 Prior to December 7, 1941, the United States had signed a Proclamation of Neutrality. They did not want to get pulled into World War II, any more than they had World War I and any of the other wars they were involved in. Still, I think everyone knew that it was inevitable…even before the Japanese attack. Early on the Sunday morning of December 7, 1941, the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, and almost simultaneously at other locations in the Pacific, would end any continued semblance of neutrality, and the United States prepared for war. The response to the attack was quick and decisive. The US Army Air Force (USAAF), under the command of Major General Henry Harley “Hap” Arnold was authorized to equip, man, and train itself into the world’s most powerful air force, and to do so quickly. The first order of business was to establish air force bases. By early 1942, the USAAF had committed to building scores of air bases across the United States. Everyone wanted to help, so a Chamber of Commerce delegation from Casper, Wyoming, traveled to Washington DC, to lobby for one of the proposed air bases. According to Joye Kading, longtime secretary at the Casper Army Air Base, they marketed the “zephyr wind” that whips around the western end of Casper Mountain as part of what made it a perfect location. The USAAF agreed.
Prior to December 7, 1941, the United States had signed a Proclamation of Neutrality. They did not want to get pulled into World War II, any more than they had World War I and any of the other wars they were involved in. Still, I think everyone knew that it was inevitable…even before the Japanese attack. Early on the Sunday morning of December 7, 1941, the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, and almost simultaneously at other locations in the Pacific, would end any continued semblance of neutrality, and the United States prepared for war. The response to the attack was quick and decisive. The US Army Air Force (USAAF), under the command of Major General Henry Harley “Hap” Arnold was authorized to equip, man, and train itself into the world’s most powerful air force, and to do so quickly. The first order of business was to establish air force bases. By early 1942, the USAAF had committed to building scores of air bases across the United States. Everyone wanted to help, so a Chamber of Commerce delegation from Casper, Wyoming, traveled to Washington DC, to lobby for one of the proposed air bases. According to Joye Kading, longtime secretary at the Casper Army Air Base, they marketed the “zephyr wind” that whips around the western end of Casper Mountain as part of what made it a perfect location. The USAAF agreed.
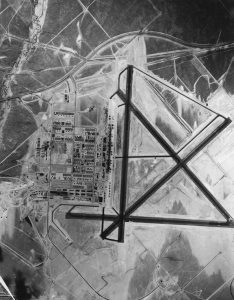
In March 1942, the US Army Corps of Engineers leased the old Casper City Hall at Center and Eighth streets in downtown Casper, in preparation for the construction of the new Army Air Base at Casper. The site they selected was a high, flat, sagebrush-covered terrace located nine miles west of town on US Highway 20-26 and adjacent to the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy railroad. After the war, the site became the Natrona County Municipal Airport and the land and all buildings became county property…later the name was changed to Casper-Natrona County International Airport when the airport achieved international status. The Casper Air Base was built in record time. Ground was broken in April, and six months later, on September 1, 1942, the base was officially opened. B-17 bomber crews began their Combat Crew Training School at the facility that consisted of four mile-long runways and around 400 buildings. With in six months, in the spring of 1943, the base transitioned from B-17 to B-24 crew training. Kading said, “The base was built to accommodate 20,000 men to be trained. They would come out there, and they were trained to do the last of their training in the B-17s and the B-24s because they could go around the east end of Casper Mountain and hit the zephyrs…our famous west winds…to take them right up to the sky.” By war’s end, almost 18,000 men had been trained at the Casper Army Air Base.
Not all was fun and games in learning to fly. Pilots did face risks too, as they gained experience. Flying over mountains can bring downdrafts, and turbulence, and it can make for a risky flight for the inexperienced pilot. The base had it’s share of accidents. Kading said, “The fellows hit something in the wind that they didn’t know how to handle, and they would have a plane wreck and they were lost. A lot of our pilots were in training, and we had some of our planes [that] were wrecked in other states. The soldiers’ bodies were then shipped back home to their families.” In the war years, the base was almost a third of the size of the city that was it’s host. On any given day, the base had an average of approximately 2,250 Army Air Force personnel and 800 civilians. I’m told by my Aunt Sandy Pattan that some of my aunts were among the civilians who worked there. The training class sizes varied, with as many as 6,000 in training during peak times. The men arrived in Casper by train, in newly assembled crews, each consisting of two pilots, a navigator, a bombardier, a radioman, flight engineer, and four gunners, to begin a strict regimen of training.
In one record-setting month, crews flew more than 7,500 hours at Casper Army Air Base. The remains of these activities are scattered across the high plains of Wyoming in the form of spent .50-caliber bullets, shells and links, 100-pound practice bomb fragments, and the wreckage of more than 70 aircraft. At the height of training, more than one million .50-caliber rounds and one thousand 100-pound training bombs would be expended per month. Now that, for some reason, amazes me. To think of spent bullets and parts of bombs or planes just lying around in the plains of Wyoming…just amazing, but of course, logical. One hundred forty Casper Army Air Base aviators perished in 90 plane crashes in training. Many more died later in combat. One hundred forty Casper Army Air Base aviators perished in 90 plane crashes between September 1942 and March 1945. Most of the crashes were in Wyoming, but many occurred out of state when the fliers were on longer training flights.
Most of the soldiers who came to Casper were not from Wyoming, but they embraced Wyoming and felt like their time in Casper was very special. Not only did Casper Army Air Base become a part of them forever, but they became a part of it too. Some of the soldiers wanted to show just how special the base was to them, so they decided to paint murals at the enlisted men’s club. Casper artist and art historian, Eric Wimmer, later researched the series of murals that depicted Wyoming’s history, and found that they were painted by some of the soldiers. Wimmer said, “They served for a short time, and then many soldiers were stationed at another base or sent overseas to fight in the war. This became the driving inspiration behind the concept [Cpl.] Leon Tebbetts developed for painting a set of murals in the Servicemen’s Club. He planned to give these temporary residents a history lesson on the state of Wyoming before they left.” The work began in October 1943, Tebbetts and three other soldiers with art backgrounds…JP Morgan, William Doench, and David Rosenblatt…started the series of 15 murals that included American Indians, travel on the trails in pioneer days, and other historic subjects. The murals are still there to this day.
The Casper Army Air Base closed in 1945, when the war ended. Today, the site of the old bomber base is largely intact with 90 of the original buildings still standing, including all six of the original hangars. I know that one of the barracks was moved to North Casper, because my grandfather, George Byer bought it to expand his small house to accommodate his large family of nine children. I remember playing back in that large room as a child. Visitors to the Wyoming Veterans Memorial museum in the base’s former Servicemen’s Club encounter a variety of stories: a gunnery instructor who gained his experience against the Japanese fleet during the Battle of Midway; a base commander who was known as the best machine gunner in the world; and a bomber navigator who was blown out of his B-17 and held prisoner in Germany. In addition, there are accounts of the 
 tragedy of the Casper Mountain bomber crash that I am certain was the crash that my then 8-year-old mother, Collene (Byer) Spencer witnessed. The base was also witness to the adventures of renowned test pilot Chuck Yeager, and saw the time that comedian Bob Hope paid a visit to the soldiers stationed there.
tragedy of the Casper Mountain bomber crash that I am certain was the crash that my then 8-year-old mother, Collene (Byer) Spencer witnessed. The base was also witness to the adventures of renowned test pilot Chuck Yeager, and saw the time that comedian Bob Hope paid a visit to the soldiers stationed there.


One Response to Casper Army Air Base