troops
 Many people know about the Christmas truce of 1914, when in World War I, thousands of British, French, and German troops, exhausted from fighting took the night of Christmas Eve to stop fighting, leave their trenches, and meet the enemy forces in what was known as “No Man’s Land” to exchange gifts, food, and stories. For the soldiers, it was a moral boost, but the Generals disagreed, and determined to prevent further fraternization in the future, saw to it that such activities would be severely punished, thereby ending future Christmas truces for the rest of that war, or the following war. I suppose the Christmas “truce” would have been better called a “cease fire” since they weren’t supposed to fraternize.
Many people know about the Christmas truce of 1914, when in World War I, thousands of British, French, and German troops, exhausted from fighting took the night of Christmas Eve to stop fighting, leave their trenches, and meet the enemy forces in what was known as “No Man’s Land” to exchange gifts, food, and stories. For the soldiers, it was a moral boost, but the Generals disagreed, and determined to prevent further fraternization in the future, saw to it that such activities would be severely punished, thereby ending future Christmas truces for the rest of that war, or the following war. I suppose the Christmas “truce” would have been better called a “cease fire” since they weren’t supposed to fraternize.
In World War II, of course, there was no such truce called, and the fighting continued without taking notice of the holiday. Nevertheless, in 1944, during the Battle of the Bulge, the generals lost just a little bit of their control over the people, when in defiance of the orders, a small group of unlikely guests made their way to a little cabin in the Hurtgen Forest, for a little Christmas Truce of their own. They could have been in so much trouble had they been found out by superior officers, but at the time it just didn’t seem to matter, or maybe it was their host, one Elisabeth Vincken, who along with her 12 year old son stood up to the soldiers, and held off the battle for a few hours. After their home in Aachen was completely destroyed, Elisabeth and her son, Fritz were sent to their cabin, about four miles from Monschau in the Hurtgen Forest near the Belgian border. Her husband visited them as often as he could, but he needed to work. On that Christmas, Elisabeth and Fritz, had been hoping her husband would arrive to spend Christmas with them, but now they knew it was too late. Their Christmas meal would now have to wait for his arrival. Elisabeth and Fritz were alone in the cabin.
Then, the miracle began. Lost in the snow-covered Ardennes Forest, three American soldiers…one badly wounded, wandered around, trying to find the American lines. These poor men had been walking for three days while the sounds of battle echoed in the hills and valleys all around them. They had now idea who was shooting, so they dared not enter the area. Then, on Christmas Eve, they came upon a small cabin in the woods. They cautiously knocked at the door, hoping that they didn’t get shot. Elisabeth blew out the candles and opened the door to find two enemy American soldiers standing at the door and a third lying in the snow behind them. These men might have been soldiers, but were hardly older than boys. The men were armed and  could have simply pushed their way in, but they hadn’t, so she invited them inside and they carried their wounded comrade into the warm cabin. Elisabeth didn’t speak English and they didn’t speak German, but they managed to communicate in broken French. After she heard their story and saw the wounded soldier, Elisabeth gave up the idea of saving the Christmas meal for when her husband could get there. She started preparing a meal for the men. She sent Fritz to get six potatoes and Hermann the rooster…his stay of execution while they waited for her husband was now rescinded. Hermann had been named after Hermann Goering, the Nazi leader, who Elisabeth didn’t care much for. Maybe killing the rooster would make her feel better.
could have simply pushed their way in, but they hadn’t, so she invited them inside and they carried their wounded comrade into the warm cabin. Elisabeth didn’t speak English and they didn’t speak German, but they managed to communicate in broken French. After she heard their story and saw the wounded soldier, Elisabeth gave up the idea of saving the Christmas meal for when her husband could get there. She started preparing a meal for the men. She sent Fritz to get six potatoes and Hermann the rooster…his stay of execution while they waited for her husband was now rescinded. Hermann had been named after Hermann Goering, the Nazi leader, who Elisabeth didn’t care much for. Maybe killing the rooster would make her feel better.
While Hermann roasted and dinner was being prepared, there was another knock on the door. Fritz went to open it, thinking there might be more lost Americans, but instead there were four armed German soldiers. Seeing the German soldiers, and realizing that she could be killed for harboring the enemy, Elisabeth turned white as a ghost. She quickly pushed past Fritz and stepped outside. There was a corporal and three very young soldiers, who wished her a Merry Christmas, but they were lost and hungry. Knowing she had no choice, Elisabeth told them they were welcome to come into the warmth and eat until the food was all gone, but that there were others inside who they would not consider friends. The reaction she expected came when the corporal asked sharply if there were Americans inside and she said there were three who were lost and cold like they were and one was wounded. The corporal stared hard at her. She had to do something, so she said, “Es ist Heiligabend und hier wird nicht geschossen.” In German, that means, “It is the Holy Night and there will be no shooting here.” She insisted they leave their weapons outside. The men couldn’t believe that this woman was standing up to them in such a way. Nevertheless, the men decided to comply and Elisabeth went inside, demanding the same of the Americans. She took their weapons and put them outside next to the Germans’.
Understandably, the fear and tension in the cabin was high as the Germans and Americans eyed each other warily. Nevertheless, the warmth and smell of roast Hermann and potatoes soon eased the tension, and while the men were still wary, the meal was somewhat cordial. The Germans produced a bottle of wine and a loaf of bread. While Elisabeth tended to the cooking, one of the German soldiers, an ex-medical student, examined the wounded American. In English, he explained that the cold had prevented infection, but the man had lost a lot of blood. He needed food and rest. By the time the meal was ready, the atmosphere in the cabin was more relaxed. Two of the Germans were only sixteen, and the corporal was only 23. As Elisabeth said grace, Fritz  noticed tears in the exhausted soldiers’ eyes…both German and American. The moment had somehow touched them all. The unauthorized and very much unplanned “truce” lasted through the rest of that night, and into the morning. The German corporal looked at the map the Americans had, and pointed out the best way for the men to get back to their lines. He also gave them a compass. The Americans asked if they should instead go to Monschau, but the corporal shook his head and said that the Germans had taken Monschau. Elisabeth returned all their weapons and the enemies shook hands and left the cabin, in opposite directions. Soon they were all out of sight, and the truce was over.
noticed tears in the exhausted soldiers’ eyes…both German and American. The moment had somehow touched them all. The unauthorized and very much unplanned “truce” lasted through the rest of that night, and into the morning. The German corporal looked at the map the Americans had, and pointed out the best way for the men to get back to their lines. He also gave them a compass. The Americans asked if they should instead go to Monschau, but the corporal shook his head and said that the Germans had taken Monschau. Elisabeth returned all their weapons and the enemies shook hands and left the cabin, in opposite directions. Soon they were all out of sight, and the truce was over.
 There was, during the Second World War, a somewhat strange and almost morbid plan that was concocted to dupe the Germans into believing that the Allies were going to invade Greece in 1943, when in fact, they were going to invade Sicily, some 500 miles away. The success of the mission really depended on the element of surprise, and in the end, the Allies needed something that would be believable to the Germans.
There was, during the Second World War, a somewhat strange and almost morbid plan that was concocted to dupe the Germans into believing that the Allies were going to invade Greece in 1943, when in fact, they were going to invade Sicily, some 500 miles away. The success of the mission really depended on the element of surprise, and in the end, the Allies needed something that would be believable to the Germans.
The thing that made the operation morbid was that in the end, they would use a dead body to bring about their deception. In their plan a body was dumped in the sea, to be discovered by Axis forces, carrying fake secret documents suggesting the invasion would be staged in Greece. They were a bit shocked when their plan worked, but work it did. The German troops were diverted to Greece, and Operation Mincemeat became a huge success, but even after it was over, it remained a source of secrecy, confusion, and conspiracy theory. The biggest source of confusion being…just who was this man who was found floating in the ocean, and how did he really die? For most people, the operation remains a mystery to this day, but one man believes that he now knows the true identity of the man found floating in the ocean.
In the 1956 film called “The Man Who Never Was,” one historian claims to have finally established beyond any reasonable doubt the identity of the person who played the part of the dead man, He believes he was a homeless Welshman named Glyndwr Michael. The body, which was given the identity of a fake Royal Marine, Major William Martin, was dropped into the sea off Spain in 1943. Winston Churchill had remarked that “Anyone but a bloody fool would know it was Sicily”, but after the tides carried Major Martin’s body into the clutches of Nazi agents, Hitler and his High Command became convinced Greece was the target. “You can forget about Sicily. We know it’s in Greece,” proclaimed General Alfred Jodl, head of the German supreme command operations staff.
“Mincemeat swallowed, rod, line and sinker” was the message sent to Churchill after the Allies learned the plot had worked. In recent years, there have been repeated claims that Mincemeat’s chief planner, Lieutenant Commander Ewen Montagu, was so intent on deceiving the Germans that he stole the body of a crew member from HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy aircraft carrier which exploded off the Scottish coast in March 1943, and lied to the dead man’s relatives. In 2003, a documentary based on 14 years of research by former police officer Colin 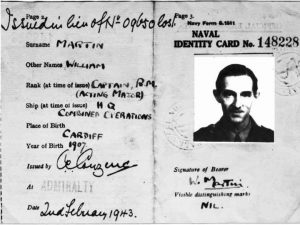 Gibbon claimed that ‘Major Martin’ was Dasher sailor Tom Martin. Then in 2004, official sanction appeared to be given to another candidate, Tom Martin’s crewmate John Melville. At a memorial service on board the current HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy patrol vessel, off the coast of Cyprus, Lieutenant Commander Mark Hill named Mr Melville as Major Martin, describing him as “a man who most certainly was”. Mr Melville’s daughter, Isobel Mackay, later told The Scotsman newspaper: “I feel very honored if my father saved 30,000 Allied lives.” I don’t suppose that we will ever know who the man really was, without exhuming his body, and that hardly seems right. Whoever he was, his family can rest assured that he saved many lives that day.
Gibbon claimed that ‘Major Martin’ was Dasher sailor Tom Martin. Then in 2004, official sanction appeared to be given to another candidate, Tom Martin’s crewmate John Melville. At a memorial service on board the current HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy patrol vessel, off the coast of Cyprus, Lieutenant Commander Mark Hill named Mr Melville as Major Martin, describing him as “a man who most certainly was”. Mr Melville’s daughter, Isobel Mackay, later told The Scotsman newspaper: “I feel very honored if my father saved 30,000 Allied lives.” I don’t suppose that we will ever know who the man really was, without exhuming his body, and that hardly seems right. Whoever he was, his family can rest assured that he saved many lives that day.
 The Korean War began on June 25, 1950, when 90,000 North Korean troops, under orders from Kim Song-Ju, stormed across the 38th parallel, catching the Republic of Korea’s forces completely off guard and throwing them into a hasty southern retreat. Two days later, United States President Harry Truman announced that the United States would intervene in the conflict, and on June 28 the United Nations approved the use of force against communist North Korea. On June 30, Truman agreed to send United States ground forces to Korea, and on July 7 the Security Council recommended that all United Nations forces sent to Korea be put under United States command. The next day, General Douglas MacArthur was named commander of all United Nations forces in Korea. North Korea’s evil dictator wanted to rule the whole nation, and he wouldn’t have stopped there. He had to be stopped. The war would go on for three long years, finally ending on July 27, 1953. The Korean War was memorialized in the minds of most people with the war series, MASH, which ran far longer than the war itself. Of course, it was a semi-fictional show about a Mobile Army Surgical Hospital in which the men and women did everything they could to put the injured soldiers back together after the ravages of battle, all the while, hating that they would go back to battle.
The Korean War began on June 25, 1950, when 90,000 North Korean troops, under orders from Kim Song-Ju, stormed across the 38th parallel, catching the Republic of Korea’s forces completely off guard and throwing them into a hasty southern retreat. Two days later, United States President Harry Truman announced that the United States would intervene in the conflict, and on June 28 the United Nations approved the use of force against communist North Korea. On June 30, Truman agreed to send United States ground forces to Korea, and on July 7 the Security Council recommended that all United Nations forces sent to Korea be put under United States command. The next day, General Douglas MacArthur was named commander of all United Nations forces in Korea. North Korea’s evil dictator wanted to rule the whole nation, and he wouldn’t have stopped there. He had to be stopped. The war would go on for three long years, finally ending on July 27, 1953. The Korean War was memorialized in the minds of most people with the war series, MASH, which ran far longer than the war itself. Of course, it was a semi-fictional show about a Mobile Army Surgical Hospital in which the men and women did everything they could to put the injured soldiers back together after the ravages of battle, all the while, hating that they would go back to battle.
Now, we have another rogue dictator of North Korea, namely Kim Jong-un, who has developed a number of bombs, and doesn’t mind shooting them off as a warning to the rest of the world that not only is he crazy, but he is armed and crazy. Kim Jong-un lobs missiles over Japan on a regular basis, and has threatened Guam as well. Unfortunately, because of soft “leadership” on the part of President Obama, Kim Jong-un was allowed to proceed with his evil plans relatively unchecked, and now, he is an out of control leader who honestly thinks that he can control the world, and doesn’t care who he kills.
Now, we are in a position of trying to figure out how to stop Kim Jong-un. I don’t presume to know the answer to this dilemma, nor would I want to be in the shoes of those who will have to do something, because I don’t believe that this problem is going to be easily solved. I do know that something is going to have to be done.  When a dictator is willing to launch a nuclear bomb, they clearly do not care about life. All they care about is ruling the world. They don’t care about freedom, the lives of their own people or even the future of mankind. That makes them…insane, in my book. So, while I would not want to be in President Trump’s shoes concerning North Korea, I will support his decisions concerning military action, because I believe that he has the best interests of the United States and the world at heart, and I also do not believe that sanctions will work…now or ever. While I don’t think that war against North Korea would be easy, I also know that we can’t just sit idly by and let Kim Jong-un continue his rampage. It just might be time to do it again where North Korea is concerned.
When a dictator is willing to launch a nuclear bomb, they clearly do not care about life. All they care about is ruling the world. They don’t care about freedom, the lives of their own people or even the future of mankind. That makes them…insane, in my book. So, while I would not want to be in President Trump’s shoes concerning North Korea, I will support his decisions concerning military action, because I believe that he has the best interests of the United States and the world at heart, and I also do not believe that sanctions will work…now or ever. While I don’t think that war against North Korea would be easy, I also know that we can’t just sit idly by and let Kim Jong-un continue his rampage. It just might be time to do it again where North Korea is concerned.
 Sometimes, the best plans can have the most disastrous results, and when you find out that it was all unnecessary…it can be almost too much to bear. World War II was a difficult war. It had so many fronts and so many nations were involved. One division might invade an area with the plan of becoming a support unit for another division, who was going to be attacking another area. Such was the case on September 14, 1944, when the United States 1st Marine Division landed on the island of Peleliu, one of the Palau Islands in the Pacific, as part of a larger operation to provide support for General Douglas MacArthur, who was preparing to invade the Philippines. The Palaus Islands are a part of the Caroline Islands. It had been ordered that they be taken from Germany and given to Japan as one of the terms of the Treaty of Versailles at the close of World War I. Now, it was thought that they were needed to help with this latest invasion.
Sometimes, the best plans can have the most disastrous results, and when you find out that it was all unnecessary…it can be almost too much to bear. World War II was a difficult war. It had so many fronts and so many nations were involved. One division might invade an area with the plan of becoming a support unit for another division, who was going to be attacking another area. Such was the case on September 14, 1944, when the United States 1st Marine Division landed on the island of Peleliu, one of the Palau Islands in the Pacific, as part of a larger operation to provide support for General Douglas MacArthur, who was preparing to invade the Philippines. The Palaus Islands are a part of the Caroline Islands. It had been ordered that they be taken from Germany and given to Japan as one of the terms of the Treaty of Versailles at the close of World War I. Now, it was thought that they were needed to help with this latest invasion.
 There were those who felt that this invasion was not necessary, and was in fact, dangerous. The operation was called Operation Stalemate. The problem was that the United States military was unfamiliar with the islands. That made them sitting ducks. Admiral William Halsey argued against Operation Stalemate, which included the Army invasion of Morotai in the Dutch East Indies. He believed that MacArthur would meet minimal resistance in the Philippines, making this operation unnecessary, especially given the risks involved. Going into a jungle without knowing where the enemy might be hiding is dangerous. The term, “know thine enemy” comes to mind. The Japanese were sneaky, and that would prove to be a big problem.
There were those who felt that this invasion was not necessary, and was in fact, dangerous. The operation was called Operation Stalemate. The problem was that the United States military was unfamiliar with the islands. That made them sitting ducks. Admiral William Halsey argued against Operation Stalemate, which included the Army invasion of Morotai in the Dutch East Indies. He believed that MacArthur would meet minimal resistance in the Philippines, making this operation unnecessary, especially given the risks involved. Going into a jungle without knowing where the enemy might be hiding is dangerous. The term, “know thine enemy” comes to mind. The Japanese were sneaky, and that would prove to be a big problem.
The Japanese defenders of the island were buried quite deep in the jungle, and the target intelligence given the Americans was faulty. When the division landed, the Marines met little immediate resistance, which I’m sure  gave them a sense of confidence that would very soon be destroyed. The lack of resistance was a ploy. Shortly after the Marines landed, Japanese machine guns opened fire, knocking out more than two dozen landing craft. Japanese tanks and troops followed, as the startled 1st and 5th Marine regiments fought for their lives. Jungle caves produced even more Japanese soldiers. Within one week of the invasion, the Marines lost 4,000 men. By the time it was all over, that number would surpass 9,000. The Japanese lost more than 13,000 men. Flamethrowers and bombs finally subdued the island for the Americans, but in the end, it was pointless. MacArthur invaded the Philippines without need of Army or Marine protection from either Peleliu or Morotai.
gave them a sense of confidence that would very soon be destroyed. The lack of resistance was a ploy. Shortly after the Marines landed, Japanese machine guns opened fire, knocking out more than two dozen landing craft. Japanese tanks and troops followed, as the startled 1st and 5th Marine regiments fought for their lives. Jungle caves produced even more Japanese soldiers. Within one week of the invasion, the Marines lost 4,000 men. By the time it was all over, that number would surpass 9,000. The Japanese lost more than 13,000 men. Flamethrowers and bombs finally subdued the island for the Americans, but in the end, it was pointless. MacArthur invaded the Philippines without need of Army or Marine protection from either Peleliu or Morotai.

