sea

 Two days ago, I wrote a story in celebration of my Uncle George Wave Hushman’s 92nd birthday. Little did I now that it would also be the day of his home-going, but it was. It is a rather rare thing, except in infant deaths, for someone to be born and die on the same day, but that is what my Uncle George did. He was born on December 20, 1926 in Rock River, Wyoming, and went home to Heaven on December 20, 2018 in Mills, Wyoming…exactly 92 years later.
Two days ago, I wrote a story in celebration of my Uncle George Wave Hushman’s 92nd birthday. Little did I now that it would also be the day of his home-going, but it was. It is a rather rare thing, except in infant deaths, for someone to be born and die on the same day, but that is what my Uncle George did. He was born on December 20, 1926 in Rock River, Wyoming, and went home to Heaven on December 20, 2018 in Mills, Wyoming…exactly 92 years later.
Uncle George led an unusual life, so I guess I shouldn’t be surprised that his home-going would be just as unusual. He lost his mother when he was just eleven years old. I’m not sure how long after her passing, before he was sent to the Wyoming State Children’s Home in Casper, Wyoming, but during those years, his guardian was listed as Ethel S. Kittle. Uncle George didn’t know much about his family for most of his life, but his dad, also named George Wave Hushman was in the Navy, stationed in the Philippines when he was killed in action on November 21, 1943…Uncle George was just 17 years old. To his knowledge, that left him very much alone in this world, except for his friend James Wesley Saint John ‘Wes” and Wes’ family, who had unofficially adopted him as a part of their family. Wes, who was three years older than Uncle George was lost at sea on September 9, 1943. While Uncle George didn’t know his father well, he did know his friend, and I find it unusual that he enlisted in the Navy too, but he did. His Draft Card listed his next of kin as WE Saint John. He mustered out on May 31, 1944, and was later listed among the wounded. I am grateful that he was one of those who made it home from the war. Uncle George, was first assigned to LCI(L) 23…Landing Craft Infantry (L)23. He later mustered out on USS Gurke (DD-783), a Gearing-class destroyer.
By 1946, Uncle George was released from the Navy, and was living in Mills, Wyoming, and falling in love with my aunt, Evelyn Byer, whom he married on September 1, 1947. He had found the love of his life, and he only wanted to be with her for the rest of his life…missing her terribly after she passed away on May 4, 2015. Aunt 
 Evelyn and Uncle George would be blessed with five children, George Hushman, Susie Young, Shelly Campbell, Shannon Limmer, and Greg Hushman. They were also blessed with many grandchildren, great grand children, and great great grandchildren. Uncle George was also blessed to be able to reunite with his half siblings over the years, although their passings brought him a feeling of losing them twice. Now that they are together again in Heaven, Uncle George will never have to be away from his beloved Evelyn, or the other loved ones who had gone before him. Rest in peace Uncle George. We love and miss you very much.
Evelyn and Uncle George would be blessed with five children, George Hushman, Susie Young, Shelly Campbell, Shannon Limmer, and Greg Hushman. They were also blessed with many grandchildren, great grand children, and great great grandchildren. Uncle George was also blessed to be able to reunite with his half siblings over the years, although their passings brought him a feeling of losing them twice. Now that they are together again in Heaven, Uncle George will never have to be away from his beloved Evelyn, or the other loved ones who had gone before him. Rest in peace Uncle George. We love and miss you very much.
 Most of the time, the oldest sibling is the first to marry, and true to that thought, my Aunt Evelyn Byer was the first of my Grandma and Grandpa Byer’s nine children to marry. The love of her life turned out to be George Hushman, a young man who was raised in the children’s home in Casper, Wyoming, after losing both of his parents at a very young age. His mother, Wyoma Woodfork Hushman passed away when George was just 11 years old, and his dad, George Wave Hushman was killed in action during World War II, when George was just 17 years old. Uncle George’s dad was unable to take care of him after his mother died, so at some point he ended up in the
Most of the time, the oldest sibling is the first to marry, and true to that thought, my Aunt Evelyn Byer was the first of my Grandma and Grandpa Byer’s nine children to marry. The love of her life turned out to be George Hushman, a young man who was raised in the children’s home in Casper, Wyoming, after losing both of his parents at a very young age. His mother, Wyoma Woodfork Hushman passed away when George was just 11 years old, and his dad, George Wave Hushman was killed in action during World War II, when George was just 17 years old. Uncle George’s dad was unable to take care of him after his mother died, so at some point he ended up in the  children’s home. I’m sure many people would think that his would always be a sad story, but it wasn’t. Uncle George had a friend James Wesley Saint John…who went by Wes. They were good friends, and Uncle George spent a lot of time at his parents house. Wes’ mom, Hettie Saint John became like an adopted mom to Uncle George. She was a very stabilizing influence in his life. As the years went on the two men grew up and went into the service. Unfortunately, only one of them would come back home. Wes was lost at sea in 1944, and they never found out what happened to him. It was a hard loss for Hettie, and for Uncle George.
children’s home. I’m sure many people would think that his would always be a sad story, but it wasn’t. Uncle George had a friend James Wesley Saint John…who went by Wes. They were good friends, and Uncle George spent a lot of time at his parents house. Wes’ mom, Hettie Saint John became like an adopted mom to Uncle George. She was a very stabilizing influence in his life. As the years went on the two men grew up and went into the service. Unfortunately, only one of them would come back home. Wes was lost at sea in 1944, and they never found out what happened to him. It was a hard loss for Hettie, and for Uncle George.

Uncle George went on to marry my Aunt Evelyn on September 1, 1947. While the sadness of losing his friend and not knowing any of his family lingered, Uncle George was a very happy family man. He and Aunt Evelyn would be blessed with five children, and they would be married for almost 68 years before Aunt Evelyn’s passing in 2015. Uncle George has been in frail health since Aunt Evelyn’s passing, but I know that their time together is still vivid in his mind, because she was the love of his life. I remember so many fun times they had with my parents. they bowled together, double dated, went to dances, and spent time at each others house. They were more that sisters and brothers-in-law, they were best friends. I really miss those good times they had, because w, their kids got to have those good times too. Today is Uncle George’s 92nd birthday. What an amazing milestone that is. Happy birthday Uncle George!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
 With new technology, always comes some risk of failure. Sometimes, the the failure doesn’t hurt anything, but other times, it can be deadly. In the world of submarines, the atomic submarine was the latest thing in the 1960s. The USS Thresher was launched on July 9, 1960, from Portsmouth Naval Yard in New Hampshire. It was built with the latest technology, and was the first submarine assembled as part of a new class that could run more quietly and dive deeper than any that had come before it. The designers and the Navy expected great things from Thresher, and initially, the submarine met their expectations.
With new technology, always comes some risk of failure. Sometimes, the the failure doesn’t hurt anything, but other times, it can be deadly. In the world of submarines, the atomic submarine was the latest thing in the 1960s. The USS Thresher was launched on July 9, 1960, from Portsmouth Naval Yard in New Hampshire. It was built with the latest technology, and was the first submarine assembled as part of a new class that could run more quietly and dive deeper than any that had come before it. The designers and the Navy expected great things from Thresher, and initially, the submarine met their expectations.
Then on April 10, 1963, at just before 8am, the Thresher was conducting drills off the coast of Cape Cod. At 9:13am, the USS Skylark, another ship participating in the drills, received a communication from the Thresher that the sub was experiencing  minor problems. Unfortunately, the minor problems turned into a very major problem…almost instantly. Other attempted communications with Thresher failed and, only five minutes later, sonar images showed the Thresher breaking apart as it fell to the bottom of the sea, 300 miles off the coast of New England. Sixteen officers, 96 sailors and 17 civilians were on board. All were killed.
minor problems. Unfortunately, the minor problems turned into a very major problem…almost instantly. Other attempted communications with Thresher failed and, only five minutes later, sonar images showed the Thresher breaking apart as it fell to the bottom of the sea, 300 miles off the coast of New England. Sixteen officers, 96 sailors and 17 civilians were on board. All were killed.
On April 12, President John F. Kennedy ordered that flags across the country be flown at half-staff to commemorate the lives lost in this disaster. A subsequent investigation revealed that a leak in a silver-brazed joint in the engine room had caused a short circuit in critical electrical systems. The problems quickly spread, making the equipment needed to bring the Thresher to the surface inoperable. The submarine went into a freefall to the bottom. There was no time to do anything to stop it or find a way of escape…if one existed.

The disaster forced improvements in the design and quality control of submarines. Twenty-five years later, in 1988, Vice Admiral Bruce Demars, the Navy’s chief submarine officer, said “The loss of Thresher initiated fundamental changes in the way we do business–changes in design, construction, inspections, safety checks, tests, and more. We have not forgotten the lessons learned. It’s a much safer submarine force today.” I don’t think there was necessarily anything that was done so wrong that it could have prevented what happened, but I could be wrong. Obviously, there is always room for improvement in any design, but unfortunately, sometimes the only way to know that an improvement is needed, is to have a disaster strike.
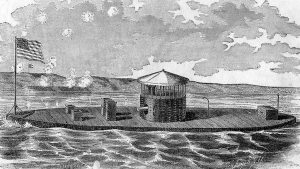 The worst fate a ship can suffer is to end up at the bottom of the sea. Nevertheless, it is a hazard that goes with the territory. Most of these lost ships simply litter the ocean floor, never seeing the light of day again, but once in a while, a ship…or part of a ship finds itself being raised up from the bottom again. Such was the case with USS Monitor, a Civil War era naval warship, that sunk to a watery grave in a storm on March 9, 1862, taking with it, 16 members of it’s crew, who were afraid to go topside in the storm.
The worst fate a ship can suffer is to end up at the bottom of the sea. Nevertheless, it is a hazard that goes with the territory. Most of these lost ships simply litter the ocean floor, never seeing the light of day again, but once in a while, a ship…or part of a ship finds itself being raised up from the bottom again. Such was the case with USS Monitor, a Civil War era naval warship, that sunk to a watery grave in a storm on March 9, 1862, taking with it, 16 members of it’s crew, who were afraid to go topside in the storm.
A short nine months before the tragedy of the USS Monitor, the ship had been part of a revolution in naval warfare. On March 9, 1862, it dueled to a standstill with the CSS Virginia in one of the most famous moments in naval history. It was the first time two ironclads ships faced each other in a naval engagement. During the battle, the two ships circled one another, jockeying for position as they fired their guns, but the cannon balls were no match for the ironclad ships, and they simply deflected off of the sides. In the early afternoon, the Virginia pulled back to Norfolk. Neither ship was seriously damaged, but the Monitor effectively ended the short reign of terror that the Confederate ironclad had brought to the Union navy. What a strange battle that must have been.
The USS Monitor was designed by Swedish engineer John Ericsson. Probably the most strange part of the design was the fact that Monitor had an unusually low profile, rising from the water only 18 inches. The ship sat so low to the water, that it could easily have resembled a submarine. The flat iron deck had a 20 foot cylindrical  turret rising from the middle of the ship. The turret housed two 11 inch Dahlgren guns. The shift had a draft of less than 11 feet so it could operate in the shallow harbors and rivers of the South. It was commissioned on February 25, 1862, and arrived at Chesapeake Bay just in time to engage the Virginia. After the famous duel with the CSS Virginia, the Monitor provided gun support on the James River for George B. McClellan’s Peninsular Campaign. By December 1862, it was clear the ship was no longer needed in Virginia, so she was sent to Beaufort, North Carolina, to join a fleet being assembled for an attack on Charleston.
turret rising from the middle of the ship. The turret housed two 11 inch Dahlgren guns. The shift had a draft of less than 11 feet so it could operate in the shallow harbors and rivers of the South. It was commissioned on February 25, 1862, and arrived at Chesapeake Bay just in time to engage the Virginia. After the famous duel with the CSS Virginia, the Monitor provided gun support on the James River for George B. McClellan’s Peninsular Campaign. By December 1862, it was clear the ship was no longer needed in Virginia, so she was sent to Beaufort, North Carolina, to join a fleet being assembled for an attack on Charleston.
The Monitor was an ideal type of ship in the sheltered waters of Chesapeake Bay, but the heavy, low-slung ship was no good in the open sea. Knowing that, the USS Rhode Island towed the ironclad around the rough waters of Cape Hatteras…a plan that would prove disastrous. As the Monitor pitched and swayed in the rough seas, the caulking around the gun turret loosened and water began to leak into the hull. More leaks developed as the journey continued. High seas tossed the craft, causing the ship’s flat armor bottom to slap the water. Each roll opened more seams, and by nightfall on December 30, it was clear that the Monitor was going to sink. That evening, the Monitor’s commander, J.P. Bankhead, signaled the Rhode Island that they needed to abandon ship. The USS Rhode Island pulled as close as safety allowed to the stricken USS Monitor, and two lifeboats were lowered to retrieve the crew. Many of the sailors were rescued, but some men were too terrified to venture onto the deck in such rough seas. The Monitor’s pumps stopped working, and the ship sank before 16 of its crew members could be rescued. It amazes me that a ship that could deflect cannon balls, was taken  down by loosened calking.
down by loosened calking.
On this day in 2002, the rusty iron gun turret of the USS Monitor rose up from the bottom of its watery grave, and into the daylight for the first time in 140 years. The ironclad warship was raised from the floor of the Atlantic, where it had rested since it went down in a storm off Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, during the Civil War. Divers had been working for six weeks to bring it to the surface. The remains of two of the 16 lost sailors were discovered by divers during the Monitor’s 2002 reemergence. Many of the ironclad’s artifacts are now on display at the Mariners’ Museum in Newport News, Virginia.
 Sometimes, it has to be accepted that just maybe, something is impossible. Still, when a challenge seems impossible, there is always someone who comes along and proves that it can be done. Alcatraz island, and the prison that is located there were known to be impossible to escape from. Over the years that Alcatraz was open, there were 14 escape attempts. Myths and mysteries surrounded Alcatraz, and it’s seemingly inescapable water fortress for years. One of the many myths about Alcatraz is that it was impossible to survive a swim from the island to the mainland because of sharks. In fact, there are no “man-eating” sharks in San Francisco Bay, only small bottom-feeding sharks. The real obstacles the prisoners faced were the cold temperatures…which averaged 50 to 55 degrees Fahrenheit, the strong currents in the water, and the distance to shore, which was at least 1¼ miles. Those things combined were known to have bested most people who attempted to make it from Alcatraz to San Francisco.
Sometimes, it has to be accepted that just maybe, something is impossible. Still, when a challenge seems impossible, there is always someone who comes along and proves that it can be done. Alcatraz island, and the prison that is located there were known to be impossible to escape from. Over the years that Alcatraz was open, there were 14 escape attempts. Myths and mysteries surrounded Alcatraz, and it’s seemingly inescapable water fortress for years. One of the many myths about Alcatraz is that it was impossible to survive a swim from the island to the mainland because of sharks. In fact, there are no “man-eating” sharks in San Francisco Bay, only small bottom-feeding sharks. The real obstacles the prisoners faced were the cold temperatures…which averaged 50 to 55 degrees Fahrenheit, the strong currents in the water, and the distance to shore, which was at least 1¼ miles. Those things combined were known to have bested most people who attempted to make it from Alcatraz to San Francisco.
The prisoners tried every possible escape plan they could think of…from simply climbing over a fence to the most elaborate attempt which was made famous by the movie “Escape From Alcatraz,” when on June 11, 1962, 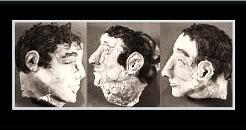 Frank Morris, and brothers John and Clarence Anglin cut through the walls, and made false walls to conceal their work, then placing “dummy heads” in their beds, so they would have all night to make their escape. Using raincoats turned into floatation devises, they made their escape. A cell house search turned up the drills, heads, wall segments, and other tools, while the water search found two life vests…one in the bay, the other outside the Golden Gate, oars, as well as letters and photographs belonging to the Anglins that had been carefully wrapped to be watertight. No sign of the men was found. Several weeks later a man’s body dressed in blue clothing similar to the prison uniform was found a short distance up the coast from San Francisco, but the body was too badly deteriorated to be identified. Speculation continues to this day as to whether or not the other two made it to safety.
Frank Morris, and brothers John and Clarence Anglin cut through the walls, and made false walls to conceal their work, then placing “dummy heads” in their beds, so they would have all night to make their escape. Using raincoats turned into floatation devises, they made their escape. A cell house search turned up the drills, heads, wall segments, and other tools, while the water search found two life vests…one in the bay, the other outside the Golden Gate, oars, as well as letters and photographs belonging to the Anglins that had been carefully wrapped to be watertight. No sign of the men was found. Several weeks later a man’s body dressed in blue clothing similar to the prison uniform was found a short distance up the coast from San Francisco, but the body was too badly deteriorated to be identified. Speculation continues to this day as to whether or not the other two made it to safety.
The official statement says they drown, and while it is likely that they did, it has been proven that it was indeed possible to swim from Alcatraz to San Francisco. Prior to the Federal institution opening in 1934, a teenage girl swam to the island to prove it was possible. Fitness guru Jack LaLanne swam to the island pulling a rowboat,  and several years ago two 10 year old children also made the swim. The official stand on that is that if a “person is well trained and conditioned, it is possible to survive the cold waters and fast currents. However, for prisoners, who had no control over their diet, no weightlifting or physical training (other than situps and pushups), and no knowledge of high and low tides, the odds for success were slim.” As to the escape attempts in which no body was ever found, we will never really know if they somehow managed to beat the odds and went on to live a quiet life under an assumed name or if they were swept away to be basically buried at sea. Either way, it is a very interesting subject to speculate on. I personally think that at least one of the three men made it.
and several years ago two 10 year old children also made the swim. The official stand on that is that if a “person is well trained and conditioned, it is possible to survive the cold waters and fast currents. However, for prisoners, who had no control over their diet, no weightlifting or physical training (other than situps and pushups), and no knowledge of high and low tides, the odds for success were slim.” As to the escape attempts in which no body was ever found, we will never really know if they somehow managed to beat the odds and went on to live a quiet life under an assumed name or if they were swept away to be basically buried at sea. Either way, it is a very interesting subject to speculate on. I personally think that at least one of the three men made it.
 Over the centuries, many ships have been lost at sea, but it isn’t every day that 33 ships are lost together. That was the case in September of 1871, however, when the ice off of the coast of Alaska trapped 33 out of 40 commercial whaling ships who were hunting for bowhead whales in the Artic Ocean. Normally, when ice traps a ship, it eventually releases it’s grip with the shifting winds, but in this case that didn’t happen, and the results were disastrous. Within a few weeks, the ships were destroyed, and the families and crew members had to evacuate and head for one of the ships that was not trapped. As the 1,219 additional people boarded the remaining 7 ships, those ships became overloaded. They had to throw things overboard to allow for the extra weight. Things like their equipment and their precious cargo were lost. The already struggling whaling industry in the United States was basically dealt a final blow. The amazing thing was that no one died, but the loss of 33 ships over those weeks was devastating enough to the whaling industry.
Over the centuries, many ships have been lost at sea, but it isn’t every day that 33 ships are lost together. That was the case in September of 1871, however, when the ice off of the coast of Alaska trapped 33 out of 40 commercial whaling ships who were hunting for bowhead whales in the Artic Ocean. Normally, when ice traps a ship, it eventually releases it’s grip with the shifting winds, but in this case that didn’t happen, and the results were disastrous. Within a few weeks, the ships were destroyed, and the families and crew members had to evacuate and head for one of the ships that was not trapped. As the 1,219 additional people boarded the remaining 7 ships, those ships became overloaded. They had to throw things overboard to allow for the extra weight. Things like their equipment and their precious cargo were lost. The already struggling whaling industry in the United States was basically dealt a final blow. The amazing thing was that no one died, but the loss of 33 ships over those weeks was devastating enough to the whaling industry.
Not much was found of the ships for many years, although debris washed up on shore periodically. Still, no artifacts specifically tied to the shipwrecks could be found beneath beneath the water. In 2015, thanks to technological advances, archaeologists have found the wreckage of what appears to be two of the lost ships. They are located at the bottom of the Chukchi Sea off the coast of Wainwright, Alaska, but an exact location is not being given. Brad Barr, an archaeologist with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), estimated the losses caused by what has been dubbed the Great Whaling Disaster of 1871 would have reached the equivalent of a little more than $33 million today. As Barr told LiveScience: “The event has been attributed as possibly a major contributory factor in the demise of whaling in the U.S.”
Barr began his hunt in late August 2015. He and a team of researchers from the Maritime Heritage Program of the NOAA’s Office of National Marine Sanctuaries surveyed the floor of the Chukchi Sea off the coast of the Inupiat village of Wainwright, in northwestern Alaska. They used state of the art sonar and underwater sensing technologies. They found the magnetic signatures of two shipwrecks they believe are part of the lost 1871 fleet, including the outlines of their flattened hulls. Underwater video revealed anchors, fasteners, pins, and ballast. They even discovered some of the special brick lined pots that the whalers used to heat the whale blubber to turn it into whale oil that was used to fire up oil lamps and make soap, margarine, and other products before the advent of petroleum. While the scientists can’t say definitively that the two wrecked ships were among the 33 lost in 1871, there are a lot of signs that point to it. More than half of all the ships known to have wrecked in the area went down in the 1871 event, and both wrecks, their beams and hull timbers were similar to those used in whaling ships from the late 19th century. The team was also aided in their efforts by changing sea ice levels, increasing opportunities to uncover lost shipwrecks even off Alaska’s northern coast. During the  expedition to the Chukchi Sea, the absence of ice was notable, and the archaeologists reportedly found artifacts from the wrecked ships “just sitting there” for them to find, Barr’s said. The team discovered remnants of a sandbar, which they believe protected the artifacts from sea ice. The NOAA is not really worried that the historic site will be disturbed, because historic preservation laws still apply. Also, there is no gold bullion, jewels or other precious cargo that might draw fortune hunters. Nevertheless, they are not publicizing the site’s exact location. Instead, they will provide all information to the Alaska Office of History and Archaeology, the agency in charge of protecting sites and relics in Alaska.
expedition to the Chukchi Sea, the absence of ice was notable, and the archaeologists reportedly found artifacts from the wrecked ships “just sitting there” for them to find, Barr’s said. The team discovered remnants of a sandbar, which they believe protected the artifacts from sea ice. The NOAA is not really worried that the historic site will be disturbed, because historic preservation laws still apply. Also, there is no gold bullion, jewels or other precious cargo that might draw fortune hunters. Nevertheless, they are not publicizing the site’s exact location. Instead, they will provide all information to the Alaska Office of History and Archaeology, the agency in charge of protecting sites and relics in Alaska.

