Caryn

 My niece, Jessi (Hadlock) Sawdon grew up in a household of much laughter and joking, as well as many “nicknames.” She and her three siblings, Ryan, Lindsay, and Kellie love to come up with new nicknames, and they are all very inventive. Jessi has had names like Jeffica, Jeffica Hadddlo, Jeff, Jessicar, Aunt Jessi, Aunt Jessica, mom, wife, and sister. Of course, “Jeffica” has had a part in passing the nicknames to her other siblings too. It’s quite a tradition.
My niece, Jessi (Hadlock) Sawdon grew up in a household of much laughter and joking, as well as many “nicknames.” She and her three siblings, Ryan, Lindsay, and Kellie love to come up with new nicknames, and they are all very inventive. Jessi has had names like Jeffica, Jeffica Hadddlo, Jeff, Jessicar, Aunt Jessi, Aunt Jessica, mom, wife, and sister. Of course, “Jeffica” has had a part in passing the nicknames to her other siblings too. It’s quite a tradition.
Much has changed for Jessi in recent months. Her sister, Lindsay Moore tells me that Jessi is blooming where planted, meaning that Jessi really likes living in Cheyenne, where she and her husband, Jason Sawdon moved a while back so he could take a wonderful promotion with the Wyoming Highway Patrol. They have found a great church and have made really great connections there. Of course, Jessi immediately got involved in church things! That doesn’t surprise me at all. Jessi loves the Lord, and she is a very social person, so making friends comes easy to her. They found a great home, and they have been settling in and doing some updating as they go…putting their own personal touches on it. 
She still runs on “Jessi Time,” which for those who don’t know, is always a little late. In our family, there are a number of people who run on their own time, and so if you really need them to be somewhere on-time, you should probably tell them that things start half an hour early. It’s been a running joke in our family, particularly my mom’s family (Byer Time) and Jessi’s mom Allyn Hadlock, who operates on Hadlock Time. The Hadlock family has also found out that Jessi isn’t the only offending party in her own little family, because Jason may actually be less punctual than Jessi. Strangely, their daughter Addie may be the only one in the house keeping them on time. A fact that I find very funny. The child keeping the parents in line!! Hahaha!!!
For Lindsay, who lives in Laramie, and so is now only about an hour away from her sister, having Jessi in Cheyenne has proven to be a great blessing. Lindsay tells me that Jessi is an excellent sister and she been blessed to be able to see more of her. The girls get together often since they live closer now. It’s so easy to pop 
 over for the day or go stay overnight. Plus, the nearness allows them to participate in more of each other’s celebrations, but the real joy is that they get to see their girls, Addi and Lindsay’s daughter, Mackenzie be close and play together! That is something Lindsay hasn’t had before, because Laramie is the closest she has lived to her family since her college days. I’m really happy for both families that they have this new-found closeness. It has been wonderful for all of them. Today is Jessi’s birthday. Happy birthday Jessi!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
over for the day or go stay overnight. Plus, the nearness allows them to participate in more of each other’s celebrations, but the real joy is that they get to see their girls, Addi and Lindsay’s daughter, Mackenzie be close and play together! That is something Lindsay hasn’t had before, because Laramie is the closest she has lived to her family since her college days. I’m really happy for both families that they have this new-found closeness. It has been wonderful for all of them. Today is Jessi’s birthday. Happy birthday Jessi!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

 To call the Pearl Harbor attack, a “mistake on the part of the Japanese,” seems like a case of serious misinformation, on the part of the one who made such a comment, Admiral Chester A Nimitz. Nevertheless, that is what he said on Christmas Day, 1941, after he toured the destruction of his new duty station shortly after his Christmas Eve arrival. Anyone who would have heard Nemitz comments probably thought the new Commander of the Pacific Fleet might be just a little bit “off his rocker!!” Where everyone else saw all the ships sunken and knew of the 3,800 men who lost their lives that day, and in their minds, there was nothing good about all this, so what was the admiral thinking.
To call the Pearl Harbor attack, a “mistake on the part of the Japanese,” seems like a case of serious misinformation, on the part of the one who made such a comment, Admiral Chester A Nimitz. Nevertheless, that is what he said on Christmas Day, 1941, after he toured the destruction of his new duty station shortly after his Christmas Eve arrival. Anyone who would have heard Nemitz comments probably thought the new Commander of the Pacific Fleet might be just a little bit “off his rocker!!” Where everyone else saw all the ships sunken and knew of the 3,800 men who lost their lives that day, and in their minds, there was nothing good about all this, so what was the admiral thinking.
Sunday, December 7th, 1941, found Admiral Chester Nimitz attending a concert in Washington, DC. He received a page and was told that he had a phone call. On the other end was President Franklin Delano Roosevelt, who told Admiral Nimitz that his new assignment was to be the Commander of the Pacific Fleet. Admiral Nimitz flew to Hawaii to assume command of the Pacific Fleet, arriving to see such a spirit of despair, dejection, and defeat. It seemed that everyone thought the Japanese had already won the war. As the tour boat returned to dock, the young helmsman of the boat asked, “Well Admiral, what do you think after seeing all this destruction?” The admiral’s reply shocked everyone within the sound of his voice. Admiral Nimitz said, “The Japanese made three of the biggest mistakes an attack force could ever make, or God was taking care of America. Which do you think it was?” Shocked and surprised, the young helmsman asked, “What do mean by saying the Japanese made the three biggest mistakes an attack force ever made?”
What was meant, is really the difference between the thinking of an enlisted man, and the thinking of a great strategist, such as Admiral Nemitz was. I’m actually quite sure most of us would have fallen more in line with 
 the enlisted helmsman…basically seeing the trees and missing the forest. So, Admiral Nemitz had to enlighten those around him. The first mistake made by the Japanese, is actually one I had heard before, and likely the “best” mistake for the people concerned. The attack on Pearl Harbor took place on a Sunday morning…when many of the men who might have been on the ships, were on leave. In fact, nine out of ten of the men stationed on the ships were on leave. That cut the loss of life down by 90%. As Admiral Nemitz told the people, “If those same ships had been lured to sea and been sunk–we would have lost 38,000 men instead of 3,800.” Now the Japanese had angered the “Sleeping Giant” that was the United States and left the majority of the fighting force to exact their revenge.
the enlisted helmsman…basically seeing the trees and missing the forest. So, Admiral Nemitz had to enlighten those around him. The first mistake made by the Japanese, is actually one I had heard before, and likely the “best” mistake for the people concerned. The attack on Pearl Harbor took place on a Sunday morning…when many of the men who might have been on the ships, were on leave. In fact, nine out of ten of the men stationed on the ships were on leave. That cut the loss of life down by 90%. As Admiral Nemitz told the people, “If those same ships had been lured to sea and been sunk–we would have lost 38,000 men instead of 3,800.” Now the Japanese had angered the “Sleeping Giant” that was the United States and left the majority of the fighting force to exact their revenge.
Of course, that was only their first mistake. Their second mistake was that when the Japanese saw all those battleships lined up in a row, they got so carried away sinking the battleships, they either didn’t notice, or forgot about the dry docks opposite those ships. Leaving the dry docks, meant that instead of towing every one of those ships to the America to be repaired, they could simply be raised from the shallow water they were in, and one tug could pull them over to the dry docks. Any salvageable ships could be repaired and back out at sea by the time they could have towed them to the America. Add that fact to the already established fact that Admiral Nemitz already had crews ashore anxious to man those ships. They were ready to fight.
The final mistake made by the Japanese was that they were either unaware of or forgot about the above-ground fuel storage tanks located just five miles away over the next hill. In fact, every drop of fuel in the Pacific theater of war was sitting out there in those tanks, and even if the ships were ready to go and fully manned, the lack of fuel would have prevented an attack on the Japanese fleet.
While everyone around him was thinking of the devastation and the defeat of the attack on Pearl Harbor, Admiral Nemitz saw the three biggest mistakes of the Japanese government, or as he preferred to call it, that 
 “God was taking care of America.” I tend to agree with Admiral Nemitz in that I, too, think it was God taking care of us. My thought is that the Japanese knew about the dry docks and the fuel storage, but in their “excitement” at pulling off the surprise attack, they forgot all about them. Of course, there is that first mistake of planning an attack of God’s Day. Seriously, they chose to take on the whole Pacific Fleet…and God too!! Wow!! It’s hard to be more “stupid” than that.
“God was taking care of America.” I tend to agree with Admiral Nemitz in that I, too, think it was God taking care of us. My thought is that the Japanese knew about the dry docks and the fuel storage, but in their “excitement” at pulling off the surprise attack, they forgot all about them. Of course, there is that first mistake of planning an attack of God’s Day. Seriously, they chose to take on the whole Pacific Fleet…and God too!! Wow!! It’s hard to be more “stupid” than that.

 It seems like every year, right about Christmastime, I start feeling a longing for the trails and my summertime early morning walks. During the winter, my walking moves from the outdoor trails and particularly the Sage Trail at the end of my block to the now famous (at least for those who know me well) carpet trail that runs through a section of my house. I have a treadmill, but I seldom use it, because it doesn’t feel like a “trail” to me. The Sage Trail is really a walking path nestled between an alley and a creek bed with the Sage Creek, now contained in a blocks-long culvert to keep it mostly in check…unless we get a lot of rain, after which, the Sage Creek overflows its containment through the grates provided for such overflow events.
It seems like every year, right about Christmastime, I start feeling a longing for the trails and my summertime early morning walks. During the winter, my walking moves from the outdoor trails and particularly the Sage Trail at the end of my block to the now famous (at least for those who know me well) carpet trail that runs through a section of my house. I have a treadmill, but I seldom use it, because it doesn’t feel like a “trail” to me. The Sage Trail is really a walking path nestled between an alley and a creek bed with the Sage Creek, now contained in a blocks-long culvert to keep it mostly in check…unless we get a lot of rain, after which, the Sage Creek overflows its containment through the grates provided for such overflow events.
It is during this time, that my mind turns to trail pictures, trail information, and basically looking for the next  trail challenge. The trail that has come to mind this time is the Bright Angel Trail at the Grand Canyon in Arizona. Of course, we will not be hiking this trail anytime soon, but with tools like Google Earth, you can actually take a “hike” without leaving the comfort of your own home…which is the “hike” I can do at this time of year in Wyoming. My Husband Bob and I, during a visit to the Grand Canyon a few years ago, walked down into the canyon on the Bright Angel Trail for a very short distance. We weren’t really prepared for a long hike, and especially one that went down into the canyon and then, of course, back up the trail again. The signs warned people, not saying “What goes up, must come down,” but rather that “What goes down, must come up!!!” In other words, if you can’t hike out of the canyon, you had better not hike into the canyon. While we were is good shape, and probably could have hiked down and then back up, we simply didn’t have enough time to hike it. The trail is 8.1 miles…one way, and 8.1 miles back. The downhill version is said to take about 3.5 hours and the uphill version 4.8 hours. I guess that is why most people who hike the trail do it over a two-day timeframe. There is a ranch at the bottom that provides a place to sleep and meals, so it really would be a cool hike to take someday, but I don’t know if we will ever get around to it. Nevertheless, I can always dream, and the virtual views provided by Google Earth make me feel like I’m there…almost.
trail challenge. The trail that has come to mind this time is the Bright Angel Trail at the Grand Canyon in Arizona. Of course, we will not be hiking this trail anytime soon, but with tools like Google Earth, you can actually take a “hike” without leaving the comfort of your own home…which is the “hike” I can do at this time of year in Wyoming. My Husband Bob and I, during a visit to the Grand Canyon a few years ago, walked down into the canyon on the Bright Angel Trail for a very short distance. We weren’t really prepared for a long hike, and especially one that went down into the canyon and then, of course, back up the trail again. The signs warned people, not saying “What goes up, must come down,” but rather that “What goes down, must come up!!!” In other words, if you can’t hike out of the canyon, you had better not hike into the canyon. While we were is good shape, and probably could have hiked down and then back up, we simply didn’t have enough time to hike it. The trail is 8.1 miles…one way, and 8.1 miles back. The downhill version is said to take about 3.5 hours and the uphill version 4.8 hours. I guess that is why most people who hike the trail do it over a two-day timeframe. There is a ranch at the bottom that provides a place to sleep and meals, so it really would be a cool hike to take someday, but I don’t know if we will ever get around to it. Nevertheless, I can always dream, and the virtual views provided by Google Earth make me feel like I’m there…almost.

 Summer will be here before I know it, and while most of my hikes will be taken on the Sage Trail, and maybe the nearby Platte River Trail, I know I will feel much better about it all, because while I’m fine with walking the “Carpet Trail,” the scenery leaves something to be desired. While I love my house, it just doesn’t have the classic scenic views of hiking or walking in the great outdoors.
Summer will be here before I know it, and while most of my hikes will be taken on the Sage Trail, and maybe the nearby Platte River Trail, I know I will feel much better about it all, because while I’m fine with walking the “Carpet Trail,” the scenery leaves something to be desired. While I love my house, it just doesn’t have the classic scenic views of hiking or walking in the great outdoors.

 It’s hard for me to believe that my husband’s aunt, Linda Cole has been in Heaven for over six years now. I remember so well the times we went to visit her and Uncle Bobby Cole, when they lived in Kennebec, South Dakota when our girls, Corrie Petersen and Amy Royce were little. It wasn’t that going to the small, and I do mean small town, with a population of 334 in the 1980s, that has dwindled to 281 in 2020, but rather that Linda and Bobby were fun people to be around. Pretty much, we sat around and played cards. It wasn’t the card games, but rather the laughter and jokes, the fun conversations, and really just the time together that made the trips fun. There was also the added benefit of cousins, Sheila and Pat for the girls to play with. And the additional added benefit of a vacation with little cost. Of course, that was not why we wet. We went because we liked Linda and Bobby, and the visit was always fun. Following a fire at the hotel that Linda and Bobby owned in Kennebec, they made the decision to move to Winnemucca, Nevada and that was when the yearly visits ended. We did go, but it was further to go, and so not as easy to manage, and so happened less and less often. It was the end of an era.
It’s hard for me to believe that my husband’s aunt, Linda Cole has been in Heaven for over six years now. I remember so well the times we went to visit her and Uncle Bobby Cole, when they lived in Kennebec, South Dakota when our girls, Corrie Petersen and Amy Royce were little. It wasn’t that going to the small, and I do mean small town, with a population of 334 in the 1980s, that has dwindled to 281 in 2020, but rather that Linda and Bobby were fun people to be around. Pretty much, we sat around and played cards. It wasn’t the card games, but rather the laughter and jokes, the fun conversations, and really just the time together that made the trips fun. There was also the added benefit of cousins, Sheila and Pat for the girls to play with. And the additional added benefit of a vacation with little cost. Of course, that was not why we wet. We went because we liked Linda and Bobby, and the visit was always fun. Following a fire at the hotel that Linda and Bobby owned in Kennebec, they made the decision to move to Winnemucca, Nevada and that was when the yearly visits ended. We did go, but it was further to go, and so not as easy to manage, and so happened less and less often. It was the end of an era.
Aunt Linda was the middle child of parents, Robert and Nettie Knox, between sisters Joann Schulenberg and Margee Kountz. There were almost 16 years between Joann (my mother-in-law) and her first younger sister, Linda, and then three years between Linda and Margee. Because of the years between them, Linda became a very young aunt in 1950, when my sister-in-law, Marlyce Schulenberg was born, and she didn’t like it one bit!! It wasn’t that she didn’t love Marlyce, because she did. The problem was that Linda didn’t understand the word…aunt. As a little girl of only 3 years and 7 months. So, being a little girl, she misunderstood the word Aunt and thought she was going to be an ant!! She was absolutely not interested in being a bug!!


Linda was a funny person even as a child, and maybe that was that made her and Bobby so much fun to be around. The funny things she always said, and her infectious laugh were a big part of what I loved about her. In fact, I find that when I think about her, I really miss her to this day. While we didn’t see them as much in the last years of their lives, and I think that is really too bad. Today would have been Linda’s 76th birthday, and I am sorry that she isn’t still with us. Happy birthday in Heaven, Linda. We love and miss you very much.
 Every time I hear about a lost treasure, I wonder how many such treasures there are around the world. Some of these treasures are most likely lost forever, and one of those (so far anyway) is “The Old Spanish Treasure” which isn’t a treasure in a tropical, mysterious location from a long-ago shipwreck. Legend has it that the treasure is located in “The Old Spanish Treasure Cave,” which is actually located along the Missouri-Arkansas border. The location in and of itself, makes me wonder why no one has ever recovered the treasure.
Every time I hear about a lost treasure, I wonder how many such treasures there are around the world. Some of these treasures are most likely lost forever, and one of those (so far anyway) is “The Old Spanish Treasure” which isn’t a treasure in a tropical, mysterious location from a long-ago shipwreck. Legend has it that the treasure is located in “The Old Spanish Treasure Cave,” which is actually located along the Missouri-Arkansas border. The location in and of itself, makes me wonder why no one has ever recovered the treasure.
Apparently, about 400 years ago, Spanish conquistadors headed north in the dead of winter, raiding Native American villages as they went. During the raids, they accumulated a great amount of treasure, but the winter was raging, and they needed a place to get out of the cold. So, the conquistadors took refuge in a large cave. Of  course, they thought they were alone, but that couldn’t have been further from the truth. The Native Americans saw their campfire smoke coming out of a natural chimney at the top of the cave. Taking their revenge, the Native Americans attacked the conquistadors, leaving only one survivor.
course, they thought they were alone, but that couldn’t have been further from the truth. The Native Americans saw their campfire smoke coming out of a natural chimney at the top of the cave. Taking their revenge, the Native Americans attacked the conquistadors, leaving only one survivor.
Somehow keeping his wits about him, the survivor sealed all but one entrance and drew two maps…one on parchment, and one etched into a limestone rock. While the rock bearing the map was recovered, the treasure has yet to be found. The location of the cave is known, and I’m sure it and the map have been scoured repeatedly, but the survivor hid his treasure well. It almost makes me wonder if he hid it at all. Maybe he just took it with him or went back for it soon after it was hidden, and then simply left the map to throw people off the trail.
 The cave was sealed up until it was re-discovered in 1885 by an old Spaniard from Madrid. As the story goes, old Spaniard the legend apparently led him to two maps…one on a tree, and another on a rock. Neither these maps nor the treasure, estimated today at 40 million dollars, have ever been found, but there have been a number of artifacts found, like helmets, pieces of armor, and weapons from the period. Some have even claimed to have found a few gold coins, but there is no proof of that. The Spaniard was ill, and so did not stay long. Other people continued to search for the treasure for many years, but to no avail. To this day, the elusive treasure remains hidden, and I suppose it always will.
The cave was sealed up until it was re-discovered in 1885 by an old Spaniard from Madrid. As the story goes, old Spaniard the legend apparently led him to two maps…one on a tree, and another on a rock. Neither these maps nor the treasure, estimated today at 40 million dollars, have ever been found, but there have been a number of artifacts found, like helmets, pieces of armor, and weapons from the period. Some have even claimed to have found a few gold coins, but there is no proof of that. The Spaniard was ill, and so did not stay long. Other people continued to search for the treasure for many years, but to no avail. To this day, the elusive treasure remains hidden, and I suppose it always will.
 “Terrible Tilly” came by her name honesty, because from the start, the lighthouse seemed to be nothing but trouble. “Terrible Tilly” is the nickname of the Tillamook Lighthouse sits on top of a sea stack of basalt, more than a mile off the banks of Oregon’s North Coast. Looking to put up a lighthouse in the area Tilly’s story began in 1878 when a solid basalt rock was selected as the location for a lighthouse off the coast of Tillamook Head. Any construction work can have its dangers, but construction a mile offshore in all kinds of weather, can be particularly dangerous. Such was the case with “Terrible Tilly” when even before the work began, a master mason surveying the location was swept out to sea, never to be seen again.
“Terrible Tilly” came by her name honesty, because from the start, the lighthouse seemed to be nothing but trouble. “Terrible Tilly” is the nickname of the Tillamook Lighthouse sits on top of a sea stack of basalt, more than a mile off the banks of Oregon’s North Coast. Looking to put up a lighthouse in the area Tilly’s story began in 1878 when a solid basalt rock was selected as the location for a lighthouse off the coast of Tillamook Head. Any construction work can have its dangers, but construction a mile offshore in all kinds of weather, can be particularly dangerous. Such was the case with “Terrible Tilly” when even before the work began, a master mason surveying the location was swept out to sea, never to be seen again.
Even with the dangers and the loss, work began in 1880, and the lighthouse went into operation in 1881. In those days…the days before GPS, lighthouses were a vital part of the shipping business. The ships couldn’t see the  dangers that lurked in the night, so knowing what was just below the surface, or even above the surface of the water was very important. As ships got closer to shore, the possibility of hitting rock or small island could be disastrous. Never was that more evident that the disaster that occurred just a few weeks before the lighthouse opened. A ship sailed too close to the shore because of low visibility, and crashed, killing all 16 crew members. The need for the lighthouse was proven once again, in a very sad way.
dangers that lurked in the night, so knowing what was just below the surface, or even above the surface of the water was very important. As ships got closer to shore, the possibility of hitting rock or small island could be disastrous. Never was that more evident that the disaster that occurred just a few weeks before the lighthouse opened. A ship sailed too close to the shore because of low visibility, and crashed, killing all 16 crew members. The need for the lighthouse was proven once again, in a very sad way.
While you might think that making the lighthouse operation would have ended the tragic connections with “Terrible Tilly,” but that really wasn’t the case. The conditions on the lighthouse were extremely rough, and one lighthouse keeper even allegedly went insane. Being even just a mile offshore, made life very isolated. The storms beat on the lighthouse, and I’m sure they sometimes wondered if the lighthouse could take it. The howling wind can be enough to drive some people crazy. Living in Wyoming, I know that there are times when  we wonder if the wind will ever quit. When it finally does, it is almost shockingly quiet. Not everyone can take the howling wind.
we wonder if the wind will ever quit. When it finally does, it is almost shockingly quiet. Not everyone can take the howling wind.
As GPS came into being, the need for lighthouses is becoming less and less. It’s rather a sad fact, because these icons of history, are fading into the past, and for me, that feels very sad. Decades after the lighthouse was decommissioned in 1957, it was turned into a columbarium, which is a storehouse for urns of cremated remains. To this day, the remains of 30 people are still stored inside the lighthouse. “Terrible Tilly” was closed down in 1957 and remains off limits to the public to this day.
 No disease, especially those that are highly contagious, and for which there is no known cure, is easy to find out that one has, and for those who might have been around the victim of said disease, it can be very frightening. Mary Mallon, who was born September 23, 1869, Cookstown, County Tyrone, Northern Ireland, immigrated to the United States in 1883. Possessing minimal skills, she made her living as a domestic servant, most often as a cook. At some point, she became a carrier of the typhoid bacterium (Salmonella typhi), although no one really knows exactly when or how that happened. Nevertheless, between 1900 and 1907, nearly two dozen people fell ill with typhoid fever in households in New York City and Long Island where Mallon worked. That was the first clue that she was a carrier, because the illnesses often occurred shortly after she began working in each household, then by the time the disease was traced to its source in a household where she had recently been employed, Mallon had already moved on, with no forwarding address. The whole dilemma made it very hard to really track down the carrier, and she knew nothing about it, because she wasn’t ill. It is unusual to be asymptomatic, but not impossible, and Typhoid Mary was one of the unusual ones.
No disease, especially those that are highly contagious, and for which there is no known cure, is easy to find out that one has, and for those who might have been around the victim of said disease, it can be very frightening. Mary Mallon, who was born September 23, 1869, Cookstown, County Tyrone, Northern Ireland, immigrated to the United States in 1883. Possessing minimal skills, she made her living as a domestic servant, most often as a cook. At some point, she became a carrier of the typhoid bacterium (Salmonella typhi), although no one really knows exactly when or how that happened. Nevertheless, between 1900 and 1907, nearly two dozen people fell ill with typhoid fever in households in New York City and Long Island where Mallon worked. That was the first clue that she was a carrier, because the illnesses often occurred shortly after she began working in each household, then by the time the disease was traced to its source in a household where she had recently been employed, Mallon had already moved on, with no forwarding address. The whole dilemma made it very hard to really track down the carrier, and she knew nothing about it, because she wasn’t ill. It is unusual to be asymptomatic, but not impossible, and Typhoid Mary was one of the unusual ones.
Finally, in 1906, after 6 people in a household of 11 where Mallon had worked in Oyster Bay, New York, became sick with typhoid, the home’s owners hired New York City Department of Health sanitary engineer George Soper to investigate the outbreak. Soper’s specialty was studying typhoid fever epidemics, so he was just the man for the job. Of course, Soper was not the only investigator looking for the carrier of the dreaded typhoid disease. Typhoid can usually be cured these days using medications like Ciprofloxacin and Ceftriaxone, but in those days, it meant a death sentence for many people. As the investigation continued, it was concluded that the outbreak had likely been caused by contaminated water. Mallon continued to work as a cook, moving from household to household until 1907. Finally in the right place at the right time, Mallon was located working in a Park Avenue home in Manhattan. The winter of that year, following an outbreak in the Manhattan household that involved a death from the disease, Soper met with Mallon. Following extensive tests, he linked all 22 cases of typhoid fever that had been recorded in New York City and the Long Island area to her. It was this connection that earner her the “unwanted” nickname of Typhoid Mary.
A scared Mallon fled the area, but authorities led by Soper finally overtook her and had her committed to an isolation center on North Brother Island, which is a part of the Bronx, New York. There she stayed, despite an appeal to the US Supreme Court. She was finally released in 1910, when the health department released her on condition that she never again accept employment that involved the handling of food. These days she might have been able to go back to work as a cook, but at that time they couldn’t successfully test for the presence of the bacteria in a person, and with the very real possibility of passing the contagion through food, it was a risk they couldn’t take.
Unfortunately for Mallon, an epidemic four years later, brought her once again into the spotlight. The epidemic 
 was at a sanatorium in Newfoundland, New Jersey, and at Sloane Maternity Hospital in Manhattan. Mallon had worked as a cook at both places. Mallon was at last found in a suburban home in Westchester County, New York, and was returned to North Brother Island, where she remained for the rest of her life. In 1932, she suffered a paralytic stroke that led to her slow death six years later.
was at a sanatorium in Newfoundland, New Jersey, and at Sloane Maternity Hospital in Manhattan. Mallon had worked as a cook at both places. Mallon was at last found in a suburban home in Westchester County, New York, and was returned to North Brother Island, where she remained for the rest of her life. In 1932, she suffered a paralytic stroke that led to her slow death six years later.
Mallon claimed to have been born in the United States, but it was later determined that she was an immigrant. Although she herself was immune to the typhoid bacillus, 51 original cases of typhoid and three deaths were directly attributed to Typhoid Mary. There were also countless more that were indirectly attributed to her as people she infected, passed the illness to people they came in contact with.

 I suppose that turning on any government could be viewed at treason, but some governments are so evil and so corrupt that the citizens have no choice but to take them down, and as in the case of the Soviet regime, even the members of the government themselves could be viewed as treasonous and subject to removal. The big difference with the Soviet regime was that when the government officials were being removed, they were also being killed. The event was called The Great Purge, and as the name implies, the idea was to remove, in this case permanently, anyone who disagreed with Stalin and his way of running the regime. It was also called The Great Terror and Ezhovshchina (after the People’s Commissar of Internal Affairs, Nikolai Ezhov, who oversaw the process before he himself became one of its casualties). No one was safe from the long arm of Stalin.
I suppose that turning on any government could be viewed at treason, but some governments are so evil and so corrupt that the citizens have no choice but to take them down, and as in the case of the Soviet regime, even the members of the government themselves could be viewed as treasonous and subject to removal. The big difference with the Soviet regime was that when the government officials were being removed, they were also being killed. The event was called The Great Purge, and as the name implies, the idea was to remove, in this case permanently, anyone who disagreed with Stalin and his way of running the regime. It was also called The Great Terror and Ezhovshchina (after the People’s Commissar of Internal Affairs, Nikolai Ezhov, who oversaw the process before he himself became one of its casualties). No one was safe from the long arm of Stalin.
The Great Purge, the state-organized bloodshed…slaughter really, that overwhelmed the Communist Party and Soviet society took place from 1936 to 1938. The real reasons for these heinous attacks on government officials within the Soviet regime remain largely unknown, but it’s easy to imagine that Stalin irrationally felt like his men were trying to take over the operation, or run from it, and so they had to be removed. Of course, they said it was in response to terror attacks or threatened terror attacks, but to think anyone believed that is more insane than the act itself.
Of course, Stalin had to do things “right,” so he held three elaborately staged show trials of former high-ranking Communists. In July-August 1936, in the first show trial, Lev Kamenev, Grigorii Zinoviev, and fourteen others were convicted of having organized a Trotskyite-Zinovievite terrorist center that allegedly had been formed in 1932. In the end, they were found guilty of the assassination of Sergei Kirov in December 1934. This first trial did little to satisfy Stalin, not did the efforts of the police to investigate and liquidate such “nefarious plots.” So, Stalin replaced Genrikh Iagoda with Nikolai Ezhov as head of the NKVD in September 1936. In January 1937, a second show trial was held, with Iurii Piatakov and other leading figures in the industrialization drive as the chief defendants. At a mandatory session of the party’s Central Committee in February-March 1937, Nikolai Bukharin and Aleksei Rykov, who were the most prominent party members associated with the so-called Rightist deviation of the late 1920s and early 1930s, were accused of having collaborated with the Trotskyite-Zinovievite terrorists as well as with foreign intelligence agencies. In March 1938, in the third show trial, they along with Iagoda and others were tried, convicted, and sentenced to death.
The period of time between the second and third show trials saw the upper echelon of the Red Army, provincial party secretaries, party and state personnel among the national minorities, industrial managers, and other officials destroyed by arrests and summary executions. As the “process” of torture, threats, and executions continued, it fed upon itself. The accused under severe physical and psychological pressure from their interrogators, named names and confessed to outlandish crimes…all probably fake and forced. Millions of others, terrified of being accused themselves, became involved in the frenzied search for “enemies of the people.” On July 3, 1937, the Politbiuro ordered Ezhov to conduct “mass operations” to locate and arrest recidivist criminals, ex-kulaks, and other “anti-Soviet elements,” all of whom were prosecuted by three-person  tribunals. Ezhov actually established quotas in each district for the number of arrests, meaning that more arrests were made for trumped-up charges. Ezhov’s projected totals of 177,500 exiled and 72,950 executed were eventually exceeded in what was an absolute witch hunt.
tribunals. Ezhov actually established quotas in each district for the number of arrests, meaning that more arrests were made for trumped-up charges. Ezhov’s projected totals of 177,500 exiled and 72,950 executed were eventually exceeded in what was an absolute witch hunt.
The repercussions of this horrific time in history are unknown. The situation, that began as a bloody retribution against what was already a defeated political opposition, soon developed into a its own class of disease within the political body. Its psychological consequences among the survivors were long-lasting and incalculable…mostly fear of dying and fear of anyone in authority.
 When the automobile was invented, everyone rightly thought it was going to be the “end all, beat all” of transportation inventions. In many ways, it probably was just that…at that time anyway, but as with any form of transportation, when it’s very new, it’s also very flawed. By its very nature, and invention is often trial and error. On November 30, 1965, a 32-year-old lawyer named Ralph Nader saw something in the automobile that caused him to become very concerned…concerned enough to write a book about his findings. Nader called his book Unsafe at Any Speed: The Designed-In Dangers of the American Automobile. Just the title of the book is enough to worry the thinking consumer…or maybe what would have been the “overthinking” consumer.
When the automobile was invented, everyone rightly thought it was going to be the “end all, beat all” of transportation inventions. In many ways, it probably was just that…at that time anyway, but as with any form of transportation, when it’s very new, it’s also very flawed. By its very nature, and invention is often trial and error. On November 30, 1965, a 32-year-old lawyer named Ralph Nader saw something in the automobile that caused him to become very concerned…concerned enough to write a book about his findings. Nader called his book Unsafe at Any Speed: The Designed-In Dangers of the American Automobile. Just the title of the book is enough to worry the thinking consumer…or maybe what would have been the “overthinking” consumer.
Still, the book became a best-seller right away. It also triggered the passage of the National Traffic and Motor Vehicle Safety Act of 1966…seat-belt laws in 49 states…all but New Hampshire. It also triggered a number of other road-safety initiatives. The original automobile really did have some serious safety flaws, and while a lot of people would argue that the seatbelt doesn’t prevent death in accidents, the reality is that it prevents many of those deaths, and the ones that seatbelts don’t prevent, are so bad that nothing would have prevented death.
These days, Ralph Nader is known for his role in national politics, running unsuccessfully for President of the United States four times…running with the Green Party in 1996 and 2000, the Reform Party in 2004, and as an independent in 2008. In each campaign, Nader said he sought to highlight under-reported issues and a perceived need for electoral reform. He received nearly three million votes during his 2000 candidacy, but also stirred controversy over allegations that his campaign helped Republican candidate George W Bush win in a highly contested election against Democratic candidate Al Gore.
Nader’s book placed the automobile in a negative light for the 50 years prior to the releases of the book, saying 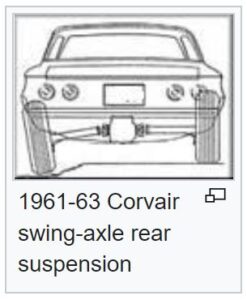 that “the automobile has brought death, injury, and the most inestimable sorrow and deprivation to millions of people.” His real complaint was that technology existed at that time to make cars safer, but automakers had little incentive to use them. He thought that the automakers skipped the important steps that could have brought about a much safer vehicle. He wrote that on the contrary, “the gigantic costs of the highway carnage in this country support a service industry,” meaning doctors, lawyers, police officers, morticians, with no real plans to change things and “there is little in the dynamics of the automobile accident industry that works for its reduction.”
that “the automobile has brought death, injury, and the most inestimable sorrow and deprivation to millions of people.” His real complaint was that technology existed at that time to make cars safer, but automakers had little incentive to use them. He thought that the automakers skipped the important steps that could have brought about a much safer vehicle. He wrote that on the contrary, “the gigantic costs of the highway carnage in this country support a service industry,” meaning doctors, lawyers, police officers, morticians, with no real plans to change things and “there is little in the dynamics of the automobile accident industry that works for its reduction.”
Nader’s book brought to light some of the harsh truths, or rather serious flaws, about and in cars and car companies that auto-safety advocates had known for some time, and seemingly done nothing about. Nader pushed hard against the automakers, and in 1956, at a series of Congressional hearings on traffic safety, doctors and other experts lamented the “wholesale slaughter” on American highways. Safety measures had all but been ignored, and that year, nearly 40,000 people were killed in cars, with no sign of a decrease in numbers on the horizon. If the consumers wanted the much-needed safety features, they could pay extra for a Ford with seatbelts and a padded dashboard, but very few did. It was estimated that only 2% of Ford buyers took the $27.00 seatbelt option. The auto industry not only made it more costly to get the safety features, but downplayed the importance of it.
In his book, Nader particularly ranted against the Chevy Corvair, a sporty car with a swing axle and rear–mounted engine that was introduced in 1959, saying that the car epitomized the triumph of “stylistic  pornography over engineering integrity.” The swing axle made the rear end unstable, causing it to “tuck under during turns and skid or roll over much more frequently than other cars did.” As it turned out, a 1972 government study vindicated the Corvair, finding that it was just as safe as any other car. I couldn’t say one way or another, but Nader called that study “rigged.” Nevertheless, the damage was done. The Corvair became an icon of dangerous, even deadly design, which was later proven to e the case. The last one rolled off the assembly line in 1969. I suppose the auto industry is a heavily funded group, and it would be easy to “fix” the numbers to say what they wanted to say.
pornography over engineering integrity.” The swing axle made the rear end unstable, causing it to “tuck under during turns and skid or roll over much more frequently than other cars did.” As it turned out, a 1972 government study vindicated the Corvair, finding that it was just as safe as any other car. I couldn’t say one way or another, but Nader called that study “rigged.” Nevertheless, the damage was done. The Corvair became an icon of dangerous, even deadly design, which was later proven to e the case. The last one rolled off the assembly line in 1969. I suppose the auto industry is a heavily funded group, and it would be easy to “fix” the numbers to say what they wanted to say.
Nader’s book mobilized a mass movement. Armed with the truth, ordinary consumers banded together to demand safer cars and better laws. When consumers take a stand, things can, and do happen. Today, seat belts, air bags, anti-lock brakes and other innovations are standard features in almost every new car. I don’t know what kind of a politician Ralph Nader was or is, but in this one thing anyway, he did something good.

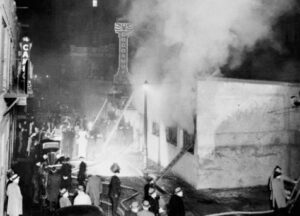 One of the saddest realities is that safety standards are often the result of a tragedy. That is exactly what happened during what is still the deadliest nightclub fire in the world, and the second-deadliest single-building fire…after the Iroquois Theatre fire. On November 28, 1942, Cocoanut Grove was well known as one of Boston’s most popular nightspots. The club attracted many celebrity guests and Boston’s most elite citizens. The fire was a tragedy that later became the catalyst for change in fire prevention, and how to survive a fire. Unfortunately, 492 people have to pay for these lessons with their lives.
One of the saddest realities is that safety standards are often the result of a tragedy. That is exactly what happened during what is still the deadliest nightclub fire in the world, and the second-deadliest single-building fire…after the Iroquois Theatre fire. On November 28, 1942, Cocoanut Grove was well known as one of Boston’s most popular nightspots. The club attracted many celebrity guests and Boston’s most elite citizens. The fire was a tragedy that later became the catalyst for change in fire prevention, and how to survive a fire. Unfortunately, 492 people have to pay for these lessons with their lives.
The Cocoanut Grove was owned by Barnet “Barney” Welansky, who was closely connected to the Mafia and to Mayor Maurice J Tobin. As often happens, anyone connected to the Mafia and/or a politician, also believes they are above the law. They do things the way they want to, cutting corners to save a buck, and then they expect their connections to get them out of trouble when and if it shows up. Welansky was no different. In the building and running of his nightclub, fire regulations had been pretty much disregarded, because as we all know, regulations are for other people to follow, but not, in this case, the Cocoanut Grove. There was a constant concern about people sneaking in the exit doors, so rather than pay for security to prevent such actions, some exit-doors had been locked to prevent said unauthorized entry. The decor wasn’t always checked for safety either, like the elaborate palm tree décor, which contained flammable materials. Also, because of wartime shortages of freon, the air-conditioning used flammable gas to cool the club. Welansky often disregarded the capacity laws to bring in bigger profits, and so it was that during the first Thanksgiving weekend since the United States had entered World War II, the Grove was filled to more than twice its legal capacity.
When disaster struck, it was in the form of a fire that was initiated by an electrical short and fueled by methyl chloride in the air conditioning unit. Once it started, the fire and its associated smoke spread rapidly through all 
 areas of the club. The problem…people were unable to escape due in part to locked exit doors. The only saving grace was that the local hospitals were especially well prepared to treat the casualties, because they had been rehearsing emergency drills in response to possible wartime attacks on the East Coast. Had that not been the case, the death toll would have likely included the 130 survivors too. If “good” can be said to come from tragedy, it would come in the form of the demonstrated value of the new blood banks and stimulated important advances in the treatment of burn victims. As always happens after a tragedy, many new laws were enacted for public establishments, including the banning of flammable decorations, a provision that emergency exits must be kept unlocked (from the inside), and that revolving doors cannot be the only exit.
areas of the club. The problem…people were unable to escape due in part to locked exit doors. The only saving grace was that the local hospitals were especially well prepared to treat the casualties, because they had been rehearsing emergency drills in response to possible wartime attacks on the East Coast. Had that not been the case, the death toll would have likely included the 130 survivors too. If “good” can be said to come from tragedy, it would come in the form of the demonstrated value of the new blood banks and stimulated important advances in the treatment of burn victims. As always happens after a tragedy, many new laws were enacted for public establishments, including the banning of flammable decorations, a provision that emergency exits must be kept unlocked (from the inside), and that revolving doors cannot be the only exit.
The investigation centered around Welansky’s blatant disregard for the safety of the very patrons who gave him his wealth by their continued patronage of his establishment. An official report revealed that “the Cocoanut Grove had been inspected by a captain in the Boston Fire Department (BFD) just ten days before the fire and declared safe. Further, it was found that the Grove had not obtained any licenses for operation for several years. There were no food handlers’ permits and no liquor licenses. Stanley Tomaszewski, the busboy who had allegedly started the fire, was underage and should not have been working there. Moreover, the recent remodeling of the Broadway Lounge had been done without building permits, using unlicensed contractors.” Tomaszewski testified at the inquiry and was exonerated, as he was not responsible for the flammable decorations or the life safety code violations. While declared innocent, Tomaszewski would pay for the “crime” anyway, in the form of being “ostracized for much of his life because of the fire.” Tomaszewski died in 1994. In the end, the blame was rightly assigned to Welansky, for violation of the existing safety standards, and upon 
 his conviction in 1943, Welansky was sentenced to 12–15 years in prison. Welansky served nearly four years before being quietly pardoned by Tobin, who had been elected governor of Massachusetts since the fire. In December 1946, diagnosed with cancer, Welansky was released from Norfolk Prison, telling reporters, “I wish I’d died with the others in the fire.” Nine weeks later on 27 Jan 1947 the cancer took his life. He was 49 years old.
his conviction in 1943, Welansky was sentenced to 12–15 years in prison. Welansky served nearly four years before being quietly pardoned by Tobin, who had been elected governor of Massachusetts since the fire. In December 1946, diagnosed with cancer, Welansky was released from Norfolk Prison, telling reporters, “I wish I’d died with the others in the fire.” Nine weeks later on 27 Jan 1947 the cancer took his life. He was 49 years old.

