World War II
 When the Germans surrendered at the end of World War II, Germany was divided into four areas of control by the Allied Powers…Great Britain in the northwest, France in the southwest, the United States in the south, and the Soviet Union in the east. Berlin, the capital city situated in Soviet territory, was also divided into four occupied zones. That gave those four countries governing control over their own sections of Germany, and the people in those areas. Not every country was exactly planning to do what the people might consider to be their best interests. The Allied countries had the control and the ability to dish out punishment as they saw fit. The Soviet Union considered the forced labor of Germans as part of German war reparations for the damage inflicted by Nazi Germany on the Soviet Union during the Axis-Soviet campaigns (1941-1945) of World War II. They wanted to exact some measure of revenge, I guess, and they were in a position to make that happen.
When the Germans surrendered at the end of World War II, Germany was divided into four areas of control by the Allied Powers…Great Britain in the northwest, France in the southwest, the United States in the south, and the Soviet Union in the east. Berlin, the capital city situated in Soviet territory, was also divided into four occupied zones. That gave those four countries governing control over their own sections of Germany, and the people in those areas. Not every country was exactly planning to do what the people might consider to be their best interests. The Allied countries had the control and the ability to dish out punishment as they saw fit. The Soviet Union considered the forced labor of Germans as part of German war reparations for the damage inflicted by Nazi Germany on the Soviet Union during the Axis-Soviet campaigns (1941-1945) of World War II. They wanted to exact some measure of revenge, I guess, and they were in a position to make that happen.
So, the Soviet authorities deported German civilians from Germany and Eastern Europe to the USSR after World  War II as forced laborers. It almost reminds me of what happened with the Holocaust, except that the Soviet Union had no interest in killing their captives. They wanted slave labor and a measure of retaliation. Ethnic Germans living in the USSR were conscripted for forced labor. German prisoners of war were also used as a source of forced labor during and after the war by the Soviet Union and by the Western Allies.
War II as forced laborers. It almost reminds me of what happened with the Holocaust, except that the Soviet Union had no interest in killing their captives. They wanted slave labor and a measure of retaliation. Ethnic Germans living in the USSR were conscripted for forced labor. German prisoners of war were also used as a source of forced labor during and after the war by the Soviet Union and by the Western Allies.
The decision was made and the fate of the German people was sealed. In 1946, the Soviet Union forcibly relocated more than 2,500 former Nazi German specialists, including scientists, engineers, and technicians who worked in specialist areas, from companies and institutions relevant to military and economic policy in the Soviet occupation zone of Germany (SBZ) and Berlin, along with around 4,000 family members, totaling more than 6,000 people, to the Soviet Union as war reparations. These specialists with all of their knowledge and abilities, could easily change the course of history in the Soviet Union, or any country they were placed in, for that matter. Still, not all of the forced labor were specialists. Many were unskilled labor, doing menial jobs.

The good thing was that the situation in Germany after World War II was appalling. Many of the people were homeless from the bombings. I suppose that, for that reason, the forced move, while scary, was not the worst thing in the world. It was possible that a new life in the Soviet Union could be favorable when compared to war-torn Germany. It is unclear whether any Germans who were sent to the Soviet Union chose to go back to Germany, because information about forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union was suppressed in the Eastern Bloc until after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Many of those records could have also been destroyed.
 Bent Faurschou Hviid, who was born January 7, 1921, later became a member of the Danish resistance group Holger Danske during World War II. Because of his red hair, Hviid was nicknamed “Flammen,” which means “The Flame.” In 1951, he and his Resistance partner Jørgen Haagen Schmith, were posthumously awarded the United States Medal of Freedom by President Harry Truman. The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, alongside the Congressional Gold Medal. The award is not limited to US citizens and, while it is a civilian award, it can also be awarded to military personnel and worn on the uniform.
Bent Faurschou Hviid, who was born January 7, 1921, later became a member of the Danish resistance group Holger Danske during World War II. Because of his red hair, Hviid was nicknamed “Flammen,” which means “The Flame.” In 1951, he and his Resistance partner Jørgen Haagen Schmith, were posthumously awarded the United States Medal of Freedom by President Harry Truman. The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, alongside the Congressional Gold Medal. The award is not limited to US citizens and, while it is a civilian award, it can also be awarded to military personnel and worn on the uniform.
If you were to ask the men who were a part of the Holger Danske, they would tell you that no other resistance member was as hated or sought after by the Germans as was Hviid. Leader of the Holger Danske from 1943 through 1945, Gunnar Dyrberg said in the 2003 Danish documentary film, “With a Right to Kill,” that no one knows exactly how many executions “The Flame” performed, but he was rumored to have killed 22 persons. In all, it is said that the Holger Danske carried out an estimated 400 executions…performed by the Resistance agents, but apparently no one man executed more than Hviid.
Hviid grew up during World War I and was 20 when the Germans occupied Denmark. He was not about to just sit back and let the Nazis take over his country…at least, not without a fight. He entered the Holger Danske resistance group in Copenhagen. He was assigned to kill Danish Nazi officials and collaborators…traitors, who in Hviid’s opinion, did not deserve to live.
“Flammen” often partnered with “Citronen” whose real name was Jørgen Haagen Schmith. “Citronen” means “the lemon.” Schmith got this nickname because he sabotaged a Citroën garage, destroying six German cars and a tank. Citronen usually drove for Flammen, who executed their given targets. The two men were the most famous resistance duo in Denmark during World War II. While they often worked together, the Germans put the highest bounty on Flammen’s head that they offered for any Resistance fighter, due to the Faurschou of Germans who were executed by Flammen.
On October 18, 1944, while Hviid was having dinner with his landlady and some other guests, someone knocked at the door. When the door was opened, a German officer demanded entry. Hviid, who was unarmed  that evening, quickly went upstairs seeking to escape across the roof. When he reached the roof, he saw that the house was surrounded. Refusing to be taken alive, Hviid chewed a cyanide capsule and was dead a few seconds later.
that evening, quickly went upstairs seeking to escape across the roof. When he reached the roof, he saw that the house was surrounded. Refusing to be taken alive, Hviid chewed a cyanide capsule and was dead a few seconds later.
The witnesses later told of how they could hear the German soldiers upstairs cheering at the sight of the corpse. For the Germans, the form of death that took “The Flammen” out made no difference to the German soldiers. All that mattered was that he was dead. The soldiers dragged Hviid downstairs feet first, repeatedly causing his head to bang against the stairs as they went. I suppose it was a show of disrespect or perhaps, triumph for them, although they did not cause his death really.
 In every army, navy, and air force, there are exceptional soldiers…even among the enemy. During World War II, the German Luftwaffe had an incredible pilot. His name was Erich Rudorffer, and he is credited with shooting down thirteen Soviet aircraft in a single mission on October 11, 1943. In that historic mission while flying an FW-190, Rudorffer downed eight Yak-7s and five Yak-9s of the Soviet Air Force. He eventually shot down 222 enemy aircraft and ended up his combat career flying the Messerschmitt ME-262, the first operational jet fighter.
In every army, navy, and air force, there are exceptional soldiers…even among the enemy. During World War II, the German Luftwaffe had an incredible pilot. His name was Erich Rudorffer, and he is credited with shooting down thirteen Soviet aircraft in a single mission on October 11, 1943. In that historic mission while flying an FW-190, Rudorffer downed eight Yak-7s and five Yak-9s of the Soviet Air Force. He eventually shot down 222 enemy aircraft and ended up his combat career flying the Messerschmitt ME-262, the first operational jet fighter.
Still, it wasn’t just the number of planes he shot down that made him remarkable. It was also the fact that he managed to survive the war despite flying over 1000 missions and being shot down an incredible 16 times. He was even forced to parachute from his stricken fighter planes 9 of those times. Not just a Soviet killer, Rudorffer also shot down 86 aircraft operated by Western Allied air forces. He became a commercial pilot after World War II.
Rudorffer was born on November 1, 1917, in Zwochau, which was a part of the Kingdom of Saxony of the German Empire at that time. Strangely, or maybe not, very little is said or known about his parents. That was typical of the German leadership of that era. They felt like the state, and not the parents should raise the children, because…well, parents had no training in such things. Not that the German leadership did either, but they decided that they knew more than the parents, so they pulled the children from their parents’ homes and put them in boarding schools to “train” them in the German ways. After his graduation from school, Rudorffer received a vocational education as an automobile metalsmith specialized in coachbuilding, which was likely another of the German or “Nazi” way of deciding the course of the lives of the children. He might have stayed a mechanic were it not for World War I. “Rudorffer joined the military service of the Luftwaffe with Flieger-Ersatz-Abteilung 61 (Flier Replacement Unit 61) in Oschatz on April 16, 1936. From September 2 to October 15, 1936, he served with Kampfgeschwader 253 (KG 253—253rd Bomber Wing) and from October16, 1936 to February 24, 1937, he was trained as an aircraft engine mechanic at the Technische Schule Adlershof, the technical school at Adlershof in Berlin. On March 14, 1937, Rudorffer was posted to Kampfgeschwader 153 (KG 153—153rd Bomber Wing), where he served as a mechanic until end October 1938. After that, he was transferred to Flieger-Ersatz-Abteilung 51 (Flier Replacement Unit 51) based at Liegnitz in Silesia, present-day Legnica in Poland, for flight training. Rudorffer was first trained as a bomber pilot and then as a Zerstörer, a heavy fighter or destroyer, pilot. In the winter of 1944 Rudorffer was trained on the ME 262 jet fighter. In February 1945, he was recalled to command I. Gruppe JG 7 “Nowotny” from Major Theodor Weissenberger who replaced Steinhoff as Geschwaderkommodore. Rudorffer claimed 12 victories with the ME 262, to bring his total to 222. His tally  included 136 on the Eastern Front, 26 in North Africa, and 60 on the Western Front including 10 heavy bombers.”
included 136 on the Eastern Front, 26 in North Africa, and 60 on the Western Front including 10 heavy bombers.”
After the war ended, Rudorffer started out flying DC-2s and DC-3s in Australia. Later, he worked for Pan Am and the Luftfahrt-Bundesamt, Germany’s civil aviation authority. Rudorffer was honored as one of the characters in the 2007 Finnish war movie “Tali-Ihantala 1944.” A FW 190 participated, painted in the same markings as Rudorffer’s aircraft in 1944. The aircraft, now based at Omaka Aerodrome in New Zealand, still wears the colors of Rudorffer’s machine. Rudorffer died in April 2016 at the age of 98. At the time of his death, he was the last living recipient of the Knight’s Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords.
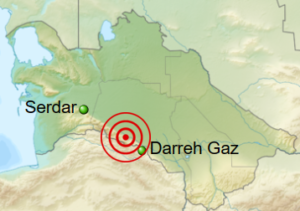 What could make a nation go through an earthquake and refuse help from another nation, like the United States? It seems like a strange question, but it is valid. On October 6, 1948, a magnitude 7.3 earthquake leveled Ashgabat, the capital of the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic—now Turkmenistan. The quake killed between 70,000 and 100,000 people. The true number will never be known. In fact, most information of the scope of the disaster remained unknown outside Central Asia until 1973, when archival records were finally unsealed by local officials. So…why seal the records…of an earthquake??
What could make a nation go through an earthquake and refuse help from another nation, like the United States? It seems like a strange question, but it is valid. On October 6, 1948, a magnitude 7.3 earthquake leveled Ashgabat, the capital of the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic—now Turkmenistan. The quake killed between 70,000 and 100,000 people. The true number will never be known. In fact, most information of the scope of the disaster remained unknown outside Central Asia until 1973, when archival records were finally unsealed by local officials. So…why seal the records…of an earthquake??
The town of Ashgabat lies at the foot of the Kopet-Dag Mountain range near the border with Iran. The area is geologically unstable and earthquake prone. That said, why should a large earthquake in an earthquake-prone area need to be hidden? Ashgabat was originally a czarist outpost, founded in 1881. The town grew quickly during World War II, due to evacuees from the war zone. The population grew to an estimated 150,000 people. With a huge influx of people came the need for a lot of new housing, so single-story houses of unreinforced brick and stone, with heavy roofs of packed clay were quickly built, without regard for the need for earthquake proofing. I suppose that was the reason that the authorities didn’t want anyone to come in to help or to know the details of the catastrophe or the number of victims. The schools, hospitals, and other public buildings were built in the same shoddy way. It was wartime, so it may have been that supplies were scarce, or that proper time was not spent on the construction. Of course, less was known about how earthquakes affect buildings too, and even though there were existing seismic standards, they were seldom met. The builders greatly underestimated the earthquake danger, and that was a fact. A 1929 quake had already caused significant property damage, but strangely, the fault zone had been unusually inactive. I suppose this could have been a warning sign. When it is overdue, it may be a sign of an impending catastrophe.
In this case, that was exactly what happened. On October 6, 1948, at 1:17am, with few people awake. Suddenly, they an ominous rumbling from the mountains, followed immediately by violent vertical shaking. It was actually two strong shocks seconds apart, and just as suddenly, Ashgabat was reduced to rubble. There was no escape…there was no time for escape. The buildings were standing one second and collapsed the next. The thing that is the most shocking was that many of the survivors, who had been conditioned by propaganda in the acute early phase of the Cold War, thought that the city had been hit by an American atomic bomb. And the government did nothing to correct their misguided thinking. So, the country did not seek help from the United States.
As suddenly as it had occurred, the quake severed all communications with the outside world. There were no emergency centers, because hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies lay in ruins. The few remaining uninjured rescue workers, members of the city’s emergency services struggled in the darkness to help the injured. Doctors, many of whom had served in the war, pulled equipment from the ruins to set up an emergency station in Karl Marx Square. Finally, by the afternoon, reinforcements and supplies began to arrive from Tashkent and Baku. Nevertheless, the number of casualties, and the inherent difficulty of evacuating gravely wounded people, meant that help came too late for many. It was estimated that half of an estimated thirty thousand people who  had life-threatening injuries died from lack of early treatment…many people died before they could even be pulled from the rubble.
had life-threatening injuries died from lack of early treatment…many people died before they could even be pulled from the rubble.
While the city workers immediately ran to the damaged central headquarters of the Communist Party, where they were told by the party’s first secretary, S Batirova to take an undamaged automobile and head northward to a functioning telephone line, and soldiers stationed at the airport used an aircraft radio to contact Baku and Sverdlovsk, it was still many hours before any details reached areas from which aid could be dispatched.Unfortunately, that wasn’t much help either, because the railway station was in ruins, tracks were blocked, the airport control tower was destroyed, and the airport and roads could not handle heavy traffic. It would take hours and even days, to get the much-needed rescue support the city needed.
Of course, because of the misguided concept that the Americans were somehow involved, the precise death toll will never be known for sure. Estimates range from a shockingly low number of 400, suggested by Nature magazine in 1948, to a more likely number of 110,000. The dead were buried in mass graves. They were not counted or identified, adding to the confusion. There were roughly 50,000 survivors in a city that had previously had a population of approximately 150,000. That suggests that a death toll of 80,000 to 100,000, or about two-thirds of the population is a more accurate number.
The death toll was enormous, and that could have also accounted for the lack of emergency workers. It’s highly likely that many of them were among the dead or injured…not to mention the fact that there may have been a gross shortage of qualified rescue workers in the poorest part of a country, which was just still recovering from long years of war, but the poor response from the rest of the Soviet Union became more and more unconscionable. On October 7, Pravda printed a brief article stating only that “geologists at the Russian Academy of Sciences had detected a strong earthquake.” The article also reported that there were supply shipments and of the evacuation of the wounded, but no mention of the scope of devastation or the number of casualties. Of course, the international press used Pravda’s limited and incorrect reportage about the quake as the source for their own news reports.
To make matters worse, a conspiracy of silence followed the destruction of Ashgabat. Most history books and almanacs of natural disasters actually omit the quake entirely!! In the typical Soviet propaganda style of the 1950’s, they actually praised the severely lacking reconstruction efforts that completely ignored seismological standards. One Soviet journalist who visited the city in 1953, later described being “forbidden to photograph the omnipresent ruins or to report a march of weeping survivors to the mass graves on the outskirts of the city.” Little was known about the devastating earthquake until 1973. Only on the twenty-fifth anniversary of the event, did officials in Turkmenistan begin to open sealed archives and acknowledge the terrible calamity. Why was this? It was largely because of the Cold War, when both sides were eager not to expose their strategic vulnerabilities. That still doesn’t make sense, however, because the destruction of Ashgabat neither compromised the Soviet Union’s defense system nor revealed grave internal weaknesses. The forced silence did nothing to improve domestic morale in Russia, and it created widespread resentment in Central Asia.  Internationally the Soviet Union could have gained propaganda points by publicizing the disaster and then criticizing the lack of response from the West, but for some reason, they didn’t so that either. Of course, the people in the Soviet Union lived in fear of Joseph Stalins sweeping purges and force silence and timidity. They didn’t dare speak of any kind of vulnerability. Until Stalin’s death in 1953, even referencing the event was considered a dangerous move. Financial aid was still desperately needed decades after the disaster, yet it still didn’t really come. Silence translated into slow reconstruction. Substantial portions of the city remain in ruins, and a significant portion of the population still lives in temporary, or inadequate and unsafe, dwellings to this day.
Internationally the Soviet Union could have gained propaganda points by publicizing the disaster and then criticizing the lack of response from the West, but for some reason, they didn’t so that either. Of course, the people in the Soviet Union lived in fear of Joseph Stalins sweeping purges and force silence and timidity. They didn’t dare speak of any kind of vulnerability. Until Stalin’s death in 1953, even referencing the event was considered a dangerous move. Financial aid was still desperately needed decades after the disaster, yet it still didn’t really come. Silence translated into slow reconstruction. Substantial portions of the city remain in ruins, and a significant portion of the population still lives in temporary, or inadequate and unsafe, dwellings to this day.
 In 1945, a Japanese scientist named Shiro Ishii devised a plan of attack on civilians in the United States called Operation PX, also known as Operation Cherry Blossoms at Night. The plan was intended to wage biological warfare upon civilian population centers in the continental United States during the final months of World War II. The plan was devious, and heinous. Ishii planned to spread plague-infected fleas over Southern California using airplanes. The original operation was abandoned shortly after its planning on March 26, 1945. Then, with modifications, it was finalized and placed back of the table to be carried out. The plan was to be carried out on September 22nd, 1945. Unfortunately for Japan, their formal surrender date was August 15th, 1945, and the war was over.
In 1945, a Japanese scientist named Shiro Ishii devised a plan of attack on civilians in the United States called Operation PX, also known as Operation Cherry Blossoms at Night. The plan was intended to wage biological warfare upon civilian population centers in the continental United States during the final months of World War II. The plan was devious, and heinous. Ishii planned to spread plague-infected fleas over Southern California using airplanes. The original operation was abandoned shortly after its planning on March 26, 1945. Then, with modifications, it was finalized and placed back of the table to be carried out. The plan was to be carried out on September 22nd, 1945. Unfortunately for Japan, their formal surrender date was August 15th, 1945, and the war was over.
Originally, the Japanese Naval General Staff, led by Vice-Admiral Jisaburi Ozawa proposed Operation PX in December 1944. The code name for the operation came from the Japanese use of the code name PX for Pestis bacillus-infected fleas. The navy partnered with Lieutenant-General Shiro Ishii of Unit 731. Ishii possessed extensive experience on weaponizing pathogenic bacteria and human vulnerability to biological and chemical  warfare, and he was an extremely evil man, willing to use his knowledge for the murders of millions of people, especially if he thought it would bring him more power.
warfare, and he was an extremely evil man, willing to use his knowledge for the murders of millions of people, especially if he thought it would bring him more power.
In Ishii’s plan, they would use Seiran aircraft launched by submarine aircraft carriers upon the West Coast of the United States, targeting specifically, the cities of San Diego, Los Angeles, and San Francisco. The attack was to be utilizing weaponized bubonic plague, cholera, typhus, dengue fever, and other pathogens in a biological terror attack upon the population of the United States. The original plan was to have the submarine crews infect themselves and run ashore in a suicide mission. When the operation was shelved in March of 1945, it was because Umezu could see the future ramifications, and conveyed as much, when he said, “If bacteriological warfare is conducted, it will grow from the dimension of war between Japan and America to an endless battle of humanity against bacteria. Japan will earn the derision of the world.”
The idea of suicide attacks was tabled, due to opposition from Yoshijiro Umezu and Torashiro Kawabe, who did not want Ishii to die in a suicide attack and asked him to instead “wait for [the] next opportunity calmly”. It was then that Ishii devised a final plan using of the biological weapons and fleas…an attack that never took place either. The world never knew of the planned attack until long after the war, when Operation PX was first 
 discussed in an interview by former captain Eno Yoshio, who was heavily involved with planning for the attack. He first spoke of it in an interview with Sankei on August 14, 1977. According to Yoshio, “This is the first time I have said anything about Operation PX, because it involved the rules of war and international law. The plan was not put into actual operation, but I felt that just the fact that it was formulated would cause international misunderstanding. I never even leaked anything to the staff of the war history archives at the Japanese Defense Agency, and I don’t feel comfortable talking about it even now. But at the time, Japan was losing badly, and any means to win would have been all right.” That interview goes to show how horrible some regimes can be.
discussed in an interview by former captain Eno Yoshio, who was heavily involved with planning for the attack. He first spoke of it in an interview with Sankei on August 14, 1977. According to Yoshio, “This is the first time I have said anything about Operation PX, because it involved the rules of war and international law. The plan was not put into actual operation, but I felt that just the fact that it was formulated would cause international misunderstanding. I never even leaked anything to the staff of the war history archives at the Japanese Defense Agency, and I don’t feel comfortable talking about it even now. But at the time, Japan was losing badly, and any means to win would have been all right.” That interview goes to show how horrible some regimes can be.

 There are certain situations when I think citizenship is a must have element, and some that I think “natural-born” citizenship is absolutely essential. On September 15, 1935, German Jews were stripped of their citizenship, reducing them to mere “subjects” of the state. This heinous crime was carried out by the “president and chancellor of Germany,” Adolf Hitler. I use the quotation marks, because Hitler should never have been allowed to be in that office. Adolf Hitler became a citizen of Germany on February 25, 1932. Hitler, who was born in Austria, had immigrated to Germany in 1913, and renounced his Austrian citizenship in 1925. Hitler was a stateless nomad from 1925 to 1931, when he decided on the political ambition of becoming president and chancellor. That was when he decided to become a citizen, in fact that was the only reason he became a citizen. Hitler had a plan to take over and completely transform Germany, and his “transformation” was to be the worst thing for Germany. I think that is why a president needs to be a “natural-born” citizen. A president needs to have a connection to his country…a connection he is born into. Then and only then does he have the ability to care about the country…not that all presidents do, but they have that ability, because they belong. I’m sure some would disagree with me, but it will not change my mind.
There are certain situations when I think citizenship is a must have element, and some that I think “natural-born” citizenship is absolutely essential. On September 15, 1935, German Jews were stripped of their citizenship, reducing them to mere “subjects” of the state. This heinous crime was carried out by the “president and chancellor of Germany,” Adolf Hitler. I use the quotation marks, because Hitler should never have been allowed to be in that office. Adolf Hitler became a citizen of Germany on February 25, 1932. Hitler, who was born in Austria, had immigrated to Germany in 1913, and renounced his Austrian citizenship in 1925. Hitler was a stateless nomad from 1925 to 1931, when he decided on the political ambition of becoming president and chancellor. That was when he decided to become a citizen, in fact that was the only reason he became a citizen. Hitler had a plan to take over and completely transform Germany, and his “transformation” was to be the worst thing for Germany. I think that is why a president needs to be a “natural-born” citizen. A president needs to have a connection to his country…a connection he is born into. Then and only then does he have the ability to care about the country…not that all presidents do, but they have that ability, because they belong. I’m sure some would disagree with me, but it will not change my mind.
His citizenship actually came about when a fellow member of the Nazi Party appointed Hitler to a low-level government job that came with automatic citizenship. Once he was a citizen, Hitler’s new status allowed him to achieve his political goals. As a citizen, he could run for office. Hitler made sure that he was well liked, and by the middle of 1934, he was in complete control of Germany as Führer und Reichskanzler (leader and chancellor). He didn’t wait long to begin, and soon redefined citizenship to serve his beliefs. He was a hate-filled man, and he used race and pan-German heritage to give citizenship to, and take it from, large groups of people. Citizenship now depended on how Hitler felt about the people. Many would say that he was a white supremacist, but the reality was that there were many races of people he didn’t like, and many of them were white, so it wasn’t about color. As World War II began, Hitler’s views on German supremacy were fueling a military campaign that destroyed borders and entire populations all across Europe. People who were born in Germany and had been citizens all their lives were being systematically stripped of their citizenship, their rights, and their lives, just because they were Jews, blacks, gypsies, and some other races. Hitler’s goal was to rid the world of anyone who was not “pure-blooded” German stock. Never mind the fact that he was not!!
Practically from the minute he took office, Hitler began issuing what we would call “Executive Orders” that barely disrupted the lives of those “pure-blooded” German stock, other than to basically elevate them to the level of “masters” over anyone who did not qualify as “pure-blooded” German stock. His dream of a “pure-blooded” society soon became a nightmare for many. Many of the German “pure-blooded” German citizen didn’t agree with what he was doing, and some didn’t really understand what he was doing, exactly, but some of them saw it as an opportunity to take from the “unqualified” citizens, anything they wanted. They became brutal in their treatment of the “unqualified” citizens, especially the Jews.
Hitler began his persecution of the Jews within the first year of office. German Jews were excluded from many high-profile vocations, such as public office, journalism, radio, theater, film, and teaching, and even farming. The professions of law and medicine were also withdrawn slowly as opportunities. “Jews Not Welcome” signs were posted on shop and hotel windows, beer gardens, and other public areas. Known as the Nuremberg Laws, these discriminatory acts became a deep-seated part of the German culture, which in turn, making them even more far-reaching. Jews were forbidden to marry “Aryans” or engage in extramarital relations with them. Jews could not employ female Aryan servants if they were less than 35 years of age. Hunger soon became a part of Jewish life, because it became difficult even to buy food, as groceries, bakeries, and dairies would not admit Jewish customers. Even pharmacies refused to sell them medicines or drugs. Their lives soon began to simply spiral towards despair and eventual death.
At first, the outside world didn’t understand what they were seeing. Unemployment had dropped exponentially under Hitler’s early commandeering of the economy. Things actually looked better to the world. A very few, some foreign visitors, even some political opponents within Germany itself, saw these racist laws and practices for what they were, but most were beguiled into thinking it was merely a phase. They assumed that the “birth 
 pains” of Hitler’s developing plans would eventually smooth out and the bad parts would fade away, as he began to focus more on the economy and less on race, but they were wrong, because Hitler was a very determined, and very focused dictator…and he was insane, as the world and the German people would soon find out. It is my opinion that even a seemingly good citizen, who is not “natural-born” is not a good candidate for president, because their ideas and plans for a nation they have no real stake in, will be very unlikely to produce good for the nation in the end.
pains” of Hitler’s developing plans would eventually smooth out and the bad parts would fade away, as he began to focus more on the economy and less on race, but they were wrong, because Hitler was a very determined, and very focused dictator…and he was insane, as the world and the German people would soon find out. It is my opinion that even a seemingly good citizen, who is not “natural-born” is not a good candidate for president, because their ideas and plans for a nation they have no real stake in, will be very unlikely to produce good for the nation in the end.
 Probably one of the deadliest weapons the Nazis ever created, was the German U-Boat. With their code system, it was hard to track a U-boat, and so they snuck up on ships and sunk them. The U-boat wasn’t a ship. It was a submarine, so the ships didn’t know it was there until they saw the torpedo coming at them…if they saw it coming. Often, they didn’t see it coming, it just hit, and it was over. On September 12, 1942, a U-boat sunk the British troop ship, the RMS Laconia, killing more than 1,400 men. The commander of the German sub, Captain Werner Hartenstein, then realized that Italians POWs were among the passengers.
Probably one of the deadliest weapons the Nazis ever created, was the German U-Boat. With their code system, it was hard to track a U-boat, and so they snuck up on ships and sunk them. The U-boat wasn’t a ship. It was a submarine, so the ships didn’t know it was there until they saw the torpedo coming at them…if they saw it coming. Often, they didn’t see it coming, it just hit, and it was over. On September 12, 1942, a U-boat sunk the British troop ship, the RMS Laconia, killing more than 1,400 men. The commander of the German sub, Captain Werner Hartenstein, then realized that Italians POWs were among the passengers.
Like many other cruise ships, the Laconia, a former Cunard White Star ship was put to use to transport troops, including prisoners of war during World War II. RMS Laconia was in the South Atlantic bound for England when  it encountered U-156. The sub attacked, sinking the troop ship and imperiling the lives of more than 2,200 passengers. But as Hartenstein, the sub commander, was to learn from survivors he began taking onboard, among those passengers were 1,500 Italian POWs. Of course, it wouldn’t look good for Hartenstein to be responsible for endangering the lives of so many of his fellow Axis members, so he quickly put out a call to an Italian submarine and two other German U-boats in the area to help rescue the survivors.
it encountered U-156. The sub attacked, sinking the troop ship and imperiling the lives of more than 2,200 passengers. But as Hartenstein, the sub commander, was to learn from survivors he began taking onboard, among those passengers were 1,500 Italian POWs. Of course, it wouldn’t look good for Hartenstein to be responsible for endangering the lives of so many of his fellow Axis members, so he quickly put out a call to an Italian submarine and two other German U-boats in the area to help rescue the survivors.
Upon hearing of the incident, one French and two British warships rushed to the scene to aid in the rescue. The German subs immediately informed the Allied ships that they had surfaced for humanitarian reasons. The Allies wisely assumed it was a trap. With that, an American B-24 bomber, the Liberator, flying from its South Atlantic base on Ascension Island, saw the German sub and bombed it…despite the fact that Hartenstein had draped a Red Cross flag prominently on the hull of the surfaced sub. The U-156, damaged by the air attack, immediately  submerged. Admiral Karl Donitz, supreme commander of the German U-boat forces, had been monitoring the rescue efforts. He ordered that “all attempts to rescue the crews of sunken ships…cease forthwith.” Consequently, more than 1,400 of the RMS Laconia’s passengers, which included Polish guards and British crewmen, drowned. This marked the end of taking POWs from torpedoed ships. There were often men who survived these attacks, but they were given no chance of survival after the attack. I suppose war is war, and death is expected. On March 8, 1943, U-156 was sunk by PBY “Catalina” aircraft from Patrol Squadron Fifty-Three (VP-53), in the Atlantic Ocean, east of Barbados. There were five survivors from U-156.
submerged. Admiral Karl Donitz, supreme commander of the German U-boat forces, had been monitoring the rescue efforts. He ordered that “all attempts to rescue the crews of sunken ships…cease forthwith.” Consequently, more than 1,400 of the RMS Laconia’s passengers, which included Polish guards and British crewmen, drowned. This marked the end of taking POWs from torpedoed ships. There were often men who survived these attacks, but they were given no chance of survival after the attack. I suppose war is war, and death is expected. On March 8, 1943, U-156 was sunk by PBY “Catalina” aircraft from Patrol Squadron Fifty-Three (VP-53), in the Atlantic Ocean, east of Barbados. There were five survivors from U-156.
 The first power-driven airship was built by a French inventor decades before the Zeppelin was developed by German inventor Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin in 1900. The Zeppelin was a motor-driven rigid airship. The earlier airships were smaller, but Hilter always wanted the most innovative, largest, and deadliest designs of everything, with was likely the reason for the Zeppelin’s size. It was by far the largest airship ever constructed. Hitler didn’t care that size was exchanged for safety. The heavy steel-framed airships were vulnerable to explosion, because they had to be lifted by highly flammable hydrogen gas instead of non-flammable helium gas.
The first power-driven airship was built by a French inventor decades before the Zeppelin was developed by German inventor Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin in 1900. The Zeppelin was a motor-driven rigid airship. The earlier airships were smaller, but Hilter always wanted the most innovative, largest, and deadliest designs of everything, with was likely the reason for the Zeppelin’s size. It was by far the largest airship ever constructed. Hitler didn’t care that size was exchanged for safety. The heavy steel-framed airships were vulnerable to explosion, because they had to be lifted by highly flammable hydrogen gas instead of non-flammable helium gas.
During World War I, the Zeppelins were used as bombers, and the Germans had great success bombing the British Isles with the Zeppelin over the course of 1915 and 1916. The first such  attack on London came on May 31, 1915. That bombing killed 28 people and wounded 60 more. The Germans killed a total of 550 Britons with aerial bombing by May 1916. During one such attack, on September 8, 1915, Heinrich Mathy was the commander of the famed German Zeppelin L13, bombing Aldersgate in central London. His bombs killed 22 people and causing £500,000 worth of damage.
attack on London came on May 31, 1915. That bombing killed 28 people and wounded 60 more. The Germans killed a total of 550 Britons with aerial bombing by May 1916. During one such attack, on September 8, 1915, Heinrich Mathy was the commander of the famed German Zeppelin L13, bombing Aldersgate in central London. His bombs killed 22 people and causing £500,000 worth of damage.
While Mathy was waiting on repairs to his ship, following a bombing run on August 24-25, 1916, he received word that the British had managed for the first time to shoot down a Zeppelin, using incendiary bullets. While he was a fearless pilot, Mathy saw the writing on the wall, and said, “It is only a question of time before we join  the rest. Everyone admits that they feel it. Our nerves are ruined by mistreatment. If anyone should say that he was not haunted by visions of burning airships, then he would be a braggart.” I’m sure he knew that the Zeppelin was a dangerous ship anyway, especially in a crash, but this new danger made matters much worse. As Mathy had predicted, his Zeppelin L31True to his prediction, Mathy’s L31 was shot down during a raid on London on the night of October 1-2, 1916. He is buried in Staffordshire, in a cemetery constructed by the British for the burial of Germans killed on British soil during both World Wars.
the rest. Everyone admits that they feel it. Our nerves are ruined by mistreatment. If anyone should say that he was not haunted by visions of burning airships, then he would be a braggart.” I’m sure he knew that the Zeppelin was a dangerous ship anyway, especially in a crash, but this new danger made matters much worse. As Mathy had predicted, his Zeppelin L31True to his prediction, Mathy’s L31 was shot down during a raid on London on the night of October 1-2, 1916. He is buried in Staffordshire, in a cemetery constructed by the British for the burial of Germans killed on British soil during both World Wars.

 I think we all have one…a second career, or a career that could have been, had we chosen to take a different road in life. Some people actually step back from the career they have, sometimes, to pursue the one that should have been, and others simply know that they could have, if they had chosen to. I was one of those people. I spent much of my working years as an insurance agent, and a good one, I believe, but after spending thirteen years as a caregiver, I also know that I could have been a nurse, had I chosen that road. My daughter, Corrie Petersen chose to make that journey transition, and now she is a nurse, after spending those same thirteen years helping my take care of her grandparents, along with her sister, Amy Royce, children Chris and Josh, niece, Shai Royce, nephew Caalab Royce, and many other family caregivers in our Caregiving Villages, but none of the rest of us made that second career choice.
I think we all have one…a second career, or a career that could have been, had we chosen to take a different road in life. Some people actually step back from the career they have, sometimes, to pursue the one that should have been, and others simply know that they could have, if they had chosen to. I was one of those people. I spent much of my working years as an insurance agent, and a good one, I believe, but after spending thirteen years as a caregiver, I also know that I could have been a nurse, had I chosen that road. My daughter, Corrie Petersen chose to make that journey transition, and now she is a nurse, after spending those same thirteen years helping my take care of her grandparents, along with her sister, Amy Royce, children Chris and Josh, niece, Shai Royce, nephew Caalab Royce, and many other family caregivers in our Caregiving Villages, but none of the rest of us made that second career choice.
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1951 to 
 1955. Apart from two years between 1922 and 1924, he was a Member of Parliament from 1900 to 1964 and represented a total of five constituencies. He was also a well-known war strategist, and a part of the reason that World War II ended the way that it did. One would think that he knew exactly what his one and only career was, and that he fulfilled his destiny, but he also had another career living inside of him, and some say that he missed his calling. Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill was a very talented artist. He actually painted 500 paintings, 50 of which were displayed professionally. In fact, it was Picasso, himself, who said that Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill missed his true calling, and very much could have chosen art as his career. My daughter, Amy Royce could have too, I think, as could my son-in-law, Kevin Petersen, and a number of others in my family. I have almost zero talent when it comes to art, but I am very impressed with those in my family
1955. Apart from two years between 1922 and 1924, he was a Member of Parliament from 1900 to 1964 and represented a total of five constituencies. He was also a well-known war strategist, and a part of the reason that World War II ended the way that it did. One would think that he knew exactly what his one and only career was, and that he fulfilled his destiny, but he also had another career living inside of him, and some say that he missed his calling. Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill was a very talented artist. He actually painted 500 paintings, 50 of which were displayed professionally. In fact, it was Picasso, himself, who said that Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill missed his true calling, and very much could have chosen art as his career. My daughter, Amy Royce could have too, I think, as could my son-in-law, Kevin Petersen, and a number of others in my family. I have almost zero talent when it comes to art, but I am very impressed with those in my family 
 who do.
who do.
I suppose that a second career that is never a road taken, would end up being called a “hobby” sometimes, although, I would not consider caregiving a “hobby” in any way, but art could fall into that category…as could writing, which I guess could have been a third career for me. Strangely, I don’t really consider myself to be an author, because I have never published a book. Is internet blogging of stories, publishing? Maybe. And maybe we all have many talents that could easily have turned into careers, had we decided to go down that road, or another road. Maybe, “That Second Career” isn’t really even the right title, nevertheless, it is the title.
 As we all know, Adolph Hitler was a liar and a murderer. He really never made a move that wasn’t calculated and devious. On September 1, 1939, German forces under the control of Adolf Hitler bombarded Poland on land and from the air. The invasion was more than just a taking of territory. Hitler knew that he might need that area later, and so he did. Hitler had been murdering people that didn’t fit into his mold of “life that had value” and that included Jews, the mentally or physically handicapped, and later gypsies and other ethnicities. Basically, he wanted to eliminate anyone that wasn’t Aryan. Aryan is a word relating to a hypothetical ethnic type illustrated by or descended from early speakers of Indo-European languages. To Hitler it meant white, with blond hair and blue eyes. Oddly, while Hitler had blue eyes, his hair was brown. Somehow that “problem” with his definition of Aryan didn’t concern Hitler. I guess he was happy to be a “special Aryan.” In reality, there are different kinds of Aryans. They can be found with blond, red, brown, white, or black hair, so that wasn’t really an issue either. Hitler considered himself Aryan because he was a native German-speaker, and he knew the definition of “Aryan” as it was used in those days. I don’t think it was ever about Aryan, per se, but rather about getting rid of any group that he decided that he didn’t like.
As we all know, Adolph Hitler was a liar and a murderer. He really never made a move that wasn’t calculated and devious. On September 1, 1939, German forces under the control of Adolf Hitler bombarded Poland on land and from the air. The invasion was more than just a taking of territory. Hitler knew that he might need that area later, and so he did. Hitler had been murdering people that didn’t fit into his mold of “life that had value” and that included Jews, the mentally or physically handicapped, and later gypsies and other ethnicities. Basically, he wanted to eliminate anyone that wasn’t Aryan. Aryan is a word relating to a hypothetical ethnic type illustrated by or descended from early speakers of Indo-European languages. To Hitler it meant white, with blond hair and blue eyes. Oddly, while Hitler had blue eyes, his hair was brown. Somehow that “problem” with his definition of Aryan didn’t concern Hitler. I guess he was happy to be a “special Aryan.” In reality, there are different kinds of Aryans. They can be found with blond, red, brown, white, or black hair, so that wasn’t really an issue either. Hitler considered himself Aryan because he was a native German-speaker, and he knew the definition of “Aryan” as it was used in those days. I don’t think it was ever about Aryan, per se, but rather about getting rid of any group that he decided that he didn’t like.
Hitler’s main purpose for the invasion of Poland was to regain lost territory and ultimately rule their eastern neighbor. Mostly, however, Hitler wanted the world to know exactly how he planned to wage war. This would become the “blitzkrieg” strategy. The Blitzkrieg was a term used to describe “a method of offensive warfare designed to strike a swift, focused blow at an enemy using mobile, maneuverable forces, including armored  tanks and air support. Such an attack ideally leads to a quick victory, limiting the loss of soldiers and artillery. After the German forces had plowed their way through, devastating a swath of territory, infantry moved in, picking off any remaining resistance.”
tanks and air support. Such an attack ideally leads to a quick victory, limiting the loss of soldiers and artillery. After the German forces had plowed their way through, devastating a swath of territory, infantry moved in, picking off any remaining resistance.”
Hitler was methodical. He established a base of operations within the target country. Then, he immediately began setting up “security” forces to take out anyone who disagreed with his Nazi ideology, whether racial, religious, or political. He set up concentration camps for slave laborers and the extermination of uncooperative civilians. It didn’t take long for the target nation, in this case Poland to become a conquered nation under German rule. Just one day after the German invasion of Poland, Hitler was busy setting up SS “Death’s Head” regiments to terrorize the people. He was preparing for his planned terror.
The Polish army tried to fight back, but they made several severe strategic miscalculations in those early days. Even with an army of 1 million soldiers, the lack of the necessary equipment was a severe detriment to the Polish forces as they attempted to take the Germans head-on, when maybe they should have fallen back to defensive positions. I think the natural way to face an enemy, is head-on. We try to “show no fear” when attacked, but in the end, this thinking, while admirable was probably behind the times, at least in battle, and the brave Polish soldiers were no match for the overwhelming and modern-mechanized German forces. To make matters worse, any hope the Polish soldiers might have had of a Soviet counter-response was lost with  the signing of the Ribbentrop-Molotov Nonaggression Pact…”a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that partitioned Eastern Europe between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop and Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov and was officially known as the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Unofficially, it has also been referred to as the Hitler–Stalin Pact, Nazi–Soviet Pact or Nazi–Soviet Alliance.” Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Great Britain responded with bombing raids over Germany three days later.
the signing of the Ribbentrop-Molotov Nonaggression Pact…”a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that partitioned Eastern Europe between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop and Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov and was officially known as the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Unofficially, it has also been referred to as the Hitler–Stalin Pact, Nazi–Soviet Pact or Nazi–Soviet Alliance.” Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Great Britain responded with bombing raids over Germany three days later.

