
 The early warning systems we have in place these days could have easily saved many of the lives of the 2551 people who lost their lives on January 31, 1953, during the North Sea Flood. The flood caused catastrophic damage and loss of life in Scotland, England, Belgium and The Netherlands. It became one of the worst peacetime disasters of the 20th century. In the course of the flood, 307 people died in England, 19 died in Scotland, 28 died in Belgium, 1,836 died in the Netherlands, and an additional 361 people died at sea.
The early warning systems we have in place these days could have easily saved many of the lives of the 2551 people who lost their lives on January 31, 1953, during the North Sea Flood. The flood caused catastrophic damage and loss of life in Scotland, England, Belgium and The Netherlands. It became one of the worst peacetime disasters of the 20th century. In the course of the flood, 307 people died in England, 19 died in Scotland, 28 died in Belgium, 1,836 died in the Netherlands, and an additional 361 people died at sea.
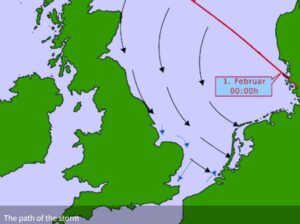
The North Sea Flood of 1953 was an unusual storm, that was caused by a number of contributing elements, that combined together to make it more deadly and devastating than the average storm or even the average flood. The annual spring tides, a deep pressure system…something that in itself can cause the sea to rise, combined with severe gale force winds…recorded at 126 miles per hour at Costa Hill in Scotland and the result was the North Sea Flood of 1953. All of these elements funneled those high tides southward toward the narrow, and shallow…just 571 feet deep, English Channel, causing the swell to rise even further. The storm surge was recorded at 18.4 feet at its peak.
The tide came in slowly at first, and nobody was alarmed. The official weather forecast was a slight drizzle and strong winds but nothing regarding waves and tidal flow. Life went on as usual, the ships set sail and people went to work or to play. Yes, life went on as usual…until it didn’t. What began as a calm evening was quickly changed into a nightmare. The tide became unpredictable and surged over the sea walls at different points during the evening, taking many by surprise and leaving no time to warn others. One survivor in Norfolk said, that it took less than 15 minutes from the water first tricking into his home, to reaching almost 5 feet. Those living closest to the sea reported that a wall of water came over almost immediately with many homes collapsing instantaneously with the force of the water rushing in. There was no warning system available to them. No one knew how bad this storm was…until it was way too late. The survivors became the first responders, because there was no one else. They couldn’t communicate the emergency need, or at the very least, communication was delayed. Outside of the affected areas, the first that many knew of what had happened was many hours after the majority of people had been killed.
Following the devastation, Questions began to emerge regarding the lack of warning given to the people, and because of that, the number of deaths. Priority was given to repairing the sea walls and rebuilding the homes of the people. In the aftermath, however it was going to be the long-term flood defenses that would change the future outcomes. The Thames Barrier was designed and built following the lessons from the 1953 flood. 
 Warning sirens were put in place at the most at risk areas and are still in use today. The Dutch government quickly formed the Delta commission to study the floods and eventually commissioned the ‘Delta Works’ to enable the closing of estuaries to prevent upstream flooding and included dams, sluices, locks, dikes, levees, and barriers. Taxes were implemented and readily accepted with a national mind-set that this must never happen again. Even today, commemorations still happen on every anniversary for the dead.
Warning sirens were put in place at the most at risk areas and are still in use today. The Dutch government quickly formed the Delta commission to study the floods and eventually commissioned the ‘Delta Works’ to enable the closing of estuaries to prevent upstream flooding and included dams, sluices, locks, dikes, levees, and barriers. Taxes were implemented and readily accepted with a national mind-set that this must never happen again. Even today, commemorations still happen on every anniversary for the dead.


Leave a Reply