 The year was 1776, and it was Christmas Day, but for the men with George Washington, it was not a day of celebration…not exactly anyway. They were in the middle of fighting a war, and the fighting didn’t just stop because it was Christmas, not this year anyway. This was to be an unusual Christmas as far as wartime Christmases went. In 1776, it was difficult to fight a war in the wintertime, because the slower modes of travel. Most times in a war, the armies took the Winter off from warring, but this army was not laying up for the Winter. This war would continue on…no matter what the weather was like.
The year was 1776, and it was Christmas Day, but for the men with George Washington, it was not a day of celebration…not exactly anyway. They were in the middle of fighting a war, and the fighting didn’t just stop because it was Christmas, not this year anyway. This was to be an unusual Christmas as far as wartime Christmases went. In 1776, it was difficult to fight a war in the wintertime, because the slower modes of travel. Most times in a war, the armies took the Winter off from warring, but this army was not laying up for the Winter. This war would continue on…no matter what the weather was like.
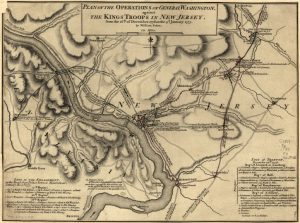
Things looked bad that year. The Continental Army had suffered a series of defeats in their battle against the British oppression. After some successful maneuvers, Colonel Henry Knox came to the attention of General George Washington who worked to place him in overall command to the Continental Army. Under his command, the Continentals brought 18 cannon over the river…3  Pounders, 4 Pounders, some 6 Pounders, horses to pull the carriages, and enough ammunition for the coming battle. The 6 Pounders, weighing as much as 1,750 pounds were the most difficult to transport to the far side of the river. But in the end all the trouble of moving this large artillery train to Trenton proved its worth. Knox would place the bulk of his artillery at the top of the town where its fire commanded the center of Trenton.
Pounders, 4 Pounders, some 6 Pounders, horses to pull the carriages, and enough ammunition for the coming battle. The 6 Pounders, weighing as much as 1,750 pounds were the most difficult to transport to the far side of the river. But in the end all the trouble of moving this large artillery train to Trenton proved its worth. Knox would place the bulk of his artillery at the top of the town where its fire commanded the center of Trenton.
The plan devised by Knox and Washington was to conduct a surprise attack upon a Hessian garrison of roughly 1,400 soldiers located in and around Trenton, New Jersey. Washington hoped that a quick victory at Trenton would bolster sagging morale in his army and encourage more men to join the ranks of the Continentals in the coming new year. After several councils of war, General George Washington set the date for the river crossing for Christmas night 1776. It was an unprecedented plan, because the expectation was always that the armies would hold up somewhere for the winter. No one had attacked in winter before, and especially on Christmas. George Washington led 2,400 troops on a daring nighttime crossing of the icy Delaware River. Stealing into New Jersey, on December 26 the Continental forces launched the surprise attack on Trenton.
 The gamble paid off. Many of the Hessians were still disoriented from the previous night’s holiday bender, and colonial forces defeated them with minimal bloodshed. While Washington had pulled off a shock victory, his army was unequipped to hold the city and he was forced to re-cross the Delaware that same day…with nearly 1,000 Hessian prisoners in tow. Washington would go on to score successive victories at the Battles of the Assunpink Creek and Princeton, and his audacious crossing of the frozen Delaware served as a crucial rallying cry for the beleaguered Continental Army. The Revolutionary War would be won by the Continental Army of course, and the rules of warfare changed forever.
The gamble paid off. Many of the Hessians were still disoriented from the previous night’s holiday bender, and colonial forces defeated them with minimal bloodshed. While Washington had pulled off a shock victory, his army was unequipped to hold the city and he was forced to re-cross the Delaware that same day…with nearly 1,000 Hessian prisoners in tow. Washington would go on to score successive victories at the Battles of the Assunpink Creek and Princeton, and his audacious crossing of the frozen Delaware served as a crucial rallying cry for the beleaguered Continental Army. The Revolutionary War would be won by the Continental Army of course, and the rules of warfare changed forever.


Leave a Reply