us navy
 Following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Japanese quickly began expanding their areas of control. They focused on the Philippine Islands, a United States territory, where tens of thousands of American and Filipino soldiers were stationed. The day after Japan bombed the US naval base at Pearl Harbor, on December 7, 1941, the Japanese invasion of the Philippines began. Without the necessary help from the US Navy, the troops stationed there quickly ran out of food and ammunition. On April 9, 1942, the soldiers had no choice but to surrender the Bataan Peninsula on the main Philippine island of Luzon to the Japanese. It was the largest army under US command ever to surrender.
Following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Japanese quickly began expanding their areas of control. They focused on the Philippine Islands, a United States territory, where tens of thousands of American and Filipino soldiers were stationed. The day after Japan bombed the US naval base at Pearl Harbor, on December 7, 1941, the Japanese invasion of the Philippines began. Without the necessary help from the US Navy, the troops stationed there quickly ran out of food and ammunition. On April 9, 1942, the soldiers had no choice but to surrender the Bataan Peninsula on the main Philippine island of Luzon to the Japanese. It was the largest army under US command ever to surrender.
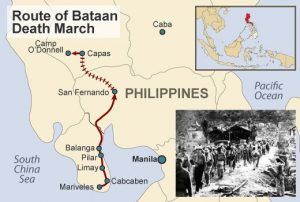
The Japanese didn’t want these prisoners of war to be visible, so a plan was devised to move them inland. The area didn’t have railways, and because they did not expect such a large group of surrendered soldiers, it was decided that they would walk the 65 miles. So, on April 9, 1942, 75,000 Filipino and American troops on Bataan were forced to make the torturous 65 mile march to Camp O’Donnell where they were to be housed. Japan was  completely unprepared for the sheer number of soldiers who surrendered that day. The Japanese troops were filled with frustration, coupled with disdain for surrendering troops, which led to shocking brutality during the march.
completely unprepared for the sheer number of soldiers who surrendered that day. The Japanese troops were filled with frustration, coupled with disdain for surrendering troops, which led to shocking brutality during the march.
The marchers made the trek in intense heat that further complicated their situation, along with the harsh treatment by the Japanese guards. Thousands of men died along the way, in what became known as the Bataan Death March. The march began at Mariveles, on the southern end of the Bataan Peninsula. It continued 65 miles to San Fernando. The men were divided into groups of approximately 100, and the march typically took each group around five days to complete. While no one knows for sure, it is believed that thousands of troops died because of the brutality of their captors, who starved and beat the marchers, giving them no food or water, and bayoneted those too weak to walk. Those who survived were taken by rail from San Fernando to prisoner-of-war camps, where thousands died from disease, mistreatment, and starvation.
 America was pulled into World War II after the attack on Pearl Harbor, and would later avenged its defeat in the Philippines with the invasion of the island of Leyte in October 1944. General Douglas MacArthur, who in 1942 had famously promised to return to the Philippines, made good on his word. In February 1945, US-Filipino forces recaptured the Bataan Peninsula, and Manila was liberated in early March. After the war, an American military tribunal tried Lieutenant General Homma Masaharu, commander of the Japanese invasion forces in the Philippines. He was held responsible for the death march, a war crime, and was executed by firing squad on April 3, 1946.
America was pulled into World War II after the attack on Pearl Harbor, and would later avenged its defeat in the Philippines with the invasion of the island of Leyte in October 1944. General Douglas MacArthur, who in 1942 had famously promised to return to the Philippines, made good on his word. In February 1945, US-Filipino forces recaptured the Bataan Peninsula, and Manila was liberated in early March. After the war, an American military tribunal tried Lieutenant General Homma Masaharu, commander of the Japanese invasion forces in the Philippines. He was held responsible for the death march, a war crime, and was executed by firing squad on April 3, 1946.
 Submarines have always fascinated me. To be able to travel completely submerged for extended periods of time is quite amazing. One of the greatest submarines ever was the USS Seawolf (SSN 575). Seawolf was not the first nuclear submarine. That honor goes to the Nautilus, but the Seawolf was an amazing submarine with an amazing future ahead of her. The Seawolf was built by the General Dynamics Corporation’s Electric Boat Division, Groton, Connecticut, and was laid September 15, 1953. Mrs. W. Sterling Cole christened the SEAWOLF at the launching ceremony on July 21, 1955 under the command of Commander Richard B. Laning, United States Navy.
Submarines have always fascinated me. To be able to travel completely submerged for extended periods of time is quite amazing. One of the greatest submarines ever was the USS Seawolf (SSN 575). Seawolf was not the first nuclear submarine. That honor goes to the Nautilus, but the Seawolf was an amazing submarine with an amazing future ahead of her. The Seawolf was built by the General Dynamics Corporation’s Electric Boat Division, Groton, Connecticut, and was laid September 15, 1953. Mrs. W. Sterling Cole christened the SEAWOLF at the launching ceremony on July 21, 1955 under the command of Commander Richard B. Laning, United States Navy.
Unlike, Nautilus, the Seawolf used liquid sodium instead of water as a moderator and cooling medium. The Seawolf was to be given many honors and awards during her time of service, with one of the greatest being on September 26, 1957, when Seawolf hosted President Dwight D.  Eisenhower for a submerged run off Newport, Rhode Island. It was the first time the Commander and Chief was transported by nuclear propulsion. That makes it an amazing event for the Seawolf and for the President. Additionally, while on a port visit in Provincetown, Massachusetts, Seawolf was host to NBC telecast of “Wide, Wide World” on December 8, 1957.
Eisenhower for a submerged run off Newport, Rhode Island. It was the first time the Commander and Chief was transported by nuclear propulsion. That makes it an amazing event for the Seawolf and for the President. Additionally, while on a port visit in Provincetown, Massachusetts, Seawolf was host to NBC telecast of “Wide, Wide World” on December 8, 1957.
One of the greatest moments, however, happened on October 6, 1958. After submerging on August 7, 1958, Seawolf remained submerged for a full 60 days. During that time she was completely independent of the Earth’s atmosphere. The submarine was self sufficient and able to produce all the life sustaining air and water the crew would need for life. It was an unheard of accomplishment. Of course, that record would be broken in  the future, including twice by Seawolf herself. In 1976, Seawolf remained submerged for a US Navy record breaking 87 days. In 1977 she again went under, this time staying submerged for 79 days. Over the years of service, Seawolf received four Battle Efficiency “E” awards for excellence in battle. She received three Engineering “E” for Excellence, three Supply “E” awards, a Communications “C” award, a Damage Control “DC” award, and the Dec Seamanship Award. In April 1986 USS Seawolf (SSN 575) was decommissioned, but her name has lived on in other submarines named in her honor. The USS Seawolf (SSN 575) was truly an amazing submarine.
the future, including twice by Seawolf herself. In 1976, Seawolf remained submerged for a US Navy record breaking 87 days. In 1977 she again went under, this time staying submerged for 79 days. Over the years of service, Seawolf received four Battle Efficiency “E” awards for excellence in battle. She received three Engineering “E” for Excellence, three Supply “E” awards, a Communications “C” award, a Damage Control “DC” award, and the Dec Seamanship Award. In April 1986 USS Seawolf (SSN 575) was decommissioned, but her name has lived on in other submarines named in her honor. The USS Seawolf (SSN 575) was truly an amazing submarine.
 When we think of the name Hitler, most of us think of the vicious dictator who was responsible for the slaughter of as many a 6 million Jewish people, not to mention all the other people he killed in his crazed state of mind. For most of us, hearing the name Hitler brings with it feelings of horror, disgust, and continued shock every time we learn a new fact about Hitler and his Third Reich. Yes, the name Hitler doesn’t usually bring any feelings of…anything good. Well, what I learned today, changed my view of that. You see, not everyone named Hitler was evil, not even everyone named Hitler during World War II, and not even everyone who had the unfortunate…misfortune of being related to Adolf Hitler. You see, for William Patrick Hitler of Liverpool, England, having the name wasn’t the worst part of his situation. William was actually the nephew of Adolf Hitler, the Führer of Nazi Germany. It was a reality that made him almost nauseous. Dealing with that reality would take William on a zigzag path leading to Germany, England, America, and finally the United States Navy. I’m sure that you, like me, thought, “How could the United States Navy allow a nephew of Adolf Hitler to join up, much less to muster out with men sent to fight his uncle.
When we think of the name Hitler, most of us think of the vicious dictator who was responsible for the slaughter of as many a 6 million Jewish people, not to mention all the other people he killed in his crazed state of mind. For most of us, hearing the name Hitler brings with it feelings of horror, disgust, and continued shock every time we learn a new fact about Hitler and his Third Reich. Yes, the name Hitler doesn’t usually bring any feelings of…anything good. Well, what I learned today, changed my view of that. You see, not everyone named Hitler was evil, not even everyone named Hitler during World War II, and not even everyone who had the unfortunate…misfortune of being related to Adolf Hitler. You see, for William Patrick Hitler of Liverpool, England, having the name wasn’t the worst part of his situation. William was actually the nephew of Adolf Hitler, the Führer of Nazi Germany. It was a reality that made him almost nauseous. Dealing with that reality would take William on a zigzag path leading to Germany, England, America, and finally the United States Navy. I’m sure that you, like me, thought, “How could the United States Navy allow a nephew of Adolf Hitler to join up, much less to muster out with men sent to fight his uncle.
Born March 12, 1911, in Liverpool, England, William Hitler was the only child of Bridget Dowling and her Austrian expatriate husband, Alois Hitler Jr, who was the half-brother of Adolf Hitler. In 1914, Alois abandoned his wife and three year old son to go traveling through Europe. The outbreak of World War I prevented him from returning to England, so he settled down in Germany, married again, despite still being married to Dowling, and started a new family. For years, Alois made no attempt to contact his wife and son back in Liverpool, but rather had someone tell Dowling that he was dead. In 1924, the truth came out. Alois was charged with bigamy in Germany, but avoided conviction because Dowling actually interceded on his behalf. That was all she did however. She drew the line, when Alois asked her to send William to Germany for a visit. She told him that she would not let her son visit until he reached his 18th birthday, in 1929. Upon turning 18, William traveled to Germany and reconnected with his father, who took him to a Nazi rally where he saw his Uncle Adolf, leader of the rising National Socialist (Nazi) Party. William visited Germany again in 1930, this time  meeting his uncle in person and receiving an autographed photo from him.
meeting his uncle in person and receiving an autographed photo from him.
I’m sure that William thought that his relationship with his uncle would be something that would advance his journalism career, but Hitler didn’t want anyone to know what he was doing. William’s articles about his Uncle Adolf Hitler, only served to be the beginning of being blackballed from everything to do with Adolf Hitler, and his disgust with Adolf Hitler and his insane ways. Hitler called William to Berlin, and reportedly ordered him to retract the articles. Now William saw a totally different side of his uncle…describing it as a “wild-eyed and tearful” outburst. Apparently Hitler even threatened to kill himself if William ever again published anything about his personal life. Now, William became persona non grata in England. He was fired from his job in 1932. Unable to find other employment in his homeland, he decided to look for work in Germany. Perhaps his increasingly influential uncle could be persuaded to help, but no warm welcome awaited in Germany. According to William, whose July 4, 1939 article for Look magazine, “Why I Hate My Uncle,” is the sole source on his dealings with his uncle Adolf Hitler, who sent William a letter during his visit, denying they were relatives. Shortly afterward, William’s father sent him back to England. I guess he was persona non grata with his dad too.
William tried using his relationship to Hitler to obtain a job in Germany, and was successful, but when he tried to send money to his mother, he was informed that Hitler would not allow it…even for family. William began to see a much more evil side of his uncle. Eventually, he left Germany and went back to England, but found that he was not welcome there either. He and his mother moved to the United States, where his relationship again caused him problems. Finally, in 1942, William wrote directly to President Franklin D. Roosevelt, begging to be allowed to serve in the US military. “I am one of many, but can render service to this great cause,” he wrote. FDR passed the letter on to FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover, who looked into William’s background and finally cleared him for military service. Sworn into the US Navy in New York City on March 6, 1944, William Hitler went on to serve three years as a pharmacist’s mate, receiving the Purple Heart for a wound he suffered. He was  discharged in 1947.
discharged in 1947.
Finally tired of the attention his controversial surname attracted, William changed it to Stuart-Houston after returning to the civilian world. He married German-born Phyllis Jean-Jacques, and the couple settled in Patchogue on New York’s Long Island, where they had four children, the first of whom bore the surprising middle name of Adolf. William ran a blood analysis lab, Brookhaven Laboratories, in his family’s home. William Stuart-Houston died on July 14, 1987, and was buried next to his late mother in Coram, New York. His children did not produce any children of their own…and so ended the line.
 In any war, each side has just one goal in mind…winning. Of course, this is not just a video game or war games, but it is really a life and death challenge. In retrospect, I find it interesting to see some of the strategies the different sides use. While I cannot agree with anything the Germans did under Hitler’s rule, because Hitler was unbelievably ruthless, hateful, and cruel, there were some strategies that either he, his admirals, or his soldiers executed that were quite spectacular, though surprising in nature, because the Germans didn’t usually coordinate their efforts this well. I would never have wanted the Germans to win in World War II, because of their horrible treatment and murders of the Jewish people, but they did have a way of fighting that has captured my interest…at least on this day.
In any war, each side has just one goal in mind…winning. Of course, this is not just a video game or war games, but it is really a life and death challenge. In retrospect, I find it interesting to see some of the strategies the different sides use. While I cannot agree with anything the Germans did under Hitler’s rule, because Hitler was unbelievably ruthless, hateful, and cruel, there were some strategies that either he, his admirals, or his soldiers executed that were quite spectacular, though surprising in nature, because the Germans didn’t usually coordinate their efforts this well. I would never have wanted the Germans to win in World War II, because of their horrible treatment and murders of the Jewish people, but they did have a way of fighting that has captured my interest…at least on this day.
The Germans had controlled and occupied France since June of 1940. Their ships docked in French ports were drawing fire from the British. It became clear that the ships needed to escape. The German battleships Gneisenau and Scharnhorst had been anchored at the port of Brest since March of 1941, and the heavy cruiser, Prinz Eugen had been there since May of 1941. They were periodically subjected to bombing raids and damage at the hands of the British. Now it was time to turn a bad situation into a successful failure, as it were. The Germans knew they were not going to hold onto France here, so now they needed to steal away in the night without getting caught.
It was decided that they would make a mad dash up the English Channel to the safety of German waters. The  key here was to make the Channel Dash right under the watchful eye of the British Royal Navy without their notice. It was quite risky. Despite the watchfulness of the British submarines and aircraft, the German Vice Admiral, Otto Ciliax launched Operation Cerberus to lead the ships out of the French port, and to the safety of the German ports.
key here was to make the Channel Dash right under the watchful eye of the British Royal Navy without their notice. It was quite risky. Despite the watchfulness of the British submarines and aircraft, the German Vice Admiral, Otto Ciliax launched Operation Cerberus to lead the ships out of the French port, and to the safety of the German ports.
On the evening of February 11, 1942, they set their plan in motion. Accompanied by six German destroyers and twenty one torpedo boats for protection, they moved north late that evening. When daylight hit, they were joined by German planes to provide air cover as well. The air cover was led by ace pilot, Adolf Galland. He was joined by 250 other fighters in a coordinated joint effort of the German Navy and the Luftwaffe…an unusually well coordinated joint effort. The British Royal Navy scrambled to coordinate its own attack, but the late start would prove to be the undoing of the attack, because they did not realize that the escape was in progress until the afternoon of February 12th. All three of the German warships made it to a German port on February 13th, although the Gneisenau and had incurred damaged by British mines along the route. In addition to the embarrassment of the well planned escape that was carried out by the Germans, the British lost 40 aircraft and six Navy Swordfish during their confrontation. The Germans, on the other had, only lost one torpedo boat and 17 aircraft.
Nevertheless, the British would exact a revenge of sorts, when British warships sunk the Scharnhorst in December of 1944, as it attempted to attack a Russian convoy. The Gneisenau was destroyed during a bombing raid, while it was still being repaired from the prior damage, and the Prinz Eugen survived the war, but  was taken over by the US Navy at the end of the war. It isn’t that I want to commend the Germans for their sneaky escape, because I don’t. They simply lived to fight…and ultimately lose, another day. It was, however, a good strategy, and I guess that even crazy dictators like Hitler, and the men he trained, could come up with an occasional good escape plan. Nevertheless, evil must not be allowed to continue, and the Germans had to be shut down, so the British, and all the other nations who stand for what is good, had to continue to fight, until Germany and its allies had no choice but to surrender. Still, February 11, 1942, the day of The Channel Dash would stand out as one of the best fights put up by the Germans, or at least, the best escape plan.
was taken over by the US Navy at the end of the war. It isn’t that I want to commend the Germans for their sneaky escape, because I don’t. They simply lived to fight…and ultimately lose, another day. It was, however, a good strategy, and I guess that even crazy dictators like Hitler, and the men he trained, could come up with an occasional good escape plan. Nevertheless, evil must not be allowed to continue, and the Germans had to be shut down, so the British, and all the other nations who stand for what is good, had to continue to fight, until Germany and its allies had no choice but to surrender. Still, February 11, 1942, the day of The Channel Dash would stand out as one of the best fights put up by the Germans, or at least, the best escape plan.

