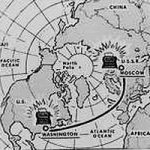
 The United States and Russia have long been frenemies, truth be told, but in October of 1962, no one would have called them that. The Cuban Missile Crisis brought the two super powers to the brink of a nuclear conflict. As we all know, that would have been devastating for the inhabitants of the earth, and in the end, both countries agreed that we could not let things escalate to that level again. In June of 1963, American and Russian representatives agreed to establish a “hot line” between Moscow and Washington DC. The idea was to speed communication between the two governments to prevent an accidental war.
The United States and Russia have long been frenemies, truth be told, but in October of 1962, no one would have called them that. The Cuban Missile Crisis brought the two super powers to the brink of a nuclear conflict. As we all know, that would have been devastating for the inhabitants of the earth, and in the end, both countries agreed that we could not let things escalate to that level again. In June of 1963, American and Russian representatives agreed to establish a “hot line” between Moscow and Washington DC. The idea was to speed communication between the two governments to prevent an accidental war.
By August of 1963, the system was ready to be tested. American teletype machines were installed in the Kremlin and at the Pentagon. Many people have thought that the machine at the Pentagon was actually in the White House, but that is incorrect. The two nations exchanged  encoding devises so that they could decipher the messages. This would allow the two nations to message each other in a matter of minutes. That would be somewhat slow in today’s high tech world of cell phones and texting, but in those days, it was state of the art. Once received, the message would have to be deciphered, which did slow things down a bit, but again, at that time, it was state of the art. The two teletype machines were connected by a 10,000 mile long cable with “scramblers” along the way to ensure that the messages could not be intercepted by unauthorized personnel.
encoding devises so that they could decipher the messages. This would allow the two nations to message each other in a matter of minutes. That would be somewhat slow in today’s high tech world of cell phones and texting, but in those days, it was state of the art. Once received, the message would have to be deciphered, which did slow things down a bit, but again, at that time, it was state of the art. The two teletype machines were connected by a 10,000 mile long cable with “scramblers” along the way to ensure that the messages could not be intercepted by unauthorized personnel.
On August 30, the United States sent its first message to the Soviet Union over the hot line: “The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog’s back 1234567890.” The message was chosen because it used every letter and number key on the teletype machine in order to see that each was in working order. Moscow returned a message in Russian indicating that every key had worked properly. In the end, the hot line was never needed  to prevent war, but instead has become a novelty item, used as a prop in movies about nuclear disaster. Fail Safe and Dr Strangelove were two movies that utilized the machines. The reality was that the two superpowers had come so close to mutual destruction back in 1962, that neither had much stomach for the proposed threat. They understood that communication was key in stopping a nuclear war. Of course, that has not stopped other nations from threatening to use nuclear weapons against other nations of the world. The Cold War ended a long time ago, but the “hot line” is still in operation between the two superpowers, and has since been supplemented by a direct secure telephone connection in 1999.
to prevent war, but instead has become a novelty item, used as a prop in movies about nuclear disaster. Fail Safe and Dr Strangelove were two movies that utilized the machines. The reality was that the two superpowers had come so close to mutual destruction back in 1962, that neither had much stomach for the proposed threat. They understood that communication was key in stopping a nuclear war. Of course, that has not stopped other nations from threatening to use nuclear weapons against other nations of the world. The Cold War ended a long time ago, but the “hot line” is still in operation between the two superpowers, and has since been supplemented by a direct secure telephone connection in 1999.


One Response to Hot Line