum age at which one can take a driving test is currently 16 for mopeds and 17 for cars, with an exception allowed at 16 for those on the higher/enhanced rate of the mobility component. In addition to a driving licence, a CBT certificate may be required before a moped or motorcycle is ridden.
In Great Britain around 1.6 million people take the practical car test per year. Approximately 43% of those who take it pass the test, and the theory test has a pass rate of about 51.6%. Now I don’t know what you think, but I think the kids in this country would be pretty upset if only half of those who took the test got to actually drive  legally. Then again, maybe kids would study harder for the test in that case. I can’t tell you how many times I have heard a kid say, “It’s all common sense.” My thought is, “What wealth of knowledge about driving a car is a 15 year old, who has never driven one, going to have.” The answer is obvious…to the parents anyway. If they don’t study, they will likely not pass, but what of the people of Great Britain and Ireland. They know the test is difficult. My guess is that they do study, but that the test is a much more advanced version than those in the United States. Maybe it’s because they want it to be more than just common sense. I’m not saying our tests are too easy…but it’s something to consider when you look at the statistics.
legally. Then again, maybe kids would study harder for the test in that case. I can’t tell you how many times I have heard a kid say, “It’s all common sense.” My thought is, “What wealth of knowledge about driving a car is a 15 year old, who has never driven one, going to have.” The answer is obvious…to the parents anyway. If they don’t study, they will likely not pass, but what of the people of Great Britain and Ireland. They know the test is difficult. My guess is that they do study, but that the test is a much more advanced version than those in the United States. Maybe it’s because they want it to be more than just common sense. I’m not saying our tests are too easy…but it’s something to consider when you look at the statistics.
 Fire safety measures have vastly improved over the years, but in the early 1900s, no such safety measures existed. That would prove deadly on March 25, 1911 in New York City. People didn’t really know about materials that were more flammable, other than wood. Nevertheless, wood was the main material used in buildings, and in fact, still is today. The Triangle Shirtwaist Company factory was owned by Max Blanck and Isaac Harris. It was located in the top three floors of the Asch Building, on the corner of Greene Street and Washington Place, in Manhattan. These days that is not really a place we would expect to see a factory…much less a sweatshop, but the Triangle Shirtwaist Company’s factory was a true sweatshop. They employed mostly young immigrant women who worked in a cramped space at lines of sewing machines. Nearly all the workers were teenaged girls who did not speak English and made only about $15 per week working 12 hours a day, every day.
Fire safety measures have vastly improved over the years, but in the early 1900s, no such safety measures existed. That would prove deadly on March 25, 1911 in New York City. People didn’t really know about materials that were more flammable, other than wood. Nevertheless, wood was the main material used in buildings, and in fact, still is today. The Triangle Shirtwaist Company factory was owned by Max Blanck and Isaac Harris. It was located in the top three floors of the Asch Building, on the corner of Greene Street and Washington Place, in Manhattan. These days that is not really a place we would expect to see a factory…much less a sweatshop, but the Triangle Shirtwaist Company’s factory was a true sweatshop. They employed mostly young immigrant women who worked in a cramped space at lines of sewing machines. Nearly all the workers were teenaged girls who did not speak English and made only about $15 per week working 12 hours a day, every day.
In 1911, the Asch Building had four elevators with access to the factory floors, but only one was fully operational and the workers had to file down a long, narrow corridor in order to reach it. There were also two stairways down to the street, but one was locked from the outside to prevent stealing and the door of the other only opened inward. The fire escape was so narrow that it would have taken hours for all the workers to use it, even in the best of circumstances…in an emergency, it was almost useless. Pretty much everyone knew about the danger of fire in factories like the Triangle Shirtwaist Company factory, but high levels of corruption in both the garment industry and city government ensured that no useful precautions were taken to prevent fires. The  problem was that making the factories safe cost money, and dug into the profits, so the owners didn’t want to do what was necessary to save lives. The Triangle Shirtwaist Company factory’s owners were known to be particularly anti-worker in their policies and had played a critical role in breaking a large strike by workers the previous year.
problem was that making the factories safe cost money, and dug into the profits, so the owners didn’t want to do what was necessary to save lives. The Triangle Shirtwaist Company factory’s owners were known to be particularly anti-worker in their policies and had played a critical role in breaking a large strike by workers the previous year.
On March 25, a Saturday afternoon, there were 600 workers at the factory when a fire began in a rag bin. The manager attempted to use the fire hose to extinguish it, but was unsuccessful. The hose was rotted and its valve was rusted shut. They were at the mercy of the raging inferno. The fire grew and the workers panicked. They tried to exit the building by the elevator, but it could only hold 12 people and the operator was able to make just four trips before it broke down due to the heat and flames. In a desperate attempt to escape the flames. The girls left behind waiting for the elevator plunged down the shaft to their deaths. The girls who fled by way of the stairwells also met awful fates. When they found a locked door at the bottom of the stairs, many were burned alive. In all, 145 workers between the ages of 14 and 43, mostly women and mostly in their teens and early twenties, died that day. Six of them would not be identified until February, 2011…100 years later.
Once the fire was reported, the firefighters tried to put it out, but their ladders would only reach the seventh floor. The fire was on the eighth floor. When escape was proven to be impossible, the girls, desperate to escape the searing heat and flames, began to jump. The bodies of those who jumped landed on the hoses, hampering the flow. The firemen got out nets to catch the girls, but they jumped three at a time, tearing the nets. The nets were of no real help. Within 18 minutes, it was all over. Of the dead, 49 workers had burned to death or been suffocated by smoke, 36 were dead in the elevator shaft and 58 died from jumping to the sidewalks. Two 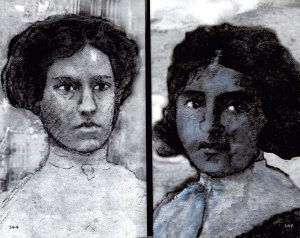 more died later from their injuries. The workers’ union set up a march on April 5 on New York’s Fifth Avenue to protest the conditions that had led to the fire. It was attended by 80,000 outraged people. Despite a good deal of evidence that the owners and management had been horribly negligent in the fire, a grand jury failed to indict them on manslaughter charges. The tragedy did result in some good, however. The International Ladies Garment Workers Union was formed in the aftermath of the fire and the Sullivan-Hoey Fire Prevention Law was passed in New York that October. Both were crucial in preventing similar disasters in the future. Still, I think that it will take the memory of the victims of corruption to ever really inspire people to change the way things are.
more died later from their injuries. The workers’ union set up a march on April 5 on New York’s Fifth Avenue to protest the conditions that had led to the fire. It was attended by 80,000 outraged people. Despite a good deal of evidence that the owners and management had been horribly negligent in the fire, a grand jury failed to indict them on manslaughter charges. The tragedy did result in some good, however. The International Ladies Garment Workers Union was formed in the aftermath of the fire and the Sullivan-Hoey Fire Prevention Law was passed in New York that October. Both were crucial in preventing similar disasters in the future. Still, I think that it will take the memory of the victims of corruption to ever really inspire people to change the way things are.
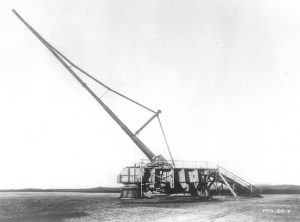
 It seems as if the nations will never be satisfied until they have a new and stronger weapon that will easily destroy a massive amount of people in one shot. Wars are a part of life here on Earth, and will be until the end of time, so we might as well get used to that fact. World War I was not a different time when it comes to weapons of war, in fact on March 23, 1918 at 7:20am, an explosion took place in the Place de la Republique in Paris, and it hailed the first attack of a new German gun. The Pariskanone, Paris-Geschütz, or Paris gun, as it came to be known, was manufactured by Krupps. The Pariskanone was 210mm, with a 118-foot-long barrel. It could fire a shell an impressive distance of some 130,000 feet…25 miles into the air. Three of them fired on Paris that day from a gun site at CrÉpy-en-Laonnaise, a full 74 miles away. The city of Paris was reeling. Paris had withstood all earlier attempts at its destruction, including scattered bombings, but this would be different. It was first thought by the Paris Defense Service, that the city was being bombed, but soon they determined that it was actually being hit by artillery fire. It was a previously unimagined situation. I’m sure everyone wondered how the Germans could have made such a weapon.
It seems as if the nations will never be satisfied until they have a new and stronger weapon that will easily destroy a massive amount of people in one shot. Wars are a part of life here on Earth, and will be until the end of time, so we might as well get used to that fact. World War I was not a different time when it comes to weapons of war, in fact on March 23, 1918 at 7:20am, an explosion took place in the Place de la Republique in Paris, and it hailed the first attack of a new German gun. The Pariskanone, Paris-Geschütz, or Paris gun, as it came to be known, was manufactured by Krupps. The Pariskanone was 210mm, with a 118-foot-long barrel. It could fire a shell an impressive distance of some 130,000 feet…25 miles into the air. Three of them fired on Paris that day from a gun site at CrÉpy-en-Laonnaise, a full 74 miles away. The city of Paris was reeling. Paris had withstood all earlier attempts at its destruction, including scattered bombings, but this would be different. It was first thought by the Paris Defense Service, that the city was being bombed, but soon they determined that it was actually being hit by artillery fire. It was a previously unimagined situation. I’m sure everyone wondered how the Germans could have made such a weapon.
Before the day was over, the shelling had killed 16 people and wounded 29 more. The Germans continued the shelling of that year in several phases between March 23 and August 9, 1918. Over that time, the gun caused a total of 260 deaths in Paris. It was a low number due to the fact that the residents of Paris quickly learned to avoid gathering in large groups during periods of shelling. With less people in each area, the casualties were limited substantially. Nevertheless, the weapon had a terrifying effect on the people and a horrific impact on property in the areas of the shelling. Almost all information about the Pariskanone, one of the most sophisticated weapons to emerge out of World War I, disappeared after the war ended. Later, the Nazis tried 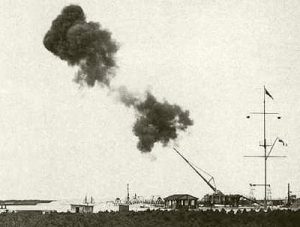
 without success to reproduce the gun from the few pictures and diagrams that remained. Copies were deployed in 1940 against Britain across the English Channel, but failed to cause any significant damage….a good thing for the people of the Britain at that time. When I look at the pictures of the weapon, I am reminded of the old “Wild, Wild, West” show. There always seemed to be some strange new fangled weapon of destruction in use there too.
without success to reproduce the gun from the few pictures and diagrams that remained. Copies were deployed in 1940 against Britain across the English Channel, but failed to cause any significant damage….a good thing for the people of the Britain at that time. When I look at the pictures of the weapon, I am reminded of the old “Wild, Wild, West” show. There always seemed to be some strange new fangled weapon of destruction in use there too.

 When World War I broke out, many young men were called into service. It is a common part of war…one we all know about, and most parents dread. World War I was unique in one way, however. There was a soldier who went to war who was different. He was not different in the way he served exactly, but rather in some other very obvious ways. His speech was different. His mentality was somewhat different, and his looks were different. I’m not being discriminatory, but simply stating a fact. His name was Jackie, and he was different because he was a monkey, well actually, he was a Chacma baboon (Papio ursinus). Jackie was found in August 1915 near the Marr’s family farm in Villeria, Pretoria, South Africa by Albert Marr and soon became a beloved pet.
When World War I broke out, many young men were called into service. It is a common part of war…one we all know about, and most parents dread. World War I was unique in one way, however. There was a soldier who went to war who was different. He was not different in the way he served exactly, but rather in some other very obvious ways. His speech was different. His mentality was somewhat different, and his looks were different. I’m not being discriminatory, but simply stating a fact. His name was Jackie, and he was different because he was a monkey, well actually, he was a Chacma baboon (Papio ursinus). Jackie was found in August 1915 near the Marr’s family farm in Villeria, Pretoria, South Africa by Albert Marr and soon became a beloved pet.
When the war started and the young men were drafted, Albert was no exception. The thing is that Albert couldn’t stand the thought of leaving his beloved pet at home. Albert was assigned to service at Potchefstroom in the North West province of South Africa as private number 4927 for the newly formed 3rd Transvaal Regiment of the 1st South African Infantry Brigade on the 25th August 1915. He approached his superiors and requested that Jackie be allowed to go with him and amazingly was given permission. I’m sure that seems as odd to you as it did to me, but it goes further. Once enlisted Jackie was given a special uniform complete with buttons, a cap, regimental badges, a pay book and his own rations. He was a true member of the regiment, but that doesn’t mean he was accepted as a part of it…at first anyway. The other members of the regiment initially ignored Jackie, but like most people around a monkey, or in this case, baboon, it was hard to ignore him for very long. Jackie soon became the official mascot of the 3rd Transvaal Regiment. Jackie took his duties very seriously, however. He wasn’t there just to eat and fool around!
Jackie was very smart, and when he saw a superior officer passing, he would stand to attention and even provide them with the correct salute. He would light cigarettes for his comrades in arms and was, without a doubt, the best sentry around, due to his great senses of hearing and smelling which allowed him to be able to detect any enemy long before any of his other army mates could even notice their approach. He wasn’t a coddled pet protected for the battles either. Jackie spent three years in the front line amongst the trenches of France and Flanders in Europe. During the Senussi Campaign on 26 February 1916 in Egypt, Jackie’s beloved Albert got wounded on his shoulder by an enemy bullet. Jackie stayed beside him until the stretcher bearers arrived, licking the wound and doing what he could to comfort his friend.
Albert and Jackie both held the rank of private, and in April of 1918, both got injured in the Passchendaele area in Belgium during a heavy fire. With explosions surrounding them, Jackie was seen trying to get some protection by building a little fortress of stones around himself. He didn’t manage to finish his little safe area soon enough, and was hit by a chunk of shrapnel from a shell explosion nearby, which also injured Albert. Jackie’s right leg was seriously wounded and later had to be amputated. Jackie and Albert both made a full recovery and shortly before the armistice, Jackie was promoted to corporal, and awarded a medal for valor.
At the end of April, Jackie was officially discharged at the Maitland Dispersal Camp, Cape Town, South Africa, while wearing on his arm a gold wound stripe and three blue service chevrons indicating three years of frontline service. He was given a parchment discharge paper, a military pension and a Civil Employment Form for 
 discharged soldiers. After his service, Jackie returned to the Marr’s farm where he lived until May 22, 1921…a sad day for all who knew him. Albert Marr lived until the age of 84 and died in Pretoria in August 1973. Jackie was an amazing Chacma Baboon who, because of a fateful connection, ended up as the only monkey to reach the rank of Corporal of the South African Infantry and fight in Egypt, Belgium and France during World War I. Now that’s amazing!!!
discharged soldiers. After his service, Jackie returned to the Marr’s farm where he lived until May 22, 1921…a sad day for all who knew him. Albert Marr lived until the age of 84 and died in Pretoria in August 1973. Jackie was an amazing Chacma Baboon who, because of a fateful connection, ended up as the only monkey to reach the rank of Corporal of the South African Infantry and fight in Egypt, Belgium and France during World War I. Now that’s amazing!!!
 When we think of computers, most of us think of the modern day laptop, or even our smart phones, and when we think of who invented the computer, we think of a man, and that would probably be right, but when NASA thinks of computers, they also have to include the Women of NASA. They were known as “human computers” long before desktop, laptops, or even multi-function calculators existed. Barbara “Barby” Canright joined California’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in 1939. She was the first female “human computer” and her job was to calculate anything from how many rockets were needed to make a plane airborne to what kind of rocket propellants were needed to propel a spacecraft. She did her calculations by hand, with only a pencil and graph paper. It often took more than a week to complete, and her work commonly filled six to eight notebooks with data and formulas. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, her work, along with that of her mostly male teammates, took on a new meaning. There was important work to be done to secure the safety of our nation. The army needed to lift a 14,000 pound bomber into the air, and Barby was responsible for determining the thrust-to-weight ratio and comparing the performance of engines under various conditions, so they could make that happen. Due to the amount of work it was going to take to accomplish this task, more “computers” were hired, including three women Melba Nea, Virginia Prettyman and Macie Roberts.
When we think of computers, most of us think of the modern day laptop, or even our smart phones, and when we think of who invented the computer, we think of a man, and that would probably be right, but when NASA thinks of computers, they also have to include the Women of NASA. They were known as “human computers” long before desktop, laptops, or even multi-function calculators existed. Barbara “Barby” Canright joined California’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in 1939. She was the first female “human computer” and her job was to calculate anything from how many rockets were needed to make a plane airborne to what kind of rocket propellants were needed to propel a spacecraft. She did her calculations by hand, with only a pencil and graph paper. It often took more than a week to complete, and her work commonly filled six to eight notebooks with data and formulas. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, her work, along with that of her mostly male teammates, took on a new meaning. There was important work to be done to secure the safety of our nation. The army needed to lift a 14,000 pound bomber into the air, and Barby was responsible for determining the thrust-to-weight ratio and comparing the performance of engines under various conditions, so they could make that happen. Due to the amount of work it was going to take to accomplish this task, more “computers” were hired, including three women Melba Nea, Virginia Prettyman and Macie Roberts.
It was a time when women were mostly homemakers, and in fact, often looked at as probably not able to understand complicated things like math, science, and engineering, but times were changing. We were a nation at war, and many of the men were fighting. Not only did the women step up to the plate, but they showed that they could understand the work they did, as well as, if not better than their male counterparts. In fact, they did their work so well, that their calculations would end up charting the course of many ground breaking missions that would carry United States astronauts to the moon and beyond. These women were an elite team of mathematicians, engineers and scientists, who were tasked with turning numbers into meaningful data at what would later become NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center. They challenged NASA to let them show what they could do, and when NASA did so, they really shined. It was an eye-opening accomplishment, and one that I’m pretty sure many men thought couldn’t be done.
It’s a funny thing, in my mind, that they were called “human computers” though. I suppose the work they did was computing, but the terminology just seems odd. These days, we talk about someone having the mind of a computer, but we don’t call them a computer. I guess that’s because we have computers, and no one would think of a person in that way. The reality is that, while these women were breaking ground in previously uncharted territory, their services would never really become unnecessary. In fact, one of the earliest human computers still works at Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Sue Finley is 80 now, and NASA’s longest serving female employee. She was originally hired in 1958 to work on trajectory computations for rocket launches, and is now  a software tester and subsystem engineer. She is currently working on NASA’s mission to Jupiter. Her legacy, and that of the other early human computers, is literally written in the stars. What really amazes me is that many people over 70 have no idea how to work a computer, and yet here is this 80 year old woman who is a software tester and subsystem engineer. Amazing!! Totally amazing!!
a software tester and subsystem engineer. She is currently working on NASA’s mission to Jupiter. Her legacy, and that of the other early human computers, is literally written in the stars. What really amazes me is that many people over 70 have no idea how to work a computer, and yet here is this 80 year old woman who is a software tester and subsystem engineer. Amazing!! Totally amazing!!
 Imagine being a mail carrier between 1863 and 1922. I’m sure that you are wondering why those dates would be so important. Well, they really are. In 1863, the United States Postal Service began what they called Free City Delivery. This service brought about the beginning of home delivery of the mail, at least in the cities. I suppose it also brought on the need for the mail carrier. What it didn’t bring with it was a large degree of efficiency. The mail carrier was required to go to the door of the patron receiving mail, and knock. Then they waited patiently for someone to answer the door to take the mail. That is about the strangest idea to me. The person would either need to be home every day at the time the mail carrier was supposed to be
Imagine being a mail carrier between 1863 and 1922. I’m sure that you are wondering why those dates would be so important. Well, they really are. In 1863, the United States Postal Service began what they called Free City Delivery. This service brought about the beginning of home delivery of the mail, at least in the cities. I suppose it also brought on the need for the mail carrier. What it didn’t bring with it was a large degree of efficiency. The mail carrier was required to go to the door of the patron receiving mail, and knock. Then they waited patiently for someone to answer the door to take the mail. That is about the strangest idea to me. The person would either need to be home every day at the time the mail carrier was supposed to be  there, or somehow know the date something was coming…an impossible task in those days, or have someone else there to watch for the carrier. It was estimated that the carriers lost over 1.5 hours a day, waiting on the patrons to come to the door.
there, or somehow know the date something was coming…an impossible task in those days, or have someone else there to watch for the carrier. It was estimated that the carriers lost over 1.5 hours a day, waiting on the patrons to come to the door.
As early as 1880, the post office began to suggest that people put a letter box on their door, so that the mail could be left at the house, even if no one was home. The Post Office wanted wall-mounted mailboxes to the outside of the houses instead of mail slots. They wanted them to be mounted at the height of a standing man. The plan was that the carrier would not have to bend over to deposit mail, and the outgoing mail would stay dry. People are notoriously slow to accept change, and I’m sure this situation was no different.

By 1916, with little change in the situation, the post office began working on a plan to achieve the compliance they needed. The deadline was set. The homes were to have a letter box by March 20, 1922. After that date, the mail would be held at the post office, if no letter box was in place. As we look back now, it seems strange to think that anyone would fight the letter box plan. It’s such a simple way to get your mail, and it does not involve a daily trip to the post office. I can’t imagine why anyone would want the hassle that not having a mail box at your home would bring. I think they probably felt same way after they had one for a while.
 Recently, I found out that President Dwight D Eisenhower is my sixth cousin six times removed. We are connected on my mother’s side through her Pattan roots, which is her mother’s side. Eisenhower was the 34th president of the Unites States, serving from January 20, 1953 to January 20, 1961. He was also a five-star general in the United States Army during World War II and served as Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Forces in Europe. Eisenhower was responsible for planning and supervising the invasion of North Africa in Operation Torch in 1942 – 1943 and the successful invasion of France and Germany in 1944 – 1945 from the Western Front. In 1951, he became the first Supreme Commander of NATO.
Recently, I found out that President Dwight D Eisenhower is my sixth cousin six times removed. We are connected on my mother’s side through her Pattan roots, which is her mother’s side. Eisenhower was the 34th president of the Unites States, serving from January 20, 1953 to January 20, 1961. He was also a five-star general in the United States Army during World War II and served as Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Forces in Europe. Eisenhower was responsible for planning and supervising the invasion of North Africa in Operation Torch in 1942 – 1943 and the successful invasion of France and Germany in 1944 – 1945 from the Western Front. In 1951, he became the first Supreme Commander of NATO.
With everything else that he did, it seems odd, I suppose, to mention the fact that on March 18, 1959, he signed the Admission Act. Basically, the act dissolved the Territory of Hawaii and established the State of Hawaii as the 50th state to be admitted into the Union. Statehood became effective on August 21, 1959…the last state to join the United States. Eisenhower, in fact, was the president who signed the last two states into the United States. To me that must have been such an awe inspiring thing to get to do. My guess is that Eisenhower really had no idea that Hawaii would forever be the last state in the United States, and I suppose that it is still possible that 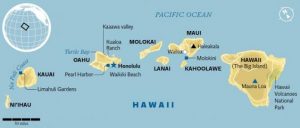 another may join, but it has been almost 58 years, so it seems highly unlikely that there will be another. I wonder if, as his life was drawing to a close, Eisenhower gave any thought to the fact that he got to do that…to bring in the final two states in the United States. I also wonder if anyone thought there would ever be more states after Arizona and New Mexico were added in 1912, almost 47 years earlier. Maybe, adding another state to our country didn’t seem like such an important thing for a president to do, but I think it is. And to be the president to add the last two states…well, I just think that is very cool.
another may join, but it has been almost 58 years, so it seems highly unlikely that there will be another. I wonder if, as his life was drawing to a close, Eisenhower gave any thought to the fact that he got to do that…to bring in the final two states in the United States. I also wonder if anyone thought there would ever be more states after Arizona and New Mexico were added in 1912, almost 47 years earlier. Maybe, adding another state to our country didn’t seem like such an important thing for a president to do, but I think it is. And to be the president to add the last two states…well, I just think that is very cool.
 Like many avid genealogists, I find myself looking at my roots often. As Saint Patrick’s Day rolls around, I find myself contemplating my Irish roots. I’m sure there are more than I can begin to count, but I specifically know of the Shaw family. These are my grandmother, Harriett Byer’s ancestors. The thing that I find to be sad is that the records are not as extensive as I wish they were. My DNA connects me to this family, but the 1600s is as far as I have been able to trace. I suppose that many people would think that the 1600s is a long way back, but it is barely to the point of their immigration from Ireland to the United States. Even in America, the records aren’t well kept. I find it quite sad that some families are so meticulous in their record keeping, while others just weren’t.
Like many avid genealogists, I find myself looking at my roots often. As Saint Patrick’s Day rolls around, I find myself contemplating my Irish roots. I’m sure there are more than I can begin to count, but I specifically know of the Shaw family. These are my grandmother, Harriett Byer’s ancestors. The thing that I find to be sad is that the records are not as extensive as I wish they were. My DNA connects me to this family, but the 1600s is as far as I have been able to trace. I suppose that many people would think that the 1600s is a long way back, but it is barely to the point of their immigration from Ireland to the United States. Even in America, the records aren’t well kept. I find it quite sad that some families are so meticulous in their record keeping, while others just weren’t.
My Grandma Byer and her siblings were proud of their Irish roots. In their later years, they took a trip to Ireland to search for family information, graves, and living family members. I’m not sure if they found much  information, but without computers, information was harder to find then. It’s not that computers didn’t exist, but rather the simple fact that none of them knew how to use one. Nevertheless, they had a wonderful trip. They explored castles, town and villages, and they saw the amazing green fields that are synonymous of Ireland. They also did something that I have found interesting, when the had the opportunity to kiss the Blarney Stone. For those who don’t know about the Blarney Stone, “The Blarney Stone (Irish: Cloch na Blarnan) is a block of Carboniferous limestone built into the battlements of Blarney Castle, Blarney, about 8 kilometers (5 miles) from Cork, Ireland. According to legend, kissing the stone endows the kisser with the gift of the gab (great eloquence or skill at flattery).” It’s really just a goofy tradition, but I suppose it is a fun idea, and one they decided was worth testing.
information, but without computers, information was harder to find then. It’s not that computers didn’t exist, but rather the simple fact that none of them knew how to use one. Nevertheless, they had a wonderful trip. They explored castles, town and villages, and they saw the amazing green fields that are synonymous of Ireland. They also did something that I have found interesting, when the had the opportunity to kiss the Blarney Stone. For those who don’t know about the Blarney Stone, “The Blarney Stone (Irish: Cloch na Blarnan) is a block of Carboniferous limestone built into the battlements of Blarney Castle, Blarney, about 8 kilometers (5 miles) from Cork, Ireland. According to legend, kissing the stone endows the kisser with the gift of the gab (great eloquence or skill at flattery).” It’s really just a goofy tradition, but I suppose it is a fun idea, and one they decided was worth testing.
The big Saint Patrick’s Day parties are far more an American tradition than it is as Irish one. In fact, people might be surprised at the real background of the day. Saint Patrick’s Day was made an official Christian feast day in the early 17th century and is observed by the Catholic Church, the Anglican Communion (especially the Church of Ireland), the Eastern Orthodox Church, and the Lutheran Church. In reality, It is a day that  commemorates Saint Patrick and the arrival of Christianity in Ireland. It also celebrates the heritage and culture of the Irish in general. Celebrations generally involve public parades and festivals, cèilidhs (a social event at which there is Scottish or Irish folk music and singing, traditional dancing, and storytelling), and the wearing of green attire or shamrocks. Some Catholic Christians also attend church services and historically in Ireland the Lenten restrictions on eating and drinking alcohol were lifted for the day, which is likely where the holiday’s tradition of alcohol consumption came from. So, whether you celebrate in the tradition of America or the tradition of Ireland, Happy Saint Patrick’s Day to one and all.
commemorates Saint Patrick and the arrival of Christianity in Ireland. It also celebrates the heritage and culture of the Irish in general. Celebrations generally involve public parades and festivals, cèilidhs (a social event at which there is Scottish or Irish folk music and singing, traditional dancing, and storytelling), and the wearing of green attire or shamrocks. Some Catholic Christians also attend church services and historically in Ireland the Lenten restrictions on eating and drinking alcohol were lifted for the day, which is likely where the holiday’s tradition of alcohol consumption came from. So, whether you celebrate in the tradition of America or the tradition of Ireland, Happy Saint Patrick’s Day to one and all.

