cheyenne indians
 The Dog Soldiers were an elite group Indian warriors. Originally, they fought against other Indian tribes, but in the 1860s they increasingly became one of the biggest enemies of the United States Government in what became the bloody Plains Indian Wars. Tall Bull was a prominent leader of the Cheyenne Dog Soldier Warrior Society. He was the most distinguished of several Cheyenne warriors who bore the hereditary name over the years. Because it was an honorable name to inherit, the name was passed down many times, to many warriors over the years.
The Dog Soldiers were an elite group Indian warriors. Originally, they fought against other Indian tribes, but in the 1860s they increasingly became one of the biggest enemies of the United States Government in what became the bloody Plains Indian Wars. Tall Bull was a prominent leader of the Cheyenne Dog Soldier Warrior Society. He was the most distinguished of several Cheyenne warriors who bore the hereditary name over the years. Because it was an honorable name to inherit, the name was passed down many times, to many warriors over the years.
In October 1868, Tall Bull and his Dog Soldiers viciously attacked an American cavalry force in Colorado. The following winter in Oklahoma, they confronted General Philip Sheridan’s forces. Near the Washita River, Sheridan’s Lieutenant Colonel George Custer attacked a peaceful Cheyenne village under Chief Black Kettle. More than 100 Cheyenne Indians were killed, and Custer’s soldiers brutally butchered more than 800 of their horses. However, Custer was forced to flee when Tall Bull and other chiefs camped in nearby villages began to mass for attack. Custer’s attack had badly weakened the Cheyenne, but Tall Bull refused to surrender to the White Man, under any circumstances. He was a warrior and he would fight to the bitter end.
 In the spring of 1869, Tall Bull and his Dog Soldiers took their revenge by staging a series of very successful attacks against the soldiers, who were searching for him. Determined to destroy the chief, the US Army formed a special expeditionary force under the command of General Eugene Carr. On July 11, 1869, Carr surprised Tall Bull and his warriors in their camp at Summit Springs, Colorado. In the battle that followed, Tall Bull was killed and the Dog Soldiers were overwhelmed. Without the dynamic leadership of their chief, the surviving Dog Soldiers’ resistance was broken. Although others in the Cheyenne nation continued to fight the US Army for another decade, they did so without the aid of their greatest warrior society and its leader…Tall Bull.
In the spring of 1869, Tall Bull and his Dog Soldiers took their revenge by staging a series of very successful attacks against the soldiers, who were searching for him. Determined to destroy the chief, the US Army formed a special expeditionary force under the command of General Eugene Carr. On July 11, 1869, Carr surprised Tall Bull and his warriors in their camp at Summit Springs, Colorado. In the battle that followed, Tall Bull was killed and the Dog Soldiers were overwhelmed. Without the dynamic leadership of their chief, the surviving Dog Soldiers’ resistance was broken. Although others in the Cheyenne nation continued to fight the US Army for another decade, they did so without the aid of their greatest warrior society and its leader…Tall Bull.
 As a young boy of just 15 years, Andy Schulenberg was hunting with a friend, Howard Stewart on an October day in 1921. He leaned his rifle against a tree and it fell over, discharging and hitting Andy in the leg. That event would begin a 2 year long stay in the hospital, and Andy would lose his leg about a year into that stay, in June of 1922. While devastated over this event, Andy dug deep inside himself and decided that he would not be an invalid. Fitted with a wooden leg, that had a simple table like rubberized end to it, Andy proceeded to live the rest of his life. This would not break him, because he was not a quitter. Andy did whatever he wanted to do. Throughout his life, Andy did things his way. He became quite competitive. For a time, his family hauled beets, and Andy could out load anyone when it came to loading the truck. His arms were so strong, by way of compensation for his lack of a leg, and the fact that Andy was a big strong man. Many times while loading those trucks, he could load the truck he was working, faster than two men on the other truck…and then he went over and finished loading their truck too. Nobody could beat Andy Schulenberg!
As a young boy of just 15 years, Andy Schulenberg was hunting with a friend, Howard Stewart on an October day in 1921. He leaned his rifle against a tree and it fell over, discharging and hitting Andy in the leg. That event would begin a 2 year long stay in the hospital, and Andy would lose his leg about a year into that stay, in June of 1922. While devastated over this event, Andy dug deep inside himself and decided that he would not be an invalid. Fitted with a wooden leg, that had a simple table like rubberized end to it, Andy proceeded to live the rest of his life. This would not break him, because he was not a quitter. Andy did whatever he wanted to do. Throughout his life, Andy did things his way. He became quite competitive. For a time, his family hauled beets, and Andy could out load anyone when it came to loading the truck. His arms were so strong, by way of compensation for his lack of a leg, and the fact that Andy was a big strong man. Many times while loading those trucks, he could load the truck he was working, faster than two men on the other truck…and then he went over and finished loading their truck too. Nobody could beat Andy Schulenberg!
In 1955 Andy Schulenberg became the sheriff of Rosebud County, Montana. That was really an amazing feat for a man with a wooden peg for a leg. Andy became a sheriff who didn’t carry a gun. That is such an odd thing to think about. There might be a television show sheriff who didn’t need a gun, but the reality is that a real life sheriff carries a gun…at least any I knew of until Andy Schulenberg. You do have to recall that Andy maybe didn’t just love guns…making his decision to become a lawman a strange one, I suppose. I’m sure that most people must think that Andy lived in an area much like Mayberry on the Andy Griffith Show, but they would be wrong. Andy used different tools in his work as sheriff. He knew a lot of the Indian elders in the area, and they respected him. If Andy was looking for a specific brave, he would go to the elders and ask where he was. They would simply bring the young man to him. There are a number of young men who would be glad to tell you that had it not been for Andy Schulenberg, they would probably have ended up in prison. As I said, Andy was a different kind of sheriff. He believed in second chances, and he earned not only the respect of the elders, but of the young braves, and in fact all the young men and women in the area. He was honest and fair, and they knew they would get a fair shake from him.
There were some comical arrests, however. One in particular was the time Andy was called to Ashland, Montana. Two young Cheyenne Indians had decided to break into a liquor store. They made off with about a case of whiskey. They were down on the brush lined banks of Otter Creek when Andy caught up with them. On the reservation, Andy was known as Cottonwood, because of his wooden leg. When he found the young braves,  they were a little tipsy from the whiskey. They had crossed a log bridge to get to an island to have a little party. Andy cuffed the boys and told them to wait by the car. He went back for the evidence. On his way back, with several bottles of whiskey, Andy slipped and fell into the water. Under normal circumstances that might not have been a big deal, but wood floats, and Andy’s leg was made of wood. As he struggled to get his leg back under him without losing the evidence, the Indian braves sat on the side of the creek bank laughing hysterically. They assumed that the evidence would be lost, and they would get off scot-free, but they were wrong. Andy managed to get his leg under him, and save one bottle of whiskey. Then he took the braves…who had not even considered running, by the way, back to jail. And he did it all without a gun.
they were a little tipsy from the whiskey. They had crossed a log bridge to get to an island to have a little party. Andy cuffed the boys and told them to wait by the car. He went back for the evidence. On his way back, with several bottles of whiskey, Andy slipped and fell into the water. Under normal circumstances that might not have been a big deal, but wood floats, and Andy’s leg was made of wood. As he struggled to get his leg back under him without losing the evidence, the Indian braves sat on the side of the creek bank laughing hysterically. They assumed that the evidence would be lost, and they would get off scot-free, but they were wrong. Andy managed to get his leg under him, and save one bottle of whiskey. Then he took the braves…who had not even considered running, by the way, back to jail. And he did it all without a gun.
 Anyone who has lived in Wyoming for any length of time knows that the state is dotted with forts from the old west. These forts shaped the state by protecting the inhabitants from the Indians…or at least the did their very best to do so. One such fort that didn’t work out so well was Fort Phil Kearney. Construction on the fort began Friday July 13, 1866 by 18th Infantry Companies A, C, E and H of the 2nd Battalion, under the direction of the regimental commander and Mountain District commander Colonel Henry B Carrington. The post was named for Major General Philip Kearny, who was a popular figure in the American Civil War. The fort was located along the east side of the Bighorn Mountains in what is now northern Johnson County, approximately 15 miles north of Buffalo, Wyoming. Along with Fort Reno and Fort C F Smith, Fort Phil Kearney was established along the Bozeman Trail in the Powder River Country at the height of the Indian Wars to protect prospective miners from the Indians while they were
Anyone who has lived in Wyoming for any length of time knows that the state is dotted with forts from the old west. These forts shaped the state by protecting the inhabitants from the Indians…or at least the did their very best to do so. One such fort that didn’t work out so well was Fort Phil Kearney. Construction on the fort began Friday July 13, 1866 by 18th Infantry Companies A, C, E and H of the 2nd Battalion, under the direction of the regimental commander and Mountain District commander Colonel Henry B Carrington. The post was named for Major General Philip Kearny, who was a popular figure in the American Civil War. The fort was located along the east side of the Bighorn Mountains in what is now northern Johnson County, approximately 15 miles north of Buffalo, Wyoming. Along with Fort Reno and Fort C F Smith, Fort Phil Kearney was established along the Bozeman Trail in the Powder River Country at the height of the Indian Wars to protect prospective miners from the Indians while they were 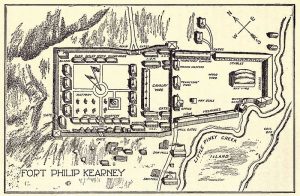 traveling north from the Oregon Trail to what is now Montana.
traveling north from the Oregon Trail to what is now Montana.
By fall, Carrington had erected an imposing symbol of American military power. A tall wooden wall surrounded a compound the size of three football fields. Inside the walls, Carrington built nearly 30 buildings, including everything from barracks and mess halls to a stage for the regimental band. Only the most massive and determined Indian attack would have been capable of taking Fort Phil Kearny. Unfortunately, Carrington’s mighty fortress had one important flaw…a failure to plan really. The nearest stands of timber were several miles away. To obtain the wood essential for heating and further construction, a detachment had to leave the protection of the fort every day. The Indians naturally began to prey on these Wood Trains. In December, a massive Indian ambush wiped out a force of 80 soldiers under the command of Captain William Fetterman.

Fort Phil Kearney was named the “hated post on the Little Piney” by the Indians, and it played an important role in Red Cloud’s War. The area around the fort was the site of the Fetterman Fight in 1866 and the Wagon Box Fight in 1867. By 1868, the Union Pacific Railroad had reached far enough west that emigrants could reach the Montana gold fields through what is now Idaho, which made the dangerous Bozeman Trail an unnecessary route. All three forts along the trail were abandoned as part of the Treaty of Fort Laramie in 1868. Shortly after the treaty, Fort Phil Kearney was burned to the ground by Cheyenne Indians. I guess they really did hate it.

