thomas jefferson

 In 1800, President John Adams approved legislation that appropriated $5,000 to purchase “such books as may be necessary for the use of Congress.” The initial collection of books, ordered from London, arrived in 1801. These were stored in the US Capitol. The books were the library’s first. The inaugural library catalog, dated April 1802, listed 964 volumes and nine maps. The library was President Adams’ pride and joy. In 1814, in what was a largely symbolic maneuver, the British entered Washington DC and burned down the capitol and the library. The fire was dramatic, but really had little relevance, because the city didn’t have an especially large population and, since much of the US government had fled before the British could overtake them, there was little strategic value in the destruction. Nevertheless, the about 3,000 books were lost in that fire.
In 1800, President John Adams approved legislation that appropriated $5,000 to purchase “such books as may be necessary for the use of Congress.” The initial collection of books, ordered from London, arrived in 1801. These were stored in the US Capitol. The books were the library’s first. The inaugural library catalog, dated April 1802, listed 964 volumes and nine maps. The library was President Adams’ pride and joy. In 1814, in what was a largely symbolic maneuver, the British entered Washington DC and burned down the capitol and the library. The fire was dramatic, but really had little relevance, because the city didn’t have an especially large population and, since much of the US government had fled before the British could overtake them, there was little strategic value in the destruction. Nevertheless, the about 3,000 books were lost in that fire.
The Library of Congress must seem like an institution that is unable to be defeated, but the reality is that while it has been there practically forever, acting as the nation’s biggest library, it has been almost destroyed three times. The Library of Congress is one of the largest libraries in the world, with over 170 million items in its collections at present, according to the Library of Congress itself. It possesses a world class collection of rare books and holds the largest known collection of audio recordings, maps, and films, among other materials. It is accessible not only to the Congressional representatives who work nearby in the Capitol, but also to all Americans and members of the public. That was not always the case, however. At its inception, the Library of Congress was for congressional use only.
Once the fires of the British died down, they left Washington, and the American lawmakers returned. As has always been the way of Americans, they knew it was time to rebuild. While Congress was putting itself back together, it became clear that most wanted the Library of Congress to return as well. At that point, former president Thomas Jefferson stepped in. He offered to sell his own library to reconstitute the one lost in 1814. It is certainly logical that Jefferson was one proposing such a deal. According to the Library of Congress, he was an avid book reader and lifelong learner with an extensive personal library. While he committed to the notion of an informed, intellectual Congress, Jefferson may have also empathized on a deeper level. In 1770, his own home had burned, and Jefferson, gazing at the ashes, most acutely felt the loss of his books. Later, he would come to possess the largest private library in the United States.
The Library of Congress faced at least three fires in its fight to exist. In fact, its existence as an institution has been challenged numerous obstacles throughout its more than 200 years of existence. The Library of Congress faced space shortages, understaffing, and lack of funding, until the American Civil War increased the importance of legislative research to meet the demands of a growing federal government. Then, in 1870, the library gained the right to receive two copies of every copyrightable work printed in the United States. It also built its collections through acquisitions and donations. Between 1890 and 1897, a new library building, which has now 
 been renamed the Thomas Jefferson Building, was constructed. Two additional buildings, the John Adams Building (opened in 1939) and the James Madison Memorial Building (opened in 1980), were later added. In total, the Library of Congress has faced major fires at least three times in its history.
been renamed the Thomas Jefferson Building, was constructed. Two additional buildings, the John Adams Building (opened in 1939) and the James Madison Memorial Building (opened in 1980), were later added. In total, the Library of Congress has faced major fires at least three times in its history.
According to the United States House of Representatives, the 1825 fire occurred on the evening of December 22nd. Massachusetts Representative Edward Everett, who was leaving a nearby party, noticed a strange light coming from the library windows. When he informed a Capitol police officer, who did not have a key, Everett dismissed the situation. However, as the glow intensified, it became increasingly difficult to ignore. Eventually, more officers, along with Librarian of Congress George Watterson, discovered the dreadful truth: Library of Congress was on fire…again!!
Both representatives and firefighters fought the blaze, including’s fellow Massachusetts representative, Daniel Webster, and Tennessee politician Sam Houston. They extinguished fire before it spread to the rest of the Capitol. Ultimately, it was determined that the cause was a candle left lit in the room. The damage was not nearly as extensive as the 1814, though some books and a rug were lost.
On December 24, 1851, what is thought to be the most devastating fire destroyed 35,000 books, two-thirds of the library’s collection, and two-thirds of Jefferson’s original transfer. In 1852, Congress appropriated $168,700 to replace the books but not to acquire new materials. By 2008, the librarians of Congress had found replacements for all but 300 of the works documented as being in Jefferson’s original collection. This marked the beginning of a conservative period in the library’s administration under librarian John Silva Meehan and joint committee chairman James A. Pearce, who restricted the library’s activities. Meehan and Pearce’s views on limiting the Library of Congress’s scope were shared by members of Congress. As a librarian, Meehan and perpetuated the notion that “the congressional library should play a limited role on the national scene and its collections, by and large, should emphasize American materials obvious use to the US Congress.” In 1859, Congress transferred the library’s public document distribution activities to the Department of the Interior and its international book exchange program to the Department of State.
These days, the library is open for academic research to anyone with a Reader Identification Card. The library items may not be removed from the reading rooms or the library buildings. Most of the library’s general collection of books and journals are in the closed stacks of Jefferson and Adams Buildings. Specialized collections of books and other materials are in stacks in three main library buildings or stored off-site. Access to the closed stacks not permitted under any circumstances, except to authorized library staff and occasionally to dignitaries. Only reading room reference collections are on open shelves.

 Since 1902, American libraries have been able to request books other items through interlibrary loan from the Library of Congress, if these are not available elsewhere. Through this system, the Library of Congress has served as a “library of last resort,” according to former librarian of Congress Herbert Putnam. The Library of Congress lends books to other libraries with the stipulation that they be used only inside the borrowing library. In 2017, the Library of Congress began development of a reader’s card for children under the age of sixteen.
Since 1902, American libraries have been able to request books other items through interlibrary loan from the Library of Congress, if these are not available elsewhere. Through this system, the Library of Congress has served as a “library of last resort,” according to former librarian of Congress Herbert Putnam. The Library of Congress lends books to other libraries with the stipulation that they be used only inside the borrowing library. In 2017, the Library of Congress began development of a reader’s card for children under the age of sixteen.

 One of the most iconic monuments in the United States, in my opinion is that of Mount Rushmore. I’m sure some people might not agree with me on that, but I have been to Mount Rushmore more times than I could possibly count, and it just never gets old. The monument was the vision of Doane Robinson, a South Dakota historian who was looking to draw more visitors to the state. While that was a cool idea, it was dwarfed, in the end, by the absolute grandeur of the finished product. Maybe it was the vision of the sculptor, Gutzon Borglum, who Robinson commissioned to chisel the faces into the mountain, or maybe it was because it would transform a mountain into an awesome tribute to four really great presidents. I can’t say for sure, but the monument ended up being so much more than a tourist attraction. Every time I am there, I feel the awesomeness of the place, almost as if it is hallowed ground…though not in the Biblical sense.
One of the most iconic monuments in the United States, in my opinion is that of Mount Rushmore. I’m sure some people might not agree with me on that, but I have been to Mount Rushmore more times than I could possibly count, and it just never gets old. The monument was the vision of Doane Robinson, a South Dakota historian who was looking to draw more visitors to the state. While that was a cool idea, it was dwarfed, in the end, by the absolute grandeur of the finished product. Maybe it was the vision of the sculptor, Gutzon Borglum, who Robinson commissioned to chisel the faces into the mountain, or maybe it was because it would transform a mountain into an awesome tribute to four really great presidents. I can’t say for sure, but the monument ended up being so much more than a tourist attraction. Every time I am there, I feel the awesomeness of the place, almost as if it is hallowed ground…though not in the Biblical sense.
The sculpting of Mount Rushmore was a monumental task, particularly in 1927. Nevertheless, the carving began on October 4th on the likenesses of the four great men of Mount Rushmore, located in the Black Hills National Forest of South Dakota. The project was to be far from quickly finished. Instead, it would take an additional 12 years to complete the granite likenesses of four esteemed American presidents…George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Abraham Lincoln, and Theodore Roosevelt. Each time a likeness was completed, it was big news, and people came from miles around to watch the unveiling ceremony. Of course, the project was not without conflict. The Lakota Sioux people, who consider the Black Hills to be sacred ground, strongly opposed the project. The mountain was previously part of the Great Sioux Reservation before being taken away  from them by the US government. Nevertheless, there were no skirmishes over the project, and these days, the likeness of Crazy Horse is also being carved into a mountain in the Black Hills.
from them by the US government. Nevertheless, there were no skirmishes over the project, and these days, the likeness of Crazy Horse is also being carved into a mountain in the Black Hills.
The first face “chiseled” by Borglum, was that of George Washington. Initially, Borglum sculpted the head in an egg shape and added the features afterward. The plan was to place Thomas Jefferson’s likeness to the right of Washington, but after two years, it developed severe cracks. The workers were forced to remove the damaged sculpture with dynamite. They tried going deeper, but the kept coming up with more quartz, which was unsuitable for the enduring sculpture that today exists on Mount Rushmore. So, Borglum repositioned Jefferson on Washington’s left side and started again.
Washington’s face was completed in 1934. Jefferson’s was dedicated in 1936…with then…president Franklin Roosevelt in attendance. Lincoln’s likeness was completed a year later. In 1939, Teddy Roosevelt’s face was completed. The project, which cost $1 million, was funded primarily by the federal government. When we think of sculpting in stone, we think of hammers and chisels, but much of Mount Rushmore was “sculpted” with dynamite. With 450,000 tons of granite to be removed, chisels were definitely not going to be enough. Throughout the fourteen years of carving, from 1927 to 1941, nearly 400 workers, including both men and women, labored at the memorial. The work was demanding, the hours extensive, the wages modest, and job security was unpredictable. Even under severe and perilous conditions, there were no fatalities during the carving process. While for some, this work represented merely a job, for others, it evolved into a profound vocation. For those that embraced the project, I can imagine that they somehow felt the same sense of this being hallowed ground that I feel each time I’m there.
At the time of Borglum’s death, the sculpture was not finished. He continued to touch up his work at Mount Rushmore until he died suddenly in 1941. Borglum had originally hoped to also carve a series of inscriptions into the mountain, outlining the history of the United States. After his passing, his son Lincoln Borglum finished 
 the sculpture to its current point. It isn’t exactly the sculpture Gutzon Borglum has imagined, because it was to have featured the presidents to their waists, but I think it is perfect as it stands today, from its four carved heads to the secret room, known as “The Hall of Records,” behind the structure, that no one is permitted to see without an act of Congress. That is something I would love to be allowed to see someday. As it stands, it too remains unfinished.
the sculpture to its current point. It isn’t exactly the sculpture Gutzon Borglum has imagined, because it was to have featured the presidents to their waists, but I think it is perfect as it stands today, from its four carved heads to the secret room, known as “The Hall of Records,” behind the structure, that no one is permitted to see without an act of Congress. That is something I would love to be allowed to see someday. As it stands, it too remains unfinished.
 It never really occurred to me that the formation of new states in the United States would be the huge undertaking that it actually became. I just assumed that as the settlers moved into an area, they eventually got populated enough to decide to be a state. Of course, I realized that they would have to “petition” the national government for acceptance, but that wasn’t all there was to it at all. The United States had acquired the Northwest Territory (the Midwest today) in a number of steps. First, when it was relinquished by the British. Second, extinguishment of states’ claims west of the Appalachians. And finally, usurpation or purchase of lands from the Native Americans. Originally, the Hudson’s Bay Company acquired the area under a charter from Charles II in 1670. Then, in 1869, the Canadian government bought the land from the company. The boundaries we now have were set in 1912. In 1870, Canada acquired an area known as Rupert’s Land and the North-Western Territory from the Hudson’s Bay Company for £300,000 (Canadian $1.5 million) and a large land grant.
It never really occurred to me that the formation of new states in the United States would be the huge undertaking that it actually became. I just assumed that as the settlers moved into an area, they eventually got populated enough to decide to be a state. Of course, I realized that they would have to “petition” the national government for acceptance, but that wasn’t all there was to it at all. The United States had acquired the Northwest Territory (the Midwest today) in a number of steps. First, when it was relinquished by the British. Second, extinguishment of states’ claims west of the Appalachians. And finally, usurpation or purchase of lands from the Native Americans. Originally, the Hudson’s Bay Company acquired the area under a charter from Charles II in 1670. Then, in 1869, the Canadian government bought the land from the company. The boundaries we now have were set in 1912. In 1870, Canada acquired an area known as Rupert’s Land and the North-Western Territory from the Hudson’s Bay Company for £300,000 (Canadian $1.5 million) and a large land grant.
That left the United States with a kind of dilemma, since they wanted to make sure these new states were run in the way they had originally designed. So, on July 13, 1787, Congress enacts the Northwest Ordinance, to structure the settlement of the Northwest Territory. Since the formation of new states was a new venture for  the young nation, they had to create a policy for the addition of these new states. Vitally important was the need to make sure their new nation thrived and survived. The members of Congress knew that if their new confederation were to survive intact, it had to resolve issue of the states’ competing claims to western territory.
the young nation, they had to create a policy for the addition of these new states. Vitally important was the need to make sure their new nation thrived and survived. The members of Congress knew that if their new confederation were to survive intact, it had to resolve issue of the states’ competing claims to western territory.
That said, in 1781, the state of Virginia began the process by ceding its extensive land claims to Congress. That bold move made other states more comfortable in doing the same. Thomas Jefferson first proposed a method of incorporating these western territories into the United States in 1784. His plan was to basically turn the territories into colonies of the existing states. Since each state was to have their own constitution, the ten new northwestern territories would select the constitution of an existing state that closely aligned with their own values. Once that process was complete, the new territory (colony) had to wait until its population reached 20,000 to join the confederation as a full member. That process made Congress nervous, because they feared that the new states…10 in the Northwest as well as Kentucky, Tennessee and Vermont…would quickly gain enough power to outvote the old ones, so Congress never passed Thomas Jefferson’s proposal.
It would be three more years before the Northwest Ordinance which proposed that “three to five new states be created from the Northwest Territory. Instead of adopting the legal constructs of an existing state, each territory would have an appointed governor and council. When the population reached 5,000, the residents could elect their own assembly, although the governor would retain absolute veto power. When 60,000 settlers 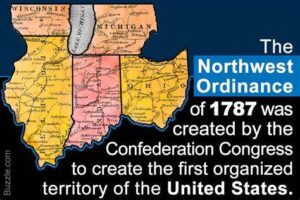 resided in a territory, they could draft a constitution and petition for full statehood. The ordinance provided for civil liberties and public education within the new territories, but did not allow slavery.”
resided in a territory, they could draft a constitution and petition for full statehood. The ordinance provided for civil liberties and public education within the new territories, but did not allow slavery.”
The last part angered the pro-slavery Southerners, but they were willing to go along with this because they hoped that the new states would be populated by white settlers from the South. They believed that although these Southerners would have no enslaved workers of their own, they would not join the growing abolition movement of the North. Of course, we all know how that played out.

 With the election of Thomas Jefferson as third president, on February 17, 1801, came the first peaceful transfer of power from one political party to another in the United States. Nevertheless, the election was an unusual one. By this time, Jefferson had helped to draft the Declaration of Independence, had served in two Continental Congresses, as minister to France, as secretary of state under George Washington and as John Adams’ vice president. These credentials probably made him the best person for the job in the entire world.
With the election of Thomas Jefferson as third president, on February 17, 1801, came the first peaceful transfer of power from one political party to another in the United States. Nevertheless, the election was an unusual one. By this time, Jefferson had helped to draft the Declaration of Independence, had served in two Continental Congresses, as minister to France, as secretary of state under George Washington and as John Adams’ vice president. These credentials probably made him the best person for the job in the entire world.
While it was obvious that Jefferson was the best man for the job, vicious partisan warfare was the name of the game during the campaign of 1800 between Democratic-Republicans Jefferson and Aaron Burr and Federalists John Adams, Charles C Pinckney and John Jay. The ongoing battle raged between Democratic-Republican supporters of the French, who were involved in their own bloody revolution, and the pro-British Federalists who wanted to implement English-style policies in American government. The Federalists hated the French revolutionaries because of their overzealous use of the guillotine and, as a result, were less forgiving in their foreign policy toward the French. They pushed for a strong centralized government, a standing military, and financial support of emerging industries.
Jefferson’s Democratic-Republicans, on the other hand, preferred limited government, complete and absolute states’ rights and a primarily agricultural economy. They feared that Federalists would abandon revolutionary ideals and revert to the English monarchical tradition. When Jefferson was secretary of state under Washington, he opposed Secretary of the Treasury Hamilton’s proposal to increase military expenditures and resigned when Washington supported the leading Federalist’s plan for a national bank.
A bloodless, but ugly campaign ensued, in which candidates and influential supporters on both sides used the press, often anonymously, as a forum to fire slanderous volleys at each other. It sounds a lot like some of our election campaigns of today. Then came the laborious and confusing process of voting, that began in April 1800. Individual states scheduled elections at different times, which I think further confuses the situation, and although Jefferson and Burr ran on the same ticket, as president and vice president respectively, the Constitution still demanded votes for each individual to be counted separately. As a result, by the end of January 1801, Jefferson and Burr emerged tied at 73 electoral votes apiece. Adams came in third at 65 votes. While that left Adams out, it left a tie for Jefferson and Burr. The result created a big problem.
The resulting tie sent the final vote to the House of Representatives. That would not make for an easy decision e ither. A number of those in the Federalist-controlled House of Representatives insisted on following the Constitution’s flawed rules and refused to elect Jefferson and Burr together on the same ticket. The highly influential Federalist Alexander Hamilton, who mistrusted Jefferson, but hated Burr more, persuaded the House to vote against Burr, whom he called the most unfit man for the office of president. Of course, that cause a hatred between Hamilton and Burr that led Burr to challenge Hamilton to a duel in 1804. Burr won the duel when he killed Hamilton. Two weeks before the scheduled inauguration, Jefferson emerged victorious, and Burr was confirmed as his vice president. It was the first of only two times the presidency has been decided by the House of Representatives.
ither. A number of those in the Federalist-controlled House of Representatives insisted on following the Constitution’s flawed rules and refused to elect Jefferson and Burr together on the same ticket. The highly influential Federalist Alexander Hamilton, who mistrusted Jefferson, but hated Burr more, persuaded the House to vote against Burr, whom he called the most unfit man for the office of president. Of course, that cause a hatred between Hamilton and Burr that led Burr to challenge Hamilton to a duel in 1804. Burr won the duel when he killed Hamilton. Two weeks before the scheduled inauguration, Jefferson emerged victorious, and Burr was confirmed as his vice president. It was the first of only two times the presidency has been decided by the House of Representatives.
 Many people have had to switch from their dominant hand due to an accident, stroke, or amputation, but we rarely think of a president find himself in that position. Nevertheless, Thomas Jefferson had to do just that. It can happen to anyone really, but like many a young man, Thomas Jefferson was out to impress a girl. The strange part was that when it happened, Thomas wasn’t a young man. He was, nevertheless, trying to impress a girl. Thomas was 42 years old. He wasn’t the president of the United States yet, but he had been married. He married Martha Wayles in 1772, but she passed away in 1782, so he was alone. He and Martha had six children. Of the six children born to Thomas and Martha, only two survived to adulthood, Martha and Mary. His wife, Martha died four months after the birth of her last child. He had been happy, but his marriage was short. Thomas Jefferson was not perfect, and in fact he made lots of mistakes, and even had children with his slave, but he was a good president…and which of us is perfect, after all.
Many people have had to switch from their dominant hand due to an accident, stroke, or amputation, but we rarely think of a president find himself in that position. Nevertheless, Thomas Jefferson had to do just that. It can happen to anyone really, but like many a young man, Thomas Jefferson was out to impress a girl. The strange part was that when it happened, Thomas wasn’t a young man. He was, nevertheless, trying to impress a girl. Thomas was 42 years old. He wasn’t the president of the United States yet, but he had been married. He married Martha Wayles in 1772, but she passed away in 1782, so he was alone. He and Martha had six children. Of the six children born to Thomas and Martha, only two survived to adulthood, Martha and Mary. His wife, Martha died four months after the birth of her last child. He had been happy, but his marriage was short. Thomas Jefferson was not perfect, and in fact he made lots of mistakes, and even had children with his slave, but he was a good president…and which of us is perfect, after all.
In 1785, Thomas was in Paris, and he met a woman named Maria Cosway, who was a married woman. Thomas Jefferson took a liking to her, and he was trying to impress her. Well, he shouldn’t have been doing what he did. He knew it, and we know it to this day, but he did try to impress her, by trying to jump over a fence. In the ensuing accident, whereby he fell, Thomas Jefferson broke his right wrist. The surgeon set his wrist, but he didn’t really do a good job of it. After they set his wrist bones, he suffered chronic pain in his left hand for the rest of his life. He was really unable to use his left hand much at all after that. 
The accident forced Thomas Jefferson to stay in his house for a month, during which time, his secretary, William Short, had to write his letters for him. For a few months, he used his left hand to write letters including the famous “Head and Heart” letter on October 12 to Maria Cosway. The broken wrist caused him to have to cut short the planned sightseeing trip with Maria Cosway, and it also cause him to have to postpone his journey to the south of France. In the end, his wrist finally healed, but it was never to the point that he could use it as his dominant hand, so he had to switch out his dominant hand and live the rest of his life as a lefty. I suppose some might have said that his infatuation with Maria Cosway cost him the use of his hand, in a sort of “repercussion for bad behavior” scenario, but I don’t believe in the “God will hit you with a lightning bolt” kind of punishment. I know that it likely wouldn’t have happened if he had left Maria Cosway alone, but I just think God tries for grace first.

 Historians, who have studied the lives of Presidents John Adams and Thomas Jefferson, agree that while the two men were friends, they also had a long history as “frenemies.” It is fairly common with politicians, because each one has definite ideas about how things should be run. So, the two rivals always had a volatile relationship.
Historians, who have studied the lives of Presidents John Adams and Thomas Jefferson, agree that while the two men were friends, they also had a long history as “frenemies.” It is fairly common with politicians, because each one has definite ideas about how things should be run. So, the two rivals always had a volatile relationship.
Their friendship began in the early days of the nation, despite their vastly different political views. Adams was a strong believer in a strong central government, and Jefferson championed states’ rights. I would imagine that there was a measure of frustration for Adams, as he watched his administration being dismantled in the early years of the Jefferson administration. Nevertheless, as a Conservative, I have to agree with the Thomas Jefferson way of government.
Adams preceded Jefferson as president friend 1797 to 1800. During the Adams presidency, it became very apparent that the two men were very different, and their political views were just as different. The hot-tempered Adams was a firm believer in a strong centralized government, while the genteel Jefferson believed federal government should take a more hands-off approach and defer to individual states’ rights. They clashed loudly and often. As Adams’ vice president, Jefferson was horrified by what he considered to be Adams’ abuse  of the presidential power…particularly his passage of the restrictive Alien and Sedition Acts of 1798. Jefferson abandoned Adams and Washington for his estate at Monticello. There, he plotted how to bring his Republican faction back into power in the presidential election of 1800. After an exceptionally bitter campaign, in which both parties engaged in slanderous attacks on each other in print, Jefferson emerged victorious. It appeared the former friends would be eternal enemies. The former revolutionaries went on to resume their friendship over 14 years of correspondence during their golden years.
of the presidential power…particularly his passage of the restrictive Alien and Sedition Acts of 1798. Jefferson abandoned Adams and Washington for his estate at Monticello. There, he plotted how to bring his Republican faction back into power in the presidential election of 1800. After an exceptionally bitter campaign, in which both parties engaged in slanderous attacks on each other in print, Jefferson emerged victorious. It appeared the former friends would be eternal enemies. The former revolutionaries went on to resume their friendship over 14 years of correspondence during their golden years.
On July 4, 1826, the 50th anniversary of the adoption of The Declaration of Independence, these “frenemies” died on the same day and within five hours of each other. Jefferson and Adams were the last surviving members of the original American revolutionaries who had stood up to the British empire and forged a new political system in the former colonies. When Adams died at the age of 90, his last words, as the country celebrated Independence Day were, “Thomas Jefferson still survives.” Adams was wrong. Jefferson had died five hours earlier at Monticello at the age of 83.
 Shortly after President Thomas Jefferson completed the Louisiana Purchase from France, which made it an American territory, William Ashley, who was a Virginia native, made the decision to move to Missouri. Ashley was a young man, who was looking to make a name for himself. He entered into a partnership with Andrew Henry to manufacture gunpowder and lead. Opportunists, Ashley and Henry took advantage of the fact that these two commodities were in short supply in young America.
Shortly after President Thomas Jefferson completed the Louisiana Purchase from France, which made it an American territory, William Ashley, who was a Virginia native, made the decision to move to Missouri. Ashley was a young man, who was looking to make a name for himself. He entered into a partnership with Andrew Henry to manufacture gunpowder and lead. Opportunists, Ashley and Henry took advantage of the fact that these two commodities were in short supply in young America.
Ashley’s business prospered during the War of 1812, and he also joined the Missouri militia. He eventually achieved the rank of general. When Missouri became a state in 1822, Ashley used his military fame, and his business success to win election at lieutenant governor. Once elected, Ashley set about looking for opportunities to enrich both Missouri and his own pocketbook. Because he knew the area, he realized that Saint Louis was in a perfect place to exploit the fur trade on the upper Missouri River.
Ashley recruited his old business partner, Henry to join him in this new venture. Then, Ashley placed an advertisement in the Missouri Gazette and Public Advisor seeking 100 “enterprising young men” to engage in fur trading on the Upper Missouri. The advertisement was a big success. Scores of young men responded and came to Saint Louis. Among them were such future legendary mountain men as Jedediah Smith and Jim Bridger, as well as the famous river man Mike Fink. In time, these men and dozens of others would go on to uncover many of the geographic mysteries of the Far West, but for now they were looking to make a living trapping animals for their furs.
1822 found Ashley and a small band of his fur trappers building a trading post on the Yellowstone River in Montana in order to expand outward from the Missouri River. The Arikara Indians didn’t like this invasion, and they were deeply hostile to Ashley’s attempts to undercut their long-standing position as middlemen in the fur trade. The ensuing attacks eventually forced the men to abandon the Yellowstone post. Out of desperation, Ashley hit on a new strategy. Instead of building central permanent forts along the major rivers, he decided to send his trappers overland in small groups traveling by horseback. By avoiding the river arteries, the trappers could both escape detection by hostile Indians and develop new and untapped fur regions. Almost by accident, Ashley invented the famous “rendezvous” system that revolutionized the American fur trade. The necessary supplies were delivered and furs were delivered at meetings in a large meadow near the Henry’s Fork of Wyoming’s Green River in the early summer of 1825.
Ashley’s first fur trapper rendezvous was very successful. Ashley took home a tidy profit for his efforts. The fur  trappers not only had an opportunity to trade for supplies, but a chance to enjoy a few weeks of often drunken socializing. Ashley organized a second highly profitable rendezvous in 1826, and then decided to sell out. While he was no longer a part of it, his rendezvous system continued to be used by others. The system eventually became the foundation for the powerful Rocky Mountain Fur Company. With plenty of money in the bank, Ashley was able to return to his first love…politics. He was elected to Congress three times and once to the Senate, where he helped further the interests of the western land that had made him rich.
trappers not only had an opportunity to trade for supplies, but a chance to enjoy a few weeks of often drunken socializing. Ashley organized a second highly profitable rendezvous in 1826, and then decided to sell out. While he was no longer a part of it, his rendezvous system continued to be used by others. The system eventually became the foundation for the powerful Rocky Mountain Fur Company. With plenty of money in the bank, Ashley was able to return to his first love…politics. He was elected to Congress three times and once to the Senate, where he helped further the interests of the western land that had made him rich.
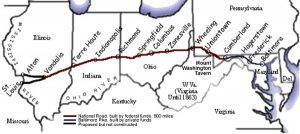
 George Washington and Thomas Jefferson believed that a trans-Appalachian road was necessary to connect this young country. In 1806 Congress authorized construction of the road and President Jefferson signed the act establishing the National Road. It would connect Cumberland, Maryland to the Ohio River. Construction on the road, known in many places as Route 40, and in others as the Cumberland Road, began in 1811 and continued until 1834. It was designed to reach the western settlements, and was the first federally funded road in United States history.
George Washington and Thomas Jefferson believed that a trans-Appalachian road was necessary to connect this young country. In 1806 Congress authorized construction of the road and President Jefferson signed the act establishing the National Road. It would connect Cumberland, Maryland to the Ohio River. Construction on the road, known in many places as Route 40, and in others as the Cumberland Road, began in 1811 and continued until 1834. It was designed to reach the western settlements, and was the first federally funded road in United States history.
The first contract was awarded in 1811, and included the first 10 miles of road. These days that seems like such a short distance, but in the early 1800s, I’m sure it was considered a big job. By 1818 the road was completed to Wheeling, West Virginia. It was at this point that mail coaches began using the road. By the 1830s the federal government turned over part of the road’s maintenance responsibility to the states through which it ran. In order to help pay for the road’s upkeep, tollgates and tollhouses were built by the states. As work on the road progressed a settlement pattern developed that is still visible. Original towns and villages that were found along the National Road, remain barely touched by the passing of time. The road, also called the Cumberland Road, National Pike and other names, became Main Street in these early settlements, earning the nickname “The Main Street of America.” The height of the National Road’s popularity came in 1825 when it was celebrated in song, story, painting and poetry, but hard times hit in 1834, and construction on the road was tabled. During the 1840s popularity soared again. Travelers and drovers, westward bound, crowded the inns and taverns along the route. Huge Conestoga wagons hauled produce from farms on the frontier to the East Coast, and then returned with staples such as coffee and sugar for the western settlements. Thousands of people moved west in covered wagons and stagecoaches that traveled the road keeping to regular schedules.
In the 1870s, however, the railroads came and some of the excitement of the national road faded. In 1912 the road became part of the National Old Trails Road and its popularity returned in the 1920s with the automobile. Federal Aid became available for improvements in the road to accommodate the automobile. In 1926 the road became part of US 40 as a coast-to-coast highway. As the interstate system has grown throughout America, interest in the National Road again waned. However, now when we want to have a relaxing journey with some history thrown in, we again travel the National Road. Cameras capture old buildings, bridges and old stone mile markers. Old brick schoolhouses from early years sporadically dot the countryside and some are found in the small towns on the National Road. Many are still used, some are converted to a private residence and others stand abandoned.
Historic stone bridges dot their way along the National Road, and they have their own stories to tell. The craftsmanship of the early engineers was amazing. The S Bridge, was so named because of its design and it stands 4 miles east of Old Washington, Ohio. It was built in 1828 as part of the National Road. It is a single arch stone structure. This one of four in the state is deteriorated and is now used for only pedestrian traffic. However the owners of the bridge are attempting to obtain funding for its restoration. The stone Casselman River Bridge still stands east of Grantsville, Maryland. It is a product of the early 19th century federal government improvements program along the National Road, the Casselman River Bridge was constructed in 1813-1814. Its 80-foot span, is the largest of its type in America, and it connected Cumberland to the Ohio River. In 1933 a new steel bridge joined the banks of the Casselman River. The old stone bridge, partially restored by the State of Maryland in the 1950s is now the center of Casselman River Bridge State Park. Mile markers have been used in Europe for more than 2,000 years and our European ancestors continued that tradition here in America. These markers tell travelers how far they are from their destination and were an important icon in early National Road travel. Kids ask what they are fr, and adults nostalgically seek them out for photographing. A drive through National Road towns usually reveals one of these markers, such as the one standing by the historic Red Brick Tavern in Lafayette, Ohio.
In the 1960s Interstate 70, bypassed Route 40 and much of the National Road, leaving many businesses by the wayside. People were looking for faster cars and quicker arrival times. Life runs at a much faster pace these 
 days. These old roads are a great way to relax, take your time and see some sights. Traveling the National Road, you can see the timeless little villages with small restaurants where you can get a home cooked meal and a trip back in time. The Interstate often parallels the National Road, but we leave behind the old inns and farmhouses in our rush to arrive about destination.
days. These old roads are a great way to relax, take your time and see some sights. Traveling the National Road, you can see the timeless little villages with small restaurants where you can get a home cooked meal and a trip back in time. The Interstate often parallels the National Road, but we leave behind the old inns and farmhouses in our rush to arrive about destination.
 With everyone arguing about whether or not religion has a place in politics, today seemed a good day to discuss the common misconception people have about the constitutional amendment they so often quote as the basis for their arguments. Our founding fathers came to this country, largely because in England they were forced to attend the Church of England…by law. Whether they agreed or not, or even whether the church was teaching correctly or not, was completely irrelevant. That was the church, and that was where people were expected to go. For any who wonder why so many of us are against the influx of Muslims, this is the reason…not because we disagree with their religion, but because it is the goal of Islam to force the entire world to convert to Islam. Our founding fathers, and indeed most Americans believe so strongly in the right to choose which religion, or even the lack of a religion, we want to practice, that we are willing to fight to keep that right. This amendment is simply not negotiable.
With everyone arguing about whether or not religion has a place in politics, today seemed a good day to discuss the common misconception people have about the constitutional amendment they so often quote as the basis for their arguments. Our founding fathers came to this country, largely because in England they were forced to attend the Church of England…by law. Whether they agreed or not, or even whether the church was teaching correctly or not, was completely irrelevant. That was the church, and that was where people were expected to go. For any who wonder why so many of us are against the influx of Muslims, this is the reason…not because we disagree with their religion, but because it is the goal of Islam to force the entire world to convert to Islam. Our founding fathers, and indeed most Americans believe so strongly in the right to choose which religion, or even the lack of a religion, we want to practice, that we are willing to fight to keep that right. This amendment is simply not negotiable.
Nevertheless, the misconception comes when people misstate the first amendment, claiming that it means that religion has no place in politics. That statement is fundamentally wrong, and not what Thomas Jefferson had in mind when in 1779, he wrote the “Bill for Establishing Religious Freedom.” America was settled by people who wanted religious freedom, and Jefferson believed in freedom of religion, too. He didn’t believe that churches  should be funded by taxes, thereby giving the government authority in the beliefs of the church. The bill said that “no man shall be compelled (forced) to frequent (go to) or support any religious worship, place or ministry whatsoever.” Some people were against it even then, and it did not become law at that time. It did, however, create a friendship between Jefferson and James Madison, who believed the say way.
should be funded by taxes, thereby giving the government authority in the beliefs of the church. The bill said that “no man shall be compelled (forced) to frequent (go to) or support any religious worship, place or ministry whatsoever.” Some people were against it even then, and it did not become law at that time. It did, however, create a friendship between Jefferson and James Madison, who believed the say way.
In 1784, Jefferson left for Paris, France to perform his duties as US foreign minister to France. That left James Madison with the task of making the bill into law. No easy task, because it had failed on its first attempt. Undaunted, Madison presented the bill to the Virginia Assembly, and with a few minor changes, it passed in 1786. Elated, Madison sent word to Jefferson in Paris. When the bill passed, Virginia became the first state to free religions from state rule. It is still part of Virginia’s constitution. It was used as a model for other state’s constitutions. It was also used as a model for the religious language in the Bill of Rights: “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof.” If people would read the Constitutional amendment and the Bill of Rights carefully, they would, indeed find that it says nothing at all about keeping religion out of politics, and everything about keeping the government out of religions. Thomas  Jefferson believed the Virginia Statute of Religious Freedom was one of his greatest achievements. So strongly did he believe in his accomplishments, that he wanted his tombstone to list the “things that he had given the people.” It reads: “Here was buried Thomas Jefferson Author of the Declaration of Independence of The Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom And Father of the University of Virginia.” Why did Jefferson want the Statute for Religious Freedom on his tombstone? It was because he could see what could happen when one religion was allowed to hold hostage the rest of the nation, or indeed, the world. That is why we will never give up the fight, and we will oppose all religions that would try to force themselves on us. People should stop using this convenient misconception to try to further their own agendas in this nation.
Jefferson believed the Virginia Statute of Religious Freedom was one of his greatest achievements. So strongly did he believe in his accomplishments, that he wanted his tombstone to list the “things that he had given the people.” It reads: “Here was buried Thomas Jefferson Author of the Declaration of Independence of The Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom And Father of the University of Virginia.” Why did Jefferson want the Statute for Religious Freedom on his tombstone? It was because he could see what could happen when one religion was allowed to hold hostage the rest of the nation, or indeed, the world. That is why we will never give up the fight, and we will oppose all religions that would try to force themselves on us. People should stop using this convenient misconception to try to further their own agendas in this nation.

