horseback

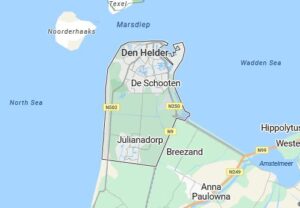 Anytime a country, engaged in a war, can capture a ship belonging to their enemy, they will find themselves strategically in a better position than before, but to capture the entire fleet…now that can mean the difference between winning and losing the war. On January 23, 1795, at Den Helder, North Holland, Netherlands, an extremely rare occurrence took place when a French Revolutionary Hussar cavalry regiment came across a Dutch fleet at anchor in the Nieuwediep, just east of the town of Den Helder. While it was not unusual to come across ships at anchor, what is extremely rare is an interaction between warships and cavalry. One being on land and one on the water, usually prevented any interaction, since the men on horses couldn’t carry guns big enough to reach the ships under normal conditions. The difference in this situation was, of course, that the Dutch fleet was frozen at anchor, not simply sitting at anchor. They had no place they could go. The men on the Dutch fleet knew that they were “sitting ducks” with no recourse, so after some of the Hussars had approached across the frozen Nieuwediep, a negotiation began. It was decided that all 14 Dutch warships would remain at anchor. It was a pretty easy negotiation, because in reality, the Dutch fleet had no other choice. They were now prisoners of war and their capture had happened without violence or even a battle. In an extremely rare even the Dutch fleet was captured by the French Revolutionary Hussars on horseback.
Anytime a country, engaged in a war, can capture a ship belonging to their enemy, they will find themselves strategically in a better position than before, but to capture the entire fleet…now that can mean the difference between winning and losing the war. On January 23, 1795, at Den Helder, North Holland, Netherlands, an extremely rare occurrence took place when a French Revolutionary Hussar cavalry regiment came across a Dutch fleet at anchor in the Nieuwediep, just east of the town of Den Helder. While it was not unusual to come across ships at anchor, what is extremely rare is an interaction between warships and cavalry. One being on land and one on the water, usually prevented any interaction, since the men on horses couldn’t carry guns big enough to reach the ships under normal conditions. The difference in this situation was, of course, that the Dutch fleet was frozen at anchor, not simply sitting at anchor. They had no place they could go. The men on the Dutch fleet knew that they were “sitting ducks” with no recourse, so after some of the Hussars had approached across the frozen Nieuwediep, a negotiation began. It was decided that all 14 Dutch warships would remain at anchor. It was a pretty easy negotiation, because in reality, the Dutch fleet had no other choice. They were now prisoners of war and their capture had happened without violence or even a battle. In an extremely rare even the Dutch fleet was captured by the French Revolutionary Hussars on horseback.
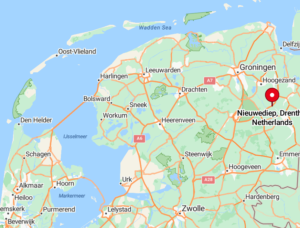
Jean-Charles Pichegru was the leader of the French units…the 8th Hussar Regiment and the Voltigeur company of the 15th Line Infantry Regiment of the French Revolutionary Army, who had been assigned to invade the Dutch Republic. The Dutch fleet was commanded by captain Hermanus Reintjes. This rare event took place during the War of the First Coalition, which was part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The little town of Den Helder is located at the tip of the North Holland peninsula, south of the island of Texel, near the shallow Zuiderzee bay (which means Southern Sea). The Zuiderzee was closed off and partly drained in the 20th century, and what is left of it now forms the freshwater IJsselmeer.
Nevertheless, in the fall of 1794, during the War of the First Coalition of the French Revolutionary Wars, the area was the site of one of the most bizarre captures in history. That day, the Dutch proclaimed the Batavian Republic, effectively ending the war with France and allying itself with France instead. Suddenly, the French were no longer enemies of the Dutch, which seems like a good move in light of the capture. Nevertheless, there were those among the Dutch Navy and the army there who remained loyal to the Stadtholder, and there were fears that Navy ships from Den Helder might sail for England to rejoin William V, Prince of Orange. For that reason, the new Batavian interim Government issued orders to all its fleets at Vlissingen, Hellevoetsluis and at Den Helder, not to fight against the French if they appeared, and to keep the ships at anchor to make sure they could be ready to defend the new Republic against the British.
This event might not have been possible, were it not for the fact that the winter of 1794–1795 was exceptionally cold, causing the Zuiderzee to freeze. Pichegru saw an opportunity and ordered General of Brigade Jan Willem de Winter to lead a squadron of the 8th Hussar Regiment to Den Helder. De Winter had been serving with the French since 1787 and would later command the Dutch fleet in the disastrous Battle of Camperdown. So, while he was successful in one operation, he might not have been the best leader in the long 
 run. Still, the operation was carried out with no casualties. The French simply received the assurance from the Dutch captain that the vessels and their crews would remain at anchor until the political situation in the Dutch Republic would have become clear. The situation was finally settled in May 1795 under the Treaty of The Hague, when the Batavian Republic officially became a French ally. Now, its ships would serve a common cause.
run. Still, the operation was carried out with no casualties. The French simply received the assurance from the Dutch captain that the vessels and their crews would remain at anchor until the political situation in the Dutch Republic would have become clear. The situation was finally settled in May 1795 under the Treaty of The Hague, when the Batavian Republic officially became a French ally. Now, its ships would serve a common cause.

 My husband, Bob Schulenberg and I love to hike the Black Hills, and with Independence Day and Bob’s birthday on July 10th, it is always a perfect time for us to go and spend a week in one of the places we love the most. We aren’t always able to hike our favorite trail, up to Harney Peak (now called Black Elk Peak), because sometimes, one or the other of us isn’t in shape for it. We always miss that hike when we are unable to go there and look forward to getting “back in the saddle” again, so to speak. It’s not that we ride the trails on horseback, but it might be one way to get up there in a
My husband, Bob Schulenberg and I love to hike the Black Hills, and with Independence Day and Bob’s birthday on July 10th, it is always a perfect time for us to go and spend a week in one of the places we love the most. We aren’t always able to hike our favorite trail, up to Harney Peak (now called Black Elk Peak), because sometimes, one or the other of us isn’t in shape for it. We always miss that hike when we are unable to go there and look forward to getting “back in the saddle” again, so to speak. It’s not that we ride the trails on horseback, but it might be one way to get up there in a 
 pinch. I think I might have to consider that option, if it is too many years before we can get back up there.
pinch. I think I might have to consider that option, if it is too many years before we can get back up there.
After being together for more than 48 years, married for just over 47 years, we are comfortable in our life. We are one of the forever marriages, and that means that we must like doing many of the same things. It stands to reason, and we find ourselves thinking and acting alike. The same activities are fun for both of us, and yes…we can finish each other’s sentences. It is almost impossible not to. That’s what long term married couples do. They just know each other, and how their mate would react to things. That is the case with my husband and me. We are soulmates, and that is perfectly ok with us.

 Bob spends much of his free time working on vehicles, for us and his friends. Thats a good thing, because he would probably go just a little crazy without his favorite pastime to keep him busy. Bob loves working on cars, and he is very good at it. He has a knack for finding out what is wrong with a vehicle and then fixing it. What would drive someone else crazy, keeps his mind sharp and on track. Mechanics is like a puzzle for him. Every piece has its proper place and finding that proper place is his passion…and the people whose vehicles he works on, reap the benefits. And they consider themselves blessed. Today is Bob’s birthday. Happy birthday Bob!! You are the love of my life, and I am so blessed to be your wife. Have a great day!! We love you!!
Bob spends much of his free time working on vehicles, for us and his friends. Thats a good thing, because he would probably go just a little crazy without his favorite pastime to keep him busy. Bob loves working on cars, and he is very good at it. He has a knack for finding out what is wrong with a vehicle and then fixing it. What would drive someone else crazy, keeps his mind sharp and on track. Mechanics is like a puzzle for him. Every piece has its proper place and finding that proper place is his passion…and the people whose vehicles he works on, reap the benefits. And they consider themselves blessed. Today is Bob’s birthday. Happy birthday Bob!! You are the love of my life, and I am so blessed to be your wife. Have a great day!! We love you!!
 The Spencer ancestry is riddled with names that have been passed down from generation to generation. So much so, in fact, that it can get confusing when researching one’s ancestry. Common names are William, Robert, Thomas, John, Allen, and Christopher. My dad’s family was no different than any other of the Spencer families. The boys in the family were William, named after his grandfather, William, who had a great grandfather named William, and many more I’m sure. My dad was Allen, who was named after his dad Allen, who was named after his grandfather Allen. And many of the children also used those same names, so there were cousins named William and Allen too. Most of the time it only created problems with the ancestry, mail, school things, and such, but when a man named Ethan Allen Spencer (relation, I’m sure, but just how I don’t know) decided that he needed a little bit of excitement in his life, he decided to go from a law-abiding farm family background to becoming a bank and train robber. Ethan Allen “Al” Spencer was born the day after Christmas in 1887 near Lenepah in Nowata County. He came from a law-abiding farm family. He married and soon was the father of a baby girl. So, why would he abandon all that to become a criminal.
The Spencer ancestry is riddled with names that have been passed down from generation to generation. So much so, in fact, that it can get confusing when researching one’s ancestry. Common names are William, Robert, Thomas, John, Allen, and Christopher. My dad’s family was no different than any other of the Spencer families. The boys in the family were William, named after his grandfather, William, who had a great grandfather named William, and many more I’m sure. My dad was Allen, who was named after his dad Allen, who was named after his grandfather Allen. And many of the children also used those same names, so there were cousins named William and Allen too. Most of the time it only created problems with the ancestry, mail, school things, and such, but when a man named Ethan Allen Spencer (relation, I’m sure, but just how I don’t know) decided that he needed a little bit of excitement in his life, he decided to go from a law-abiding farm family background to becoming a bank and train robber. Ethan Allen “Al” Spencer was born the day after Christmas in 1887 near Lenepah in Nowata County. He came from a law-abiding farm family. He married and soon was the father of a baby girl. So, why would he abandon all that to become a criminal.
“Al” Spencer became a criminal as the era of horseback riding was coming to an end, and modern motorized criminals were just getting started. That fact, made Spencer an almost forgotten outlaw. Spencer began his career in crime by getting caught stealing cattle in his early 30s. Then in 1919, he and two men burglarized a clothing store in Neodesha, Kansas. Detectives recovered most of the stolen property and arrested Spencer in La Junta, Colorado. The Kansas court convicted and sentenced him to five years in prison. Then the Oklahoma authorities gained custody of Spencer so they could try him on charges of cattle theft. Spencer pleaded guilty and was sentenced to three to 10 years in the Oklahoma penitentiary at McAlester. He began serving his sentence in March 1920. If you ask me, he should have stuck to farming, because he wasn’t very good at crime. Spencer became friends with another convict named Henry Wells and learned a great deal about crime…becoming better, I suppose…at least as long has Wells was with him. In the 1920s, it was not unusual for Oklahoma governors to grant convicts a leave of absence from prison…even some convicted of major crimes. Spencer was given leave on July 26, 1921, to attend to “some family business” supposedly. He returned to McAlester a month later and became a trustee and was trained to be an electrician. Early in 1922, he was assigned to do electrical work outside the prison in someone’s home. He completed the work, but then he packed up his tools and didn’t return to the prison.
Within a month, Spencer had hooked up with Silas Meigs, who had escaped in a similar fashion from the prison. The pair robbed the American National Bank at Pawhuska, making a “major” haul of $147. Soon the two men robbed a bank at Broken Bow, and this one netted a little more profit. They escaped with between $7,000 and $8,500. They forced a motorist to take them three miles north of town where they had left two horses. The robbers rode away. A few days later Meigs was killed in a gun battle with lawmen northwest of Bartlesville, where he had gone to visit his brother. Spencer remained hidden in the Osage Hills, a vast stretch of country with timber, rocky canyons and thickets of almost impenetrable scrub oak. Friends and relatives brought him food. Spencer later joined up with Henry Wells and two other criminals and robbed a bank at Pineville in  southwest Missouri. Spencer soon hopped a freight train bound for Oklahoma. Spencer found three other men to help him burglarize a store in Ochelata south of Bartlesville. They were surprised by the town’s night marshal who was shot and killed before the outlaws fled in a car. On June 16, Spencer and another man robbed the Elgin State Bank in Chautauqua County, Kansas. They fled with about $2,000 in cash and $20,000 in bonds.
southwest Missouri. Spencer soon hopped a freight train bound for Oklahoma. Spencer found three other men to help him burglarize a store in Ochelata south of Bartlesville. They were surprised by the town’s night marshal who was shot and killed before the outlaws fled in a car. On June 16, Spencer and another man robbed the Elgin State Bank in Chautauqua County, Kansas. They fled with about $2,000 in cash and $20,000 in bonds.
Exactly how many banks were robbed by Ethan Allen “Al” Spencer during the eighteen months following his escape is not known. Evidence suggests he probably robbed at least 20 banks in Oklahoma, Kansas, Missouri and Arkansas. The end of his crime spree came on a Saturday evening, September 15, 1923, when he was shot and killed. There is, however, debate on just how he was killed. U.S. Marshal Alva McDonald, a veteran lawman and personal friend of Teddy Roosevelt, claimed he and other lawmen shot Spencer just south of Caney, Kansas. Another account reported that Spencer was killed about five miles north of Coffeyville, Kansas. The third account came from outlaw Henry Wells’ autobiography. Wells claims that Stanley Snyder, a friend of Spencer’s, killed the outlaw with a shotgun while Spencer was eating supper. Some friend he must have been, but then I guess there is no honor among thieves. Al Spencer’s outlaw days were over, nevertheless, and a new breed of bad men soon took his place using only automobiles. Spencer was the last major Oklahoma outlaw to use horses in his crimes.

