History

 These days, as wars are fought, we often see, hear, and read the stories written by embedded reporters. It seems almost commonplace, and yet in reality, whenever these reporters go into a war zone, they are risking almost as much as the soldiers. Of course, the reporters don’t go out to attack the enemy, but because of where they are, and who they are with, they make themselves a target to the enemy too. Even as far back as the World Wars, embedded reporters seemed like a common phenomenon, but who would have thought of an embedded reporter as far back as the Indian wars? I certainly didn’t. Nevertheless, journalists were there. One such journalist, who became famous, mostly because he was killed, was Marcus Kellogg, who was traveling with Custer’s 7th Cavalry. Kellogg was a native of Ontario, Canada before immigrating to New York with his family in 1835. As a young man he mastered the art of the telegraph and went to work for the Pacific Telegraphy Company in Wisconsin. During the Civil War, he felt led toward a different calling. He left his career in telegraphy, and became a journalist. Then in 1873, he again felt the calling to change his life, when he decided to move west to the frontier town of Bismarck in Dakota Territory and became the assistant editor of the Bismarck Tribune.
These days, as wars are fought, we often see, hear, and read the stories written by embedded reporters. It seems almost commonplace, and yet in reality, whenever these reporters go into a war zone, they are risking almost as much as the soldiers. Of course, the reporters don’t go out to attack the enemy, but because of where they are, and who they are with, they make themselves a target to the enemy too. Even as far back as the World Wars, embedded reporters seemed like a common phenomenon, but who would have thought of an embedded reporter as far back as the Indian wars? I certainly didn’t. Nevertheless, journalists were there. One such journalist, who became famous, mostly because he was killed, was Marcus Kellogg, who was traveling with Custer’s 7th Cavalry. Kellogg was a native of Ontario, Canada before immigrating to New York with his family in 1835. As a young man he mastered the art of the telegraph and went to work for the Pacific Telegraphy Company in Wisconsin. During the Civil War, he felt led toward a different calling. He left his career in telegraphy, and became a journalist. Then in 1873, he again felt the calling to change his life, when he decided to move west to the frontier town of Bismarck in Dakota Territory and became the assistant editor of the Bismarck Tribune.
Then, while returning from a trip to the East, Kellogg happened to be on the same train as George Custer and his wife, Elizabeth. Custer was on his way to Fort Abraham Lincoln, near Bismarck, where he was going to lead the 7th Cavalry in a planned assault on several bands of Indians who had refused to be confined to reservations. There journey was delayed by an unusually heavy winter storm. The train became snowbound. Being the expert that he was, Kellogg improvised a crude telegraph key, connected it to the wires running alongside the track, and sent a message ahead to the fort asking for help. Custer’s brother, Tom, arrived soon after with a sleigh to rescue them. Custer had enjoyed being made famous by the nation’s newspapers during the Civil War, and now, as he prepared for what he hoped would be his greatest victory ever, Custer wanted to make sure his glorious deeds would be adequately covered in the press. Initially, Custer had planned to take his old friend Clement Lounsberry, who was Kellogg’s employer at the Tribune, with him into the field with the 7th Cavalry, but after meeting Kellogg, he chose him to go instead, mostly because Custer had been impressed by his resourcefulness with a telegraph key.
That one chance event in the winter of 1876, took Kellogg in an unexpected direction…toward the Little Big Horn. When Custer led his soldiers out of Fort Abraham Lincoln and headed west for Montana on May 31, Kellogg rode with him. During the next few weeks, Kellogg filed three dispatches from the field to the Bismarck Tribune, which in turn passed the stories on to the New York Herald. Wanting to make sure the word got out, Custer also sent three anonymous reports on his progress to the Herald. Kellogg’s first dispatches, dated May 31 and June 12, recorded the progress of the expedition westward. His final report, dated June 21, came from the army’s camp along the Rosebud River in southern Montana, not far from the Little Big Horn River. “We leave the Rosebud tomorrow,” Kellogg wrote, “and by the time this reaches you we will have met and fought the red devils, with what result remains to be seen.” The results, of course, were disastrous. Four days later, Sioux and Cheyenne warriors wiped out Custer and his men along the Little Big Horn River. Kellogg was the only journalist to witness the final moments of Custer’s 7th Cavalry. Had he been able to file a story he would have become a national celebrity, but Kellogg did not live to tell the tale, he died alongside Custer’s soldiers.
On July 6, the Bismarck Tribune printed a special extra edition with a top headline reading: “Massacred: Gen. Custer and 261 Men the Victims.” Further down in the column, in substantially smaller type, a sub-headline reported: “The Bismarck Tribune’s Special Correspondent Slain.” The article went on to report, “The body of Kellogg alone remained unstripped of its clothing, and was not mutilated.” The reporter speculated that this 
 might have been a result of the Indian’s “respect for this humble shover of the lead pencil.” I doubt that the Sioux and Cheyenne respected Kellogg for his journalistic abilities, but his death in one of the most notorious events in the nation’s history made him something of an martyr among newspapermen. The New York Herald later erected a monument to Kellogg over the supposed site of his grave on the Little Big Horn battlefield. Being an embedded journalist might be exciting, but it’s quite risky too.
might have been a result of the Indian’s “respect for this humble shover of the lead pencil.” I doubt that the Sioux and Cheyenne respected Kellogg for his journalistic abilities, but his death in one of the most notorious events in the nation’s history made him something of an martyr among newspapermen. The New York Herald later erected a monument to Kellogg over the supposed site of his grave on the Little Big Horn battlefield. Being an embedded journalist might be exciting, but it’s quite risky too.
 In any wartime situation, there always seem to be those who think the United States should not get involved…mostly because they think that if we just stay out of it, the enemy will leave us alone. Of course, history does not prove that theory. When we look at the wars that the United States has been drawn into, only after we were attacked too, we find that the enemy always intended to take on the United States too, and we were only delaying the inevitable. It seems like every wartime president has had to deal with the naysayers, and President Eisenhower was no different. During the Cold War years when the Communists were trying to take over the world, Eisenhower chose a strong United States defense against it, but his view of a strong defense was much different that General Hoyt Vandenberg’s view. Vandenberg wanted a massive increase in conventional land, air, and sea forces, while Eisenhower said that a cheaper and more efficient defense could be built around the nation’s nuclear arsenal. Senator Robert Taft argued that if efforts to reach a peace agreement in Korea failed, the United States should withdraw from the United Nations forces and make its own policy for dealing with North Korea, basically a completely independent foreign policy, or what one “might call the ‘fortress’ theory of defense.” While both of these suggestions might seem like the best course of action, history tells us that Senator Taft’s suggestion would make us look weak, and possibility bring about attacks on the United States, and while I would tend to agree with General Vandenberg, that we need a strong defense system, I also understand that as technology changes, nations must change with it. Having hundreds of fighter planes is not necessary, if a few can drop a bomb that will settle the matter once and for all. It is similar to the use of pen and paper when we live in a computer age.
In any wartime situation, there always seem to be those who think the United States should not get involved…mostly because they think that if we just stay out of it, the enemy will leave us alone. Of course, history does not prove that theory. When we look at the wars that the United States has been drawn into, only after we were attacked too, we find that the enemy always intended to take on the United States too, and we were only delaying the inevitable. It seems like every wartime president has had to deal with the naysayers, and President Eisenhower was no different. During the Cold War years when the Communists were trying to take over the world, Eisenhower chose a strong United States defense against it, but his view of a strong defense was much different that General Hoyt Vandenberg’s view. Vandenberg wanted a massive increase in conventional land, air, and sea forces, while Eisenhower said that a cheaper and more efficient defense could be built around the nation’s nuclear arsenal. Senator Robert Taft argued that if efforts to reach a peace agreement in Korea failed, the United States should withdraw from the United Nations forces and make its own policy for dealing with North Korea, basically a completely independent foreign policy, or what one “might call the ‘fortress’ theory of defense.” While both of these suggestions might seem like the best course of action, history tells us that Senator Taft’s suggestion would make us look weak, and possibility bring about attacks on the United States, and while I would tend to agree with General Vandenberg, that we need a strong defense system, I also understand that as technology changes, nations must change with it. Having hundreds of fighter planes is not necessary, if a few can drop a bomb that will settle the matter once and for all. It is similar to the use of pen and paper when we live in a computer age.
President Eisenhower was no stranger to sending the military might of the United States out to attack the enemy, and in his days as a general, he made those decisions every day, but as every one should realize, the  more men you have to send, the more possibility of losing them. The decision to send soldiers to their deaths was not one that Eisenhower ever took lightly. With a strong nuclear arsenal, the enemy nation knew that they had better think twice before taking on the United States.
more men you have to send, the more possibility of losing them. The decision to send soldiers to their deaths was not one that Eisenhower ever took lightly. With a strong nuclear arsenal, the enemy nation knew that they had better think twice before taking on the United States.
Without naming either man, President Eisenhower responded to both during a speech at the National Junior Chamber of Commerce meeting in Minneapolis. His forceful speech struck back at critics of his Cold War foreign policy. He insisted that the United States was committed to the worldwide battle against communism and that he would maintain a strong United States defense. It was just a few months into his presidency, and the Korean War still raging, but Eisenhower laid out his basic approach to foreign policy with this speech. He began by characterizing the Cold War as a battle “for the soul of man himself.” He rejected Taft’s idea that the United States should pursue isolationism, and instead he insisted that all free nations had to stand together saying, “There is no such thing as partial unity.” To Vandenberg’s criticisms of the new Air Force budget, in which the president proposed a $5 billion cut from the Air Force budget, Eisenhower explained that vast numbers of aircraft were not needed in the new atomic age. Just a few planes armed with nuclear weapons could “visit on an enemy as much explosive violence as was hurled against Germany by our entire air effort throughout four years of World War II.” With this speech, Eisenhower thus pointed out the two major points of what came to be known at the time as his “New Look” foreign policy. First was his advocacy of multi-nation responses to communist aggression in preference to unilateral action by the United States. Second was the idea that came to be known as the “bigger bang for the buck” defense strategy.
 Anytime a nation is facing war, it is a stressful time for its people, but no nation will do well using the isolation strategy, because a nation that appears to be weak in its own defense, will ultimately become a target for attack. I am not an advocate for the United Nations, and in fact, I believe we need to disband the United Nations, but I do believe that a nation must have allies…nations with like values, who are willing to go to war to back up their allies, and that we must not allow bully nations to take over smaller nations, because that only strengthens their resolve to expand further. I also believe that when technology becomes available, it must be properly combined with human forces to achieve the best result in the most efficient way.
Anytime a nation is facing war, it is a stressful time for its people, but no nation will do well using the isolation strategy, because a nation that appears to be weak in its own defense, will ultimately become a target for attack. I am not an advocate for the United Nations, and in fact, I believe we need to disband the United Nations, but I do believe that a nation must have allies…nations with like values, who are willing to go to war to back up their allies, and that we must not allow bully nations to take over smaller nations, because that only strengthens their resolve to expand further. I also believe that when technology becomes available, it must be properly combined with human forces to achieve the best result in the most efficient way.
 For most of us, taking a fall, of any kind is no fun. Taking a fall off of a one story roof is terrifying, and if we were to fall from a two story building, we might not expect to live through it. For Serbian flight attendant, Vesna Vulovic a two story fall is like stubbing her toe. On January 26, 1972, while she was working on JAT Flight 367, a terrorist bomb exploded on the plane. Vesna found herself in a freefall without a parachute at an altitude of 33,333 feet. Vulovic, who was just 22 years old, and thought she had landed a wonderful career that would allow her to travel to exotic places. Never in a million years did she imagine that her career would end this way.
For most of us, taking a fall, of any kind is no fun. Taking a fall off of a one story roof is terrifying, and if we were to fall from a two story building, we might not expect to live through it. For Serbian flight attendant, Vesna Vulovic a two story fall is like stubbing her toe. On January 26, 1972, while she was working on JAT Flight 367, a terrorist bomb exploded on the plane. Vesna found herself in a freefall without a parachute at an altitude of 33,333 feet. Vulovic, who was just 22 years old, and thought she had landed a wonderful career that would allow her to travel to exotic places. Never in a million years did she imagine that her career would end this way.
Flight 367 was flying over Srbská Kamenice in Czechoslovakia, which is now part of the Czech Republic. She had not been scheduled to be on that flight, but she had been mixed up with another flight attendant who was also named Vesna. I’m sure she wished she had not been as she was falling through the air that awful day in 1972. While falling 33,333 feet, a person has a good bit of time to think about what they wished they had done, or not done. And at 22, I’m sure there were many things she had hoped to accomplish in her lifetime, and now those things could never happen.
The official report of the Czechoslovak investigation commission, which was handed over to the ICAO on May 7,  1974, stated that there had been an explosion in the front baggage compartment of the plane. The Czechoslovak secret service, which was leading the investigation, presented parts of an alarm clock ten days after the crash which they claimed came from a bomb. The report concluded that a bomb brought down Flight 367. That morning, an anonymous man called the newspaper Kvällsposten published in Malmö, Sweden, claiming, in broken Swedish, that he was a Croat and member of a nationalist group that placed the bomb on the plane. Shortly after the phone call, the Yugoslav government blamed the Ustaše. According to the official report the explosion tore the McDonnell Douglas DC-9-32 to pieces in mid-air. Vulovic was the only survivor.
1974, stated that there had been an explosion in the front baggage compartment of the plane. The Czechoslovak secret service, which was leading the investigation, presented parts of an alarm clock ten days after the crash which they claimed came from a bomb. The report concluded that a bomb brought down Flight 367. That morning, an anonymous man called the newspaper Kvällsposten published in Malmö, Sweden, claiming, in broken Swedish, that he was a Croat and member of a nationalist group that placed the bomb on the plane. Shortly after the phone call, the Yugoslav government blamed the Ustaše. According to the official report the explosion tore the McDonnell Douglas DC-9-32 to pieces in mid-air. Vulovic was the only survivor.
Vulovic suffered a fractured skull, three broken vertebrae, one of which was crushed completely, and that left her temporarily paralyzed from the waist down, and two broken legs. She was in a coma for 27 days. In an interview, she commented that according to the man who found her, “…I was in the middle part of the plane. I was found with my head down and my colleague on top of me. One part of my body with my leg was in the plane and my head was out of the plane. A catering trolley was pinned against my spine and kept me in the 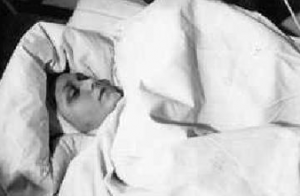 plane. The man who found her said she was lucky. He was in the German Army as a medic during World War II. He knew how to treat trauma. The medic is identified as Bruno Henke. Vulovic continued working for JAT Airways at a desk job following a full recovery from her injuries. She regained the use of her legs and continued to fly sporadically. She claimed she had no fear of flying, which she attributed to her loss of memory of the crash, and she even enjoyed watching movies with plane crashes. She was considered a national heroine throughout the former Yugoslavia and was awarded the Guinness Record title by Paul McCartney at a ceremony in 1985. As to becoming the world record freefall holder, Vesna comments, “I am like a cat, I have had nine lives.”
plane. The man who found her said she was lucky. He was in the German Army as a medic during World War II. He knew how to treat trauma. The medic is identified as Bruno Henke. Vulovic continued working for JAT Airways at a desk job following a full recovery from her injuries. She regained the use of her legs and continued to fly sporadically. She claimed she had no fear of flying, which she attributed to her loss of memory of the crash, and she even enjoyed watching movies with plane crashes. She was considered a national heroine throughout the former Yugoslavia and was awarded the Guinness Record title by Paul McCartney at a ceremony in 1985. As to becoming the world record freefall holder, Vesna comments, “I am like a cat, I have had nine lives.”
 The manner in which battles are fought and won, never ceases to amaze me. In 1916, British forces began planning the Battle of Messines Ridge. For 18 months, soldiers worked to place nearly 1 million pounds of explosives in tunnels under the German positions. The tunnels extended to some 2,000 feet in length, and some were as much as 100 feet below the surface of the ridge, where the Germans had long since been entrenched. The Germans had no idea that they were there, and no idea what was going to happen. I find myself in complete amazement, that all those soldiers were working a mere 100 feet below ground, and the German soldiers above them had no idea. It was the element of surprise that was the whole key to this successful attack.
The manner in which battles are fought and won, never ceases to amaze me. In 1916, British forces began planning the Battle of Messines Ridge. For 18 months, soldiers worked to place nearly 1 million pounds of explosives in tunnels under the German positions. The tunnels extended to some 2,000 feet in length, and some were as much as 100 feet below the surface of the ridge, where the Germans had long since been entrenched. The Germans had no idea that they were there, and no idea what was going to happen. I find myself in complete amazement, that all those soldiers were working a mere 100 feet below ground, and the German soldiers above them had no idea. It was the element of surprise that was the whole key to this successful attack.
 At 3:10am on June 7, 1917, a series of simultaneous explosions rocked the area. The explosions were heard as far away as London. A German observer described the explosions saying, “nineteen gigantic roses with carmine petals, or enormous mushrooms, rose up slowly and majestically out of the ground and then split into pieces with a mighty roar, sending up multi-colored columns of flame mixed with a mass of earth and splinters high in the sky.” While Messines Ridge itself was considered a relatively limited victory, it had a considerable effect. German losses that day included more than 10,000 men who died instantly, along with some 7,000 prisoners…men who were too stunned and disoriented by the explosions to resist the infantry assault.
At 3:10am on June 7, 1917, a series of simultaneous explosions rocked the area. The explosions were heard as far away as London. A German observer described the explosions saying, “nineteen gigantic roses with carmine petals, or enormous mushrooms, rose up slowly and majestically out of the ground and then split into pieces with a mighty roar, sending up multi-colored columns of flame mixed with a mass of earth and splinters high in the sky.” While Messines Ridge itself was considered a relatively limited victory, it had a considerable effect. German losses that day included more than 10,000 men who died instantly, along with some 7,000 prisoners…men who were too stunned and disoriented by the explosions to resist the infantry assault.

It was a crushing victory over the Germans. The German army was forced to retreat to the east. This retreat and the sacrifice that it entailed marked the beginning of their gradual, but continuous loss of territory along the Western Front. It also secured the right flank of the British army’s push towards the much-contested Ypres region, which was the eventual objective of the planned attack. Over the next month and a half, British forces continued to push the Germans back toward the high ridge at Passchendaele. Then on July 31 the British army launched it’s offensive, known as the Battle of Passchendaele or the Third Battle of Ypres.

 On this D-Day, a subject I have previously written about, I began to wonder about a different side of the story of this age old battle that everyone has heard of, even if some don’t know what it was all about. My thoughts turned to General Eisenhower. It was he who had the unfortunate task of deciding to attack the Germans who were occupying France, by way of the beaches of Normandy, France. It was he who had to carry the emotional burden of knowing that if the attack was made, he would be sending men to die. I would not have wanted to be in his shoes as he pondered this monumental decision. Nevertheless, someone had to make the decision. Things could not go on as they were. The future of the free world was dependent on the decisions made by this one man.
On this D-Day, a subject I have previously written about, I began to wonder about a different side of the story of this age old battle that everyone has heard of, even if some don’t know what it was all about. My thoughts turned to General Eisenhower. It was he who had the unfortunate task of deciding to attack the Germans who were occupying France, by way of the beaches of Normandy, France. It was he who had to carry the emotional burden of knowing that if the attack was made, he would be sending men to die. I would not have wanted to be in his shoes as he pondered this monumental decision. Nevertheless, someone had to make the decision. Things could not go on as they were. The future of the free world was dependent on the decisions made by this one man.
As families listened to their radio stations on the morning of June 6, 1944, one Valerie Lauder, who was 18 at the time, had graduated from Stephens Junior College that May and was not due at Northwestern University and the Medill School of Journalism until September was among the listeners. Her father was listening too, until he had to go to work. She said that President Roosevelt came on the radio and offered a prayer. Then, she heard General Eisenhower’s recorded reading of the order of the day, the troops in LSTs and transports heard it over loudspeakers. At that point, Val decided that she would really like to meet General Eisenhower, and given her chosen profession as a journalist, she was able to eventually make that happen. In fact, she was not only able to meet General Eisenhower 2½ years later, but was also able to preside at his press conference with the student press club that she had created and the Chicago Daily News sponsored.
She related the scene, “On January 18, 1947, Wearing two battle ribbons on his waist-length “Eisenhower jacket,” the supreme commander of the Allied Expeditionary Forces in Europe stood to my left, facing 165 student editors and photographers from high school and college newspapers throughout the greater Chicago area gathered in the Drake Hotel. Dressed in their Sunday best, pencils poised, notebooks open, they were seated on straight-back chairs set out in rows of 10 on either side of a center aisle. Ike stood at the end of the center aisle, about three feet in front of me. I introduced him.” As Val introduced General Eisenhower, she asked him, “General Eisenhower, what was the greatest decision you had to make during the war?” Eisenhower contemplated her question for a moment, and then answered her in a somber and serious tone about the D-Day landings. “To ensure the success of the Allied landings in Normandy,” he explained, “it was imperative that we prevent the enemy from bringing up reinforcements. All roads and rail lines leading to the areas of fighting on and around the beaches had to be cut or blocked. If reinforcements were allowed to reach the areas of fighting there, in our first, precarious attempts to get a foothold on the continent, the whole operation could be jeopardized. The landings might fail. The success of the landings on the beaches,” Ike said, reaching the end of the first row, starting back, “might well turn on the success of the paratroopers behind the lines.”
Then, on May 30, just six days before the scheduled landings, which were to have been June 5, a trusted aide and personal friend came to him, deeply concerned about the airborne landing. Val later that learned it was British Air Chief Marshal Sir Trafford Leigh-Mallory, who had been assigned to the Allied forces, with the title of Air Commander in Chief, which made him the air commander of the Allied invasion. He was apologetic about how late it was, so close to the jump-off time. But, he’d gone over it, and over it, and over it, and felt it simply would not succeed. The casualties would be too great. He pleaded with Eisenhower. “Casualties to glider troops would be 90% before they ever reached the ground,” he said. “The killed and wounded among the paratroopers would be 75%.” Eisenhower knew that would mean an unbearably high percentage of the 18,000 men who would drop into the darkness over Nazi-occupied France would become casualties. This would also mean that the survivors would be too few in number to succeed in their crucial mission of seizing, and holding the causeways. “The man was absolutely sincere, absolutely convinced it wouldn’t work,” Eisenhower said. “As a highly respected, capable officer, I trusted his judgment. I told him I’d think it over.”
After agonizing over the possible losses, he was still undecided just four days before the planned date. Eisenhower slowing, turned to face the students, he said, “I let the order stand.” With the words, his face seemed to relax. I suppose you would have to decide that you were going to be ok with the decision, or else it 
 would drive you crazy. The students sat in stunned silence. “The airborne boys did their job.” Eisenhower went on with relief almost bordering on elation. “And, I am happy to say, the casualties were only 8%.” Eisenhower was not just a general setting up a battle, but rather a man with a heartfelt concern for the men in the airborne divisions and the men in the landing craft headed for the beaches. As he put it in his book, Crusade in Europe, “It would be difficult to conceive of a more soul-racking problem.” I have to agree. To only lose 8% of the men in that situation, well that is…unbelievable!!
would drive you crazy. The students sat in stunned silence. “The airborne boys did their job.” Eisenhower went on with relief almost bordering on elation. “And, I am happy to say, the casualties were only 8%.” Eisenhower was not just a general setting up a battle, but rather a man with a heartfelt concern for the men in the airborne divisions and the men in the landing craft headed for the beaches. As he put it in his book, Crusade in Europe, “It would be difficult to conceive of a more soul-racking problem.” I have to agree. To only lose 8% of the men in that situation, well that is…unbelievable!!
 When we think of disasters at sea, Titanic is the first ship that most likely comes to mind, and while Titanic was a terrible tragedy, it was not the worst disaster at sea, by any means. It is amazing to me, however, that some of the others are never talked about at all, and in fact, you may have never heard about them. Titanic had a capacity of 3547 people, but was only carrying 2223 with passengers and crew. The loss of more than 1500 lives, was horrific to be sure, but it was not the worst disaster at sea in history. That distinction goes to The Wilhelm Gustloff.
When we think of disasters at sea, Titanic is the first ship that most likely comes to mind, and while Titanic was a terrible tragedy, it was not the worst disaster at sea, by any means. It is amazing to me, however, that some of the others are never talked about at all, and in fact, you may have never heard about them. Titanic had a capacity of 3547 people, but was only carrying 2223 with passengers and crew. The loss of more than 1500 lives, was horrific to be sure, but it was not the worst disaster at sea in history. That distinction goes to The Wilhelm Gustloff.
The Wilhelm Gustloff was built by the Blohm & Voss shipyards. It measured 684 feet 1 inch long by 77 feet 5 inches wide with a capacity of 25,484 gross register tons. The ship was launched on 5 May 1937. Originally the ship was intended to be named Adolf Hitler, but was named after Wilhelm Gustloff, a leader of the National Socialist Party’s Swiss branch, who had been assassinated by a Jewish medical student in 1936. Hitler decided on the name change after sitting next to Gustloff’s widow during his memorial service. I guess Hitler managed to do a few nice things in his horrid lifetime. The ship was the first purpose-built cruise liner for the German Labour Front or Deutsche Arbeitsfront,  DAF and used by subsidiary organization Kraft durch Freude, KdF meaning Strength Through Joy. The purpose of the ship was to provide recreational and cultural activities for German functionaries and workers, including concerts, cruises, and other holiday trips, and as a public relations tool, to present “a more acceptable image of the Third Reich.” She was the flagship of the KdF cruise fleet, her last civilian role, until the spring of 1939.
DAF and used by subsidiary organization Kraft durch Freude, KdF meaning Strength Through Joy. The purpose of the ship was to provide recreational and cultural activities for German functionaries and workers, including concerts, cruises, and other holiday trips, and as a public relations tool, to present “a more acceptable image of the Third Reich.” She was the flagship of the KdF cruise fleet, her last civilian role, until the spring of 1939.
The Wilhelm Gustloff became a German hospital ship from September 1939 to November 1940, with its official designation being Lazarettschiff. Then, beginning on 20 November 1940, the medical equipment was removed from the ship and she was repainted from the hospital ship colors of white with a green stripe to standard naval grey. As a consequence of the British blockade of the German coastline, she was used as a barracks ship for approximately 1,000 U-boat trainees of the 2nd Submarine Training Division in the port of Gdynia, which had been occupied by Germany and renamed Gotenhafen. The ship was based near Danzig. Then, as things started to go from bad to worse during World War II, the Germans decided that they needed to evacuate as many people as possible from Courland, East Prussia and Danzig, West Prussia. On  January 30, 1945 during Operation Hannibal, which was the naval evacuation of German troops and civilians from Courland, East Prussia, and Danzig, West Prussia as the Soviet Army advanced. The Wilhelm Gustloff’s final voyage was to evacuate German refugees and military personnel as well as technicians who worked at advanced weapon bases in the Baltic from Gdynia, then known to the Germans as Gotenhafen, to Kiel. The ship’s capacity was 1465, but because they were evacuating people, about 9,400 people were onboard. The ship was hit by a torpedo from Soviet submarine S-13 in the Baltic Sea. It quickly sank, taking all 9,400 people with it. The loss of the Wilhelm Gustloff remains the worst disaster at sea in history.
January 30, 1945 during Operation Hannibal, which was the naval evacuation of German troops and civilians from Courland, East Prussia, and Danzig, West Prussia as the Soviet Army advanced. The Wilhelm Gustloff’s final voyage was to evacuate German refugees and military personnel as well as technicians who worked at advanced weapon bases in the Baltic from Gdynia, then known to the Germans as Gotenhafen, to Kiel. The ship’s capacity was 1465, but because they were evacuating people, about 9,400 people were onboard. The ship was hit by a torpedo from Soviet submarine S-13 in the Baltic Sea. It quickly sank, taking all 9,400 people with it. The loss of the Wilhelm Gustloff remains the worst disaster at sea in history.
 It’s a tiny island in the middle of the vast Pacific Ocean, so what possible impact could a battle for control of Midway Island have had? The answer is…much more than you might think. Sometimes, it’s not about the size of the nation, but rather about the might of its army. Japan is a little nation, it had built a mighty army and it was systematically defeating the Allies. Although other battles would soon make Midway seem like a small battle, no naval battle of World War II…and few others, if any, in all of naval history…would have so many momentous consequences ascribed to it as this one battle. So complete was Japan’s defeat at Midway, and so stunned was the Imperial High Command, that it would keep the results of the battle a secret from the Japanese people for the rest of the World War II.
It’s a tiny island in the middle of the vast Pacific Ocean, so what possible impact could a battle for control of Midway Island have had? The answer is…much more than you might think. Sometimes, it’s not about the size of the nation, but rather about the might of its army. Japan is a little nation, it had built a mighty army and it was systematically defeating the Allies. Although other battles would soon make Midway seem like a small battle, no naval battle of World War II…and few others, if any, in all of naval history…would have so many momentous consequences ascribed to it as this one battle. So complete was Japan’s defeat at Midway, and so stunned was the Imperial High Command, that it would keep the results of the battle a secret from the Japanese people for the rest of the World War II.
The story of the battle has been told many times over the years, and Midway continues to hold an almost mysterious place in the collective memory of the United States Navy and the United States in general. However, in recent decades a new generation of scholars has studied the facts of the battle. In some ways they  have removed the mystery of how such a “miracle” victory came to be and in other ways they have chalked it up to chance, luck, and the weather. The Americans had heard something about an attack, but the Japanese used the code location as “AF” to keep the attack location secret. The Americans suspected that it was Midway, so they sent a radio message that the island’s desalinization plant had broken down. The radio message was broadcast without encryption to ensure that Japan could read it if it was intercepted. The radio message was duly intercepted by Japan and reported by a message encoded in JN25 stating that AF’s desalinization plant was out of order and was intercepted by Station HYPO. “AF” was thus confirmed as Midway.
have removed the mystery of how such a “miracle” victory came to be and in other ways they have chalked it up to chance, luck, and the weather. The Americans had heard something about an attack, but the Japanese used the code location as “AF” to keep the attack location secret. The Americans suspected that it was Midway, so they sent a radio message that the island’s desalinization plant had broken down. The radio message was broadcast without encryption to ensure that Japan could read it if it was intercepted. The radio message was duly intercepted by Japan and reported by a message encoded in JN25 stating that AF’s desalinization plant was out of order and was intercepted by Station HYPO. “AF” was thus confirmed as Midway.
That was the beginning of the end for Japan. The Americans began to prepare for the attack. American scholars of Midway have long tried to explain away the many coincidences by characterizing the result of the battle as little short of a “miracle.” Walter Lord would name his 1967 narrative of Midway Incredible Victory, and 15  years later Gordon Prange’s posthumously published account of the battle was straightforwardly entitled Miracle at Midway. One battle participant’s memoir stated, “God was at Midway.” He saw divine intervention at work. The concept of the miracle has helped to explain the elements of the battle that have eluded detection, explication, or understanding. Some say that over the years, Midway has become less of a miracle, but that many mysteries remain. I say, that it was a miracle. God was at work at Midway. Even the weather worked against the Japanese when cloud cover prevented them from seeing what was right in front of them, and at the end of their attack…less than a week later, four Japanese fleet carriers would be twisted ruins on the bottom of the Pacific.
years later Gordon Prange’s posthumously published account of the battle was straightforwardly entitled Miracle at Midway. One battle participant’s memoir stated, “God was at Midway.” He saw divine intervention at work. The concept of the miracle has helped to explain the elements of the battle that have eluded detection, explication, or understanding. Some say that over the years, Midway has become less of a miracle, but that many mysteries remain. I say, that it was a miracle. God was at work at Midway. Even the weather worked against the Japanese when cloud cover prevented them from seeing what was right in front of them, and at the end of their attack…less than a week later, four Japanese fleet carriers would be twisted ruins on the bottom of the Pacific.
 A declaration of war usually means that the people in both areas within the dispute had better prepare for eminent attack, because the declaration of war is like firing the warning shot before the actual open-fire begins. Of course, it may not be an immediate attack, but the attack always comes…or does it. On September 3, 1939, the United Kingdom and France declared war on Nazi Germany, after the Germans invaded Poland. Over the next eight months, at the start of World War II, there were no major military land operations on the Western Front. Strange, considering that the United Kingdom and France had declared war on Nazi Germany. You would think that they would attack or something, but nothing happened. During those eight months, Poland was overrun. It took about five weeks for the German Invasion of Poland beginning September 1, 1939 and the Soviet invasion beginning on 17 September 1939. Still, the Western Allies did nothing. I guess I don’t understand that. War had been declared by each side, but no Western power would
A declaration of war usually means that the people in both areas within the dispute had better prepare for eminent attack, because the declaration of war is like firing the warning shot before the actual open-fire begins. Of course, it may not be an immediate attack, but the attack always comes…or does it. On September 3, 1939, the United Kingdom and France declared war on Nazi Germany, after the Germans invaded Poland. Over the next eight months, at the start of World War II, there were no major military land operations on the Western Front. Strange, considering that the United Kingdom and France had declared war on Nazi Germany. You would think that they would attack or something, but nothing happened. During those eight months, Poland was overrun. It took about five weeks for the German Invasion of Poland beginning September 1, 1939 and the Soviet invasion beginning on 17 September 1939. Still, the Western Allies did nothing. I guess I don’t understand that. War had been declared by each side, but no Western power would  launch a significant land offensive…even though the terms of the Anglo-Polish and Franco-Polish military alliances obligated the United Kingdom and France to assist Poland. They simply stood by and let it happen.
launch a significant land offensive…even though the terms of the Anglo-Polish and Franco-Polish military alliances obligated the United Kingdom and France to assist Poland. They simply stood by and let it happen.
The quiet of the so-named Phoney War was marked by a few Allied actions. During the Saar Offensive in September, France attacked Germany with the intention of assisting Poland, but the attack fizzled out within days and the French withdrew. In November, the Soviets attacked Finland in the Winter War. This resulted in much debate in France and Britain about helping Finland, but this campaign was delayed until the Winter War ended in March. The Allied discussions about a Scandinavian campaign caused concern in Germany and resulted in the German invasion of Denmark and Norway in April. Then the Allied troops that were previously assembled for Finland were redirected to Norway instead. Fighting there continued until June when the Allies evacuated, ceding Norway to Germany in response to the German invasion of France, which had taken place on May 10, 1940.

The Germans launched attacks at sea during the autumn and winter of 1939, against British aircraft carriers and destroyers, sinking several including the carrier HMS Courageous with the loss of 519 lives. Action in the air began on October 16, 1939 when the Luftwaffe launched air raids on British warships. There were various minor bombing raids and reconnaissance flights on both sides, but nothing that could possibly be viewed as a clear offensive….and during that whole time, people were dying and being subjected to various atrocities, because no one would help. Yes, war was declared, but it was a phony war, and apparently a phony declaration.

 May 30, 2002 dawned, a typically warm New York City day, but this was not a typical day at all. It had been a long, emotionally grueling 8 months and 19 days of cleanup after the September 11, 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center, the Pentagon, and the crash site in Shanksville, Pennsylvania. The majority of the lost were in the World Trade Center in New York City. Those 8 months and 19 days were filled with every possible emotion there could be…from joy when one was found alive, to grief over the lost, to anger at the attack, to hate for the Muslim attackers, to love for the survivors and the families of the lost. It was something that we all knew that we could never really wrap our heads around, and something that we knew we would never forget. It was a senseless attack that proved only that the attackers were insane and filled with hate for Americans and Christians. It was a time when America came together as one, and donated time, money, letters, and love to each other, because we were all victims of this attack, after all.
May 30, 2002 dawned, a typically warm New York City day, but this was not a typical day at all. It had been a long, emotionally grueling 8 months and 19 days of cleanup after the September 11, 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center, the Pentagon, and the crash site in Shanksville, Pennsylvania. The majority of the lost were in the World Trade Center in New York City. Those 8 months and 19 days were filled with every possible emotion there could be…from joy when one was found alive, to grief over the lost, to anger at the attack, to hate for the Muslim attackers, to love for the survivors and the families of the lost. It was something that we all knew that we could never really wrap our heads around, and something that we knew we would never forget. It was a senseless attack that proved only that the attackers were insane and filled with hate for Americans and Christians. It was a time when America came together as one, and donated time, money, letters, and love to each other, because we were all victims of this attack, after all.
On May 29, 2002, the last beam was removed from the site…marking the end of the cleanup effort that had been expected to last a year. There were many disappointments in the cleanup, because there were very few people pulled out alive after that first day, and in fact, the last survivor was pulled out 27 hours after the attack. There would be no more lives saved. People were lined up to donate blood in the hope that someone’s life could be saved, but the sad reality was that very few whole bodies were even pulled from the rubble. Most were bits and pieces, body parts, and even just fragments of bone or teeth. Authorities put the final death toll from the World Trade Center’s destruction at 2,823. Of those 2823 people, only 1,102 victims have been identified, and only 289 intact bodies were recovered.
The ceremony…if it could really be called that, because ceremony usually means a happy event…began in silence. There would be no speeches. Thousands of people stood silently in one place…Ground Zero, and no one spoke…no one spoke!! The ceremony began with the sound of a fire bell ringing for the fallen firefighters at 10:29 am ET, the same time the World Trade Center’s north tower collapsed on September 11, 2001. Thousands of people stood in silence, some with tears streaming from their eyes, as an honor guard made up of police, firefighters, and representatives of other agencies walked slowly up a ramp from the site carrying a stretcher bearing only an American flag. The flag, symbolizing the victims who were killed on September 11, but never found, was placed into a waiting ambulance. It was followed by a flatbed truck carrying the last 50 ton steel column from the site of the Trade Center ruins. The beam was part of the southeast corner of the south tower. It was hoisted onto a flatbed truck and shrouded in black cloth after its removal on May 29, 2002. Ten minutes into the ceremony, a pair of buglers…one from New York’s Police Department, the other from the New York Fire Department…played “Taps,” followed by a flyover of NYPD helicopters. Among the dead following the horrific attack, were 343 New York firefighters and an estimated 70 police officers from various departments, including 37 from New York’s Port Authority and 23 from the New York Police Department. Fewer than half of the firefighters who died were recovered. Five of them were from the Chelsea Firehouse, Engine 3 and Ladder 12. At the fire stations and police stations in New York City, dozens of family and friends watched the tribute on television. Hundreds of workers had labored around the clock since September 11 to recover the 
 bodies of those who died in the attack and to remove the 1.6 million tons of steel and concrete left behind. The debris was moved to a Staten Island landfill, but reminders of the attack remain in the area. “It’s over, but it will never be forgotten,” said FDNY Battalion Commander Richard Picciotto, who was in the north tower when it was hit. He was right. Today marks the 15th anniversary of that ceremony, and we have not forgotten.
bodies of those who died in the attack and to remove the 1.6 million tons of steel and concrete left behind. The debris was moved to a Staten Island landfill, but reminders of the attack remain in the area. “It’s over, but it will never be forgotten,” said FDNY Battalion Commander Richard Picciotto, who was in the north tower when it was hit. He was right. Today marks the 15th anniversary of that ceremony, and we have not forgotten.
 Memorial Day…the day we set aside to remember the heroes of our wars, who paid the ultimate price for the freedoms we hold dear. The men and women who were killed in the attack on Pearl Harbor come to mind, as do those lost on the beaches of Normandy, but there are so many others. From the fliers, to the foot soldiers, to the sailors…men and women, from the Revolutionary War, to the War on Terror, have set aside their goals in life, left their families at home, pushed back their fears, and done their duty to serve their country, and for so many of them, it was a one way ticket over there. They fought and died so that someone they didn’t know could be free and have the rights that so many take for granted. They looked away when they were protested, but deep down they wondered why people didn’t understand. They tried not to watch the news of death and destruction. They just did their job, until they lost their lives in a war they wished had never started.
Memorial Day…the day we set aside to remember the heroes of our wars, who paid the ultimate price for the freedoms we hold dear. The men and women who were killed in the attack on Pearl Harbor come to mind, as do those lost on the beaches of Normandy, but there are so many others. From the fliers, to the foot soldiers, to the sailors…men and women, from the Revolutionary War, to the War on Terror, have set aside their goals in life, left their families at home, pushed back their fears, and done their duty to serve their country, and for so many of them, it was a one way ticket over there. They fought and died so that someone they didn’t know could be free and have the rights that so many take for granted. They looked away when they were protested, but deep down they wondered why people didn’t understand. They tried not to watch the news of death and destruction. They just did their job, until they lost their lives in a war they wished had never started.
 Most of us knew very few soldiers who lost their lives in defense of their country, and some of us may not have known any at all, even though some of our ancestors might have been casualties of a war. I think that sometimes the families of the lost feel alone in their grief. Unless someone has been in that position, they have a difficult time really understanding the depth of the loss. People try to be understanding, imagining how they would feel if it was them, but the reality is that our imaginations are not that good. Those who have lost a loved one to war can never forget the loss or the grief they feel. Grief has no timetable, and some pain just never goes away. No pain is more horrible than losing your child, and losing them in war, seriously compounds that pain.
Most of us knew very few soldiers who lost their lives in defense of their country, and some of us may not have known any at all, even though some of our ancestors might have been casualties of a war. I think that sometimes the families of the lost feel alone in their grief. Unless someone has been in that position, they have a difficult time really understanding the depth of the loss. People try to be understanding, imagining how they would feel if it was them, but the reality is that our imaginations are not that good. Those who have lost a loved one to war can never forget the loss or the grief they feel. Grief has no timetable, and some pain just never goes away. No pain is more horrible than losing your child, and losing them in war, seriously compounds that pain.
Memorial Day, or Decoration Day as it was first called, started three years after the Civil War ended, on May 5,  1868. It was established by the head of an organization of Union veterans…the Grand Army of the Republic. Decoration Day was a time for the nation to decorate the graves of the war dead with flowers. Major General John A Logan declared that Decoration Day should be observed on May 30. It is believed that date was chosen because flowers would be in bloom all over the country. The first large observance was held that year at Arlington National Cemetery, across the Potomac River from Washington, DC. It was a day for all citizens to remember the sacrifice of the brave fallen heroes. And to let the families know that their fallen soldier would ever be forgotten. In honor of all the fallen, may you rest in peace. Thank you for your great sacrifice. Your nation is grateful.
1868. It was established by the head of an organization of Union veterans…the Grand Army of the Republic. Decoration Day was a time for the nation to decorate the graves of the war dead with flowers. Major General John A Logan declared that Decoration Day should be observed on May 30. It is believed that date was chosen because flowers would be in bloom all over the country. The first large observance was held that year at Arlington National Cemetery, across the Potomac River from Washington, DC. It was a day for all citizens to remember the sacrifice of the brave fallen heroes. And to let the families know that their fallen soldier would ever be forgotten. In honor of all the fallen, may you rest in peace. Thank you for your great sacrifice. Your nation is grateful.

