american revolutionary war

 The American Revolutionary War actually began on April 19, 1775, with the Battles of Lexington and Concord. At that time, it wasn’t considered a full-blown war, and attempts were still being made by July 5, 1775, to avoid that full-blown war. The Olive Branch Petition, adopted by the Second Continental Congress on July 5, 1775, and signed on July 8th, was the final attempt to avoid the full-blown war between Great Britain and the Thirteen Colonies in America, that became known as the American Revolutionary War, and ended with full independence of the United States.
The American Revolutionary War actually began on April 19, 1775, with the Battles of Lexington and Concord. At that time, it wasn’t considered a full-blown war, and attempts were still being made by July 5, 1775, to avoid that full-blown war. The Olive Branch Petition, adopted by the Second Continental Congress on July 5, 1775, and signed on July 8th, was the final attempt to avoid the full-blown war between Great Britain and the Thirteen Colonies in America, that became known as the American Revolutionary War, and ended with full independence of the United States.
It seemed that in the early days of the Revolutionary War, the main weapon was a volley of petitions and proclamations. The Second Continental Congress had already authorized the invasion of Canada more than a week earlier, but the Olive Branch Petition affirmed American loyalty to Great Britain, asking King George III to prevent further conflict. The petition was followed up with a July 6th Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms, making the success of the Olive Branch Petition unlikely in London. By August 1775, London officially declared the colonies to be in rebellion by the Proclamation of Rebellion, and the Olive Branch Petition was rejected by the British government. In fact, King George had refused to read it before declaring that the colonists were traitors.
The Second Continental Congress convened in May 1775. At that time, most and most delegates followed John Dickinson in his quest to reconcile with King George. He could not picture a world with an independent United States. I suppose there are always those people without a vision for the future. However, there was a small group of delegates, led by John Adams, who could see that war was inevitable, and that we would need to become independent of Great Britain. Nevertheless, there is a right time, so they decided that the wisest course of action was to remain quiet and wait for the opportune time to rally the people. This allowed Dickinson and his followers to pursue their own course for a reconciliation that would ultimately never happen.
Dickinson was the primary author of the Olive Branch Petition, along with Benjamin Franklin, John Jay, John Rutledge, and Thomas Johnson, all of whom also served on the drafting committee. Dickinson claimed that the colonies did not want independence, but rather, wanted more equitable trade and tax regulations. He asked that the King establish a lasting settlement between the Mother Country and the colonies “upon so firm a basis as to perpetuate its blessings, uninterrupted by any future dissensions, to succeeding generations in both countries” beginning with the repeal of the Intolerable Acts. The introductory paragraph of the letter named twelve of the thirteen colonies, all except Georgia. The letter was approved on July 5 and signed by John Hancock, President of the Second Congress, and by representatives of the named twelve colonies. It was sent to London on July 8, 1775, in the care of Richard Penn and Arthur Lee. Dickinson hoped that news of the Battles of Lexington and Concord combined with the “humble petition” would persuade the King to respond with a counterproposal or open negotiations.
Finally, Adams wrote to a friend, telling him that the petition served no purpose. Everyone knew that war was inevitable. Adams said that the colonies should have already raised a navy and taken the British officials prisoner. Unfortunately, the letter was intercepted by British officials and news of its contents reached Great Britain at about the same time as the petition itself. British advocates of a military response used Adams’ letter to claim that the petition itself was insincere, and it was rejected. The hostilities which Adams had foreseen undercut the petition, and the King had answered it before it even reached him.


With the King’s refusal to consider the petition, came the opportunity Adams and others needed to push for independence. Now the colonists viewed the King as unwilling and uninterested concerning the colonists’ grievances. The colonists finally knew that they had just two choices…complete independence or complete submission to British rule. They chose complete independence, and the rest, as we all know, is history.
 Few people think about the American Revolutionary War any more, because it was so long ago, and we have been an independent nation for so long now, that is almost seems unimportant, but nothing could be further from the truth. The strategies used then, were among the most amazing ever, when you consider the times, and the weapons available to these armies. Just moving the cannon from one place to another was a huge undertaking. Each one weighed upwards of 4500 pounds. The cannon was a major weapon, and was truly necessary if the army was to have a chance of winning a battle. Guns didn’t shoot far enough to have much safety from enemy fire. Getting close enough to successfully fight the enemy meant putting the troops at great risk, during a time when medical assistance was not readily available.
Few people think about the American Revolutionary War any more, because it was so long ago, and we have been an independent nation for so long now, that is almost seems unimportant, but nothing could be further from the truth. The strategies used then, were among the most amazing ever, when you consider the times, and the weapons available to these armies. Just moving the cannon from one place to another was a huge undertaking. Each one weighed upwards of 4500 pounds. The cannon was a major weapon, and was truly necessary if the army was to have a chance of winning a battle. Guns didn’t shoot far enough to have much safety from enemy fire. Getting close enough to successfully fight the enemy meant putting the troops at great risk, during a time when medical assistance was not readily available.
For the English, fighting on American soil was hazardous anyway. They had the disadvantage of not knowing the terrain well, so hiding places were much more well known to the Americans. The British were at a serious 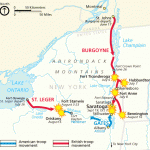 disadvantage. Then, on January 28, 1777, John Burgoyne, a poet, playwright, and British general, submitted a plan to isolate New England from the other colonies, which took in modern day New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island and Connecticut. That area might not have been a really big area, as territories go, but it was a big undertaking for any army. Nevertheless, it was the plan that the British decided to use. Burgoyne’s plan called for 8,000 British troops from Canada to move southward through New York by way of Lake Champlain and the Mohawk River. He planned to take the Americans by surprise. General Burgoyne thought he and his troops could take control of the Hudson River and isolate New England from the other colonies.
disadvantage. Then, on January 28, 1777, John Burgoyne, a poet, playwright, and British general, submitted a plan to isolate New England from the other colonies, which took in modern day New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island and Connecticut. That area might not have been a really big area, as territories go, but it was a big undertaking for any army. Nevertheless, it was the plan that the British decided to use. Burgoyne’s plan called for 8,000 British troops from Canada to move southward through New York by way of Lake Champlain and the Mohawk River. He planned to take the Americans by surprise. General Burgoyne thought he and his troops could take control of the Hudson River and isolate New England from the other colonies.
In his plan, the isolation of New England was designed to free British General William Howe to attack Philadelphia. Unfortunately, while the plan seemed to be working, Burgoyne miscalculated the part distance would play on his plan. His supply line was stretched in a long, narrow strip from the northern tip of Lake Champlain south to  the northern curve of the Hudson River at Fort Edward, New York. As Burgoyne’s army marched south, the Patriot militia was circling north. They cut off the British supply line. What had begun as a major victory, ended up as a defeat in Bennington, Vermont, and bloody draws at Bemis Heights, New York. On October 17, 1777, a frustrated Burgoyne was forced to retreat 10 miles and finally surrendered his remaining 6,000 British forces to the Patriots at Saratoga. France, upon hearing of the Patriot victory, agreed to recognize the independence of the United States. With France’s support, the Patriots took the ultimate victory. Following the defeat at Saratoga General Burgoyne returned home in shame and defeat. He was severely criticized and soon retired from active service.
the northern curve of the Hudson River at Fort Edward, New York. As Burgoyne’s army marched south, the Patriot militia was circling north. They cut off the British supply line. What had begun as a major victory, ended up as a defeat in Bennington, Vermont, and bloody draws at Bemis Heights, New York. On October 17, 1777, a frustrated Burgoyne was forced to retreat 10 miles and finally surrendered his remaining 6,000 British forces to the Patriots at Saratoga. France, upon hearing of the Patriot victory, agreed to recognize the independence of the United States. With France’s support, the Patriots took the ultimate victory. Following the defeat at Saratoga General Burgoyne returned home in shame and defeat. He was severely criticized and soon retired from active service.
 When most of us think of submarines, we think of the modern day nuclear subs that are basically underwater mobile cities, but as we all know, submarines have been around a lot longer…just how long was a surprise to me, although a learned history buff might not have been shocked at all. The idea of being able to operate underwater, actually dates back to ancient times when people used a hollow stick to breathe underwater. I’m not sure how successful any of those early attempts were, especially in the use of a vehicle of some kind, but probably not successful enough to warrant any kind of mass production.
When most of us think of submarines, we think of the modern day nuclear subs that are basically underwater mobile cities, but as we all know, submarines have been around a lot longer…just how long was a surprise to me, although a learned history buff might not have been shocked at all. The idea of being able to operate underwater, actually dates back to ancient times when people used a hollow stick to breathe underwater. I’m not sure how successful any of those early attempts were, especially in the use of a vehicle of some kind, but probably not successful enough to warrant any kind of mass production.
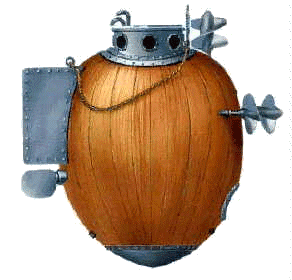
The first documented record of a submarine being used in combat, came as quite a surprise to me. The submarine, named Turtle, but usually called American Turtle, was used during the American Revolutionary War in 1776. Turtle was built in Old Saybrook, Connecticut in 1775 by American, David Bushnell as a means of attaching explosive charges to ships in a harbor. Turtle was designed  for use against British Royal Navy vessels occupying North American harbors. Then Connecticut governor, Jonathan Trumbull recommended the invention to George Washington. Even though Washington had his doubts, he provided funds and support for the submarine’s development and testing.
for use against British Royal Navy vessels occupying North American harbors. Then Connecticut governor, Jonathan Trumbull recommended the invention to George Washington. Even though Washington had his doubts, he provided funds and support for the submarine’s development and testing.
By 1776, Turtle was ready for testing. Several attempts were made by submarine operator, Sergeant Ezra Lee to affix explosives to the undersides of British warship HMS Eagle on September 7, 1776 in New York Harbor. Unfortunately, all of them failed, and Turtle’s transport ship was sunk later that year by the British…with Turtle aboard. Bushnell claimed to have recovered Turtle, but that has not been proven. Replicas of Turtle have been built and they are on display at the Connecticut River Museum, the U.S. Navy’s Submarine Force Library and Museum, the Royal Navy Submarine Museum and the 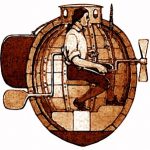 Oceanographic Museum in Monaco.
Oceanographic Museum in Monaco.
While Turtle was not successful, it was innovative, and it inspired other inventors to come up with ways that a submarine could be successful in combat, as well as exploration. I have to wonder if David Bushnell, or any of the other early inventors of crafts that operated under water had any idea how far below the surface of the oceans the submarine would eventually be able to go. Think of all the ships and planes that would never have been located, if we had no way to peer beneath the surface, and how much cargo would never have been recovered if we could not travel far below to not only locate, but salvage the cargo lost at sea. The submarine is truly amazing.

