bombs
 I had never heard the expression, “war sand” before, but when I think about it, the presence of it makes perfect sense. It would be impossible to have any kind of a battle and not leave behind spent bullets, as well as bits of shrapnel from bombs littering the battlefield. In the case of the D-Day Battle, there were more that 5,000 tons of bombs that littered the beaches of Normandy. The beaches were literal chaos, and it was all they could do to rescue the wounded, recover the bodies, and remove the equipment, much less save bits of metal and spent bullets left behind. On D-Day, more than 5,000 tons of bombs were dropped by the Allies on the Axis powers as part of the prelude to the Normandy landings…and then there was the bullets and such that hit the beaches during the battle.
I had never heard the expression, “war sand” before, but when I think about it, the presence of it makes perfect sense. It would be impossible to have any kind of a battle and not leave behind spent bullets, as well as bits of shrapnel from bombs littering the battlefield. In the case of the D-Day Battle, there were more that 5,000 tons of bombs that littered the beaches of Normandy. The beaches were literal chaos, and it was all they could do to rescue the wounded, recover the bodies, and remove the equipment, much less save bits of metal and spent bullets left behind. On D-Day, more than 5,000 tons of bombs were dropped by the Allies on the Axis powers as part of the prelude to the Normandy landings…and then there was the bullets and such that hit the beaches during the battle.
These days, scientists estimate that 4% of the Normandy beaches are made up of shrapnel from the D-Day Landings. They have studied the sand on the beaches of Normandy, and they’ve found microscopic bits of smoothed-down shrapnel from the landings. The sand on the Normandy beaches is known as “war sand,” which is defined as “sand that is a result from wartime operations.” I had heard of beaches that are made of glass that has been rubbed smooth by the water against the ground, but I hadn’t ever thought about the water being able to smooth the sharp bits of shrapnel to make them smooth. Nevertheless, the beaches of Normandy are  covered in a fine dust created from particles deposited there during or right before the D-Day operations of World War II. The grains are hidden among the beaches of the Normandy. It makes me wonder how many other beaches have shrapnel and bullets as a secret part of their makeup.
covered in a fine dust created from particles deposited there during or right before the D-Day operations of World War II. The grains are hidden among the beaches of the Normandy. It makes me wonder how many other beaches have shrapnel and bullets as a secret part of their makeup.
Earle McBride, a geologist from the University of Texas at Austin, figures the sands shrapnel level at 4%. That doesn’t seem like much, but considering the years since D-Day, and the number of people who have walked those beaches, possibly looking for closure concerning lost loved ones, 4% is quite a bit. One might wonder how he could have come to that conclusion, but apparently the sand-sized fragments of steel are magnetic, making them easily discernible under a microscope. Of course, there are still relics from the battle. The artificial landscape of eroded machinery is still detectable using special instruments in the coastal dunes.
The shrapnel content of the beaches will eventually disappear. It is estimated that at the present rate of deterioration, the magnetic particles will probably be wiped from the sands in another 100 years. The shrapnel is subject to waves, storms, and rust, which will wipe these spherical magnetic shards from the coasts. 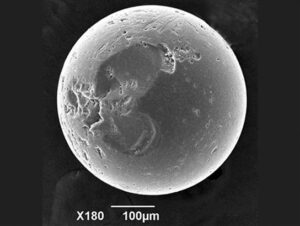 Strangely, Earle McBride didn’t set out to find these shards, but a visit to Omaha Beach in 1988 resulted in the discovery of these tiny remnants of shrapnel. I wonder how he noticed the shrapnel. Oddly, the shards were collected 20 years ago and only analyzed recently. Why did it take so long to examine them? Of course, I have answered my own question. While he may have known what he had, it is possible that he really didn’t or at least didn’t know the significance of what he had. He might have simply collected the sand as a keepsake of his visit. Nevertheless, upon examination, the samples revealed that the jagged-edged grains had a metallic sheen and a rust-colored coating. The angular grains proved to be magnetic…they proved to be shrapnel from that long ago battle.
Strangely, Earle McBride didn’t set out to find these shards, but a visit to Omaha Beach in 1988 resulted in the discovery of these tiny remnants of shrapnel. I wonder how he noticed the shrapnel. Oddly, the shards were collected 20 years ago and only analyzed recently. Why did it take so long to examine them? Of course, I have answered my own question. While he may have known what he had, it is possible that he really didn’t or at least didn’t know the significance of what he had. He might have simply collected the sand as a keepsake of his visit. Nevertheless, upon examination, the samples revealed that the jagged-edged grains had a metallic sheen and a rust-colored coating. The angular grains proved to be magnetic…they proved to be shrapnel from that long ago battle.
 When the airmen went off to war, their hope was that their plane would be able to stand up to the attacks that would be coming their way. In World War II, big war planes were very new. The men who spent the war in them, needed a plane that would take a hit and keep on flying. They would love to have a flying suit of armor, but it also had to be able to fly. A plane that was too heavy, obviously wouldn’t fly, and yet, they needed a plane that could get hit with shrapnel or bullets and still stay in the air. They knew that they couldn’t make sure that every plane that was hit would make it home, but they needed as many as possible to do just that.
When the airmen went off to war, their hope was that their plane would be able to stand up to the attacks that would be coming their way. In World War II, big war planes were very new. The men who spent the war in them, needed a plane that would take a hit and keep on flying. They would love to have a flying suit of armor, but it also had to be able to fly. A plane that was too heavy, obviously wouldn’t fly, and yet, they needed a plane that could get hit with shrapnel or bullets and still stay in the air. They knew that they couldn’t make sure that every plane that was hit would make it home, but they needed as many as possible to do just that.
There were a number of planes that were considered almost indestructible, or at least as indestructible as it is possible to be for an airplane in a war zone. Two of them…the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC), and the Boeing B-29 Superfortress, a US 4-engine propeller bomber, manufactured from 1943 to 1946 and used throughout the Korean War, as well as World War II. The name “Fortress” was coined when B-17, with its heavy firepower and multiple machine gun emplacements, made its public debut in July 1935. A reporter for The Seattle Times, Richard Williams, exclaimed, “Why, it’s a flying fortress!” The Boeing Company saw the value of that name and immediately had it trademarked. The truth of the matter is, however, that the planes had the ability to take a hit and still bring their boys home most of the time, provided the damage wasn’t too heavy.
These heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of bombs, as well as the longest range, which is takeoff to landing distance, of their era. For those reasons, the heavy bombers are  usually among the largest and most powerful military aircraft at any point in time. Nevertheless, as the 20th century wound down, the heavy bombers were largely superseded by strategic bombers. The strategic bombers were often smaller in size, which allowed for much longer ranges and by necessity, these were capable of delivering nuclear bombs. It was a sign of the times, but for all World War II buffs, like me, it was a sad end of an era. The newer planes are great, don’t get me wrong, but they just don’t have the presence, at least in my mind, that the World War II heavy bombers did. Those old planes had a grace that the newer stuff simply doesn’t have. I suppose that my love of the B-17, at least, stems from the fact that it was the plane that brought my dad home safely…so he could become my dad.
usually among the largest and most powerful military aircraft at any point in time. Nevertheless, as the 20th century wound down, the heavy bombers were largely superseded by strategic bombers. The strategic bombers were often smaller in size, which allowed for much longer ranges and by necessity, these were capable of delivering nuclear bombs. It was a sign of the times, but for all World War II buffs, like me, it was a sad end of an era. The newer planes are great, don’t get me wrong, but they just don’t have the presence, at least in my mind, that the World War II heavy bombers did. Those old planes had a grace that the newer stuff simply doesn’t have. I suppose that my love of the B-17, at least, stems from the fact that it was the plane that brought my dad home safely…so he could become my dad.
 On November 21, 1974, after two Irish Republican Army (IRA) bombs exploded in two separate Birmingham pubs, killing 21 people and injuring hundreds, an investigation was opened to find the culprits. Almost immediately, the investigation centered on six men, later known as the Birmingham Six. For years the IRA and the British government had been at odds over the status of Northern Ireland, in fact you had to be hiding under a rock if you didn’t know about it. Still, on that November day, it all came to a head. The bombs exploded, destroying everything and killing or hurting everyone in sight.
On November 21, 1974, after two Irish Republican Army (IRA) bombs exploded in two separate Birmingham pubs, killing 21 people and injuring hundreds, an investigation was opened to find the culprits. Almost immediately, the investigation centered on six men, later known as the Birmingham Six. For years the IRA and the British government had been at odds over the status of Northern Ireland, in fact you had to be hiding under a rock if you didn’t know about it. Still, on that November day, it all came to a head. The bombs exploded, destroying everything and killing or hurting everyone in sight.
The most immediate reaction of the British government was to outlaw the IRA. Virtually overnight, they were declared a terrorist group in all the United Kingdom. Thus began the worst miscarriage of justice in British history. Immediately, authorities rushed to arrest and convict the IRA members who were responsible for these horrific acts. Six Irish suspects were picked up. They were Hugh Callaghan, Patrick Joseph Hill, Gerard Hunter, Richard McIlkenny, William Power, and John Walker. During interrogation, four of the men signed confessions, which made no sense, because even the IRA, which had claimed responsibility for the Birmingham bombings, said that the six were not members of its organization.
That begs the question, that if the IRA claimed responsibility and specifically said these men were part of their organization, how could these men be tried, found guilty, and sentenced. Nevertheless, they were, and they  served 16 years before something was done about it. These men declared their innocence almost from the beginning…if you take the signed confessions at face value, and assume they were not coerced. The men stated and never wavered, that the police had beaten the confessions out of them. Many people would agree. Of course, the prosecutors denied this and also came up with forensic evidence that apparently proved that the Birmingham Six had handled explosives shortly before their arrest. It appeared that they just wanted to get a conviction so things could settle down. I’m sure they were under a lot of pressure to solve the crime.
served 16 years before something was done about it. These men declared their innocence almost from the beginning…if you take the signed confessions at face value, and assume they were not coerced. The men stated and never wavered, that the police had beaten the confessions out of them. Many people would agree. Of course, the prosecutors denied this and also came up with forensic evidence that apparently proved that the Birmingham Six had handled explosives shortly before their arrest. It appeared that they just wanted to get a conviction so things could settle down. I’m sure they were under a lot of pressure to solve the crime.
Following their convictions, the men were sentenced to lengthy prison terms. In all they spent 16 years in prison, before something changed. I’m sure they thought they would never be free again, but their convictions were declared “unsafe and unsatisfactory” and quashed by the Court of Appeal on 14 March 1991. Apparently, this all came about as a result of the widespread questioning of their guilt by the British people. They started seeing that things just didn’t add up, and yet, here were these men, locked up and seemingly innocent of any crime. In the face of all this, the British authorities released the so-called “Birmingham Six.” The six Irish men who had been sent to prison 16 years earlier for the 1974 terrorist bombings of two pubs in Birmingham, England. To further prove the error, in 1985, the forensic evidence was exposed by scientists as unreliable at best!! The nightmare for the Birmingham Six was coming to an end, and the nightmare for the British government was just beginning. In 1987 an appeals judge conceded that the same results could be obtained  from testing people who recently touched playing cards or cigarette paper, and yet these men were convicted of a bombing based on that same lack of credible evidence. Even with all that information, it took until March 1991, before the people across Britain and Ireland began calling for their release. Finally, they were freed after years in prison. They were free, but their story didn’t end there. Seven years later, a British court of appeals formally overturned their sentences, citing serious doubts about the legitimacy of the police evidence and the treatment of the suspects during their interrogation. The six men were later awarded compensation ranging from £840,000 to £1.2 million.
from testing people who recently touched playing cards or cigarette paper, and yet these men were convicted of a bombing based on that same lack of credible evidence. Even with all that information, it took until March 1991, before the people across Britain and Ireland began calling for their release. Finally, they were freed after years in prison. They were free, but their story didn’t end there. Seven years later, a British court of appeals formally overturned their sentences, citing serious doubts about the legitimacy of the police evidence and the treatment of the suspects during their interrogation. The six men were later awarded compensation ranging from £840,000 to £1.2 million.

 The world was embarking on the industrial revolution, and it was during World War I that we found out just how much of a difference that industrial revolution could make in wartime. From the introduction of airplanes to the use of tanks and railway guns on the battlefield, soldiers had to contend not only with each other but with the productions of the factory floor. Even the recent invention of the telephone made its way into battlefield units, where soldiers used it to convey orders or direct artillery fire.
The world was embarking on the industrial revolution, and it was during World War I that we found out just how much of a difference that industrial revolution could make in wartime. From the introduction of airplanes to the use of tanks and railway guns on the battlefield, soldiers had to contend not only with each other but with the productions of the factory floor. Even the recent invention of the telephone made its way into battlefield units, where soldiers used it to convey orders or direct artillery fire.
Nevertheless, there was one area where technology was not as “up to date” as it needed to be. The telephone while a great invention, was not as reliable as the commanders of Europe would have liked. I guess that anyone who has used a modern-day cellular phone can relate that. I’m sure that they could envision the need to arrange their operations, and they weren’t too sure the information was completely safe. So, they brainstormed alternatives in an attempt to improve combat communications. The leaders of World War I turned to a much older form of communication…the carrier pigeon.
Pigeons had been used for communication for many, many years. These unsung heroes of World War I, the carrier pigeons, used by both the Allied and Central Powers, helped assist their respective commanders with an accuracy and clarity unmatched by the modern technology. The National Archives holds a vast collection of messages that these feathered fighters delivered for American soldiers. Using these messages and the history of the carrier pigeon in battle, we can look at what hardship these fearless fowls endured and how their actions  saved American lives. One of the most impressive things about the war records of the carrier pigeons was how widely the birds were used. Their service as battlefield messengers is their most known use, and the pigeons found homes in every branch of service.
saved American lives. One of the most impressive things about the war records of the carrier pigeons was how widely the birds were used. Their service as battlefield messengers is their most known use, and the pigeons found homes in every branch of service.
The rudimentary airplanes of the embattled countries used pigeons to provide updates midair. Launched mid-mission, the birds would fly back to their coops and update ground commanders on what the pilots had observed. These strange update methods were born of the essential need for leaders to know what the battlefield looked like and what the enemy was doing in its own trenches. Planes flying over and pigeons bringing the information back quickly was the best way to stay ahead of the enemy. In addition, tanks carried the birds in order to relay the advance of individual units. Even after the introduction of the radio, pigeons were often the easiest way to help coordinate tank units without exposing the men to dangerous fire. Radios to be overheard. Of course, while it made the soldiers safer, the pigeons were not necessarily safer. Many of them didn’t make it back home, having been shot down and/or used for food for starving families. Still, without a radio set, the soldiers would have had to leave the relative safety of their tanks to relay or receive orders. These birds saved lives, even if it meant sacrificing their own. Their owners also saved lives by allowing their pigeons to be involved. They were a great asset to the war effort of more than one war.
The birds’ most effective use was on the front line, as they were brought forward with their armies to help update commanders and planners in the rear. When the birds were away from their home lofts, they stayed in mobile units, which were usually converted horse carriages or even double-decker buses. I’m sure it made a 
 strange sight. The mobile lofts were useful when the armies outpaced their established lines of communications or when the enemy disrupted communications lines for the telegraphs or telephones, as they often did during battle. While the other Allied powers were first to use birds, the United States did not lag far behind when we entered the fray. During the course of the war, many birds performed heroic deeds in the course of service and became heroes in their own rights.
strange sight. The mobile lofts were useful when the armies outpaced their established lines of communications or when the enemy disrupted communications lines for the telegraphs or telephones, as they often did during battle. While the other Allied powers were first to use birds, the United States did not lag far behind when we entered the fray. During the course of the war, many birds performed heroic deeds in the course of service and became heroes in their own rights.

 After World War II, many of the veterans were hesitant to talk about their experiences. My dad, Allen Spencer was one of those men. We were never exactly sure why he didn’t talk about it, but thought that he didn’t want to brag. I don’t really think that was it at all.
After World War II, many of the veterans were hesitant to talk about their experiences. My dad, Allen Spencer was one of those men. We were never exactly sure why he didn’t talk about it, but thought that he didn’t want to brag. I don’t really think that was it at all.
While listening to an audiobook called Citizen Soldiers, which covers the D-Day battle and the Battle of the Bulge, it hit me…even before the author said it. The reason soldiers didn’t talk much about war was a deliberate effort to forget. Unfortunately for most of her them, forgetting was impossible. Their minds were filled with haunted memories. The book mostly covers the thoughts of the infantry, but touches on the air war too.
After listening to the author’s account of the battle, I don’t think I could ever forget either, and I wasn’t there. Memories of the 19 year old farm boy away from home for the first time, and not really trained for combat. When the shooting started, he stood up to fire. Other soldiers told him to get down, by it was too late. His first battle had become his last, as an enemy bullet pierced his forehead. The soldiers who witnessed it, felt sick to 
 their stomachs. It was a time when a seasoned veteran was just 22 years old…and he had been made an office when his commanding officer was killed. There weren’t very many of the older men left…and by older I mean 30.
their stomachs. It was a time when a seasoned veteran was just 22 years old…and he had been made an office when his commanding officer was killed. There weren’t very many of the older men left…and by older I mean 30.
There were memories of a young prisoner of war, packed into a train to the POW camps was singing in his beautiful tenor voice, all the Christmas music he could think of to help raise moral. It was working, but suddenly the trains were under attack. The prisoners couldn’t get out, and the guards had run away. Finally a skinny boy was able to get out through a tiny window. He opened the door to his car and the men moved to free the other prisoners. There was really nowhere to go, but they escaped the attack. Then, the guards came back and loaded them back on the train. When someone asked the tenor to sing some more, they were told that he hadn’t made it back. His sweet voice was forever silenced. The men on the train were silent too…sick at heart.
The fighters in the plane’s overhead knew that it was kill or be killed, but whenever a plane went down, enemy 
 or one of theirs, they counted the parachutes, hoping the men got out alive. For them non the planes dropping bombs, they knew that someone below went to work that day, having no idea tat they would not be returning home again. They had been simple factory workers, just doing what they were told. And what of the missed targets that landed bombs on schools and other civilian locations. The men in the planes above had to live with that. They had done their duty, but it certainly didn’t feel good.
or one of theirs, they counted the parachutes, hoping the men got out alive. For them non the planes dropping bombs, they knew that someone below went to work that day, having no idea tat they would not be returning home again. They had been simple factory workers, just doing what they were told. And what of the missed targets that landed bombs on schools and other civilian locations. The men in the planes above had to live with that. They had done their duty, but it certainly didn’t feel good.
 I have long been interested in war, and especially World War II. Every aspect of it interests me, and I find myself wondering about the enemy. I’m sure that might seem odd to many people, but as we have found in the United States, just because the government goes to war, does not mean that every citizen, or even every soldier agrees with the reasons the country has gone to war. I have been listening to a couple of audiobooks that have taken in D-Day, and I came across something interesting.
I have long been interested in war, and especially World War II. Every aspect of it interests me, and I find myself wondering about the enemy. I’m sure that might seem odd to many people, but as we have found in the United States, just because the government goes to war, does not mean that every citizen, or even every soldier agrees with the reasons the country has gone to war. I have been listening to a couple of audiobooks that have taken in D-Day, and I came across something interesting.
Without going into all of that amazing strategy of warfare, I want to focus on one of the bombing maneuvers that took place. One of the soldiers on the ground was trying to take cover from incoming German bombs. After the bombing stopped, he looked out and was shocked to see eight bombs embedded in the ground near his foxhole. They had not gone off. He knew that it is possible for bombs to be duds, but he hadn’t heard of any American bombs that had turned out to be duds…especially eight of them at the same time, in the same place.  He wasn’t bragging on the American bombs, their craftmanship, or their ingenuity, but rather, wondering how so many German bombs could have been duds…all at the same time.
He wasn’t bragging on the American bombs, their craftmanship, or their ingenuity, but rather, wondering how so many German bombs could have been duds…all at the same time.
Then the soldier made an observation that I had not considered, but that fell right into my view that not everyone in Germany agreed with Hitler. The American bomb builders were doing their job willingly. They were working to make the bombs efficient, because Germany needed to be defeated. In contrast, the German bomb builders were actually Polish slaves. Hitler had invaded their nation and was forcing them to play a part in a war that they disagreed with. The soldier considered these things and came to the conclusion that somehow the Polish slaves had been able to build a bomb that they knew would not explode, but would still pass the inspections of the Germans. The soldier believed that eight unexploded bombs could not be coincidental. It had to be sabotage.

In my research, I have seen situations where the citizens have helped the enemy, at great risk to their own safety. I have seen situations where the citizens have given aid to the enemy. And this situation was a blatant sabotage of the weapons of warfare. Within their nations, these acts were acts of treason, but they were actually fighting the evil that had tried to take over their nation. Within their confines, they were standing up for their values…for good, and for what was right. They were the enemy, in location only, because in their hearts, the were fighting for what was right, and I have to respect them for that.
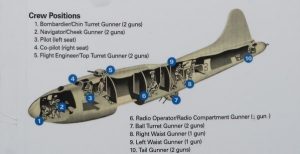 B-17 crews were a tight group. Mostly these crews flew with the same crew on missions, but sometimes, someone was sick, went home, or was killed, and crews changed. For that reason, it was vital that everyone know their responsibilities. We shouldn’t write about the B-17 as a bomber without writing about the crew. In reality, the crew and their Fortress worked much like one unit. I think the crew came to love the fortress that kept them safe.
B-17 crews were a tight group. Mostly these crews flew with the same crew on missions, but sometimes, someone was sick, went home, or was killed, and crews changed. For that reason, it was vital that everyone know their responsibilities. We shouldn’t write about the B-17 as a bomber without writing about the crew. In reality, the crew and their Fortress worked much like one unit. I think the crew came to love the fortress that kept them safe.
In the cockpit, you would find the standard, pilot and co-pilot. The pilot was the commander of the crew. He was in command of the B-17, but he was also responsible for all aspects of crew training, discipline, safety and efficiency at all times, but he was more than the commander, he was also one of the crew, he wasn’t a gunner, but it was his job to bring these men home. The co-pilot was the executive officer. He must be as familiar as the pilot with all aspects of flying the B-17, ready to take over both as pilot and commander, if necessary. The B-17 required a flight crew of two to fly the plane, much like modern day jets. The co-pilot operated the instruments on the right and instruments on the left were run by the pilot. Nevertheless, in an emergency, one could fly the plane.
The navigator had the job of making sure that the plane made it to the target, and back home again. He used one or more ways of navigating: dead reckoning; using charts and visual references; pilotage, using charts along with time, distance, and speed calculations; use of radio navigation aides; and using the sun observations or at night using stars and planets. As the B-17 gets close to the target, the bombardier takes over command of the plane (including flying) as they approached the bomb target. Then, when they arrived at the target he released the bombs. Accurate bombing was crucial and that was the bombardier’s responsibility. If he wasn’t accurate, they could hit a school, a neighborhood, or other civilian area. Later on in WW II, the navigator and bombardier positions were combined into one position done by one man.
The radio operator’s job was communications, working the radios, and keeping the radios in good working order. There was a lot of radio equipment in the B-17 that allowed for both communications and navigation. He maintained a log and was often the photographer of the crew. A good radio operator knew his equipment inside out. But the radio operator was also a trained gunner. The flight engineer was one of the most important people on the plane. He knew all the equipment on the B-17 better than the pilot or any other crew member from the engines to the radio equipment to the armament to the engines to the electrical system and everything else. Many flight engineers served as maintenance crew chiefs before moving to the position of a B-17 flight engineer. The flight engineer was the final person to advise the pilot of the airworthiness of the plane before each mission. A wise pilot listened. The flight engineer doubles as top turret gunner.
 A typical crew had four gunners, sometimes less. In a configuration of four gunners there were two waist gunners (right and left), a tail gunner, and a ball turret gunner. The two waist gunners station was in the middle of the plane. As the name implies, the tail gunner’s position was in the tail and the ball turret gunner (a small man) position was in a turret underneath the B-17. Each gunner was responsible for their own armament and ensuring that their guns were in working order. Their whole job was to keep the enemy planes and enemy fire off of the B-17. So close was the relationship that these 10 men shared, that many would go on to remain friends for life, and even name their children after their respected crew mates.
A typical crew had four gunners, sometimes less. In a configuration of four gunners there were two waist gunners (right and left), a tail gunner, and a ball turret gunner. The two waist gunners station was in the middle of the plane. As the name implies, the tail gunner’s position was in the tail and the ball turret gunner (a small man) position was in a turret underneath the B-17. Each gunner was responsible for their own armament and ensuring that their guns were in working order. Their whole job was to keep the enemy planes and enemy fire off of the B-17. So close was the relationship that these 10 men shared, that many would go on to remain friends for life, and even name their children after their respected crew mates.

 World War I found the British Army with a big problem. The German 4th Army was deeply entrenched at Messines Ridge in northern France, and the British had to remove them…somehow. The British came up with a plan, and for the 18 months prior to June 7, 1917, soldiers had been secretly working to place nearly 1 million pounds of explosives in tunnels under the German positions. The tunnels extended to some 2,000 feet in length, and some were as much as 100 feet below the surface of the ridge, where the German stronghold positions were located. The plan was put into action by the British 2nd Army under the supervision of General Sir Herbert Plumer. The joint explosion of the mines at Messines ranks among the largest non-nuclear explosions of all time. The evening before the attack, General Sir Charles Harington, Chief of Staff of the Second Army, remarked to the press, “Gentlemen, I don’t know whether we are going to make history tomorrow, but at any rate we shall change geography”.
World War I found the British Army with a big problem. The German 4th Army was deeply entrenched at Messines Ridge in northern France, and the British had to remove them…somehow. The British came up with a plan, and for the 18 months prior to June 7, 1917, soldiers had been secretly working to place nearly 1 million pounds of explosives in tunnels under the German positions. The tunnels extended to some 2,000 feet in length, and some were as much as 100 feet below the surface of the ridge, where the German stronghold positions were located. The plan was put into action by the British 2nd Army under the supervision of General Sir Herbert Plumer. The joint explosion of the mines at Messines ranks among the largest non-nuclear explosions of all time. The evening before the attack, General Sir Charles Harington, Chief of Staff of the Second Army, remarked to the press, “Gentlemen, I don’t know whether we are going to make history tomorrow, but at any rate we shall change geography”.
On June 7, 1917, they were ready to carry out their secret attack. The explosions created 19 large craters. It would be a crushing victory over the Germans who had no idea of the impending disaster they were about to face. This attack would mark the successful beginning of an Allied offensive designed to break the grinding stalemate on the Western Front in World War I. The time of the attack was set for 3:10am. Precisely on schedule, a series of simultaneous explosions rocked the area. The blast from the detonation of all those landmines was heard as far away as London. A German observer described the explosions, “nineteen gigantic roses with carmine petals, or enormous mushrooms, rose up slowly and majestically out of the ground and 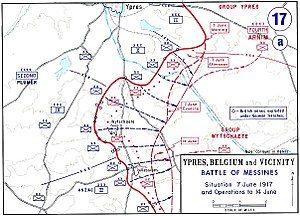
 then split into pieces with a mighty roar, sending up multi-colored columns of flame mixed with a mass of earth and splinters high in the sky.” German losses that day included more than 10,000 men who died instantly, along with some 7,000 prisoners…men too stunned and disoriented by the explosions to resist the infantry assault.
then split into pieces with a mighty roar, sending up multi-colored columns of flame mixed with a mass of earth and splinters high in the sky.” German losses that day included more than 10,000 men who died instantly, along with some 7,000 prisoners…men too stunned and disoriented by the explosions to resist the infantry assault.
Although Messines Ridge battle was, itself was a relatively limited victory, it had a considerable effect on the German morale. The Germans were forced to retreat to the east, a sacrifice that marked the beginning of their gradual, but continuous loss of territory on the Western Front. It also secured the right flank of the British thrust towards the highly contested Ypres region, which was the eventual objective of the planned offensive. Over the next month and a half, British forces continued to push the Germans back toward the high ridge at Passchendaele, which on July 31 saw the launch of the British offensive known as the Battle of Passchendaele. The Battle of Messines marked the high point of mine warfare. On August 10, 1917, the Royal Engineers fired the last British deep mine of the war, at Givenchy-en-Gohelle near Arras.
The explosions left a mine crater 40 feet deep. The attack had done its job. Still, after the war was over, the crater remained, and some wanted to change the “feel” of the place. Nowadays, this mine crater is a serene, contemplative place. I’m sure that many who visit there feel the significance of the location, but also know just  how necessary it was to ensure the freedom of France from the tyranny of the German forces. Named The Pool of Peace, it is a 40 foot deep lake near Messines, Belgium. It fills one of the craters made in 1917 when the British detonated a mine containing 45 tons of explosives. The pool stretches 423 feet across, and remains a place of solace that receives many visitors every year. It seems to me that, while most of those killed in the mine fields on June 7, 1917, were Germans, and therefore, the enemy, they were also people, many of whom didn’t want to be there any more than the Allies did. They were there under orders, and that was all there was to it. For that reason, I believe that place should be, finally, a place of peace.
how necessary it was to ensure the freedom of France from the tyranny of the German forces. Named The Pool of Peace, it is a 40 foot deep lake near Messines, Belgium. It fills one of the craters made in 1917 when the British detonated a mine containing 45 tons of explosives. The pool stretches 423 feet across, and remains a place of solace that receives many visitors every year. It seems to me that, while most of those killed in the mine fields on June 7, 1917, were Germans, and therefore, the enemy, they were also people, many of whom didn’t want to be there any more than the Allies did. They were there under orders, and that was all there was to it. For that reason, I believe that place should be, finally, a place of peace.
 When we think of the attack on Pearl Harbor, we mostly think of the events that took place at Pearl Harbor, but that attack was felt far and wide. I’m sure there are many stories, But this one struck me as particularly poignant. The Japanese bombing of the US naval base in Pearl Harbor 75 years ago sent a seismic shock around the world. Nicholas Best charts how stunned onlookers across the planet…from Dirk Bogarde to Adolf Hitler to Mao Zedong…reacted to the news. Their reactions might have been interesting, but I was moved by the thoughts and reactions of Joan Fawcett, who was simply a passenger on the Dutch ship Jägersfontein. Joan was just 21 years old that December 7th, and she was traveling to India from San Francisco. After several days at sea, she was looking forward to arriving in Honolulu soon after breakfast. Joan didn’t want to miss a moment as the ship approached the Hawaiian island of Oahu from the south.
When we think of the attack on Pearl Harbor, we mostly think of the events that took place at Pearl Harbor, but that attack was felt far and wide. I’m sure there are many stories, But this one struck me as particularly poignant. The Japanese bombing of the US naval base in Pearl Harbor 75 years ago sent a seismic shock around the world. Nicholas Best charts how stunned onlookers across the planet…from Dirk Bogarde to Adolf Hitler to Mao Zedong…reacted to the news. Their reactions might have been interesting, but I was moved by the thoughts and reactions of Joan Fawcett, who was simply a passenger on the Dutch ship Jägersfontein. Joan was just 21 years old that December 7th, and she was traveling to India from San Francisco. After several days at sea, she was looking forward to arriving in Honolulu soon after breakfast. Joan didn’t want to miss a moment as the ship approached the Hawaiian island of Oahu from the south.
Many other passengers were up early too. They were all enjoying the view of Diamond Head as they prepared to enter harbor. To add to the fun, the US navy was carrying out some sort of naval exercise ahead of them. As Joan later recalled: “I noticed a few puffs of grey smoke in the sky, just over the harbor, and as they seemed  strange clouds I asked the boys what explanation they could give and we decided that they were the puffs from anti-aircraft fire. By this time there were many grey spots and soon we could hear the report of the guns. We thought it was just a practice maneuver and a welcome salute for us. By nine o’clock we had had breakfast and were all up on deck watching the planes fly over. We did see things drop into the water, and one only 50 yards away, but thought nothing more of it. Later we heard eight bombs were aimed at our ship. We made a beautiful target for we were entering the harbor, and being in the mined area could not swerve left or right in the cleared channel. We were thoroughly enjoying the display.” The ship’s agent hurried aboard as soon as they docked. He told the passengers it was no exercise. The US Navy’s Pacific fleet up the coast at Pearl Harbor was being attacked by the Japanese. Within hours, news of the outrage was racing around the world, leaving people shocked, dismayed…and, in some cases, delighted…in its wake.
strange clouds I asked the boys what explanation they could give and we decided that they were the puffs from anti-aircraft fire. By this time there were many grey spots and soon we could hear the report of the guns. We thought it was just a practice maneuver and a welcome salute for us. By nine o’clock we had had breakfast and were all up on deck watching the planes fly over. We did see things drop into the water, and one only 50 yards away, but thought nothing more of it. Later we heard eight bombs were aimed at our ship. We made a beautiful target for we were entering the harbor, and being in the mined area could not swerve left or right in the cleared channel. We were thoroughly enjoying the display.” The ship’s agent hurried aboard as soon as they docked. He told the passengers it was no exercise. The US Navy’s Pacific fleet up the coast at Pearl Harbor was being attacked by the Japanese. Within hours, news of the outrage was racing around the world, leaving people shocked, dismayed…and, in some cases, delighted…in its wake.
Thinking about Joan Fawcett, I have wondered how she must have felt when she found out that they were  sailing right into a battle. She may not have known it at all until the agent rushed onboard to try to pull people to safety. Imagining the awe of the beautiful harbor, and then having the images dissolving into horror, fear, and death. Now she finds herself running for her life alongside all the other passengers, praying that they can get to safety before one of those bombs hits them. There is no place that is safe to go. It was chaos…everywhere. She and the rest of the passengers are caught in the middle of their worst nightmare, and they can never get those pictures out of their heads. Most of the people alive then, and anyone who has ever studied the attack, could never get that picture out of their head.
sailing right into a battle. She may not have known it at all until the agent rushed onboard to try to pull people to safety. Imagining the awe of the beautiful harbor, and then having the images dissolving into horror, fear, and death. Now she finds herself running for her life alongside all the other passengers, praying that they can get to safety before one of those bombs hits them. There is no place that is safe to go. It was chaos…everywhere. She and the rest of the passengers are caught in the middle of their worst nightmare, and they can never get those pictures out of their heads. Most of the people alive then, and anyone who has ever studied the attack, could never get that picture out of their head.

 Over the years, people have trained dogs to perform many tasks that were too dangerous for their human counterparts…knowing that the very act of doing their duty would likely cost the dog its life. I think many of us would be sickened by the things these loyal animals went through, but I suppose that in the eyes of their trainers, they were heroes. During World War II, Joseph Stalin approved the use of “canine killers” to fight against German tanks. I think that in most ground wars, the tank is probably the most dreaded weapon there is. In many ways, it is like fighting a robot…it’s almost impossible to kill. The tanks could go right into the middle of the battle, and in fact, right over the people in front of them. They could also shoot from a distance. They were a major weapon against the ground troops. Stalin wanted a weapon to use against them, and decided that the dogs were just the right weapon.
Over the years, people have trained dogs to perform many tasks that were too dangerous for their human counterparts…knowing that the very act of doing their duty would likely cost the dog its life. I think many of us would be sickened by the things these loyal animals went through, but I suppose that in the eyes of their trainers, they were heroes. During World War II, Joseph Stalin approved the use of “canine killers” to fight against German tanks. I think that in most ground wars, the tank is probably the most dreaded weapon there is. In many ways, it is like fighting a robot…it’s almost impossible to kill. The tanks could go right into the middle of the battle, and in fact, right over the people in front of them. They could also shoot from a distance. They were a major weapon against the ground troops. Stalin wanted a weapon to use against them, and decided that the dogs were just the right weapon.
The dogs, usually Alsatians, called “Hundminen” or “dog mines” were trained by the Russians to run under German tanks, at which point the bomb strapped to their backs would explode, destroying the tank…and the dog too, of course. The dogs were going to be their secret weapon, but there was just one problem, at least with the first batch of Kamikaze Dog trainees. The dogs had been trained with Soviet tanks, not German ones. Soviet and German tanks used different types of fuel, and some of the dogs sniffed out the fuel they were used to and trotted off to blow up the tanks used by the very military that trained them. I’m sure that must have been quite a shock to their trainers. The dogs were initially trained to transport explosives to tanks, armored vehicles and other various targets, and then retreat before the bomb exploded, but when that didn’t work well, the routine was replaced by impact detonation, which resulted in the dog’s death. The training began in 1930, and whether they were useful or not the dogs were used in battle. Kamikaze Dogs started to be used less and less from 1942 onwards, though there were Kamikaze Dogs that continued to be trained until 1996.
I find myself feeling horrified by the picture this practice paints. Dogs are usually very loyal, and all they want to do is please their master. They trust their master, or in this case, their trainer, only to be rewarded with 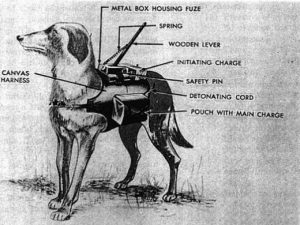
 death. I’m sure that the Russians eventually got the dogs to the point where they recognized the right targets, or the practice wouldn’t have continued until about 1990. The Soviets have said that about 300 tanks had been destroyed by Kamikaze Dogs, but that number has been questioned by many. Most people think the number was probably made up by the Soviet government in an effort to justify the program, and particularly to justify killing so many dogs with so few results. What a horrible practice.
death. I’m sure that the Russians eventually got the dogs to the point where they recognized the right targets, or the practice wouldn’t have continued until about 1990. The Soviets have said that about 300 tanks had been destroyed by Kamikaze Dogs, but that number has been questioned by many. Most people think the number was probably made up by the Soviet government in an effort to justify the program, and particularly to justify killing so many dogs with so few results. What a horrible practice.

