soviet union
 During the Cold War, the threat of a nuclear attack was the biggest concern in world relationships. During the late 1960s, the United States learned that the Soviet Union had embarked upon a massive Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) buildup designed to catch up with the United States. The situation seemed to be heating up, because the Soviet Union seemed far more likely to use such weapons, so it looked like it was time to take action. In January 1967, President Lyndon Johnson announced that the Soviet Union had begun to construct a limited Anti-Ballistic Missile (ABM) defense system around Moscow. The development of an ABM system could allow one side to launch a first strike and then prevent the other from retaliating by shooting down incoming missiles. That was completely unacceptable.
During the Cold War, the threat of a nuclear attack was the biggest concern in world relationships. During the late 1960s, the United States learned that the Soviet Union had embarked upon a massive Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) buildup designed to catch up with the United States. The situation seemed to be heating up, because the Soviet Union seemed far more likely to use such weapons, so it looked like it was time to take action. In January 1967, President Lyndon Johnson announced that the Soviet Union had begun to construct a limited Anti-Ballistic Missile (ABM) defense system around Moscow. The development of an ABM system could allow one side to launch a first strike and then prevent the other from retaliating by shooting down incoming missiles. That was completely unacceptable.
President Johnson decided to call for strategic arms limitations talks…nicknamed SALT, and in 1967, he and Soviet Premier Alexei Kosygin met at Glassboro State College in New Jersey. Johnson said they must gain “control of the ABM race,” and Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara argued that the more each reacted to the other’s escalation, the more they had chosen “an insane road to follow.” Completely abolishing nuclear weapons would be impossible, but limiting the development of both offensive and defensive strategic systems could be done, and it might help stabilize relations between the  United States and the Soviet Union. The resulting SALT-I treaty was signed in 1972. The 1972 treaty limited a wide variety of nuclear weapons, but it did not address many of the other issues, so shortly after the SALT-I treaty was ratified, talks between the United States and the Soviet Union began anew. Those talks failed to achieve any new breakthroughs. By 1979, both the United States and the Soviet Union were eager to try again. For the United States, the thought that the Soviets were leaping ahead in the arms race was the primary motivator. For the Soviet Union, the increasingly close relationship between America and communist China was a cause for growing concern.
United States and the Soviet Union. The resulting SALT-I treaty was signed in 1972. The 1972 treaty limited a wide variety of nuclear weapons, but it did not address many of the other issues, so shortly after the SALT-I treaty was ratified, talks between the United States and the Soviet Union began anew. Those talks failed to achieve any new breakthroughs. By 1979, both the United States and the Soviet Union were eager to try again. For the United States, the thought that the Soviets were leaping ahead in the arms race was the primary motivator. For the Soviet Union, the increasingly close relationship between America and communist China was a cause for growing concern.
The SALT-II agreement was the result of those many nagging issues that were left over from the successful SALT-I treaty of 1972, but it had problems of its own. The treaty basically established numerical equality between the two nations in terms of nuclear weapons delivery systems. It also limited the number of MIRV missiles (missiles with multiple, independent nuclear warheads). In truth, the treaty did little or nothing to stop, or even substantially slow down, the arms race, and it met with unrelenting criticism in the United States. The treaty was thought to be a “sellout” to the Soviets. People believed that it would leave America virtually defenseless against a whole range of new weapons not mentioned in the agreement. Even supporters of arms control were less than enthusiastic about the treaty, since it did little to actually control arms. Nevertheless, during a summit meeting in Vienna, President Jimmy Carter and Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev signed the  SALT-II agreement dealing with limitations and guidelines for nuclear weapons, on June 18, 1979. The treaty, would never formally go into effect, and it proved to be one of the most controversial agreements between the United States and the Soviet Union of the entire Cold War. Debate over SALT-II in the U.S. Congress continued for months. Then in December 1979, the Soviets invaded Afghanistan. The Soviet attack effectively killed any chance of SALT-II being passed, and Carter ensured this by withdrawing the treaty from the Senate in January 1980. SALT-II thus remained signed, but was never ratified. During the 1980s, both nations agreed to respect the agreement until such time as new arms negotiations could take place.
SALT-II agreement dealing with limitations and guidelines for nuclear weapons, on June 18, 1979. The treaty, would never formally go into effect, and it proved to be one of the most controversial agreements between the United States and the Soviet Union of the entire Cold War. Debate over SALT-II in the U.S. Congress continued for months. Then in December 1979, the Soviets invaded Afghanistan. The Soviet attack effectively killed any chance of SALT-II being passed, and Carter ensured this by withdrawing the treaty from the Senate in January 1980. SALT-II thus remained signed, but was never ratified. During the 1980s, both nations agreed to respect the agreement until such time as new arms negotiations could take place.
 After the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, the world’s first satellite, on October 4, 1957, inspiring the United States to keep up, or fall behind in the Cold War, the United States launched it’s first satellite on January 31, 1958. That satellite was called Explorer 1, and followed the first two Soviet satellites the previous year…Sputnik 1 and 2. It was the beginning the Cold War Space Race between the two nations. Explorer 1 had mercury batteries that powered the high-power transmitter for 31 days and the low-power transmitter for 105 days. Explorer 1 stopped transmission of data on May 23, 1958 when its batteries died, but remained in orbit for more than 12 years. It reentered the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean on March 31, 1970 after more than 58,000 orbits. The Explorer 1 payload consisted of the Iowa Cosmic Ray Instrument. It was without a tape data recorder, which was not modified in time to make it onto the spacecraft. The real-time data received on the ground was therefore very sparse and puzzling showing normal counting rates and no counts at all. I’m not sure what the counting was all about, so I guess I’m more confused than the scientists were. The later Explorer 3 mission, which included a tape data recorder in the payload, provided the additional data for confirmation of the earlier Explorer 1 data.
After the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, the world’s first satellite, on October 4, 1957, inspiring the United States to keep up, or fall behind in the Cold War, the United States launched it’s first satellite on January 31, 1958. That satellite was called Explorer 1, and followed the first two Soviet satellites the previous year…Sputnik 1 and 2. It was the beginning the Cold War Space Race between the two nations. Explorer 1 had mercury batteries that powered the high-power transmitter for 31 days and the low-power transmitter for 105 days. Explorer 1 stopped transmission of data on May 23, 1958 when its batteries died, but remained in orbit for more than 12 years. It reentered the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean on March 31, 1970 after more than 58,000 orbits. The Explorer 1 payload consisted of the Iowa Cosmic Ray Instrument. It was without a tape data recorder, which was not modified in time to make it onto the spacecraft. The real-time data received on the ground was therefore very sparse and puzzling showing normal counting rates and no counts at all. I’m not sure what the counting was all about, so I guess I’m more confused than the scientists were. The later Explorer 3 mission, which included a tape data recorder in the payload, provided the additional data for confirmation of the earlier Explorer 1 data.
Landsat 1, which was originally named “Earth Resources Technology Satellite 1”, was the first satellite in the United States’ Landsat program. It was the first satellite that was launched with the sole purpose of studying and monitoring the planet. Landsat 1 was a modified version of the Nimbus 4 meteorological satellite and was launched on July 23, 1972 by a Delta 900 rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its orbit was near-polar and it served as a stabilized, Earth-oriented platform for obtaining information on agricultural and forestry resources, geology and mineral resources, hydrology and water resources, geography, cartography, environmental pollution, oceanography and marine resources, and meteorological phenomena. The spacecraft was placed in a sun-synchronous orbit, with an altitude between 564 and 569 miles. The spacecraft was placed in an orbit with an inclination of 99 degrees which orbited the Earth every 103 minutes. The project was renamed to Landsat in 1975.
Landsat 1 had two sensors to achieve its primary objectives…the return beam Vidicon (RBV) and the multispectral scanner (MSS). The RBV was manufactured by the Radio Corporation of America (RCA). The RBV obtained visible light and near infrared photographic images of Earth. It was considered the primary sensor. The MSS sensor manufactured by Hughes Aircraft Company was considered an experimental and secondary sensor, until scientists reviewed the data that was beamed back to Earth. After the data was reviewed, the MSS  was considered the primary sensor. The MSS was a four-channel scanner that obtained radiometric images of Earth. From launch until 1974, Landsat 1 transmitted over 100,000 images, which covered more than 75% of the Earth’s surface. The RBV only took 1690 images. In 1976, Landsat 1 discovered a tiny uninhabited island 12 miles off the eastern coast of Canada. This island was named Landsat Island after the satellite. The MSS provided more than 300,000 images over the lifespan of the satellite. NASA oversaw 300 researchers that evaluated the data that Landsat 1 transmitted back to Earth. The Landsat 1 satellite sent data back to earth from its orbit until January of 1978 when its tape recorders malfunctioned. After that, it was taken out of service.
was considered the primary sensor. The MSS was a four-channel scanner that obtained radiometric images of Earth. From launch until 1974, Landsat 1 transmitted over 100,000 images, which covered more than 75% of the Earth’s surface. The RBV only took 1690 images. In 1976, Landsat 1 discovered a tiny uninhabited island 12 miles off the eastern coast of Canada. This island was named Landsat Island after the satellite. The MSS provided more than 300,000 images over the lifespan of the satellite. NASA oversaw 300 researchers that evaluated the data that Landsat 1 transmitted back to Earth. The Landsat 1 satellite sent data back to earth from its orbit until January of 1978 when its tape recorders malfunctioned. After that, it was taken out of service.
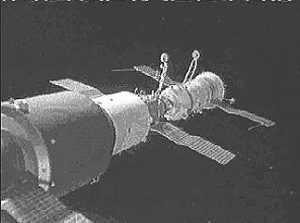 We all know about the International Space Station these days, but any previous space stations were not really very well known…at least I didn’t know much about them. The United States and Russia have been in competition for years, and over far more than the space program, but it was one area that they carried on a heated competition over. It seems like one or the other was always a little bit ahead, but there were a few places that Russia definitely beat the United States. One such area was the Space Station.
We all know about the International Space Station these days, but any previous space stations were not really very well known…at least I didn’t know much about them. The United States and Russia have been in competition for years, and over far more than the space program, but it was one area that they carried on a heated competition over. It seems like one or the other was always a little bit ahead, but there were a few places that Russia definitely beat the United States. One such area was the Space Station.
On April 19, 1971, the Soviet Union (Russia) launched Salyut 1 (English translation: Salute 1). It was the first space station of any kind. More stations followed in the Salyut program, and there are parts of that space station program that are still in use on the International Space Station today. Salyut 1 originated as a modification of the military Almaz space station program that the Soviets were developing at that time. After the landing of Apollo 11 on the Moon in July 1969, the Soviets began shifting the primary emphasis of their manned space program to orbiting space stations, with a possible lunar landing later in the 1970s if the N-1 booster became flight-worthy (which it didn’t). I suppose that since the moon landing had already happened, they decided to  focus their efforts on something they could be first at. It was the perfect motivation for the space station program…a desire to one-up the United States Skylab program, which was already in development. The basic structure of Salyut 1 was adapted from the Almaz with a few modifications and would form the basis of all Soviet space stations through Mir.
focus their efforts on something they could be first at. It was the perfect motivation for the space station program…a desire to one-up the United States Skylab program, which was already in development. The basic structure of Salyut 1 was adapted from the Almaz with a few modifications and would form the basis of all Soviet space stations through Mir.
Several military experiments were nonetheless carried on Salyut 1, including the OD-4 optical visual ranger, the Orion ultraviolet instrument for characterizing rocket exhaust plumes, and the highly classified Svinets radiometer. Construction of Salyut 1 began in early 1970 and after nearly a year, it was shipped to the Baikonur Cosmodrome. Some remaining assembly work had yet to be done and this was completed at the launch center. Launch was planned for April 12, 1971 to coincide with the 10th anniversary of Yuri Gagarin’s flight on Vostok 1, but technical problems delayed it until the 19th. The first crew launched later in the Soyuz 10 mission, but they ran into troubles while docking and were unable to enter the station; the Soyuz 10 mission was aborted and the crew returned safely to Earth. Its second crew launched in Soyuz 11 and remained on  board for 23 days. This was the first time in the history of spaceflight that a space station had been manned, and a new record in time spent in space. This success was, however, overshadowed when the crew was killed during re-entry, as a pressure-equalization valve in the Soyuz 11 re-entry capsule had opened prematurely, causing the crew to asphyxiate. After this accident, missions were suspended while the Soyuz spacecraft was redesigned. The station was intentionally destroyed by de-orbiting it after six months in orbit, because it ran out of fuel before a redesigned Soyuz spacecraft could be launched to it. Space stations have come a long way since that first station, but the Salyut 1 will always have the place of honor as the very first one.
board for 23 days. This was the first time in the history of spaceflight that a space station had been manned, and a new record in time spent in space. This success was, however, overshadowed when the crew was killed during re-entry, as a pressure-equalization valve in the Soyuz 11 re-entry capsule had opened prematurely, causing the crew to asphyxiate. After this accident, missions were suspended while the Soyuz spacecraft was redesigned. The station was intentionally destroyed by de-orbiting it after six months in orbit, because it ran out of fuel before a redesigned Soyuz spacecraft could be launched to it. Space stations have come a long way since that first station, but the Salyut 1 will always have the place of honor as the very first one.
 After the March 5, 1946, speech by former British Prime Minister Winston Spencer Churchill, condemning the Soviet Union’s policies in Europe, in which he declared, “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the continent.” It was basically the opening remark that defined the Cold War years, and everyone knew that Russia could not be trusted. I suppose that they were similar to the North Koreans today. The Cold War would continue for the next 45 years. It was a source of concern for a number of United States Presidents over the years, as well as the American people. President Ronald Reagan was one of those presidents.
After the March 5, 1946, speech by former British Prime Minister Winston Spencer Churchill, condemning the Soviet Union’s policies in Europe, in which he declared, “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the continent.” It was basically the opening remark that defined the Cold War years, and everyone knew that Russia could not be trusted. I suppose that they were similar to the North Koreans today. The Cold War would continue for the next 45 years. It was a source of concern for a number of United States Presidents over the years, as well as the American people. President Ronald Reagan was one of those presidents.
On March 8, 1983, while speaking at a convention of the National Association of Evangelicals in Florida, President Ronald Reagan publicly referred to the Soviet Union as an evil empire. It was the second time in his career that President Reagan had made this reference. He had first used the phrase in a 1982 speech at the British House of Commons. Some considered Reagan’s use of the Star Wars film-inspired terminology to be brilliant democratic rhetoric, but then in my opinion there was little about President Reagan that wasn’t brilliant. Of course, there were those within the international diplomatic community who denounced it as irresponsible bombast…typical remarks from those who would appease their enemies, thinking that it would stave off any attack. Most evil nations think of appeasement as a show of weakness…and it doesn’t do much for how the citizens of the good nations feel about their own safety either.
President Reagan was prepared to take an aggressive stance toward the Soviet Union. In his plan, known as the  Reagan Doctrine, he warned the nations of the world against what he saw as the dangerous trend of tolerating the Soviets build-up of nuclear weapons and attempts to infiltrate Third World countries in order to spread communism. President Reagan’s policy was basically peace through strength. We had to make the Soviets understand that we would never compromise our principles and standards, nor ignore the facts of history and the aggressive impulses of an evil empire. To do so would mean abandoning the struggle between right and wrong and good and evil, and he knew that must never happen. I think we, the nations of the world, have seen just how detrimental a weak security stance can be given the current mess we are digging out of.
Reagan Doctrine, he warned the nations of the world against what he saw as the dangerous trend of tolerating the Soviets build-up of nuclear weapons and attempts to infiltrate Third World countries in order to spread communism. President Reagan’s policy was basically peace through strength. We had to make the Soviets understand that we would never compromise our principles and standards, nor ignore the facts of history and the aggressive impulses of an evil empire. To do so would mean abandoning the struggle between right and wrong and good and evil, and he knew that must never happen. I think we, the nations of the world, have seen just how detrimental a weak security stance can be given the current mess we are digging out of.
Reagan proposed a policy that went beyond the Truman Doctrine of containment, urging active intervention. His plan was to increase United States military spending and, if necessary, to use force to roll back communist expansion in Third World nations. His administration provided military aid to Nicaraguan groups fighting the leftist Sandinista government and gave material support to the Afghan mujahedeen in their ongoing war against Soviets. At the same time, he reassured Americans that he would pursue an understanding with totalitarian powers and cited the United States’ effort to limit missile development as a step toward peace. Reagan’s doctrine came at the same time as a surge in international and domestic protests against the United States-Soviet arms  race. His opponents blamed the administration for causing the largest increase in American military spending since the beginning of the Cold War, a policy that swelled the nation’s budget deficit. I suppose that those who just look at the money, might think this was a bad thing, but in the late 1980s the Soviet Union collapsed, ending decades of communist rule in Russia and Eastern Europe. There were those who believed that it had collapsed under the weight of its own bloated defense spending and a protracted war in Afghanistan, but Reagan and his supporters credited his hard-line anti-communist policies for defeating Soviet communism. I am inclined to agree with President Reagan, because I have never believed that we can appease our way to peace and safety in this world.
race. His opponents blamed the administration for causing the largest increase in American military spending since the beginning of the Cold War, a policy that swelled the nation’s budget deficit. I suppose that those who just look at the money, might think this was a bad thing, but in the late 1980s the Soviet Union collapsed, ending decades of communist rule in Russia and Eastern Europe. There were those who believed that it had collapsed under the weight of its own bloated defense spending and a protracted war in Afghanistan, but Reagan and his supporters credited his hard-line anti-communist policies for defeating Soviet communism. I am inclined to agree with President Reagan, because I have never believed that we can appease our way to peace and safety in this world.
 Anytime a battle is waged between good and evil, there is always innuendo. The evil side always tries to deface the good side by calling them warmongers and racists. It doesn’t matter if the evil side is an evil nation, or an evil group within our own country. Whenever the good side tries to take a stand, they are viewed as racist, haters and warmongers. Not much has changed over the years either. If you think all of these accusations are modern day phenomenon, you are wrong. It’s been going on for many years, and has endured to this day.
Anytime a battle is waged between good and evil, there is always innuendo. The evil side always tries to deface the good side by calling them warmongers and racists. It doesn’t matter if the evil side is an evil nation, or an evil group within our own country. Whenever the good side tries to take a stand, they are viewed as racist, haters and warmongers. Not much has changed over the years either. If you think all of these accusations are modern day phenomenon, you are wrong. It’s been going on for many years, and has endured to this day.
On this day, March 5, 1946, former British Prime Minister Winston Spencer Churchill gave a speech condemning the Soviet Union’s policies in Europe and declared, “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the continent.” Many people thought that Churchill’s speech was one of the opening volleys announcing the beginning of the Cold War. After he was defeated for re-election as prime minister of Great Britain in 1945, Churchill was invited to Westminster College in Fulton, Missouri where he gave his speech. President Harry S  Truman joined him on the platform, listening intently to the speech. Churchill praised the United States as well, declaring it stood “at the pinnacle of world power.” Churchill saw the importance of a closer “special relationship” between the United States and Great Britain…the two great powers of the “English-speaking world” in organizing and policing the post World War II world.
Truman joined him on the platform, listening intently to the speech. Churchill praised the United States as well, declaring it stood “at the pinnacle of world power.” Churchill saw the importance of a closer “special relationship” between the United States and Great Britain…the two great powers of the “English-speaking world” in organizing and policing the post World War II world.
Churchill was worried about the expansionistic policies of the Soviet Union. In addition to the “iron curtain” that had descended across Eastern Europe, Churchill spoke of “communist fifth columns” that were operating throughout western and southern Europe. Churchill drew parallels with the disastrous appeasement of Hitler prior to World War II, and advised that in dealing with the Soviets there was “nothing which they admire so much as strength, and there is nothing for which they have less respect than for military weakness.”
Wisely, Truman and other United States officials received the speech in the spirit it was given. They knew that the Soviet Union was bent on expansion, and that they had to stand tough. Churchill’s “iron curtain” phrase  became a part of the official vocabulary of the Cold War era. Some of the United States officials were less than comfortable with the “special relationship” Churchill had spoken of. They knew that the English were valuable allies for the Cold War, they were also aware of Great Britain’s power, and worried about being used a pawns to help support the crumbling British empire. In the Soviet Union, Russian leader Joseph Stalin denounced the speech as “war mongering,” and referred to Churchill’s comments about the “English-speaking world” as imperialist “racism.” The rhetoric never seems to change, does it. The British, Americans, and Russians, all allies against Hitler less than a year before the speech, were drawing the battle lines of the Cold War…and it would be a long 45 year war, lasting from 1946 to 1991.
became a part of the official vocabulary of the Cold War era. Some of the United States officials were less than comfortable with the “special relationship” Churchill had spoken of. They knew that the English were valuable allies for the Cold War, they were also aware of Great Britain’s power, and worried about being used a pawns to help support the crumbling British empire. In the Soviet Union, Russian leader Joseph Stalin denounced the speech as “war mongering,” and referred to Churchill’s comments about the “English-speaking world” as imperialist “racism.” The rhetoric never seems to change, does it. The British, Americans, and Russians, all allies against Hitler less than a year before the speech, were drawing the battle lines of the Cold War…and it would be a long 45 year war, lasting from 1946 to 1991.

 On August 13, 1961, in the hours just after midnight, the East German soldiers began laying down barbed wire and bricks as a barrier between Soviet-controlled East Berlin and the democratic western section of the city. It was a day that would change life in Berlin for the next twenty eight years. In the days that followed, a wall was built to permanently close off access to the west. The citizens of East Berlin became prisoners in their own homes and city, in a prison that was built around them. The road between East and West Berlin had become a one way street. If you wanted in, you couldn’t come back out. Families were separated from each other, and those in the West had to make the choice to go be with family in East Berlin…and captivity, or not. The wall became the symbol of the Cold War. It was a literal Iron Curtain, dividing Europe.
On August 13, 1961, in the hours just after midnight, the East German soldiers began laying down barbed wire and bricks as a barrier between Soviet-controlled East Berlin and the democratic western section of the city. It was a day that would change life in Berlin for the next twenty eight years. In the days that followed, a wall was built to permanently close off access to the west. The citizens of East Berlin became prisoners in their own homes and city, in a prison that was built around them. The road between East and West Berlin had become a one way street. If you wanted in, you couldn’t come back out. Families were separated from each other, and those in the West had to make the choice to go be with family in East Berlin…and captivity, or not. The wall became the symbol of the Cold War. It was a literal Iron Curtain, dividing Europe.
When World War II ended in 1945, Germany was divided into four Allied occupation zones. Berlin, the German capital, was likewise divided into occupation sectors, even though it was located deep within the Soviet occupation zone. The future of Germany was a source of contention. Disagreements brought tensions which grew when the United States, Britain, and France moved in 1948 to unite their occupation zones into a single autonomous entity known as the Federal Republic of Germany or West Germany. In response, the Soviet Union launched a land blockage of West Berlin in an effort to force the West to abandon the city. The United States and Britain responded with a massive airlift of food and supplies to West Berlin, and in May of 1949, the Soviet Union ended the blockade in defeat.
That didn’t remove the tensions that plagued the area, however. By 1961 the Cold War tensions were running high again. The East German people became very dissatisfied with life under the communist system. West Berlin was a gateway to the West and Democracy. Between 1949 and 1961, about 2.5 million East Germans fled East Berlin to West Germany. By August of 1961, East Germans were crossing into West Germany at a rate of 2,000 people per day. Many of the refugees were skilled laborers, professionals, and intellectuals, and their loss was having a devastating effect on the East German economy. The Soviets had to figure out a way to stop the exodus, and its devastating effect on the economy. Soviet leader Nikita Khruschev made the decision to close off access from East Berlin to West Berlin.
Then came the night of August 13, 1961. The citizens of East Berlin could no longer freely pass into West Berlin. The West was taken by surprise, and threatened a trade embargo against East Germany as a retaliatory measure. The Soviets responded that such a measure would bring new blockades. The West did nothing, and the East German authorities grew more and more bold. They began closing of more and more checkpoints between East and West Berlin. On August 15, they began replacing barbed wire with concrete. The wall was supposedly designed protect their citizens from the influence of decadent capitalist culture. In realty, it protected the East German authorities from scrutiny as they did what they wanted with out retaliation.
Once it was up, the only way for East Berliners to escape the oppression of their government was to take their chances to get across in whatever way they could dream up. People attempted escape by train, tight rope, zip lines, hot air balloons, through old tunnels, impersonating soldiers, a stolen tank, and swimming. Many of these attempts ended in death for the person attempting escape. It didn’t stop them. They were so determined to live freely. About 5,000 East Germans managed to escape across the Berlin Wall to the West, but the frequency of successful escapes dwindled as the wall was increasingly fortified. Thousands of East Germans were captured during attempted crossings and 191 were killed.
On June 12, 1987 President Reagan made his great “tear down this wall” speech, but the wall remained until 
 1989, when the democratization movement began sweeping across Eastern Europe. On November 9, 1989 travel restrictions were eased. Jubilant Berliners climbed on top of the Berlin Wall, painted graffiti on it, and removed fragments as souvenirs. The next day, East German troops began dismantling the wall. In 1990, East and West Germany were formally reunited. For those in the free world, it would be almost impossible to completely understand just what Communism was like, but those who lived it, would never forget it, if they even lived through it, which many didn’t.
1989, when the democratization movement began sweeping across Eastern Europe. On November 9, 1989 travel restrictions were eased. Jubilant Berliners climbed on top of the Berlin Wall, painted graffiti on it, and removed fragments as souvenirs. The next day, East German troops began dismantling the wall. In 1990, East and West Germany were formally reunited. For those in the free world, it would be almost impossible to completely understand just what Communism was like, but those who lived it, would never forget it, if they even lived through it, which many didn’t.
 On this day, June 16, 1961, the star of the Soviet Union’s Kirov Opera Ballet Company, Rudolf Nureyev defected while on a tour with the ballet company in France. He was 23 years old. It was a huge blow to the Soviet Union, both in the loss of Kirov Opera Ballet Company’s star, and that it severely damaged Soviet propaganda that touted the political and artistic freedom in Russia. But, Nureyev was not the first to defect, nor would he be the last. Communism had taken over Russia after the Russian Civil War, in which the Red Army successfully defended the Bolshevik government against various Russian and anti-Bolshevik armies. The Bolsheviks were Communist, and Russia would never be the same after their takeover.
On this day, June 16, 1961, the star of the Soviet Union’s Kirov Opera Ballet Company, Rudolf Nureyev defected while on a tour with the ballet company in France. He was 23 years old. It was a huge blow to the Soviet Union, both in the loss of Kirov Opera Ballet Company’s star, and that it severely damaged Soviet propaganda that touted the political and artistic freedom in Russia. But, Nureyev was not the first to defect, nor would he be the last. Communism had taken over Russia after the Russian Civil War, in which the Red Army successfully defended the Bolshevik government against various Russian and anti-Bolshevik armies. The Bolsheviks were Communist, and Russia would never be the same after their takeover.
My 4th great grandfather, Johann Georg Beyer was born in Germany in 1752, but the family immigrated to Russia in the mid 1700s, probably due to a poor economy in Gemany at the time. Later, when things heated up in Russia, the family decided to make the move to America. They worried about the impact Communism would have on their family, not to mention the fact that people were being pressed into service…even as young children. I believe that they got out pretty much in the nick of time to keep their family from being torn apart, however, one son was taken and to my knowledge, never heard from again.
There are many reasons why people would do everything they can to escape a Communist regime, and I’m sure that is also why Nureyev defected. I suppose that his life was different, since he had a talent that Russia wanted more than putting him in the army, but what if he could no longer dance? And what of his family should he have one? They might not be able to dance, and so might be forced to go into the army. And Russia has been saying that they had political and artistic freedom, but as we all know, that wasn’t true in reality. After defecting, Nureyev continued his career as a dancer. Over the next 30 years he danced with England’s Royal Ballet and the American Ballet Theatre. He was in great demand as both a dancer and choreographer, and even  made a few films, including an unsuccessful stint as the silent film star Rudolf Valentino. In 1983, he took over as ballet director of the Paris Opera. In 1989, he briefly returned to the Soviet Union to perform. He died in Paris in 1993.
made a few films, including an unsuccessful stint as the silent film star Rudolf Valentino. In 1983, he took over as ballet director of the Paris Opera. In 1989, he briefly returned to the Soviet Union to perform. He died in Paris in 1993.
While, Nureyev chose to return to Russia for a performance, possibly to show them that he was a free man, my grandfather’s family chose never to return to Russia, or to German as far as I know. It could have been that they distrusted the ability to get back out, but I think they just longed for a peaceful life, in a free nation, free from the tyranny of a corrupt government. That makes me wonder what they would think of things here in America now.

