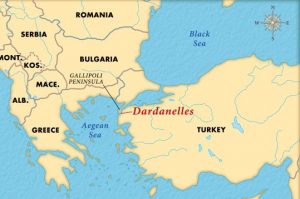
 The Dardanelles is a narrow strait running between the Black Sea in the east and the Mediterranean Sea in the west. In World War I it was a much contested area right from the start. It was the subject of a naval attack, spearheaded by Winston Churchill, who was at that time Britain’s young first lord of the Admiralty. On March 18, 1915, six English and four French battleships headed toward the strait. When they reached the area, Turkish mines blasted five of the ships, sinking three of them and forcing the Allied navy to draw back until land troops could be coordinated to begin an invasion of the Gallipoli peninsula. With troops from the Ottoman Empire and Germany mounting a spirited defense of the peninsula, however, the Gallipoli offensive turned into a significant setback for the Allies, with 205,000 casualties among British Empire troops and nearly 50,000 among the French.
The Dardanelles is a narrow strait running between the Black Sea in the east and the Mediterranean Sea in the west. In World War I it was a much contested area right from the start. It was the subject of a naval attack, spearheaded by Winston Churchill, who was at that time Britain’s young first lord of the Admiralty. On March 18, 1915, six English and four French battleships headed toward the strait. When they reached the area, Turkish mines blasted five of the ships, sinking three of them and forcing the Allied navy to draw back until land troops could be coordinated to begin an invasion of the Gallipoli peninsula. With troops from the Ottoman Empire and Germany mounting a spirited defense of the peninsula, however, the Gallipoli offensive turned into a significant setback for the Allies, with 205,000 casualties among British Empire troops and nearly 50,000 among the French.
When the Allies got involved, the latter offensives in Mesopotamia and Palestine saw more success. By September 1917, the crucial cities of Jerusalem and Baghdad were both in British hands. As the war stretched into the following year, these defeats and an Arab revolt had combined to destroy the Ottoman economy and devastate its land. Some 6 million people were dead and millions more starving. In early October 1918, unable to bank on a German victory any longer, the Turkish government in Constantinople decided to cut its losses and approached the Allies about brokering a peace deal. On October 30, 1918, British and Turkish representatives signed the Treaty of Mudros, which ended Ottoman participation in World War I. According to the terms of the treaty, Turkey had to demobilize its army, release all prisoners of war, and evacuate its Arab provinces, the majority of which were already under Allied control…and open the Dardanelles and Bosporus to Allied warships.
This last condition was fulfilled on November 12, 1918, the day after the armistice, when a squadron of British warships steamed through the Dardanelles, past the ruins of the ancient city of Troy, toward 
 Constantinople. By the post-war terms worked out by the Allies in the Treaty of Sevres in 1920, the waterways that were formerly under Ottoman rule…including the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmora and the Bosporus…were now placed under international control, with the designation that their “navigation…shall in future be open, both in peace and war, to every vessel of commerce or of war and to military and commercial aircraft, without distinction of flag.”
Constantinople. By the post-war terms worked out by the Allies in the Treaty of Sevres in 1920, the waterways that were formerly under Ottoman rule…including the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmora and the Bosporus…were now placed under international control, with the designation that their “navigation…shall in future be open, both in peace and war, to every vessel of commerce or of war and to military and commercial aircraft, without distinction of flag.”


4 Responses to The Dardanelles