shrapnel
 I had never heard the expression, “war sand” before, but when I think about it, the presence of it makes perfect sense. It would be impossible to have any kind of a battle and not leave behind spent bullets, as well as bits of shrapnel from bombs littering the battlefield. In the case of the D-Day Battle, there were more that 5,000 tons of bombs that littered the beaches of Normandy. The beaches were literal chaos, and it was all they could do to rescue the wounded, recover the bodies, and remove the equipment, much less save bits of metal and spent bullets left behind. On D-Day, more than 5,000 tons of bombs were dropped by the Allies on the Axis powers as part of the prelude to the Normandy landings…and then there was the bullets and such that hit the beaches during the battle.
I had never heard the expression, “war sand” before, but when I think about it, the presence of it makes perfect sense. It would be impossible to have any kind of a battle and not leave behind spent bullets, as well as bits of shrapnel from bombs littering the battlefield. In the case of the D-Day Battle, there were more that 5,000 tons of bombs that littered the beaches of Normandy. The beaches were literal chaos, and it was all they could do to rescue the wounded, recover the bodies, and remove the equipment, much less save bits of metal and spent bullets left behind. On D-Day, more than 5,000 tons of bombs were dropped by the Allies on the Axis powers as part of the prelude to the Normandy landings…and then there was the bullets and such that hit the beaches during the battle.
These days, scientists estimate that 4% of the Normandy beaches are made up of shrapnel from the D-Day Landings. They have studied the sand on the beaches of Normandy, and they’ve found microscopic bits of smoothed-down shrapnel from the landings. The sand on the Normandy beaches is known as “war sand,” which is defined as “sand that is a result from wartime operations.” I had heard of beaches that are made of glass that has been rubbed smooth by the water against the ground, but I hadn’t ever thought about the water being able to smooth the sharp bits of shrapnel to make them smooth. Nevertheless, the beaches of Normandy are  covered in a fine dust created from particles deposited there during or right before the D-Day operations of World War II. The grains are hidden among the beaches of the Normandy. It makes me wonder how many other beaches have shrapnel and bullets as a secret part of their makeup.
covered in a fine dust created from particles deposited there during or right before the D-Day operations of World War II. The grains are hidden among the beaches of the Normandy. It makes me wonder how many other beaches have shrapnel and bullets as a secret part of their makeup.
Earle McBride, a geologist from the University of Texas at Austin, figures the sands shrapnel level at 4%. That doesn’t seem like much, but considering the years since D-Day, and the number of people who have walked those beaches, possibly looking for closure concerning lost loved ones, 4% is quite a bit. One might wonder how he could have come to that conclusion, but apparently the sand-sized fragments of steel are magnetic, making them easily discernible under a microscope. Of course, there are still relics from the battle. The artificial landscape of eroded machinery is still detectable using special instruments in the coastal dunes.
The shrapnel content of the beaches will eventually disappear. It is estimated that at the present rate of deterioration, the magnetic particles will probably be wiped from the sands in another 100 years. The shrapnel is subject to waves, storms, and rust, which will wipe these spherical magnetic shards from the coasts. 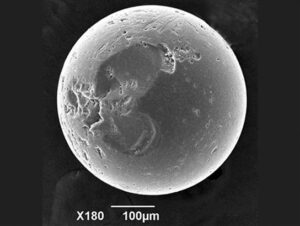 Strangely, Earle McBride didn’t set out to find these shards, but a visit to Omaha Beach in 1988 resulted in the discovery of these tiny remnants of shrapnel. I wonder how he noticed the shrapnel. Oddly, the shards were collected 20 years ago and only analyzed recently. Why did it take so long to examine them? Of course, I have answered my own question. While he may have known what he had, it is possible that he really didn’t or at least didn’t know the significance of what he had. He might have simply collected the sand as a keepsake of his visit. Nevertheless, upon examination, the samples revealed that the jagged-edged grains had a metallic sheen and a rust-colored coating. The angular grains proved to be magnetic…they proved to be shrapnel from that long ago battle.
Strangely, Earle McBride didn’t set out to find these shards, but a visit to Omaha Beach in 1988 resulted in the discovery of these tiny remnants of shrapnel. I wonder how he noticed the shrapnel. Oddly, the shards were collected 20 years ago and only analyzed recently. Why did it take so long to examine them? Of course, I have answered my own question. While he may have known what he had, it is possible that he really didn’t or at least didn’t know the significance of what he had. He might have simply collected the sand as a keepsake of his visit. Nevertheless, upon examination, the samples revealed that the jagged-edged grains had a metallic sheen and a rust-colored coating. The angular grains proved to be magnetic…they proved to be shrapnel from that long ago battle.
 When the airmen went off to war, their hope was that their plane would be able to stand up to the attacks that would be coming their way. In World War II, big war planes were very new. The men who spent the war in them, needed a plane that would take a hit and keep on flying. They would love to have a flying suit of armor, but it also had to be able to fly. A plane that was too heavy, obviously wouldn’t fly, and yet, they needed a plane that could get hit with shrapnel or bullets and still stay in the air. They knew that they couldn’t make sure that every plane that was hit would make it home, but they needed as many as possible to do just that.
When the airmen went off to war, their hope was that their plane would be able to stand up to the attacks that would be coming their way. In World War II, big war planes were very new. The men who spent the war in them, needed a plane that would take a hit and keep on flying. They would love to have a flying suit of armor, but it also had to be able to fly. A plane that was too heavy, obviously wouldn’t fly, and yet, they needed a plane that could get hit with shrapnel or bullets and still stay in the air. They knew that they couldn’t make sure that every plane that was hit would make it home, but they needed as many as possible to do just that.
There were a number of planes that were considered almost indestructible, or at least as indestructible as it is possible to be for an airplane in a war zone. Two of them…the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC), and the Boeing B-29 Superfortress, a US 4-engine propeller bomber, manufactured from 1943 to 1946 and used throughout the Korean War, as well as World War II. The name “Fortress” was coined when B-17, with its heavy firepower and multiple machine gun emplacements, made its public debut in July 1935. A reporter for The Seattle Times, Richard Williams, exclaimed, “Why, it’s a flying fortress!” The Boeing Company saw the value of that name and immediately had it trademarked. The truth of the matter is, however, that the planes had the ability to take a hit and still bring their boys home most of the time, provided the damage wasn’t too heavy.
These heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of bombs, as well as the longest range, which is takeoff to landing distance, of their era. For those reasons, the heavy bombers are  usually among the largest and most powerful military aircraft at any point in time. Nevertheless, as the 20th century wound down, the heavy bombers were largely superseded by strategic bombers. The strategic bombers were often smaller in size, which allowed for much longer ranges and by necessity, these were capable of delivering nuclear bombs. It was a sign of the times, but for all World War II buffs, like me, it was a sad end of an era. The newer planes are great, don’t get me wrong, but they just don’t have the presence, at least in my mind, that the World War II heavy bombers did. Those old planes had a grace that the newer stuff simply doesn’t have. I suppose that my love of the B-17, at least, stems from the fact that it was the plane that brought my dad home safely…so he could become my dad.
usually among the largest and most powerful military aircraft at any point in time. Nevertheless, as the 20th century wound down, the heavy bombers were largely superseded by strategic bombers. The strategic bombers were often smaller in size, which allowed for much longer ranges and by necessity, these were capable of delivering nuclear bombs. It was a sign of the times, but for all World War II buffs, like me, it was a sad end of an era. The newer planes are great, don’t get me wrong, but they just don’t have the presence, at least in my mind, that the World War II heavy bombers did. Those old planes had a grace that the newer stuff simply doesn’t have. I suppose that my love of the B-17, at least, stems from the fact that it was the plane that brought my dad home safely…so he could become my dad.
 Most of us have heard of shrapnel. Shrapnel shells have been obsolete since the end of World War I for anti-personnel use, but they were “anti-personnel artillery munitions which carried many individual bullets close to a target area and then ejected them to allow them to continue along the shell’s trajectory and strike targets individually. They relied almost entirely on the shell’s velocity for their lethality.” These days, high-explosive shells are used for that role. The functioning and principles behind Shrapnel shells are fundamentally different from high-explosive shell fragmentation. Shrapnel is named for its inventor, Lieutenant-General Henry Shrapnel (1761–1842). Shrapnel was a British artillery officer, whose experiments, initially conducted on his own time and at his own expense, culminated in the design and development of a new type of artillery shell.
Most of us have heard of shrapnel. Shrapnel shells have been obsolete since the end of World War I for anti-personnel use, but they were “anti-personnel artillery munitions which carried many individual bullets close to a target area and then ejected them to allow them to continue along the shell’s trajectory and strike targets individually. They relied almost entirely on the shell’s velocity for their lethality.” These days, high-explosive shells are used for that role. The functioning and principles behind Shrapnel shells are fundamentally different from high-explosive shell fragmentation. Shrapnel is named for its inventor, Lieutenant-General Henry Shrapnel (1761–1842). Shrapnel was a British artillery officer, whose experiments, initially conducted on his own time and at his own expense, culminated in the design and development of a new type of artillery shell.
Henry Shrapnel was born June 3, 1761 at Midway Manor in Bradford-on-Avon, Wiltshire, England, the ninth child of Zachariah Shrapnel and his wife, Lydia. Shrapnel became an artillery officer and inventor of a form of artillery case shot (shrapnel). He was commissioned in the  Royal Artillery in 1779, and served in Newfoundland, Gibraltar, and the West Indies. He was wounded in Flanders in the Duke of York’s unsuccessful campaign against the French in 1793. In 1804 he became an inspector of artillery and spent several years at Woolwich arsenal.
Royal Artillery in 1779, and served in Newfoundland, Gibraltar, and the West Indies. He was wounded in Flanders in the Duke of York’s unsuccessful campaign against the French in 1793. In 1804 he became an inspector of artillery and spent several years at Woolwich arsenal.
In 1784, while a lieutenant in the Royal Artillery, he perfected, with his own resources, an invention of what he called “spherical case” ammunition: a hollow cannonball filled with lead shot that burst in mid-air. He successfully demonstrated this in 1787 at Gibraltar. He intended the device as an anti-personnel weapon. In 1803, the British Army adopted a similar, but elongated explosive shell which immediately acquired the inventor’s name. It has lent the term “shrapnel” to fragmentation from artillery shells and fragmentation in general ever since, long after it was replaced by high explosive rounds, but this usage is not the original  meaning of the word. Until the end of World War I, the shells were still manufactured according to his original principles.
meaning of the word. Until the end of World War I, the shells were still manufactured according to his original principles.
In 1814, the British Government recognized Shrapnel’s contribution by awarding him £1200 (UK£ 85,000 in 2021) a year for life, however, bureaucracy kept him from receiving the full benefit of this award. He was promoted to the office of Colonel-Commandant, Royal Artillery, on March 6, 1827, and to the rank of lieutenant-general on January 10, 1837. Shrapnel lived at Peartree House, near Peartree Green, Southampton from about 1835 until his death on March 13, 1842 at Southampton, Hampshire.
 When people think of plastic surgery, the mind congers up images of everything from severe scar repair to vanity surgeries, but who originally came up with these procedures. Although the development of plastic surgery is popularly believed to have taken place in modern times, the origins of plastic surgery are very old. In the early part of the 1400s, the nose received the most attention from the early plastic surgeons. One of the first procedures for reconstructing the nose, a primitive precursor to the nose job, is attributed to a surgeon called Antonio Branca.
When people think of plastic surgery, the mind congers up images of everything from severe scar repair to vanity surgeries, but who originally came up with these procedures. Although the development of plastic surgery is popularly believed to have taken place in modern times, the origins of plastic surgery are very old. In the early part of the 1400s, the nose received the most attention from the early plastic surgeons. One of the first procedures for reconstructing the nose, a primitive precursor to the nose job, is attributed to a surgeon called Antonio Branca.
After that era, Plastic surgery had to wait until the late 18th century for the next significant advance in its history…the skin graft. And ironically the breakthrough came from rediscovering a procedure developed in ancient India. The severe-looking skin graft procedure was rediscovered in an ancient book called the “Sushruta Samhita,” dating back to 8th century BC. There hidden in the book’s 184 chapters was a technique using a leaf-shaped flap from the forehead to 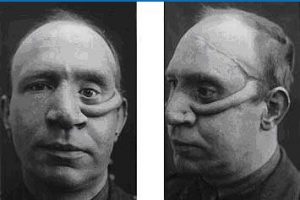 reconstruct the nose. The technique was published in the ‘Gentleman’s Magazine of Calcutta’ in October 1794 and it soon became widely used. It was known as the “Indian Method”.
reconstruct the nose. The technique was published in the ‘Gentleman’s Magazine of Calcutta’ in October 1794 and it soon became widely used. It was known as the “Indian Method”.
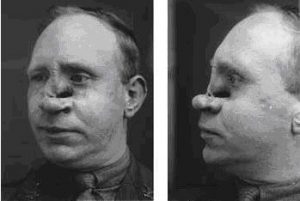
While these methods undoubtedly had a great impact on the history of plastic surgery, it would be another event that would have one of the biggest impacts on plastic surgery, and its methodology. That event was World War I. Shrapnel was the cause of many facial injuries during world War I, and unlike the straight-line wounds inflicted by bullets, the twisted metal shards produced from a shrapnel blast could easily rip a face off. Harold Gillies, a surgeon, was horrified by the injuries he saw, and he immediately took on the task of helping these victims. He saw these men as more than victims. They were heroes, and that’s how he saw them. He knew he had to do something to help these men get back to a normal life. So, he pioneered early techniques of facial reconstruction in the process.
 While these were great advances, it’s likely that the most significant improvements in the history of plastic surgery occurred in the last century. Several plastic surgery techniques were introduced during the world wars. Skin grafting techniques such as the “tubed pedicled graft,” were state of the art during World War I. Archibald McIndoe and Harold Gillies refined the techniques to treat severe facial burns. These staged procedures differed from earlier plastic surgery because they relied on the growth and development of a blood supply from the recipient bed into the grafted tissue over many weeks or months. While that all seems pretty normal these days, it was unheard of until then.
While these were great advances, it’s likely that the most significant improvements in the history of plastic surgery occurred in the last century. Several plastic surgery techniques were introduced during the world wars. Skin grafting techniques such as the “tubed pedicled graft,” were state of the art during World War I. Archibald McIndoe and Harold Gillies refined the techniques to treat severe facial burns. These staged procedures differed from earlier plastic surgery because they relied on the growth and development of a blood supply from the recipient bed into the grafted tissue over many weeks or months. While that all seems pretty normal these days, it was unheard of until then.

 When World War I broke out, many young men were called into service. It is a common part of war…one we all know about, and most parents dread. World War I was unique in one way, however. There was a soldier who went to war who was different. He was not different in the way he served exactly, but rather in some other very obvious ways. His speech was different. His mentality was somewhat different, and his looks were different. I’m not being discriminatory, but simply stating a fact. His name was Jackie, and he was different because he was a monkey, well actually, he was a Chacma baboon (Papio ursinus). Jackie was found in August 1915 near the Marr’s family farm in Villeria, Pretoria, South Africa by Albert Marr and soon became a beloved pet.
When World War I broke out, many young men were called into service. It is a common part of war…one we all know about, and most parents dread. World War I was unique in one way, however. There was a soldier who went to war who was different. He was not different in the way he served exactly, but rather in some other very obvious ways. His speech was different. His mentality was somewhat different, and his looks were different. I’m not being discriminatory, but simply stating a fact. His name was Jackie, and he was different because he was a monkey, well actually, he was a Chacma baboon (Papio ursinus). Jackie was found in August 1915 near the Marr’s family farm in Villeria, Pretoria, South Africa by Albert Marr and soon became a beloved pet.
When the war started and the young men were drafted, Albert was no exception. The thing is that Albert couldn’t stand the thought of leaving his beloved pet at home. Albert was assigned to service at Potchefstroom in the North West province of South Africa as private number 4927 for the newly formed 3rd Transvaal Regiment of the 1st South African Infantry Brigade on the 25th August 1915. He approached his superiors and requested that Jackie be allowed to go with him and amazingly was given permission. I’m sure that seems as odd to you as it did to me, but it goes further. Once enlisted Jackie was given a special uniform complete with buttons, a cap, regimental badges, a pay book and his own rations. He was a true member of the regiment, but that doesn’t mean he was accepted as a part of it…at first anyway. The other members of the regiment initially ignored Jackie, but like most people around a monkey, or in this case, baboon, it was hard to ignore him for very long. Jackie soon became the official mascot of the 3rd Transvaal Regiment. Jackie took his duties very seriously, however. He wasn’t there just to eat and fool around!
Jackie was very smart, and when he saw a superior officer passing, he would stand to attention and even provide them with the correct salute. He would light cigarettes for his comrades in arms and was, without a doubt, the best sentry around, due to his great senses of hearing and smelling which allowed him to be able to detect any enemy long before any of his other army mates could even notice their approach. He wasn’t a coddled pet protected for the battles either. Jackie spent three years in the front line amongst the trenches of France and Flanders in Europe. During the Senussi Campaign on 26 February 1916 in Egypt, Jackie’s beloved Albert got wounded on his shoulder by an enemy bullet. Jackie stayed beside him until the stretcher bearers arrived, licking the wound and doing what he could to comfort his friend.
Albert and Jackie both held the rank of private, and in April of 1918, both got injured in the Passchendaele area in Belgium during a heavy fire. With explosions surrounding them, Jackie was seen trying to get some protection by building a little fortress of stones around himself. He didn’t manage to finish his little safe area soon enough, and was hit by a chunk of shrapnel from a shell explosion nearby, which also injured Albert. Jackie’s right leg was seriously wounded and later had to be amputated. Jackie and Albert both made a full recovery and shortly before the armistice, Jackie was promoted to corporal, and awarded a medal for valor.
At the end of April, Jackie was officially discharged at the Maitland Dispersal Camp, Cape Town, South Africa, while wearing on his arm a gold wound stripe and three blue service chevrons indicating three years of frontline service. He was given a parchment discharge paper, a military pension and a Civil Employment Form for 
 discharged soldiers. After his service, Jackie returned to the Marr’s farm where he lived until May 22, 1921…a sad day for all who knew him. Albert Marr lived until the age of 84 and died in Pretoria in August 1973. Jackie was an amazing Chacma Baboon who, because of a fateful connection, ended up as the only monkey to reach the rank of Corporal of the South African Infantry and fight in Egypt, Belgium and France during World War I. Now that’s amazing!!!
discharged soldiers. After his service, Jackie returned to the Marr’s farm where he lived until May 22, 1921…a sad day for all who knew him. Albert Marr lived until the age of 84 and died in Pretoria in August 1973. Jackie was an amazing Chacma Baboon who, because of a fateful connection, ended up as the only monkey to reach the rank of Corporal of the South African Infantry and fight in Egypt, Belgium and France during World War I. Now that’s amazing!!!

