History

 My grandniece, Anna Masterson is her own person. She likes what she likes, and she doesn’t care if that makes her different. She doesn’t care if the things she is into are the popular things that others are into or not. If others don’t Ike what she likes…oh well. Anna is not bothered by her uniqueness…and neither am I.
My grandniece, Anna Masterson is her own person. She likes what she likes, and she doesn’t care if that makes her different. She doesn’t care if the things she is into are the popular things that others are into or not. If others don’t Ike what she likes…oh well. Anna is not bothered by her uniqueness…and neither am I.
Anna is a quiet girl, but she’s not a shy girl. People think she is shy, but she is a listener. Anna gets to know people and what they are all about before she dives into the conversation. She likes to “figure you out” as her mom, Dustie would say. Once she figures you out, she will let you into her world. Anna thinks before she speaks, and her mom says Anna tends to astound her with with her observations and thoughts. Anna is a realist. She has questions about a lot of things and she wants a real answer, not a sugar coated one intended to make her think the world is all soft and sweet. Anna loves to sit and watch documentaries with her mom. She doesn’t care what it’s about, just that it’s real. She’s very smart and her favorite subjects in school are Math and Science.
She loves God, family, and country, in that order. Her loyalty to all of those is second to none. Her cousin, Aleesia Spethman is like a little sister to her. They are both the youngest in their family, and they are just like sisters, complete with sibling rivalry and the fighting that goes along with it. Nevertheless, as annoyed as she may get with her younger cousin, She also councils her, comforts her and protects Aleesia even from Anna’s brother, Matthew who is Anna’s best friend. Sometimes, When Matthew is to much for Anna to handle alone, she pulls out the big guns, her big sister, Raelynn. These days, since Raelynn had to have back surgery, Anna is extremely protective of of her older sister too. If she hears her sister crying in the night from pain, she is the first one there to comfort her.

 Anna has a bright future ahead of her, quite possibly in the area of science. Her close relationship with God will guide her to what he has planned for her. Her parents have no worries about this girl, who is very comfortable in her own skin. She does have a funny side too, though, and according to her mom, loves cheesy puns. One night, she and her mom were making pizza crust. When they were all done and went to wash their hands off, Anna said that they “had just gotten out of a very sticky situation.” Today is Anna’s 10th birthday. Happy birthday Anna!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
Anna has a bright future ahead of her, quite possibly in the area of science. Her close relationship with God will guide her to what he has planned for her. Her parents have no worries about this girl, who is very comfortable in her own skin. She does have a funny side too, though, and according to her mom, loves cheesy puns. One night, she and her mom were making pizza crust. When they were all done and went to wash their hands off, Anna said that they “had just gotten out of a very sticky situation.” Today is Anna’s 10th birthday. Happy birthday Anna!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
 I think we have all had times when we couldn’t seem to concentrate on our work. Or maybe you had a child who couldn’t concentrate on their homework. Well, in 1925, an inventor named Hugo Gernsback, a Luxembourgish-American inventor, writer, editor, and magazine publisher, invented a helmet to make sure a person focused on their work. It was called the Isolator, and it was…well, bizarre. Gernsback was often known as “The Father Of Science Fiction,” and one look at his invention can tell you why that might be. The Isolator was a wooden helmet that blocked out sound and vision in order to help the wearer focus on whatever task was at hand. Gernsback claimed that the helmet blocked out sound by up to 95%, and the tiny glass spy-hole ensured that no amount of movement nearby could be seen, so that the wearer was not distracted. This would eliminate all outside distractions, and barely give enough room for the wearer to see the work in front of them, and nothing else.
I think we have all had times when we couldn’t seem to concentrate on our work. Or maybe you had a child who couldn’t concentrate on their homework. Well, in 1925, an inventor named Hugo Gernsback, a Luxembourgish-American inventor, writer, editor, and magazine publisher, invented a helmet to make sure a person focused on their work. It was called the Isolator, and it was…well, bizarre. Gernsback was often known as “The Father Of Science Fiction,” and one look at his invention can tell you why that might be. The Isolator was a wooden helmet that blocked out sound and vision in order to help the wearer focus on whatever task was at hand. Gernsback claimed that the helmet blocked out sound by up to 95%, and the tiny glass spy-hole ensured that no amount of movement nearby could be seen, so that the wearer was not distracted. This would eliminate all outside distractions, and barely give enough room for the wearer to see the work in front of them, and nothing else.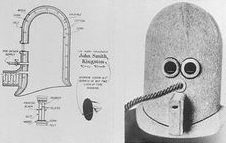
While it might have been a great device to help the wearer focus, it looked more like some kind of medieval torture device. The front of the device had an oxygen tube that was attached to a bottle of oxygen, so it was impossible to eat and study too. So, with no sound, no food, no way to play video games, the modern child would have no choice but to focus on homework. Now, I don’t know if the device could be locked in place…only to be removed when the work at hand was done, but if that is the case, I would think the wearer would get right to the task, so that the device could come off sooner. Just think of how much studying a college student could accomplish. Of course, my guess would be that even a person who was not claustrophobic before wearing the Isolator, would be claustrophobic after wearing it…not to mention a little paranoid, and leery of the person  who made them wear the Isolator in the first place.
who made them wear the Isolator in the first place.
The Isolator never really caught on, and I think anyone can see why that might be, but I guess it might have been a good idea, had it not been so archaic and confining. Of course, that was only part of the problem. The wearer also looked ridiculous, and while they could be anonymously ridiculous looking in some places, it didn’t work that way at the office or in study hall, where everyone knew who was in the office or class. And, of course, it would be really creepy sitting next to someone who was wearing the Isolator. I think we will have to chalk this one up to a good idea gone crazy.
 When I think of Independence Day, I often think about how the fireworks remind me of the many battles that went on in order to win our freedom. Then, I began to wonder if there was ever a time when the 13 colonies almost didn’t become the United States. Britain was, after all, the world’s greatest superpower at the time. British soldiers fought on 5 continents and they had an amazing navy. They massacred rebels and civilians in Jamaica and India around the same time and retained those colonies. So, why not the 13 colonies of North America? There are many explanations, but the one I found most interesting seems, almost to tie to the way things are in America right now…and really all along.
When I think of Independence Day, I often think about how the fireworks remind me of the many battles that went on in order to win our freedom. Then, I began to wonder if there was ever a time when the 13 colonies almost didn’t become the United States. Britain was, after all, the world’s greatest superpower at the time. British soldiers fought on 5 continents and they had an amazing navy. They massacred rebels and civilians in Jamaica and India around the same time and retained those colonies. So, why not the 13 colonies of North America? There are many explanations, but the one I found most interesting seems, almost to tie to the way things are in America right now…and really all along.
The reality is that Britain won many times on the battlefield, but…lost in the taverns. The taverns, you say. How  could that be? Well, taverns were everywhere. They were the social network of colonial life, much like the town hall meetings, and even more, like Facebook or Twitter today. Some areas of Massachusetts and Pennsylvania had taverns every few miles. People could get their mail there, hire a worker, talk to friends, sell crops, buy land, and eat a good meal. It was in these places that opinions were formed. People discussed the problems they had with British rule, and talked about how to get rid of the yoke of the Mother country.
could that be? Well, taverns were everywhere. They were the social network of colonial life, much like the town hall meetings, and even more, like Facebook or Twitter today. Some areas of Massachusetts and Pennsylvania had taverns every few miles. People could get their mail there, hire a worker, talk to friends, sell crops, buy land, and eat a good meal. It was in these places that opinions were formed. People discussed the problems they had with British rule, and talked about how to get rid of the yoke of the Mother country.
Some say that Britain might have had a chance if they had been represented in the taverns too, but I don’t think so. The time had come for Americans to think for themselves, and to run their own lives and their own country. First came the Stamp Act and the Americans protested. More oppression followed, as did the protests.  The resistance grew and grew, until war broke out. No matter what it took, the colonies were determined not to lose. The tavern meetings had accomplished what they needed to. No matter how many times it looked like Britain might win, they would not, because of…well, social networking. Social networking, when people get together to discuss right from wrong, and to discuss solutions. Sometimes the solutions are simple, and other times they create enough of a stir to bring about a revolution. No matter what the reason, the colonies were not about to lose, and because of that, we are a free nation and it was on this day, July 4, 1776 that our independence was made a reality, and we became the land of the free and the home of the brave. Happy Independence Day America!!
The resistance grew and grew, until war broke out. No matter what it took, the colonies were determined not to lose. The tavern meetings had accomplished what they needed to. No matter how many times it looked like Britain might win, they would not, because of…well, social networking. Social networking, when people get together to discuss right from wrong, and to discuss solutions. Sometimes the solutions are simple, and other times they create enough of a stir to bring about a revolution. No matter what the reason, the colonies were not about to lose, and because of that, we are a free nation and it was on this day, July 4, 1776 that our independence was made a reality, and we became the land of the free and the home of the brave. Happy Independence Day America!!

 Prior to 1956, the road and highway system in the United States, well…lets just say, it left something to be desired…like passable roads for instance. Yes, there were a few highways, but on June 29, 1956, President Dwight Eisenhower signed the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956. This bill changed the highways by creating a 41,000-mile “National System of Interstate and Defense Highways” that would, according to Eisenhower, eliminate unsafe roads, inefficient routes, traffic jams and all of the other things that got in the way of “speedy, safe transcontinental travel.” At the same time, highway advocates argued, “in case of atomic attack on our key cities, the road net [would] permit quick evacuation of target areas.” The 1956 law, which allocated more than $30 billion for the construction, declared that the construction of an elaborate expressway system was “essential to the national interest.” The plan included a lot of discussion on things like where exactly the highways should be built, and how much of the cost should be carried by the federal government versus the individual states. Several competing bills went through Congress before 1956, like the ones spearheaded by the retired general and engineer Lucius D Clay, Senator Albert Gore Sr, and Representative George H Fallon, who called his program the “National System of Interstate and Defense Highways,” thereby linking the nationwide construction of highways with the preservation of a strong national defense.
Prior to 1956, the road and highway system in the United States, well…lets just say, it left something to be desired…like passable roads for instance. Yes, there were a few highways, but on June 29, 1956, President Dwight Eisenhower signed the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956. This bill changed the highways by creating a 41,000-mile “National System of Interstate and Defense Highways” that would, according to Eisenhower, eliminate unsafe roads, inefficient routes, traffic jams and all of the other things that got in the way of “speedy, safe transcontinental travel.” At the same time, highway advocates argued, “in case of atomic attack on our key cities, the road net [would] permit quick evacuation of target areas.” The 1956 law, which allocated more than $30 billion for the construction, declared that the construction of an elaborate expressway system was “essential to the national interest.” The plan included a lot of discussion on things like where exactly the highways should be built, and how much of the cost should be carried by the federal government versus the individual states. Several competing bills went through Congress before 1956, like the ones spearheaded by the retired general and engineer Lucius D Clay, Senator Albert Gore Sr, and Representative George H Fallon, who called his program the “National System of Interstate and Defense Highways,” thereby linking the nationwide construction of highways with the preservation of a strong national defense.
For President Eisenhower, however, who had participated in the United States Army’s first transcontinental motor convoy in 1919, during World War II, there was a realization that the country needed a better highway system. He had seen Germany’s Autobahn network, and admired the efficiency of it. In January 1956, Eisenhower repeated his 1954 State of the Union address call for a “modern, interstate highway system.” Later that month, Fallon introduced a revised version of his bill as the Federal Highway Act of 1956. It provided for a 41,000 mile national system of interstate and defense highways to be built over 13 years, with the federal government paying for 90 percent, or $24.8 billion. To raise funds for the project, Congress increased the gas tax from two to three cents per gallon and impose a series of other highway user tax changes. On June 26, 1956, the Senate approved the final version of the bill by a vote of 89 to 1. Senator Russell Long, who opposed the gas tax increase, cast the single “no” vote. That same day, the House approved the bill by a voice vote, and three days later, Eisenhower signed it into law.
The highway construction began almost immediately. With the construction came the employment of tens of thousands of workers and the use of billions of tons of gravel and asphalt. The system fueled a surge in the interstate trucking industry. That was good, but soon it pushed aside the railroads to gain the lion’s share of the domestic shipping market. Interstate highway construction also fostered the growth of roadside businesses such as restaurants, most of which were fast-food chains, hotels and amusement parks. By the 1960s, an estimated one in seven Americans was employed directly or indirectly by the automobile industry. Not only 
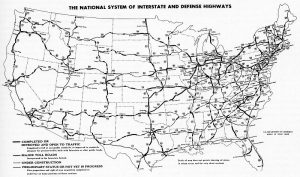 that, but America had become a nation of drivers. Legislation has extended the Interstate Highway Revenue Act three times. Many historians say it is Eisenhower’s greatest domestic achievement. Many called the years between 1956 and 1966 “the Greatest Decade.” Still, critics of the system have pointed to its less positive effects, including the loss of productive farmland and the demise of small businesses and towns in more isolated parts of the country. I suppose that’s true, but it was inevitable.
that, but America had become a nation of drivers. Legislation has extended the Interstate Highway Revenue Act three times. Many historians say it is Eisenhower’s greatest domestic achievement. Many called the years between 1956 and 1966 “the Greatest Decade.” Still, critics of the system have pointed to its less positive effects, including the loss of productive farmland and the demise of small businesses and towns in more isolated parts of the country. I suppose that’s true, but it was inevitable.

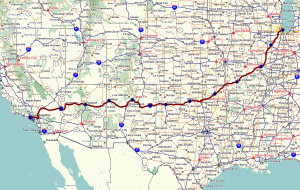 In years gone by, US Route 66 was also known as the Will Rogers Highway, the Main Street of America, or the Mother Road. It was one of the original highways within the US Highway System. US Highway 66 was established on November 11, 1926, with road signs erected the following year. The highway became one of the most famous roads in the United States, and originally ran from Chicago, Illinois, through Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona before ending at Santa Monica, California, covering a total of 2,448 miles. It was highlighted by both the hit song “(Get Your Kicks) on Route 66” and the Route 66 television show in the 1960s, and later, “Wild Hogs.” After 59 years, on June 27, 1985, when the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials decertified the road and removed all its highway signs, and the famous Route 66 entered the realm of history.
In years gone by, US Route 66 was also known as the Will Rogers Highway, the Main Street of America, or the Mother Road. It was one of the original highways within the US Highway System. US Highway 66 was established on November 11, 1926, with road signs erected the following year. The highway became one of the most famous roads in the United States, and originally ran from Chicago, Illinois, through Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona before ending at Santa Monica, California, covering a total of 2,448 miles. It was highlighted by both the hit song “(Get Your Kicks) on Route 66” and the Route 66 television show in the 1960s, and later, “Wild Hogs.” After 59 years, on June 27, 1985, when the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials decertified the road and removed all its highway signs, and the famous Route 66 entered the realm of history.
The idea of building a highway along this route was first mentioned in Oklahoma in the mid-1920s. It was a way to link Oklahoma to cities like Chicago and Los Angeles. Highway Commissioner Cyrus Avery said that it would also be a way of diverting traffic from Kansas City, Missouri and Denver. In 1926, the highway earned its official designation as Route 66. The diagonal course of Route 66 linked hundreds of mostly rural communities to the cities along its route. This was to allow farmers to have an easy transport route for grain and other types of produce for distribution to the cities. In the 1930s, the long-distance trucking industry used it as a way of competing with the railroad for dominance in the shipping market.
During the Dust Bowl years of the 1930s, Route 66 was the scene of a mass westward migration, when more than 200,000 people traveled east from poverty-stricken, drought-ridden areas of California. John Steinbeck immortalized the highway in his classic 1939 novel “The Grapes of Wrath.” Beginning in the 1950s, the building of a massive system of interstate highways made older roads increasingly obsolete, and by 1970, modern four lane 
 highways had bypassed nearly all sections of Route 66. In October 1984, Interstate 40 bypassed the last original stretch of Route 66 at Williams, Arizona. According to the National Historic Route 66 Federation, drivers can still use 85 percent of the road, and Route 66 has become a destination for tourists from all over the world. After watching Wild Hogs, Bob and I became two of the many tourists who did drive a little bit of it when we drove to Madrid, New Mexico as part of our vacation, doing all the touristy things.
highways had bypassed nearly all sections of Route 66. In October 1984, Interstate 40 bypassed the last original stretch of Route 66 at Williams, Arizona. According to the National Historic Route 66 Federation, drivers can still use 85 percent of the road, and Route 66 has become a destination for tourists from all over the world. After watching Wild Hogs, Bob and I became two of the many tourists who did drive a little bit of it when we drove to Madrid, New Mexico as part of our vacation, doing all the touristy things.
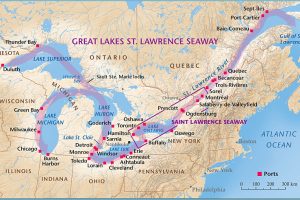 Most people know about the Great Lakes in the north-central United States, but quite possibly, many are not as familiar with the Saint Lawrence Seaway. Nevertheless, the Saint Lawrence Seaway is one of the most important parts of the Great Lakes shipping system. Prior to the Saint Lawrence Seaway there were a number of other canals. In 1871, there were locks on the Saint Lawrence River that allowed transit of vessels 186 feet long, 44 feet 6 inch wide, and 9 feet deep. The First Welland Canal, constructed from 1824–1829, had a minimum lock size of 110 feet long, 22 feet wide, and 8 feet deep, but it was generally too small to allow passage of larger ocean-going ships, which would have eliminated the majority of ships that could ship in quantity. The Welland Canal’s minimum lock size was increased to 150 feet long, 26.5 feet wide, and 9 feet deep for the Second Welland Canal, then to 270 feet long, 45 feet wide, and 14 feet deep with the Third Welland Canal, and to 766 feet long, 80 feet wide, and 30 feet deep with the fourth and current Welland Canal. Still, everyone knew that something else was going to have to be done soon.
Most people know about the Great Lakes in the north-central United States, but quite possibly, many are not as familiar with the Saint Lawrence Seaway. Nevertheless, the Saint Lawrence Seaway is one of the most important parts of the Great Lakes shipping system. Prior to the Saint Lawrence Seaway there were a number of other canals. In 1871, there were locks on the Saint Lawrence River that allowed transit of vessels 186 feet long, 44 feet 6 inch wide, and 9 feet deep. The First Welland Canal, constructed from 1824–1829, had a minimum lock size of 110 feet long, 22 feet wide, and 8 feet deep, but it was generally too small to allow passage of larger ocean-going ships, which would have eliminated the majority of ships that could ship in quantity. The Welland Canal’s minimum lock size was increased to 150 feet long, 26.5 feet wide, and 9 feet deep for the Second Welland Canal, then to 270 feet long, 45 feet wide, and 14 feet deep with the Third Welland Canal, and to 766 feet long, 80 feet wide, and 30 feet deep with the fourth and current Welland Canal. Still, everyone knew that something else was going to have to be done soon.
The first proposals for a bi-national comprehensive deep waterway along the Saint Lawrence were made in the 1890s. In the following decades, developers proposed a hydropower project that would be inseparable from the seaway,  the various governments and seaway supporters believed that the deeper water to be created by the hydro project was necessary to make the seaway channels feasible for ocean-going ships, which we all know was an essential part of the shipping business for the United States and the world. United States proposals for development up to and including World War I met with little interest from the Canadian federal government…at least at first. Later, the two national governments submitted Saint Lawrence plans to a group for study. By the early 1920s, both The Wooten-Bowden Report and the International Joint Commission recommended the project.
the various governments and seaway supporters believed that the deeper water to be created by the hydro project was necessary to make the seaway channels feasible for ocean-going ships, which we all know was an essential part of the shipping business for the United States and the world. United States proposals for development up to and including World War I met with little interest from the Canadian federal government…at least at first. Later, the two national governments submitted Saint Lawrence plans to a group for study. By the early 1920s, both The Wooten-Bowden Report and the International Joint Commission recommended the project.
The Liberal Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King really wasn’t all for the project, mostly because of opposition to the project in Quebec, in 1932. He and the United States representative finally signed a treaty of intent. The treaty was submitted to the United States Senate in November of 1932 and hearings continued until a vote was taken on March 14, 1934. The majority did vote in favor of the treaty, but it failed to gain the necessary two-thirds vote for ratification. Additional attempts between the governments in the 1930s to forge an agreement Failed due to opposition by the Ontario government of Mitchell Hepburn, and that of Quebec. In 1936, John C Beukema, who was the head of the Great Lakes Harbors Association and a member of the Great Lakes Tidewater Commission, was among a delegation of eight from the Great Lakes states to meet at the White House with United States President Franklin D Roosevelt to get his support for the Seaway project.
After much back and forth wrangling, the two countries agreed that the Saint Lawrence Seaway was a  necessary addition to the Great Lakes shipping industry, and it would later prove to be a vital part of it. In the years that my sister, my parents, and I lived in Superior, Wisconsin, the Saint Lawrence Seaway was something that, at least our parents remember being under construction. The opening ceremony took place on June 26, 1959, and was presided over by United States President Dwight D Eisenhower and Queen Elizabeth II. Once it was opened, it created a navigational channel from the Atlantic Ocean to all the Great Lakes. The seaway, made up of a system of canals, locks, and dredged waterways, extends a distance of nearly 2,500 miles, from the Atlantic Ocean through the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to Duluth, Minnesota, on Lake Superior.
necessary addition to the Great Lakes shipping industry, and it would later prove to be a vital part of it. In the years that my sister, my parents, and I lived in Superior, Wisconsin, the Saint Lawrence Seaway was something that, at least our parents remember being under construction. The opening ceremony took place on June 26, 1959, and was presided over by United States President Dwight D Eisenhower and Queen Elizabeth II. Once it was opened, it created a navigational channel from the Atlantic Ocean to all the Great Lakes. The seaway, made up of a system of canals, locks, and dredged waterways, extends a distance of nearly 2,500 miles, from the Atlantic Ocean through the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to Duluth, Minnesota, on Lake Superior.

 When Colorado Governor John Evans was looking to win a seat in the United States Senate, he made a bold, but unwise decision to attempt to remove all Native American activity in eastern Colorado Territory. On June 24, 1864, he warned that all peaceful Indians in the region must report to the Sand Creek reservation or risk being attacked. It was truly a halfhearted offer of sanctuary, with an ulterior motive. Evans then made one bad decision after another, when he issued a second proclamation that invited white settlers to indiscriminately “kill and destroy all…hostile Indians.” At the same time, Evans began creating a temporary 100-day militia force to wage war on the Indians. He placed the new regiment under the command of Colonel John Chivington, another ambitious man who hoped to gain high political office by fighting Indians.
When Colorado Governor John Evans was looking to win a seat in the United States Senate, he made a bold, but unwise decision to attempt to remove all Native American activity in eastern Colorado Territory. On June 24, 1864, he warned that all peaceful Indians in the region must report to the Sand Creek reservation or risk being attacked. It was truly a halfhearted offer of sanctuary, with an ulterior motive. Evans then made one bad decision after another, when he issued a second proclamation that invited white settlers to indiscriminately “kill and destroy all…hostile Indians.” At the same time, Evans began creating a temporary 100-day militia force to wage war on the Indians. He placed the new regiment under the command of Colonel John Chivington, another ambitious man who hoped to gain high political office by fighting Indians.
The Sioux, Cheyenne, and Arapahoe Indians of eastern Colorado had no idea of the political maneuverings of the White Man. Although some bands had violently resisted white settlers in years past, by the autumn of 1864 many Indians were becoming more receptive to Cheyenne Chief Black Kettle’s argument that they must make peace. Black Kettle had recently returned from a visit to Washington, DC, where President Abraham Lincoln had given him a huge American flag of which Black Kettle was very proud. He had seen the vast numbers of the white people and their powerful machines. The Indians, Black Kettle argued, must make peace or be crushed.
Word of Governor Evans’ June 24 offer of sanctuary was not well received by many of the Indians, most of whom still distrusted the White Man and were unwilling to give up the fight. Only Black Kettle and a few of the  lesser chiefs took Evans up on his offer of amnesty. Evans and Chivington were reluctant to see hostilities further abate before they had won a glorious victory, so they weren’t overjoyed that Black Kettle and his people accepted the offer. Nevertheless, they grudgingly promised Black Kettle that his people would be safe, if they came to Fort Lyon in eastern Colorado. In November 1864, the Indians reported to the fort as requested. Major Edward Wynkoop, the commanding federal officer, told Black Kettle to settle his band about 40 miles away on Sand Creek, where he promised they would be safe.
lesser chiefs took Evans up on his offer of amnesty. Evans and Chivington were reluctant to see hostilities further abate before they had won a glorious victory, so they weren’t overjoyed that Black Kettle and his people accepted the offer. Nevertheless, they grudgingly promised Black Kettle that his people would be safe, if they came to Fort Lyon in eastern Colorado. In November 1864, the Indians reported to the fort as requested. Major Edward Wynkoop, the commanding federal officer, told Black Kettle to settle his band about 40 miles away on Sand Creek, where he promised they would be safe.
Unfortunately, Wynkoop could not control John Chivington, and John Chivington was not inclined to honor the promise of safety. By November, the 100-day enlistment of the soldiers in his Colorado militia was nearly up, and Chivington hadn’t killed any of the Indians. With his political stock falling rapidly, and he seemed almost insane in his desire to kill Indians. “I long to be wading in gore!” he is said to have proclaimed at a dinner party. In his demented state, Chivington apparently decided that it did not matter whether he killed peaceful or hostile Indians. In his mind, Black Kettle’s village on Sand Creek became a legitimate and easy target, and he assumed that no one would ever know the difference.
Chivington led 700 men, many of them drunk, in a daybreak raid on Black Kettle’s peaceful village on November 29, 1864. Most of the Cheyenne warriors were away hunting. In the horrific hours that followed, Chivington and his men brutally slaughtered 105 women and children and killed 28 men. The soldiers scalped and mutilated the corpses, carrying body parts back to display in Denver as trophies. Somehow, Black Kettle and a number of other Cheyenne managed to escape. Chivington’s treachery would not go unnoticed as he had supposed, and in the following months, the nation learned of the horror of Sand Creek. Many Americans were 
 horrified and disgusted. Chivington and his soldiers had left the military and were beyond reach of a court martial. Still, Chivington’s horrific acts killed any chance of realizing his political ambitions, and he spent the rest of his inconsequential life wandering the West. Evans also paid a great price for the scandal. He was forced to resign as governor and his hopes of holding political office were dashed. Evans went on to a successful and lucrative career building and operating Colorado railroads, however. I suppose time can make people forget wrongs done, whether they should be forgotten or not.
horrified and disgusted. Chivington and his soldiers had left the military and were beyond reach of a court martial. Still, Chivington’s horrific acts killed any chance of realizing his political ambitions, and he spent the rest of his inconsequential life wandering the West. Evans also paid a great price for the scandal. He was forced to resign as governor and his hopes of holding political office were dashed. Evans went on to a successful and lucrative career building and operating Colorado railroads, however. I suppose time can make people forget wrongs done, whether they should be forgotten or not.
 The Indian tribes didn’t usually have much use for the White Man, especially the ones who worked for the government. It seemed all they wanted to do was to herd the Indians onto the reservations and take away their lands, culture, and their language. This made the majority of Indians pretty angry, but President Calvin Coolidge was different than most government people. It wasn’t a matter of what he was able to accomplish, but rather what he wished he could accomplish, and maybe what he set the stage for…and mostly what the Indians knew was in his heart.
The Indian tribes didn’t usually have much use for the White Man, especially the ones who worked for the government. It seemed all they wanted to do was to herd the Indians onto the reservations and take away their lands, culture, and their language. This made the majority of Indians pretty angry, but President Calvin Coolidge was different than most government people. It wasn’t a matter of what he was able to accomplish, but rather what he wished he could accomplish, and maybe what he set the stage for…and mostly what the Indians knew was in his heart.
President Coolidge had made it very clear that, on personal moral grounds, he sincerely regretted the state of poverty to which many Indian tribes had sunk after decades of legal persecution and forced assimilation had been forced upon them. Coolidge made a public policy toward Indians, that included the Indian Citizen Act of 1924, which granted automatic United States citizenship to all American tribes, something that made perfect sense, since they had been here longer than the nation had existed. Nevertheless, during his two terms in office, while Coolidge  presented a public image as a strong proponent of tribal rights, the United States government policies of forced assimilation remained in full swing during his administration. At this time, all Indian children were placed in federally funded boarding schools in an effort to familiarize them with white culture and train them in marketable skills. During their schooling, they were separated from their families and stripped of their native language and culture, something that should never have happened, and something that has since been changed.
presented a public image as a strong proponent of tribal rights, the United States government policies of forced assimilation remained in full swing during his administration. At this time, all Indian children were placed in federally funded boarding schools in an effort to familiarize them with white culture and train them in marketable skills. During their schooling, they were separated from their families and stripped of their native language and culture, something that should never have happened, and something that has since been changed.
While not able to fix all the wrongs done to the Indians, Coolidge was still considered a friend of the Indians. In 1927, he planned a trip to the Black Hills region of North Dakota. In anticipation of the trip, the Sioux County Pioneer newspaper reported that a Sioux elder named Chauncey Yellow Robe, a descendant of Sitting Bull and an Indian school administrator, had suggested that Coolidge be inducted into the tribe. The article stated that  Yellow Robe graciously offered the president a “most sincere and hearty welcome” and hoped that Coolidge and his wife would enjoy “rest, peace, quiet and friendship among us.” Calvin Coolidge was very pleased at the offer, and decided to accept. This was not something that was offered to many people, so it was a great honor. The Sioux County Pioneer newspaper of North Dakota reported that on June 23, 1927 President Calvin Coolidge would be “adopted” into a Sioux tribe at Fort Yates on the south central border of North Dakota. At the Sioux ceremony in 1927, photographers captured Coolidge, in suit and tie, as he was given a grand ceremonial feathered headdress by Sioux Chief Henry Standing Bear and officially declared an honorary tribal member.
Yellow Robe graciously offered the president a “most sincere and hearty welcome” and hoped that Coolidge and his wife would enjoy “rest, peace, quiet and friendship among us.” Calvin Coolidge was very pleased at the offer, and decided to accept. This was not something that was offered to many people, so it was a great honor. The Sioux County Pioneer newspaper of North Dakota reported that on June 23, 1927 President Calvin Coolidge would be “adopted” into a Sioux tribe at Fort Yates on the south central border of North Dakota. At the Sioux ceremony in 1927, photographers captured Coolidge, in suit and tie, as he was given a grand ceremonial feathered headdress by Sioux Chief Henry Standing Bear and officially declared an honorary tribal member.
 These days, every military veteran has available to them, a compensation package to thank them for their service. Returning servicemen have access to unemployment compensation, low-interest home and business loans, and…most importantly, funding for education, but this was not always the case. In fact, there was a time when returning veterans had to fight for bonuses they were supposed to receive, which brought about the 1932 Bonus March, in which 20,000 unemployed veterans and their families flocked in protest to Washington. I think most of us would agree that our veterans should not have to fight for the things promised to them for their service, after they have already spent time fighting for their country.
These days, every military veteran has available to them, a compensation package to thank them for their service. Returning servicemen have access to unemployment compensation, low-interest home and business loans, and…most importantly, funding for education, but this was not always the case. In fact, there was a time when returning veterans had to fight for bonuses they were supposed to receive, which brought about the 1932 Bonus March, in which 20,000 unemployed veterans and their families flocked in protest to Washington. I think most of us would agree that our veterans should not have to fight for the things promised to them for their service, after they have already spent time fighting for their country.
President Franklin D Roosevelt was responsible for the sweeping New Deal reforms, many of which were really not good for this nation or its people, but there was one part of that legislation that has been a good thing for returning veterans…the G.I. Bill. On this day June 22, 1944, President Franklin D Roosevelt signed the G.I. Bill. It was an unprecedented act of legislation designed to compensate returning members of the armed services, known as G.I.s, for their efforts in World War II. The G.I. Bill…officially the Servicemen’s Readjustment Act of 1944…was proposed in an effort to avoid a relapse into the Great Depression after the war ended. The American Legion, a veteran’s organization, successfully fought for many of the provisions included in the bill, which gave returning servicemen the compensations they now have. By giving veterans money for tuition, living expenses, books, supplies and  equipment, the G.I. Bill effectively transformed higher education in America. Before the war, college had been an option for only 10-15 percent of young Americans, and university campuses had become known as a haven for the most privileged classes. This was not what America was supposed to be about. By 1947, the contrast was striking. Veterans made up half of the nation’s college enrollment. Three years later, nearly 500,000 Americans graduated from college, compared with 160,000 in 1939. Sure, they had to serve their country, but for many young people, this was not only what they felt was their duty, but it also became a scholarship program.
equipment, the G.I. Bill effectively transformed higher education in America. Before the war, college had been an option for only 10-15 percent of young Americans, and university campuses had become known as a haven for the most privileged classes. This was not what America was supposed to be about. By 1947, the contrast was striking. Veterans made up half of the nation’s college enrollment. Three years later, nearly 500,000 Americans graduated from college, compared with 160,000 in 1939. Sure, they had to serve their country, but for many young people, this was not only what they felt was their duty, but it also became a scholarship program.
As educational institutions opened their doors to this diverse new group of students, overcrowded classrooms and residences prompted widespread improvement and expansion of university facilities and teaching staffs. The bill was not only good for the veterans, but also for the economy, as more teaching jobs were created. An array of new vocational courses were developed across the country, including advanced training in education, agriculture, commerce, mining and fishing…skills that had previously been taught only informally. Some of these classes are responsible for some of the jobs that everyday Americans, even those without college educations have held. Jobs such as mining, and farming, and even fishing became commonplace.

The G.I. Bill became one of the major forces for economic expansion in America that lasted 30 years after World War II. Only 20% of the money set aside for unemployment compensation under the bill was given out. Most veterans found jobs or pursued higher education. Low interest loans enabled millions of American families to move out of cities and buy or build homes outside the city, changing the face of the suburbs. Over 50 years, the impact of the G.I. Bill was enormous, with 20 million veterans and dependents using the education benefits and 14 million home loans guaranteed, for a total federal investment of $67 billion. Among the millions of Americans who have taken advantage of the bill are former Presidents George H.W. Bush and Gerald Ford, former Vice President Al Gore and entertainers Johnny Cash, Ed McMahon, Paul Newman and Clint Eastwood, and closer to home, my brother-in-law, Ron Schulenberg, as well as my nephew, Allen Beach and soon, his wife, Gabby.
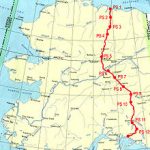
 Dependency on foreign oil has long been a problem for the United States, keeping us always at the mercy of foreign oil companies. When we are dependent on foreign oil, we are subject to their prices and their shortages, or their refusal to sell to us. This nation has always needed to be dependent on our own production of oil, and as an oil rich nation, there is no reason for us to look elsewhere for our oil supply. Of course, the environmentalists would disagree with me, and I don’t want oil spills any more than anyone else does. Still, foreign nations have us at a disadvantage, not to mention that oil production in the United States would provide a lot jobs in the United States.
Dependency on foreign oil has long been a problem for the United States, keeping us always at the mercy of foreign oil companies. When we are dependent on foreign oil, we are subject to their prices and their shortages, or their refusal to sell to us. This nation has always needed to be dependent on our own production of oil, and as an oil rich nation, there is no reason for us to look elsewhere for our oil supply. Of course, the environmentalists would disagree with me, and I don’t want oil spills any more than anyone else does. Still, foreign nations have us at a disadvantage, not to mention that oil production in the United States would provide a lot jobs in the United States.
I’m not the only one who thinks this way either. In 1968, a massive oil field was discovered on the north coast of Alaska near Prudhoe Bay, which is north of the Arctic Circle, but the ice-packed waters of the Beaufort Sea are inaccessible to oil tankers. In 1972, the Department of the Interior authorized drilling there, and after the Arab oil embargo of 1973 plans moved quickly to begin construction of a pipeline. The Alyeska Pipeline Service Company was formed by a consortium of major oil companies, and in 1974 construction began. The steel pipeline is 48 inches in diameter, and it winds through 800 miles of Alaskan wilderness, crossing three Arctic mountain ranges and hundreds of rivers and streams. Environmentalists fought to prevent its construction, saying it would destroy a pristine ecosystem, but they were ultimately overruled by Congress, who saw it as a way of lessening America’s dependence on foreign oil. The trans-Alaska pipeline was the world’s largest privately funded construction project to that date, costing $8 billion and taking three years to build. The conservation groups argued that the pipeline would destroy caribou habitats in the Arctic, melt the fragile permafrost (which is permanently frozen subsoil), along its route, and pollute the salmon-rich waters of the Prince William Sound at Valdez. Under pressure, Alyeska agreed to extensive environmental precautions, including building 50% of the pipeline above the ground to protect the permafrost from the naturally heated crude oil and to permit passage of caribou underneath.
On June 20, 1977, with the flip of a switch in Prudhoe Bay, crude oil from the nation’s largest oil field began flowing south, down the trans-Alaska pipeline to the ice-free port of Valdez, Alaska. It wasn’t without its glitches, however. Power supply problems, a cracked section of pipe, faulty welds, and an unsuccessful dynamite attack on the pipeline outside of Fairbanks delayed the arrival of oil at Valdez for several weeks. Finally, in August, the first oil tanker left Valdez en route to the lower 48 states. The trans-Alaska pipeline was great for the Alaskan economy. Today, about 800,000 barrels move through the pipeline each day. Altogether, the pipeline has carried more than 14 billion barrels of oil in its lifetime. For its first decade of existence, the pipeline was quietly applauded as an environmental success, much to the chagrin of the environmentalists. Caribou populations in the vicinity of the pipeline actually grew, partly because many of the grizzly bears and wolves were scared off by the pipeline work, and the permafrost remained intact. The only major oil spill on land occurred when an unknown saboteur blew a hole in the pipe near Fairbanks, and 550,000 gallons of oil spilled onto the ground. Then, on March 24, 1989, the worst fears of environmentalists were realized when the Exxon Valdez ran aground in the Prince William Sound after filling up at the port of Valdez. Ten million gallons of oil were dumped into the water, devastating hundreds of miles of coastline. In the 1990s, the Alaskan oil enterprise drew further controversy when the Alyeska Pipeline Service Company attempted to cover up electrical and mechanical problems in the aging pipeline.
In 2001, President George W. Bush proposed opening a portion of the 19 million acre Arctic National Wildlife 
 Refuge, east of Prudhoe Bay, to oil drilling. The environmental groups immediately opposed the proposal and it was initially defeated. Then, in 2006, the Senate voted 51-49 in favor of a budget resolution that included billions for Arctic drilling. Environmental groups are still fighting the legislation. I think, drilling at home is the best way to protect American jobs, and our economy, and as we all know, it could certainly use a serious boost right now.
Refuge, east of Prudhoe Bay, to oil drilling. The environmental groups immediately opposed the proposal and it was initially defeated. Then, in 2006, the Senate voted 51-49 in favor of a budget resolution that included billions for Arctic drilling. Environmental groups are still fighting the legislation. I think, drilling at home is the best way to protect American jobs, and our economy, and as we all know, it could certainly use a serious boost right now.

