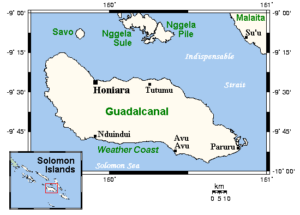
 Amazingly, the islands of the world have held an importance during wartime, that most of us would never have dreamed. These seemingly insignificant places proved to be great staging places time and again, and so became places that were fought over viciously. The Solomon Islands were among those places fought over during World War II…most specifically Guadalcanal. The island of Guadalcanal is the largest of the Solomons Islands, which is in the South Pacific Ocean, located northeast of Australia. The Solomon Islands are a group of 992 islands and atolls, 347 of which are inhabited. The Solomons have 87 Indigenous languages. They were first discovered in 1568 by Spanish navigator Alvaro de Mendana de Neyra (1541-95). By 1893, the British had annexed Guadalcanal, along with the other central and southern Solomons, which made sense, since they also owned Australia. In 1885, the Germans took control of the northern Solomons, but transferred these islands, except for Bougainville and Buka (which eventually went to the Australians) to the British in 1900. So, the Solomon Islands have been transferred around some over the centuries, as most countries have been, a time or two anyway.
Amazingly, the islands of the world have held an importance during wartime, that most of us would never have dreamed. These seemingly insignificant places proved to be great staging places time and again, and so became places that were fought over viciously. The Solomon Islands were among those places fought over during World War II…most specifically Guadalcanal. The island of Guadalcanal is the largest of the Solomons Islands, which is in the South Pacific Ocean, located northeast of Australia. The Solomon Islands are a group of 992 islands and atolls, 347 of which are inhabited. The Solomons have 87 Indigenous languages. They were first discovered in 1568 by Spanish navigator Alvaro de Mendana de Neyra (1541-95). By 1893, the British had annexed Guadalcanal, along with the other central and southern Solomons, which made sense, since they also owned Australia. In 1885, the Germans took control of the northern Solomons, but transferred these islands, except for Bougainville and Buka (which eventually went to the Australians) to the British in 1900. So, the Solomon Islands have been transferred around some over the centuries, as most countries have been, a time or two anyway.
During World War II, Guadalcanal became a hard-fought-over island, with the Japanese in control in early 1943. Then, on February 8, 1943, Japanese troops evacuate Guadalcanal, leaving the island in Allied possession after a prolonged campaign. When Japan lost Guadalcanal, it paved the way for other Allied wins in the Solomon Islands.
The Japanese had invaded the Solomon Islands in 1942 during World War II and immediately began building a strategic airfield on Guadalcanal. On August 7, 1942, US Marines landed on the island, signaling the Allies’ first major offensive against Japanese-held positions in the Pacific. The Japanese response to the US Marines “boots on the ground” was to quickly launch sea and air attacks. The battles that followed were bloody and made even more miserable in the debilitating tropical heat. Nevertheless, the Marines fought hard with Japanese troops on land, and in the waters surrounding Guadalcanal, the US Navy fought six major engagements with the Japanese between August 24 and November 30. In mid-November 1942, the five Sullivan brothers from Waterloo, Iowa, died together when the Japanese sank their ship, the USS Juneau. These days they try not to put brother together in battle, but the Sullivan brothers had requested it, and so it was granted.

Both the United States and the Japanese suffered heavy losses of men, warships, and planes in the battle for Guadalcanal. It is estimated 1,600 US troops were killed and over 4,000 were wounded. Several thousand more died from disease. The Japanese lost 24,000 soldiers. Finally, on December 31, 1942, Emperor Hirohito told his troops they could withdraw from the area. About five weeks later, the Americans secured Guadalcanal. American authorities declared Guadalcanal secure on February 9, 1943. After the war, American and Japanese groups have repeatedly visited Guadalcanal to search for remains of missing soldiers. Some 7,000 Japanese remain missing on the island, and islanders still bring the Japanese groups bones that the islanders say are those of unearthed Japanese soldiers.


Leave a Reply