galaxy

 Many of us have seen shows about a spacecraft that got lost in space and is seen wandering around trying to make their way back. Of course, those shows are fiction, but if you were going to explore beyond our galaxy, you would most likely need to send some sort of probe or spaceship out into the far reaches of space to see what it’s like out there. If the empty probe can’t function out there, it’s very likely not a good idea to send a manned spaceship out there. That is what Nasa figured anyway, and so in 1972, Pioneer 10…originally designated Pioneer F, was launched into space. Pioneer 10 is an American space probe, manufactured by TRW Inc. It isn’t overly heavy, weighing just 569 pounds. Its first mission to the planet Jupiter was completed with its closest approach happening on Dec 3, 1973. At that point, Pioneer 10 became the first of five artificial objects to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. At that point, it became part of a space exploration project that was conducted by the NASA Ames Research Center in California.
Many of us have seen shows about a spacecraft that got lost in space and is seen wandering around trying to make their way back. Of course, those shows are fiction, but if you were going to explore beyond our galaxy, you would most likely need to send some sort of probe or spaceship out into the far reaches of space to see what it’s like out there. If the empty probe can’t function out there, it’s very likely not a good idea to send a manned spaceship out there. That is what Nasa figured anyway, and so in 1972, Pioneer 10…originally designated Pioneer F, was launched into space. Pioneer 10 is an American space probe, manufactured by TRW Inc. It isn’t overly heavy, weighing just 569 pounds. Its first mission to the planet Jupiter was completed with its closest approach happening on Dec 3, 1973. At that point, Pioneer 10 became the first of five artificial objects to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. At that point, it became part of a space exploration project that was conducted by the NASA Ames Research Center in California.
“Pioneer 10 was assembled around a hexagonal bus with a 9-foot diameter parabolic dish high-gain antenna, and the spacecraft was spin stabilized around the axis of the antenna. Its electric power was supplied by four radioisotope thermoelectric generators that provided a combined 155 watts at launch. Pioneer was launched on March 2, 1972, by an Atlas-Centaur expendable vehicle from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Between July 15, 1972, and February 15, 1973, it became the first spacecraft to traverse the asteroid belt. Photography of Jupiter began November 6, 1973, at a range of 16,000,000 miles, and about 500 images were transmitted. The closest approach to the planet was on December 4, 1973, at a range of 82,178 miles. During the mission, the on-board instruments were used to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter, the solar wind, cosmic rays, and eventually the far reaches of the Solar System and heliosphere.”
I find it hard to believe that Nasa thought that the spacecraft would last as long as it did, but I suppose that the further out it went in space, the less it would encounter the kind of space debris that came from Earth. Still, there are meteors and planets, stars that it could be pulled into, and so many more things that could have meant the destruction if the craft. Nevertheless, Pioneer 10 continued to send out radio transmissions continued between Nasa and itself until January 23, 2003, and then only because of the loss of electric power for its radio transmitter. At that point, the probe was at a distance of 12 billion kilometers (7,456,454,306.848 miles) from Earth. 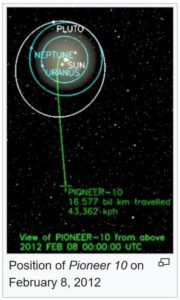

According to sources, “If left undisturbed, Pioneer 10 and its sister craft Pioneer 11 will join the two Voyager spacecraft and the New Horizons spacecraft in leaving the Solar System to wander the interstellar medium. The Pioneer 10 trajectory is expected to take it in the general direction of the star Aldebaran, currently located at a distance of about 68 light years. If Aldebaran had zero relative velocity, it would require more than two million years for the spacecraft to reach it. Well before that, in about 90,000 years, Pioneer 10 will pass about 0.23 parsecs (0.75 light-years) from the late K-type star HIP 117795. This is the closest stellar flyby in the next few million years of all the four Pioneer and Voyager spacecrafts, which are leaving the Solar System.”
 For centuries, I think most people thought Earth was alone in the universe, at least when it came to planets. It was inevitable that people would decide that they wanted to know more about the numerous stars, the moon, and the sun. Once the telescope was invented, with the earliest workings towards the design of the refracting telescope being made by German-Dutch lensmaker Hans Lippershey in 1608, people, or at least a few people, were able to see the things that really existed beyond Earth’s atmosphere. I can only imagine the shock as the first viewing proclaimed, quite loudly, that we were not alone in the universe…not even in the realm of planets, not to mention galaxies.
For centuries, I think most people thought Earth was alone in the universe, at least when it came to planets. It was inevitable that people would decide that they wanted to know more about the numerous stars, the moon, and the sun. Once the telescope was invented, with the earliest workings towards the design of the refracting telescope being made by German-Dutch lensmaker Hans Lippershey in 1608, people, or at least a few people, were able to see the things that really existed beyond Earth’s atmosphere. I can only imagine the shock as the first viewing proclaimed, quite loudly, that we were not alone in the universe…not even in the realm of planets, not to mention galaxies.
Thinking about the vastness of the universe has a tendency to make you feel very small, and I don’t suppose many people in the 1600s were very comfortable with that. These days the thought of the other planets in our galaxy doesn’t really bother us, and in fact it seems completely normal to us. As my husband, Bob and I have been going on our nightly walks, I have been watching the movement of several planets…namely Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Just the thought of these huge, star-like celestial bodies, at least to the naked eye, makes me think about how amazing God’s creation is. I have been able to picture in my mind, how these planets look in the universe, and now, the idea that they are stars seems absurd. Of course, my own “revelation” of that fact came centuries after the great men of science figured that fact out, and of course, that “revelation”didn’t creep into my mind today, but was rather taught to me over the years of my schooling. Still, sometimes while you know something is a fact, the enormity of it takes much longer to fully register in your head. That is the way i feel about it,after a fashion anyway…as if suddenly, I can almost see the planets with the naked eye.
It makes me wonder how the various scientists, who discovered each of the planets in our galaxy, felt the first time the telescope found a planet, especially a new one…or shall I say, one that was never discovered before that moment. With that thought running around in my head, I learned that on September 23, 1846, German astronomer Johann Gottfried Galle discovers the planet Neptune at the Berlin Observatory. We all now know Neptune as the eight planet in our solar system, and because it was the eighth, it was further out in space than  the seven that were discovered before it. I can only imagine the excitement he felt in that moment. He was looking upon something no other human being had seen before. I don’t know if he had any concept of how big the planet was in comparison to Earth, but we now know that Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun in the Solar System, because Pluto was later found and then after years as a planet, discounted as a planet and named a dwarf planet. In the Solar System Neptune is the fourth-largest planet by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth. At that size, I would say that Neptune’s discovery was by no means a small thing.
the seven that were discovered before it. I can only imagine the excitement he felt in that moment. He was looking upon something no other human being had seen before. I don’t know if he had any concept of how big the planet was in comparison to Earth, but we now know that Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun in the Solar System, because Pluto was later found and then after years as a planet, discounted as a planet and named a dwarf planet. In the Solar System Neptune is the fourth-largest planet by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth. At that size, I would say that Neptune’s discovery was by no means a small thing.

 It is so easy to focus on our own little planet, or our own little space, but the reality is that outside of our atmosphere, there is a huge space that makes us look like a speck of dust…if that. In centuries past, people could see the sun and the stars, and I suppose they considered the fact that there might be something else out there, but since they really had no way of viewing it better than using the naked eye, they just thought that it was what it was…somewhat like a curtain with holes poked into it, and they really didn’t ever expect to see anything more. Still, somewhere along the way, someone thought it might be possible to see further into the sky that just the few stars that were visible. Inventions came about to aid the people in seeing into the great beyond.
It is so easy to focus on our own little planet, or our own little space, but the reality is that outside of our atmosphere, there is a huge space that makes us look like a speck of dust…if that. In centuries past, people could see the sun and the stars, and I suppose they considered the fact that there might be something else out there, but since they really had no way of viewing it better than using the naked eye, they just thought that it was what it was…somewhat like a curtain with holes poked into it, and they really didn’t ever expect to see anything more. Still, somewhere along the way, someone thought it might be possible to see further into the sky that just the few stars that were visible. Inventions came about to aid the people in seeing into the great beyond.
One man who had a vision to be able to see what was out there, was Edwin Hubble. Edwin wanted to learn about space from the time he was a young boy. He said, “I knew that even if I were second or third rate, it was astronomy that mattered.” He knew that he simply couldn’t do anything else. That kind of 
 determination makes a person great, and he was determined. Hubble’s work was something his father didn’t understand, and didn’t want him to do, in fact making him promise to be a lawyer. Hubble tried, but his heart just wasn’t in it. He also worked as a teacher of Spanish, Physics, Mathematics, and coached basketball. His popularity as a teacher is recorded in the school yearbook dedicated to him: “To our beloved teacher of Spanish and Physics, who has been a loyal friend to us in our senior year, ever willing to cheer and help us both in school and on the field, we, the class of 1914, lovingly dedicate this book.”
determination makes a person great, and he was determined. Hubble’s work was something his father didn’t understand, and didn’t want him to do, in fact making him promise to be a lawyer. Hubble tried, but his heart just wasn’t in it. He also worked as a teacher of Spanish, Physics, Mathematics, and coached basketball. His popularity as a teacher is recorded in the school yearbook dedicated to him: “To our beloved teacher of Spanish and Physics, who has been a loyal friend to us in our senior year, ever willing to cheer and help us both in school and on the field, we, the class of 1914, lovingly dedicate this book.”
While Edwin Hubble’s father may have thought his son had made a terrible mistake, and that he was even one can short of a six-pack, Edwin Hubble knew that there was more to see out there, and he simply couldn’t sit idly by and miss God’s big show. In October 1923 he spotted what he first thought was a nova star flaring up dramatically in the M31 “nebula” in the constellation of Andromeda. After careful examination of photographic plates of the same area taken previously by other astronomers, including his greatest scientific rival, Harlow 
 Shapley, who thought that the Milky Way was the end of the universe, he realized that it was a Cepheid star. On December 29, 1924, all of his hard work came to fruition, when he made another startling find…all galaxies seemed to be receding from us with velocities that increased in proportion to their distance from us…a relationship now known as Hubble’s Law. On this day, December 30, 1924, Edward Hubble was finally able to make the announcement that would make his a household name…that the universe was not static, but ever expanding and that there were many other galaxies out there.
Shapley, who thought that the Milky Way was the end of the universe, he realized that it was a Cepheid star. On December 29, 1924, all of his hard work came to fruition, when he made another startling find…all galaxies seemed to be receding from us with velocities that increased in proportion to their distance from us…a relationship now known as Hubble’s Law. On this day, December 30, 1924, Edward Hubble was finally able to make the announcement that would make his a household name…that the universe was not static, but ever expanding and that there were many other galaxies out there.

 When my great aunt, Bertha Schumacher Hallgren passed way in 1984, much had changed in our world, in comparison to the world she found herself in as a young girl. To me, one of the most significant changes would have been in the area of flight…regular flight or space flight. Bertha was a very curious girl. She thought about things, and thought things through. That is the reason that she included facts of the times in her journal. I do wish she had published her works, because I think they would have been of great interest to a lot of people, even if they weren’t written about their family. The first flight took place when Bertha was just a young girl of four years, so she grew up knowing that flight was possible, but there is no indication in her writings, that she ever flew on a plane. The space program began in 1961, so she saw space flight too, and I’m quite certain that she really thought that was an amazing feat, but it did not make it into her writings either. Perhaps, by that time in her life, she thought that there just wouldn’t be much interest in her writings, aside from possibly her sister, Mina Spare’s daughter, Pauline, and later maybe her grandchildren, who were given a copy of the journal, thereby preserving this amazing book, whether accidental or not.
When my great aunt, Bertha Schumacher Hallgren passed way in 1984, much had changed in our world, in comparison to the world she found herself in as a young girl. To me, one of the most significant changes would have been in the area of flight…regular flight or space flight. Bertha was a very curious girl. She thought about things, and thought things through. That is the reason that she included facts of the times in her journal. I do wish she had published her works, because I think they would have been of great interest to a lot of people, even if they weren’t written about their family. The first flight took place when Bertha was just a young girl of four years, so she grew up knowing that flight was possible, but there is no indication in her writings, that she ever flew on a plane. The space program began in 1961, so she saw space flight too, and I’m quite certain that she really thought that was an amazing feat, but it did not make it into her writings either. Perhaps, by that time in her life, she thought that there just wouldn’t be much interest in her writings, aside from possibly her sister, Mina Spare’s daughter, Pauline, and later maybe her grandchildren, who were given a copy of the journal, thereby preserving this amazing book, whether accidental or not.
By the time Bertha passed away in 1984, she had seen the first Space Shuttle launch that took place on April 12, 1981. I have to think that she must have been very much amazed that a plane could fly into space, and return to earth again with the ability to land using its own power, to land not by dropping in the ocean, as had 
 always been the case, but rather by landing on a runway, just like a regular plane. Unfortunately, the placement of the Hubble Space Telescope came to pass just six years after Bertha’s passing, on this day, April 25, 1990. I find that particularly sad, because I think she would have loved that. I can picture her watching the news on television just to catch a glimpse of the space that surrounds our own galaxy. And I can picture her look of wonder as she thought about this amazing world of change that we live in. It was a place that always fascinated her, and I know that it did until the day she died.
always been the case, but rather by landing on a runway, just like a regular plane. Unfortunately, the placement of the Hubble Space Telescope came to pass just six years after Bertha’s passing, on this day, April 25, 1990. I find that particularly sad, because I think she would have loved that. I can picture her watching the news on television just to catch a glimpse of the space that surrounds our own galaxy. And I can picture her look of wonder as she thought about this amazing world of change that we live in. It was a place that always fascinated her, and I know that it did until the day she died.
 The year was 1959, and things were changing rapidly in the world of flight. Airplanes had been around, and actually flying since the December 17, 1903 flight of the Kitty Hawk by the Wright brothers. Air travel, while not as common as it is today, was fairly common. Now, it was time for the next step. We had looked through telescopes, found the planets, their moons, and other suns. We discovered galaxies beyond our own, and then, someone…somewhere, decided that it was time for mankind to go out there and have a look for ourselves.
The year was 1959, and things were changing rapidly in the world of flight. Airplanes had been around, and actually flying since the December 17, 1903 flight of the Kitty Hawk by the Wright brothers. Air travel, while not as common as it is today, was fairly common. Now, it was time for the next step. We had looked through telescopes, found the planets, their moons, and other suns. We discovered galaxies beyond our own, and then, someone…somewhere, decided that it was time for mankind to go out there and have a look for ourselves.
By late 1958 plans were well underway to take that first step. Seven men were picked, and on this day April 9, 1959 NASA announced that they had decided on the first seven astronauts, who would take that very first space flight. The men were dubbed The Mercury Seven, but were also called the Original Seven or Astronaut Group 1. The men were Scott Carpenter, Gordon Cooper, John Glenn, Gus Grissom, Wally Schirra, Alan Shepard, and Deke Slayton. They piloted the manned spaceflights of the Mercury program from May 1961 to May 1963. They weren’t the first men in space, but they were the first from the United States. The first human to journey into outer space, was Yuri Gagarin, when his Vostok spacecraft completed an orbit of the Earth on 12 April 1961. Alan Shepard became the first American in space  when the Freedom 7 spacecraft blasted off from Florida on May 5, 1961, just under a month after the Russian flight. Ten years later, Shepard would fly again to become the fifth man to walk on the moon…and the first to play golf there.
when the Freedom 7 spacecraft blasted off from Florida on May 5, 1961, just under a month after the Russian flight. Ten years later, Shepard would fly again to become the fifth man to walk on the moon…and the first to play golf there.
Most of these seven men went on to fly in many successful missions, with Gus Grissom being the only one to die young and on duty with NASA, in the Apollo 1 fire. Members of the group flew on all classes of NASA manned orbital spacecraft of the 20th century…Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and the Space Shuttle. John Glenn, the oldest, is the only one who is still living. He went on to become a United States senator, and flew on the Shuttle 36 years later to become the oldest person to fly in space. The others all survived past retirement from service. These men played a key part in the world as we know it today, because space travel has played a key part in many of our modern medicines and scientific research. And it all began on this day in 1959.

