 When we think of hurricanes, we think of the ocean, but on November 7, 1913, there was a storm over the Great Lakes that would go down in United States history as the largest inland maritime disaster, in terms of number of ships lost. The storm was nicknamed the White Hurricane. The storm system brought blizzard conditions to areas all around the Great Lakes, with hurricane force winds. The nature of the storm was unique and powerful, and caught even the most seasoned captain by surprise. Two low pressure centers merged and rapidly intensified over the Lake Huron, with periods of storm-force winds occurring over a four day period. Surrounding ports signaled it was a level-four storm, but for some vessels, it was already too late. Major ship wrecks took place on all the Great Lakes except for Lake Ontario. Vessels at that time could withstand 90 mile per hour winds and 35 foot waves, but it was the whiteout conditions and accumulation of ice on the ships that turned an already dangerous situation into a deadly one. Ship captains were unable to maintain navigation, resulting in 12 shipwrecks, 19 ships stranded, and an estimated 250 lives lost. On land, 24 inches of snow shut down traffic and communication, causing millions of dollars in damage.
When we think of hurricanes, we think of the ocean, but on November 7, 1913, there was a storm over the Great Lakes that would go down in United States history as the largest inland maritime disaster, in terms of number of ships lost. The storm was nicknamed the White Hurricane. The storm system brought blizzard conditions to areas all around the Great Lakes, with hurricane force winds. The nature of the storm was unique and powerful, and caught even the most seasoned captain by surprise. Two low pressure centers merged and rapidly intensified over the Lake Huron, with periods of storm-force winds occurring over a four day period. Surrounding ports signaled it was a level-four storm, but for some vessels, it was already too late. Major ship wrecks took place on all the Great Lakes except for Lake Ontario. Vessels at that time could withstand 90 mile per hour winds and 35 foot waves, but it was the whiteout conditions and accumulation of ice on the ships that turned an already dangerous situation into a deadly one. Ship captains were unable to maintain navigation, resulting in 12 shipwrecks, 19 ships stranded, and an estimated 250 lives lost. On land, 24 inches of snow shut down traffic and communication, causing millions of dollars in damage.
The storm took place before the time when weather forecasters had the luxury of computer models, the detailed surface and upper air observations, weather satellites, or radar needed to make the most accurate predictions. Had weather forecasters then been able to access modern forecasting equipment, they may have been able to determine the likely development of this type of storm system in advance, as they did with Superstorm Sandy in 2012. As part of the forecast for Sandy forecasters were able to predict storm force winds over the lower Great Lakes five days in advance. The technology and forecast models available to forecasters today led to a more accurate forecast which saved mariners, recreational boaters, and businesses millions, as they were able to make preparations in advance of Sandy’s storm force winds and near 20 foot waves.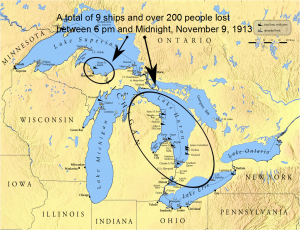
One hundred years later, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, in the Great Lakes is commemorating the Storm of 1913, not only for the pivotal role it played in the history of the Great Lakes, but also for its enduring influence. Modern systems of shipping communication, weather prediction, and storm preparedness have all been fundamentally shaped by the events of November 1913. It’s strange to think that one storm could make such a lasting impact on so many systems, but then it is the need for something better that spurs great inventive minds to invent a solution to a serious problem.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration plays a major role in protecting maritime relics of the past. Included are many of the ships lost in 1913. They have remained preserved deep below the surface of the Great Lakes. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary is a 48-square-mile area of protected territory with one of America’s best preserved and nationally significant collections of shipwrecks. Located in northwestern Lake Huron, Thunder Bay is adjacent to one of the most treacherous stretches of water within the Great Lakes system. Unpredictable weather, murky fog banks, sudden gales, and rocky shoals earned the area the name “Shipwreck Alley.” To date, more than 50 shipwrecks have been discovered within the sanctuary including the Isaac M. Scott, a 504 foot steel freighter lost in the storm of 1913.
This storm holds an interest for me, because at that time in history, my grandparents, Allen and Anna Spencer were living in the Great Lakes area. My grandfather was not part of the crew of any ship, and so any effect to them would have come in the form of very deep snow. My Aunt Laura would have been just 16 months old at  the time. I’m sure that the thought of being stranded in her home, was not a pleasant one for my grandmother, considering Aunt Laura’s very young age, but they survived the White Hurricane, as did most other people, at least those on land anyway. It still seems incredible to me that a storm of that magnitude could have brewed in an inland setting, but then anyone who knows the Great Lakes will tell you that they are so big that they might just as well be considered a sea. The November Gales have long been known as killers, especially over Lake Superior, the largest of the Great Lakes. I’m glad that modern weather forecasting equipment had at least lessened the possibility of ships and lives being lost in the Great Lakes, as well as the oceans.
the time. I’m sure that the thought of being stranded in her home, was not a pleasant one for my grandmother, considering Aunt Laura’s very young age, but they survived the White Hurricane, as did most other people, at least those on land anyway. It still seems incredible to me that a storm of that magnitude could have brewed in an inland setting, but then anyone who knows the Great Lakes will tell you that they are so big that they might just as well be considered a sea. The November Gales have long been known as killers, especially over Lake Superior, the largest of the Great Lakes. I’m glad that modern weather forecasting equipment had at least lessened the possibility of ships and lives being lost in the Great Lakes, as well as the oceans.


Leave a Reply