franklin roosevelt

 On February 15, 1933, following his return from a fishing trip in the Bahamas, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt was met by a large crowd of thousands of people. The crown was so excited to see the president, but they soon found themselves in the middle of a terrifying situation. Suddenly, before their eyes shooting began. Giuseppi Zangara, an anarchist gunman opened fire, in an attempt to assassinate President Elect Franklin D Roosevelt. Zangara shouted, “Too many people are starving!” Of course, the driving force behind the attack was the Great Depression. People were starving, jobs had been lost, banks were going under, and true depression had set in. Desperation was the next step.
On February 15, 1933, following his return from a fishing trip in the Bahamas, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt was met by a large crowd of thousands of people. The crown was so excited to see the president, but they soon found themselves in the middle of a terrifying situation. Suddenly, before their eyes shooting began. Giuseppi Zangara, an anarchist gunman opened fire, in an attempt to assassinate President Elect Franklin D Roosevelt. Zangara shouted, “Too many people are starving!” Of course, the driving force behind the attack was the Great Depression. People were starving, jobs had been lost, banks were going under, and true depression had set in. Desperation was the next step.
President Roosevelt had just delivered a speech in Miami’s Bayfront Park from the back seat of his open touring car when Zangara opened fire with six rounds. While Zangara missed the president, five people were hit. One of those hit was the mayor of Chicago, Anton Cermak, who was also in attendance. The mayor received a mortal stomach wound in the attack. While every attempt possible was used to try to save the mayor’s life, he later died of his wounds. Four other bystanders were also wounded. One of them, a woman, is was not expected to recover.
Thousands of people witnessed the shooting, which occurred in a dense crowd at Biscayne park on the Miami water front. The people acted quickly. A woman named Mrs W F Cross, of Miami was the first to seize the assassin’s gun. Zangara was quickly captured after that and people in the crowd began to beat him severely. The men that had tackled the assailant, might have beaten him to death, if Roosevelt had not intervened, telling the crowd to leave justice to the authorities. At police headquarters he was found to be of maniacal anarchistic tendencies. He ranted, “I like Roosevelt, all right, but I don’t like presidents.” President Roosevelt, who had stayed to speak to Mayor Cermak after the speech, immediately got Cermak into the Presidential Limousine and rushed him to the hospital. Cermak told the president that he was glad it was him and not the president. Noble words from a man who was about to die. Mayor Cermak, who did not lose consciousness during any of the time prior to being put on the operating table, was wounded by a single bullet which entered his back just above the right kidney.
For a time there were reports that the gunman might have been a Chicago gangster sent down here to murder 
 Mayor Cermak, but the subsequent developments showed that was not the case. Zangara was initially tried for attempted murder and sentenced to 80 years in prison, but when Mayor Cermak later died of his wounds, Zangara was retried and sentenced to death. Zangara died on the electric chair on March 20, 1933. I find myself amazed that his death came so quickly after his conviction. Most often it takes years to put someone to death. Nevertheless, just over a month later, the execution took place. At least that one time, justice was swift.
Mayor Cermak, but the subsequent developments showed that was not the case. Zangara was initially tried for attempted murder and sentenced to 80 years in prison, but when Mayor Cermak later died of his wounds, Zangara was retried and sentenced to death. Zangara died on the electric chair on March 20, 1933. I find myself amazed that his death came so quickly after his conviction. Most often it takes years to put someone to death. Nevertheless, just over a month later, the execution took place. At least that one time, justice was swift.
 Absaroka…have you ever heard of it? No…I hadn’t either, but it was of some importance to the United States, and it would have been of some significance to me and my family had it not been a temporary situation. You see, when President Franklin D Roosevelt put “The New Deal” in place, there were a lot of people who didn’t think it was such a good deal…much like “The Green New Deal” of today. “The New Deal” was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. The idea was to “help” by responding to needs for relief, reform, and recovery from the Great Depression. The plan created major federal programs and agencies, including the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), the Civil Works Administration (CWA), the Farm Security Administration (FSA), the National Industrial Recovery Act of 1933 (NIRA) and the Social Security Administration (SSA). They provided support for farmers, the unemployed, youth, and the elderly. The New Deal included new constraints and safeguards on the banking industry and efforts to re-inflate the economy after prices had fallen sharply. The New Deal programs included both laws passed by Congress, as well as presidential executive orders during the first term of the presidency of Roosevelt.
Absaroka…have you ever heard of it? No…I hadn’t either, but it was of some importance to the United States, and it would have been of some significance to me and my family had it not been a temporary situation. You see, when President Franklin D Roosevelt put “The New Deal” in place, there were a lot of people who didn’t think it was such a good deal…much like “The Green New Deal” of today. “The New Deal” was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. The idea was to “help” by responding to needs for relief, reform, and recovery from the Great Depression. The plan created major federal programs and agencies, including the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), the Civil Works Administration (CWA), the Farm Security Administration (FSA), the National Industrial Recovery Act of 1933 (NIRA) and the Social Security Administration (SSA). They provided support for farmers, the unemployed, youth, and the elderly. The New Deal included new constraints and safeguards on the banking industry and efforts to re-inflate the economy after prices had fallen sharply. The New Deal programs included both laws passed by Congress, as well as presidential executive orders during the first term of the presidency of Roosevelt.
The New Deal failed because Roosevelt misunderstood the cause of the Great Depression. When a doctor misdiagnoses the symptoms that present themselves, the doctor cannot prescribe the right medicine to cure the disease of a patient. Similarly, Roosevelt prescribed “The New Deal” to cure the economy of the United States from the Great Depression. Roosevelt’s “medicine” did not work because his administration failed to recognize the true causes of the Great Depression and therefore prescribed the wrong medicine. Roosevelt assumed that the free market, and not the government caused the Great Depression. Roosevelt believed the Great Depression was partly caused by poor investments and stock manipulations by rich people. To complicate matters, he blamed the Great Depression on bankers, speculators, and journalists. In reality, the causes of the Great Depression boiled down to three major causes…which explain why there was a banking crisis, why the 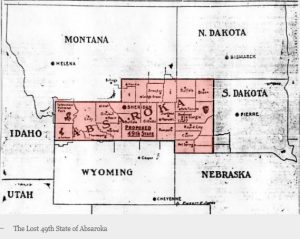 stock market declined, why exports vanished, why trading partners were upset, why major industries collapsed, and why there was uncertainty on the administration’s policies. These three explanations of the causes contrast with Roosevelt’s assumption that the private, not the public sector caused the problem. First, the negative consequences of World War I, increasing debt from less than $2 billion to over $20 billion, while at the same time, US loans to Europe amounted to over $10 billion. Second, the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act…the highest tariff in US history, which affected over 3,000 imported items and even increased taxes on some items. As a result of those high tariffs, foreign goods became less competitive and similar domestic goods more competitive. Third, the Federal Reserve did not prevent a banking crisis, but rather helped cause one. It was argued that the economic contraction was exacerbated because of the bank failures and the massive withdrawals of currency from the financial system while the Federal Reserve did not provide the necessary liquidity that the system required.
stock market declined, why exports vanished, why trading partners were upset, why major industries collapsed, and why there was uncertainty on the administration’s policies. These three explanations of the causes contrast with Roosevelt’s assumption that the private, not the public sector caused the problem. First, the negative consequences of World War I, increasing debt from less than $2 billion to over $20 billion, while at the same time, US loans to Europe amounted to over $10 billion. Second, the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act…the highest tariff in US history, which affected over 3,000 imported items and even increased taxes on some items. As a result of those high tariffs, foreign goods became less competitive and similar domestic goods more competitive. Third, the Federal Reserve did not prevent a banking crisis, but rather helped cause one. It was argued that the economic contraction was exacerbated because of the bank failures and the massive withdrawals of currency from the financial system while the Federal Reserve did not provide the necessary liquidity that the system required.
As people became more and more agitated about the unsuccessful New Deal, an idea began to form…secession. One of the leaders of the secessionist movement was A R Swickard, the street commissioner of Sheridan, Wyoming, who appointed himself “governor” and started hearing grievances in the “capital” of Sheridan. The new state was to be called Absaroka, which means “children of the large-beaked bird.” They planned secession in 1939. This region largely belongs to the Crow people and the Sioux, according to the Treaty of Fort Laramie (1851). Absaroka is also the namesake of the Absaroka mountain range. The area involved was the entire northern part of Wyoming, the western part of South Dakota, including the Black Hills, and the southeastern corner of Montana. Increasing tourism to the region was a motivation for the proposed state because Mount Rushmore (constructed 1927–1941) would be within Absaroka according to some plans.
The region’s complaints came from ranchers and independent farmers in remote parts of the three states, who  resented the New Deal and Democratic control of state governments, especially the government of Wyoming. In preparation for state secession, state automobile license plates bearing the name were distributed, as well as pictures of Miss Absaroka 1939. The movement was unsuccessful and fairly short-lived. The chief record of its existence comes from the Federal Writers’ Project, which included a story about the plan as an example of Western eccentricity. Oh those eccentric Westerners!! Imagine wanting to limit government, high taxes, and strict laws and mandates!! What were they thinking? Freedom, limited government, capitalism vs socialism…yep among other things, that’s what they were thinking.
resented the New Deal and Democratic control of state governments, especially the government of Wyoming. In preparation for state secession, state automobile license plates bearing the name were distributed, as well as pictures of Miss Absaroka 1939. The movement was unsuccessful and fairly short-lived. The chief record of its existence comes from the Federal Writers’ Project, which included a story about the plan as an example of Western eccentricity. Oh those eccentric Westerners!! Imagine wanting to limit government, high taxes, and strict laws and mandates!! What were they thinking? Freedom, limited government, capitalism vs socialism…yep among other things, that’s what they were thinking.

 A sneak attack…not something that happens overnight. That kind of attack takes planning. Relations between the United States and Japan had not been good, but now with Japan’s occupation of Indo-China and the implicit menacing of the Philippines, an American protectorate, they were deteriorating rapidly. The Americans had retaliated by seizing of all Japanese assets in the United States. That action was followed by the closing of the Panama Canal to Japanese shipping. In September 1941, President Roosevelt issued a statement, drafted by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, that threatened war between the United States and Japan should the Japanese encroach any farther on territory in Southeast Asia or the South Pacific.
A sneak attack…not something that happens overnight. That kind of attack takes planning. Relations between the United States and Japan had not been good, but now with Japan’s occupation of Indo-China and the implicit menacing of the Philippines, an American protectorate, they were deteriorating rapidly. The Americans had retaliated by seizing of all Japanese assets in the United States. That action was followed by the closing of the Panama Canal to Japanese shipping. In September 1941, President Roosevelt issued a statement, drafted by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, that threatened war between the United States and Japan should the Japanese encroach any farther on territory in Southeast Asia or the South Pacific.
The Japanese were keen to wield more power on the people of the earth. To do that, they had to take down the biggest super power, the United States of America. And to protect themselves, they needed to take Hawaii out of the hands of the United States, because it was a gateway in the Pacific that they couldn’t afford to have in the hands of the Allies. On September 24, 1941, the Japanese consul in Hawaii was instructed to divide Pearl Harbor into five zones, calculate the number of battleships in each zone, and report the findings back to Japan. They were preparing for the attack they had planned for December.
The Japanese military had long dominated Japanese foreign affairs. The official negotiations between the United States secretary of state and his Japanese counterpart to ease tensions were still ongoing, but Hideki Tojo, the minister of war who would soon be prime minister, had no intention of withdrawing from captured territories…even if the negotiations required it. He also decided that the American “threat” of war as an ultimatum, and he made plans to attack first in a Japanese-American confrontation: the bombing of Pearl Harbor.
As the plans began to gear up, Japan didn’t know that the United States had intercepted the message. Most unfortunate, was the fact that the message was sent back to Washington for decrypting. There were not a lot of 
 flights east, so the message was sent via sea. That process took more time. When it finally arrived at the capital, staff shortages and other priorities further delayed the decryption. When the message was finally unscrambled in mid-October, it was dismissed as being of no great consequence. It was a huge error on the part of the American intelligence community, and on December 7th, everyone would know that.
flights east, so the message was sent via sea. That process took more time. When it finally arrived at the capital, staff shortages and other priorities further delayed the decryption. When the message was finally unscrambled in mid-October, it was dismissed as being of no great consequence. It was a huge error on the part of the American intelligence community, and on December 7th, everyone would know that.
 These days, every military veteran has available to them, a compensation package to thank them for their service. Returning servicemen have access to unemployment compensation, low-interest home and business loans, and…most importantly, funding for education, but this was not always the case. In fact, there was a time when returning veterans had to fight for bonuses they were supposed to receive, which brought about the 1932 Bonus March, in which 20,000 unemployed veterans and their families flocked in protest to Washington. I think most of us would agree that our veterans should not have to fight for the things promised to them for their service, after they have already spent time fighting for their country.
These days, every military veteran has available to them, a compensation package to thank them for their service. Returning servicemen have access to unemployment compensation, low-interest home and business loans, and…most importantly, funding for education, but this was not always the case. In fact, there was a time when returning veterans had to fight for bonuses they were supposed to receive, which brought about the 1932 Bonus March, in which 20,000 unemployed veterans and their families flocked in protest to Washington. I think most of us would agree that our veterans should not have to fight for the things promised to them for their service, after they have already spent time fighting for their country.
President Franklin D Roosevelt was responsible for the sweeping New Deal reforms, many of which were really not good for this nation or its people, but there was one part of that legislation that has been a good thing for returning veterans…the G.I. Bill. On this day June 22, 1944, President Franklin D Roosevelt signed the G.I. Bill. It was an unprecedented act of legislation designed to compensate returning members of the armed services, known as G.I.s, for their efforts in World War II. The G.I. Bill…officially the Servicemen’s Readjustment Act of 1944…was proposed in an effort to avoid a relapse into the Great Depression after the war ended. The American Legion, a veteran’s organization, successfully fought for many of the provisions included in the bill, which gave returning servicemen the compensations they now have. By giving veterans money for tuition, living expenses, books, supplies and  equipment, the G.I. Bill effectively transformed higher education in America. Before the war, college had been an option for only 10-15 percent of young Americans, and university campuses had become known as a haven for the most privileged classes. This was not what America was supposed to be about. By 1947, the contrast was striking. Veterans made up half of the nation’s college enrollment. Three years later, nearly 500,000 Americans graduated from college, compared with 160,000 in 1939. Sure, they had to serve their country, but for many young people, this was not only what they felt was their duty, but it also became a scholarship program.
equipment, the G.I. Bill effectively transformed higher education in America. Before the war, college had been an option for only 10-15 percent of young Americans, and university campuses had become known as a haven for the most privileged classes. This was not what America was supposed to be about. By 1947, the contrast was striking. Veterans made up half of the nation’s college enrollment. Three years later, nearly 500,000 Americans graduated from college, compared with 160,000 in 1939. Sure, they had to serve their country, but for many young people, this was not only what they felt was their duty, but it also became a scholarship program.
As educational institutions opened their doors to this diverse new group of students, overcrowded classrooms and residences prompted widespread improvement and expansion of university facilities and teaching staffs. The bill was not only good for the veterans, but also for the economy, as more teaching jobs were created. An array of new vocational courses were developed across the country, including advanced training in education, agriculture, commerce, mining and fishing…skills that had previously been taught only informally. Some of these classes are responsible for some of the jobs that everyday Americans, even those without college educations have held. Jobs such as mining, and farming, and even fishing became commonplace.

The G.I. Bill became one of the major forces for economic expansion in America that lasted 30 years after World War II. Only 20% of the money set aside for unemployment compensation under the bill was given out. Most veterans found jobs or pursued higher education. Low interest loans enabled millions of American families to move out of cities and buy or build homes outside the city, changing the face of the suburbs. Over 50 years, the impact of the G.I. Bill was enormous, with 20 million veterans and dependents using the education benefits and 14 million home loans guaranteed, for a total federal investment of $67 billion. Among the millions of Americans who have taken advantage of the bill are former Presidents George H.W. Bush and Gerald Ford, former Vice President Al Gore and entertainers Johnny Cash, Ed McMahon, Paul Newman and Clint Eastwood, and closer to home, my brother-in-law, Ron Schulenberg, as well as my nephew, Allen Beach and soon, his wife, Gabby.

 In the height of World War II, on January 14, 1943, President Franklin D Roosevelt made history when he became the first president to travel by airplane on official business. The trip was not without danger. The German U-boats were wreaking havoc on Allied war ships in the Atlantic, and it was decided that a face to face conference was needed to discuss strategy. The man President Roosevelt was going to see, was my fifteenth cousin once removed, Winston Spencer-Churchill. No American President had flown on official business before, but with security in the Atlantic uncertain, Roosevelt’s advisors reluctantly agreed that he should fly. I’m sure his frail health at 60 years of age played a part in their decision too. The secret trip began on January 11, and the plane had to make several stops along the way. They took off from Florida with a first stop in the Caribbean to refuel and allow the president to rest. They then took off and headed south along the South American coast to Brazil, then across the Atlantic to Gambia, finally reaching Casablanca on this day, January 14, 1943.
In the height of World War II, on January 14, 1943, President Franklin D Roosevelt made history when he became the first president to travel by airplane on official business. The trip was not without danger. The German U-boats were wreaking havoc on Allied war ships in the Atlantic, and it was decided that a face to face conference was needed to discuss strategy. The man President Roosevelt was going to see, was my fifteenth cousin once removed, Winston Spencer-Churchill. No American President had flown on official business before, but with security in the Atlantic uncertain, Roosevelt’s advisors reluctantly agreed that he should fly. I’m sure his frail health at 60 years of age played a part in their decision too. The secret trip began on January 11, and the plane had to make several stops along the way. They took off from Florida with a first stop in the Caribbean to refuel and allow the president to rest. They then took off and headed south along the South American coast to Brazil, then across the Atlantic to Gambia, finally reaching Casablanca on this day, January 14, 1943.
It seems strange to us now that they would take such a roundabout route, but things were different then. The Boeing 314 Flying Boat that had been dubbed the Dixie Clipper was a big heavy plane. It had a flight range of 3,500 miles, and the direct route would have been about 4326 miles, making at lease one stop necessary. Since the Secret Service considered air travel for a president as risky anyway, I’m sure they wanted to take a  route that would keep them as far away from any fighting as they could. Also, the final leg of the trip required that the group transfer to an Army transport plane. The C-54 was required to fly at 15,000 feet to cross the Atlas Mountains…an altitude that seems insignificant today, but must have been quite high then. The Secret Service personnel and FDR’s advisors were worried about the oxygen levels affecting the president, and in the end, he did have to go on oxygen for a time during that part of the flight.
route that would keep them as far away from any fighting as they could. Also, the final leg of the trip required that the group transfer to an Army transport plane. The C-54 was required to fly at 15,000 feet to cross the Atlas Mountains…an altitude that seems insignificant today, but must have been quite high then. The Secret Service personnel and FDR’s advisors were worried about the oxygen levels affecting the president, and in the end, he did have to go on oxygen for a time during that part of the flight.
The flight was mastered successfully, and the two men were safely tucked into the Anfa Hotel where Roosevelt and Churchill were both in suites that were close together, making it the perfect place for the conference to take place…after the rooms were cleared of listening devises that had been planted by unknown persons, that is. The advisors and chiefs of staff did most of the hard work of the negotiations, but the presence of Roosevelt and Churchill kept them on task and working toward an agreement. The conference was very important to both sides, as the British were being hit very hard, and Roosevelt needed to keep the American troops advancing and winning their battles, so he could demonstrate to the American people that the tide of this war was turning. People get weary of war quite quickly, and in order to keep their support, victory in battle is key.
The Casablanca Conference was looked at by some as a victory for the British negotiators, because Churchill’s strategy prevailed, but they had missed the fact that the Americans also gained British commitments to long-term goals that went beyond the immediate objectives in the Mediterranean. The Americans agreed to attack Sicily after the victory in North Africa and the British agreed to allow a massive buildup of Allied Forces in  Britain, which would allow for an invasion of France with a target date of May 1, 1944. The invasion actually took place on June 6, 1944, and would become a day we all know as D-Day, when the troops stormed the beaches of Normandy…and that is where my dad came in. Since he was one of the Allied Forces that was stationed in England, his B-17G Bomber was one of those that provided cover for that invasion. It seems quite strange to me that a conference that took place over a year before, and 2 months prior to my dad’s enlistment, would ultimately place him in a position to fight in one of the most well known battles of World War II.
Britain, which would allow for an invasion of France with a target date of May 1, 1944. The invasion actually took place on June 6, 1944, and would become a day we all know as D-Day, when the troops stormed the beaches of Normandy…and that is where my dad came in. Since he was one of the Allied Forces that was stationed in England, his B-17G Bomber was one of those that provided cover for that invasion. It seems quite strange to me that a conference that took place over a year before, and 2 months prior to my dad’s enlistment, would ultimately place him in a position to fight in one of the most well known battles of World War II.

