bighorn mountains
 Anyone who has lived in Wyoming for any length of time knows that the state is dotted with forts from the old west. These forts shaped the state by protecting the inhabitants from the Indians…or at least the did their very best to do so. One such fort that didn’t work out so well was Fort Phil Kearney. Construction on the fort began Friday July 13, 1866 by 18th Infantry Companies A, C, E and H of the 2nd Battalion, under the direction of the regimental commander and Mountain District commander Colonel Henry B Carrington. The post was named for Major General Philip Kearny, who was a popular figure in the American Civil War. The fort was located along the east side of the Bighorn Mountains in what is now northern Johnson County, approximately 15 miles north of Buffalo, Wyoming. Along with Fort Reno and Fort C F Smith, Fort Phil Kearney was established along the Bozeman Trail in the Powder River Country at the height of the Indian Wars to protect prospective miners from the Indians while they were
Anyone who has lived in Wyoming for any length of time knows that the state is dotted with forts from the old west. These forts shaped the state by protecting the inhabitants from the Indians…or at least the did their very best to do so. One such fort that didn’t work out so well was Fort Phil Kearney. Construction on the fort began Friday July 13, 1866 by 18th Infantry Companies A, C, E and H of the 2nd Battalion, under the direction of the regimental commander and Mountain District commander Colonel Henry B Carrington. The post was named for Major General Philip Kearny, who was a popular figure in the American Civil War. The fort was located along the east side of the Bighorn Mountains in what is now northern Johnson County, approximately 15 miles north of Buffalo, Wyoming. Along with Fort Reno and Fort C F Smith, Fort Phil Kearney was established along the Bozeman Trail in the Powder River Country at the height of the Indian Wars to protect prospective miners from the Indians while they were 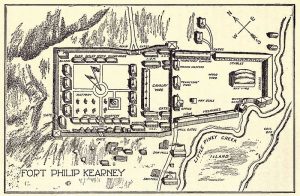 traveling north from the Oregon Trail to what is now Montana.
traveling north from the Oregon Trail to what is now Montana.
By fall, Carrington had erected an imposing symbol of American military power. A tall wooden wall surrounded a compound the size of three football fields. Inside the walls, Carrington built nearly 30 buildings, including everything from barracks and mess halls to a stage for the regimental band. Only the most massive and determined Indian attack would have been capable of taking Fort Phil Kearny. Unfortunately, Carrington’s mighty fortress had one important flaw…a failure to plan really. The nearest stands of timber were several miles away. To obtain the wood essential for heating and further construction, a detachment had to leave the protection of the fort every day. The Indians naturally began to prey on these Wood Trains. In December, a massive Indian ambush wiped out a force of 80 soldiers under the command of Captain William Fetterman.

Fort Phil Kearney was named the “hated post on the Little Piney” by the Indians, and it played an important role in Red Cloud’s War. The area around the fort was the site of the Fetterman Fight in 1866 and the Wagon Box Fight in 1867. By 1868, the Union Pacific Railroad had reached far enough west that emigrants could reach the Montana gold fields through what is now Idaho, which made the dangerous Bozeman Trail an unnecessary route. All three forts along the trail were abandoned as part of the Treaty of Fort Laramie in 1868. Shortly after the treaty, Fort Phil Kearney was burned to the ground by Cheyenne Indians. I guess they really did hate it.

