History
 Yesterday, I had the unique opportunity to listen to a Holocaust survivor speak at a seminar. Her name was Inge Auerbacher, and she was an amazing woman. Inge was the last Jewish child born in Kippenheim, a village in South Western Germany located at the foot of the Black Forest. She was the only child of Berthold (1898–1987) and Regina Auerbacher (née Lauchheimer, 1905–1996). Both of her parents came from observant Jewish families who had lived for many generations in Germany. Her father proudly served in the German army, but when the Nazis came for them, his loyal service meant nothing to them. They were Jewish, and that fact condemned them to the concentration camps. Loyal service could not compensate for Hitler’s crazed hatred of the Jewish people.
Yesterday, I had the unique opportunity to listen to a Holocaust survivor speak at a seminar. Her name was Inge Auerbacher, and she was an amazing woman. Inge was the last Jewish child born in Kippenheim, a village in South Western Germany located at the foot of the Black Forest. She was the only child of Berthold (1898–1987) and Regina Auerbacher (née Lauchheimer, 1905–1996). Both of her parents came from observant Jewish families who had lived for many generations in Germany. Her father proudly served in the German army, but when the Nazis came for them, his loyal service meant nothing to them. They were Jewish, and that fact condemned them to the concentration camps. Loyal service could not compensate for Hitler’s crazed hatred of the Jewish people.
Inge had barely started school when her family as deported to Czechoslovakia and sentenced to the Terezin camp. When she and her parents went in, Inge was seven years old when she went into Terezin. She would be there for three years. I will not  say she called it home for three years, because it was definitely not a home. Inge tells of the companions she always knew would be there…the rats, mice, fleas, and bed bugs. The prisoners were allowed two showers a year…yes, I said a year. No wonder those companions hung around. Another occasional companion was lice which meant shaved heads to make removal easier. All of this was horrible, but it was the least of the nightmare. The guards gave brutal beatings…especially the women guards. The scientists performed experiments on the people, and they were given very little to eat. They were doing everything they could to kill their prisoners. Nevertheless, it was all too slow for Hitler.
say she called it home for three years, because it was definitely not a home. Inge tells of the companions she always knew would be there…the rats, mice, fleas, and bed bugs. The prisoners were allowed two showers a year…yes, I said a year. No wonder those companions hung around. Another occasional companion was lice which meant shaved heads to make removal easier. All of this was horrible, but it was the least of the nightmare. The guards gave brutal beatings…especially the women guards. The scientists performed experiments on the people, and they were given very little to eat. They were doing everything they could to kill their prisoners. Nevertheless, it was all too slow for Hitler.
A total of 140,000 people were shipped to Theresienstadt concentration camp near Terezin; 88,000 were sent primarily to the gas chambers in Auschwitz, and 35,000 died of malnutrition and disease in Terezin. Of the 15,000 children imprisoned in  Terezin, Inge and her parents were among the 1% that survived. Her childhood friends, especially her best friend, Ruth lost her life at Auschwitz. Ruth’s father was half Christian and half Jewish. She was raised Christian, but it didn’t make a difference. She and her family were executed for their Jewish heritage. Poor Ruth was deported to Auschwitz in one of the last transports. Ruth and the other children marched with their parents to their final destination, not knowing what was to come. They were told they were going to the showers, but it was the gas chambers, and their parents would not tell them otherwise. It would have been far too cruel. For me, the picture that Inge found years later, of Ruth as a little girl, has stayed vividly in my mind. She was a sweet, innocent little girl, who had done nothing wrong, but her life was taken away from her because she was pat Jewish…because Hitler hated the Jewish people. Hate…an ugly word. Inge says that this type of treatment happens when people lose their humanity. She would tell you, “Never lose your humanity.”
Terezin, Inge and her parents were among the 1% that survived. Her childhood friends, especially her best friend, Ruth lost her life at Auschwitz. Ruth’s father was half Christian and half Jewish. She was raised Christian, but it didn’t make a difference. She and her family were executed for their Jewish heritage. Poor Ruth was deported to Auschwitz in one of the last transports. Ruth and the other children marched with their parents to their final destination, not knowing what was to come. They were told they were going to the showers, but it was the gas chambers, and their parents would not tell them otherwise. It would have been far too cruel. For me, the picture that Inge found years later, of Ruth as a little girl, has stayed vividly in my mind. She was a sweet, innocent little girl, who had done nothing wrong, but her life was taken away from her because she was pat Jewish…because Hitler hated the Jewish people. Hate…an ugly word. Inge says that this type of treatment happens when people lose their humanity. She would tell you, “Never lose your humanity.”
 First chronicled by the famous western writer, Zane Grey, in his 1934 novel The Code of the West, no “written” code ever actually existed. However, the hardy pioneers who lived in the west were bound by these unwritten rules that centered on hospitality, fair play, loyalty, and respect for the land. These days, little of that code remains, or so it seems. These days, the more someone can get away with, he better they seem to like it. That just wasn’t the case for the people of thee old West. They needed to know that they could count on their neighbors, friends, and yes, even strangers
First chronicled by the famous western writer, Zane Grey, in his 1934 novel The Code of the West, no “written” code ever actually existed. However, the hardy pioneers who lived in the west were bound by these unwritten rules that centered on hospitality, fair play, loyalty, and respect for the land. These days, little of that code remains, or so it seems. These days, the more someone can get away with, he better they seem to like it. That just wasn’t the case for the people of thee old West. They needed to know that they could count on their neighbors, friends, and yes, even strangers
Ramon Adams, a Western historian, explained it best in his 1969 book, The Cowman and His Code of Ethics, saying, in part: “Back in the days when the cowman with his herds made a new frontier, there was no law on the range. Lack of written law made it necessary for him to frame some of his own, thus developing a rule of behavior which became known as the “Code of the West.” These homespun laws, being merely a gentleman’s agreement to certain rules of conduct for survival, were never written into statutes, but were respected everywhere on the range.”
Though the cowman might break every law of the territory, state and federal government, he took pride in upholding his own unwritten code. His failure to abide by it did not bring formal punishment, but the man who broke it became, more or less, a social outcast. His friends “hazed him into the cutbacks” and he was subject to the punishment of the very code he had broken. Though the Code of the West was always unwritten, here is a “loose” list of some of the guidelines: Don’t inquire into a person’s past. Take the measure of a man for what he is today. Never steal another man’s horse. A horse thief pays with his life. Defend yourself whenever  necessary. Look out for your own. Remove your guns before sitting at the dining table. Never order anything weaker than whiskey. Don’t make a threat without expecting dire consequences. Never pass anyone on the trail without saying “Howdy”. When approaching someone from behind, give a loud greeting before you get within shooting range. Don’t wave at a man on a horse, as it might spook the horse. A nod is the proper greeting. After you pass someone on the trail, don’t look back at him…it implies you don’t trust him. Riding another man’s horse without his permission is nearly as bad as making love to his wife. Never even bother another man’s horse. Always fill your whiskey glass to the brim. A cowboy doesn’t talk much; he saves his breath for breathing. No matter how weary and hungry you are after a long day in the saddle, always tend to your horse’s needs before your own, and get your horse some feed before you eat. Cuss all you want, but only around men, horses and cows. Complain about the cooking and you become the cook. Always drink your whiskey with your gun hand, to show your friendly intentions. Do not practice ingratitude. A cowboy is pleasant even when out of sorts. Complaining is what quitters do, and cowboys hate quitters. Always be courageous. Cowards aren’t tolerated in any outfit worth its salt. A cowboy always helps someone in need, even a stranger or an enemy. Never try on another man’s hat. Be hospitable to strangers. Anyone who wanders in, including an enemy, is welcome at the dinner table. The same was true for riders who joined cowboys on the range. Give your enemy a fighting chance. Never wake another man by shaking or touching him, as he might wake suddenly and shoot you. Real cowboys are modest. A braggart who is “all gurgle and no guts” is not tolerated. Be there for a friend when he needs you. Drinking on duty is grounds for instant dismissal and blacklisting. A cowboy is loyal to his “brand,” to his friends, and those he rides with. Never shoot an unarmed or unwarned enemy. This was also known as “the rattlesnake code”: always warn before you strike. However, if a man was being stalked, this could be ignored. Never shoot a woman no matter what.
necessary. Look out for your own. Remove your guns before sitting at the dining table. Never order anything weaker than whiskey. Don’t make a threat without expecting dire consequences. Never pass anyone on the trail without saying “Howdy”. When approaching someone from behind, give a loud greeting before you get within shooting range. Don’t wave at a man on a horse, as it might spook the horse. A nod is the proper greeting. After you pass someone on the trail, don’t look back at him…it implies you don’t trust him. Riding another man’s horse without his permission is nearly as bad as making love to his wife. Never even bother another man’s horse. Always fill your whiskey glass to the brim. A cowboy doesn’t talk much; he saves his breath for breathing. No matter how weary and hungry you are after a long day in the saddle, always tend to your horse’s needs before your own, and get your horse some feed before you eat. Cuss all you want, but only around men, horses and cows. Complain about the cooking and you become the cook. Always drink your whiskey with your gun hand, to show your friendly intentions. Do not practice ingratitude. A cowboy is pleasant even when out of sorts. Complaining is what quitters do, and cowboys hate quitters. Always be courageous. Cowards aren’t tolerated in any outfit worth its salt. A cowboy always helps someone in need, even a stranger or an enemy. Never try on another man’s hat. Be hospitable to strangers. Anyone who wanders in, including an enemy, is welcome at the dinner table. The same was true for riders who joined cowboys on the range. Give your enemy a fighting chance. Never wake another man by shaking or touching him, as he might wake suddenly and shoot you. Real cowboys are modest. A braggart who is “all gurgle and no guts” is not tolerated. Be there for a friend when he needs you. Drinking on duty is grounds for instant dismissal and blacklisting. A cowboy is loyal to his “brand,” to his friends, and those he rides with. Never shoot an unarmed or unwarned enemy. This was also known as “the rattlesnake code”: always warn before you strike. However, if a man was being stalked, this could be ignored. Never shoot a woman no matter what.
Consideration for others is central to the code, such as: Don’t stir up dust around the chuck wagon, don’t wake  up the wrong man for herd duty, etc. Respect the land and the environment by not smoking in hazardous fire areas, disfiguring rocks, trees, or other natural areas. Honesty is absolute – your word is your bond, a handshake is more binding than a contract. Live by the Golden Rule. “The Code of the West was a gentleman’s agreement to certain rules of conduct. It was never written into the statutes, but it was respected everywhere on the range.“ Ramon F. Adams
up the wrong man for herd duty, etc. Respect the land and the environment by not smoking in hazardous fire areas, disfiguring rocks, trees, or other natural areas. Honesty is absolute – your word is your bond, a handshake is more binding than a contract. Live by the Golden Rule. “The Code of the West was a gentleman’s agreement to certain rules of conduct. It was never written into the statutes, but it was respected everywhere on the range.“ Ramon F. Adams
As I read through these “codes,” I have to think just how sad it is that so little of that beautiful code is practiced these days, and how very sad that is.
 Anyone who lived through the 1960s knows about the Hippie Counterculture, or as we called it the Hippie Generation. It seems that every generation must be named. I wonder what the people who named Generation X would have called the Hippie Generation. In many ways they were much the same, with the exception of their clothes, anyway.
Anyone who lived through the 1960s knows about the Hippie Counterculture, or as we called it the Hippie Generation. It seems that every generation must be named. I wonder what the people who named Generation X would have called the Hippie Generation. In many ways they were much the same, with the exception of their clothes, anyway.
There was something that was unique, in my mind, to the Hippie Generation, and that was the Volkswagen Bus. I’m sure it was a coincidence that the VW Bus came out about the time that the whole “free love” ear was happening, but I would think that it was every parents nightmare, because it supplied a rolling motel room for kids on dates, and remember that the parents were pretty much against the whole “free love” thing. In fact, I’m quite sure it totally terrified them, because not only were their girls dating this guy was a rolling motel room, but this guy was…well, very different from the kind of man they had always hope their daughter would marry. My son-in-law, Kevin Petersen grew up around vans. His parents were at the right age to really be a part of the Hippie Generation, although I don’t know if they were really involved or not. They did love vans, however, and fixed theirs up to show.
The VW Bus, for it’s part, was the brainchild of Dutch businessman Ben Pon, an importer of the Volkswagen Beetles to the Netherlands. Pon saw a market for a small bus and in 1947 sketched out his concept. The bus went into production on March 8, 1950…technically before the Hippie Generation, so I suppose the Hippies adopted the VW Bus, and not the other way around. Known officially as the Volkswagen Type 2 (the Beetle was the Type 1) or the Transporter, the bus was a favorite mode of transportation for hippies in the United States during the 1960s and became an icon of the American counterculture movement. The bus eventually collected a number of nicknames, including the “Combi” (for combined-use vehicle) and the “Splittie” (for its split windshield); in Germany it was known as the “Bulli.” In the United States it was referred to by some as a hippie van or bus because it was used to transport groups of young people and their camping gear and other supplies to concerts and anti-war rallies. Some owners painted colorful murals on their buses and replaced the VW logo on the front with a peace symbol.
The Volkswagen Bus was only the second vehicle built by Volkswagen, a company whose history dates back to the 1930s Germany. In 1933, Adolf Hitler became chancellor of Germany and announced he wanted to build new roads and affordable cars for the German people. At that time, Austrian-born engineer Ferdinand Porsche (1875-1951) was already working on creating a small car for the masses. Hitler and Porsche later met and the engineer was charged with designing the inexpensive, mass-produced Volkswagen, or “people’s car.” In 1938, work began on the Volkswagen factory, located in what is now Wolfsburg, Germany. Full-scale vehicle  production didn’t begin until after World War II, however. In the 1950s, the Volkswagen arrived in the United States, where the initial reception was negative, due in part to the car’s historic Nazi connection as well as its small size and unusual rounded shape (which later led to it being dubbed the “Beetle”). In 1959, the advertising agency Doyle Dane Bernbach launched a groundbreaking campaign that promoted the car’s diminutive size as a distinct advantage to consumers, and over the next several years Volkswagen became the top-selling auto import in the United States. In 1972, the VW Beetle passed the Ford Model T as the world’s best-selling car, with over 15 million vehicles produced.
production didn’t begin until after World War II, however. In the 1950s, the Volkswagen arrived in the United States, where the initial reception was negative, due in part to the car’s historic Nazi connection as well as its small size and unusual rounded shape (which later led to it being dubbed the “Beetle”). In 1959, the advertising agency Doyle Dane Bernbach launched a groundbreaking campaign that promoted the car’s diminutive size as a distinct advantage to consumers, and over the next several years Volkswagen became the top-selling auto import in the United States. In 1972, the VW Beetle passed the Ford Model T as the world’s best-selling car, with over 15 million vehicles produced.
 Have you ever seen a picture of a Supreme Court session? Probably not. Photography is banned in Supreme Court, and there are only two known photographs of the Supreme Court in session. Cameras have long been banned inside the courtroom, so the only two photos were captured many decades ago by people who snuck cameras in.
Have you ever seen a picture of a Supreme Court session? Probably not. Photography is banned in Supreme Court, and there are only two known photographs of the Supreme Court in session. Cameras have long been banned inside the courtroom, so the only two photos were captured many decades ago by people who snuck cameras in.
The first photo, shown above, was shot in 1932 by a German photographer named Erich Salomon. Salomon was hired by Fortune magazine to shoot images during a tour of America. The photographer decided to sneak a camera into the Supreme Court by faking that he had a broken arm so that he could hide his camera inside his sling. Salomon was able to snap a stealthy photo, which was later published in Fortune and touted as the first photo ever made showing the court in session. That as a pretty sneaky way to get a camera into the courtroom, and while I don’t know how security is at the Supreme Court these days, but it wouldn’t surprise me to see a guard looking inside a sling to see what someone was trying to bring inside.
I can understand how a camera could be a problem, especially with old cameras. Many of them required a flash for indoor pictures, and having flashes going off all the time would be very distracting. Also, with today’s phones and cameras, videos could be taken easily, with sound that could let people outside the courtroom know about what was going inside the courtroom.
Nevertheless, five years later, in 1937, a young woman managed to take a second photo of the Supreme Court in session. This second photo was published in the June 7, 1937, edition of Time magazine, within an article titled Judiciary: Farewell Appearance. Time magazine wrote at the time, that the photo was taken by “an enterprising amateur, a young woman who concealed her small camera in her handbag, cutting a hole through which the lens peeped, resembling an ornament. She practiced shooting from the hip, without using the camera’s finder which was inside the purse.” The photographer was never named and remains a mystery to this day. The photo was also the first and only time all 9 justices of the court appeared in the same photo in session. There are rumors of a third photo of the Supreme court in session that was taken and published around the same time, but there does not appear to be any surviving record of that image.
Then, 77 years later, the inevitable happened. In 2014, an advocacy group snuck a camera into the Supreme Court and filmed the first-ever footage of the US Supreme Court in session. They captured a video that’s about 2-minutes long: The Supreme Court has officially banned cameras since 1946 when Federal Rule 53 was  enacted. It reads: Except as otherwise provided by a statute or these rules, the court must not permit the taking of photographs in the courtroom during judicial proceedings or the broadcasting of judicial proceedings from the courtroom. While Supreme Court justices have long been opposed to cameras in the courtroom, believing that cameras adversely impact the dynamic of the proceedings, they have been softening their stance in recent years. A number of justices have warmed up to the idea of cameras in the courtroom, possibly paving the way for a rule change in the future. I don’t know if I think that is a good thing or not, but somehow it seems that when you tell people they can’t do something, they ultimately find a way.
enacted. It reads: Except as otherwise provided by a statute or these rules, the court must not permit the taking of photographs in the courtroom during judicial proceedings or the broadcasting of judicial proceedings from the courtroom. While Supreme Court justices have long been opposed to cameras in the courtroom, believing that cameras adversely impact the dynamic of the proceedings, they have been softening their stance in recent years. A number of justices have warmed up to the idea of cameras in the courtroom, possibly paving the way for a rule change in the future. I don’t know if I think that is a good thing or not, but somehow it seems that when you tell people they can’t do something, they ultimately find a way.
 “Every state has ghost towns. Eastern and Midwestern States are no exception. At one time or another you may have driven your car right by a ghost town, not aware of it. If you are a hiker, backpacker, or a hunter, you may have walked past or through a ghost town not knowing one was there.” I read that statement on a web site I was using to research stories for my blog. I had read many stories about ghost towns, but this one intrigued me. My husband, Bob Schulenberg and I have hiked many of the trails in the Black Hills, and I can’t even begin to count the number of times we have walked past old abandoned, crumbling, falling down buildings. To us, they seemed like just an abandoned farmhouse and out buildings, but now I am beginning to wonder if we have been one of those hikers who have walked right through a ghost town, and didn’t even know it. In fact, I’ll bet we have walked right through many a ghost town during our many hikes.
“Every state has ghost towns. Eastern and Midwestern States are no exception. At one time or another you may have driven your car right by a ghost town, not aware of it. If you are a hiker, backpacker, or a hunter, you may have walked past or through a ghost town not knowing one was there.” I read that statement on a web site I was using to research stories for my blog. I had read many stories about ghost towns, but this one intrigued me. My husband, Bob Schulenberg and I have hiked many of the trails in the Black Hills, and I can’t even begin to count the number of times we have walked past old abandoned, crumbling, falling down buildings. To us, they seemed like just an abandoned farmhouse and out buildings, but now I am beginning to wonder if we have been one of those hikers who have walked right through a ghost town, and didn’t even know it. In fact, I’ll bet we have walked right through many a ghost town during our many hikes.
I love photographing old buildings, and often find myself wondering how long they had been there, and why  they were left to rot. Of course, the Black Hills is rich in gold rush history, so a ghost town or tow makes perfect sense. We have driven through, and by some of them, and even passed through some while riding he 1880 Train, but for some reason, it didn’t occur to me that some of the old buildings we have hiked by could have been part of a ghost town, but looking back now, it makes perfect sense. I have often found myself wondering who lived there and what their lives might have been like back when the house was newly built. Still, it didn’t occur to me that it might be part of a ghost town. I guess that is because I always thought that all the ghost towns would be well documented with signs alerting the tourists to the site. In reality, those signs would be placed by the town’s owner, who was trying to make a buck by romanticizing the site…and that’s ok too, but that doesn’t mean that every ghost town was so well documented. In reality, it’s the ghost towns that are less documented that hold the most intrigue, because much less is known about them.
they were left to rot. Of course, the Black Hills is rich in gold rush history, so a ghost town or tow makes perfect sense. We have driven through, and by some of them, and even passed through some while riding he 1880 Train, but for some reason, it didn’t occur to me that some of the old buildings we have hiked by could have been part of a ghost town, but looking back now, it makes perfect sense. I have often found myself wondering who lived there and what their lives might have been like back when the house was newly built. Still, it didn’t occur to me that it might be part of a ghost town. I guess that is because I always thought that all the ghost towns would be well documented with signs alerting the tourists to the site. In reality, those signs would be placed by the town’s owner, who was trying to make a buck by romanticizing the site…and that’s ok too, but that doesn’t mean that every ghost town was so well documented. In reality, it’s the ghost towns that are less documented that hold the most intrigue, because much less is known about them.
 I think that the next time we hike and find ourselves passing by an old rotting building, that I will feel much different about the place than I did in the past. I think I will still wonder about who lived there, but also about whether or not it was a ghost town that once sprung up, and prospered, only to be choked out when hard times hit and the people who lived there moved on in search of a better life. That was, after all, the fate of every ghost town. It was a town that sprung up with the promise of becoming a bustling city, but it was in the wrong place, and life could not be sustained there, so eventually it withered and died off, leaving only the buildings to tell of its presence, and then only to those who happened to pass by.
I think that the next time we hike and find ourselves passing by an old rotting building, that I will feel much different about the place than I did in the past. I think I will still wonder about who lived there, but also about whether or not it was a ghost town that once sprung up, and prospered, only to be choked out when hard times hit and the people who lived there moved on in search of a better life. That was, after all, the fate of every ghost town. It was a town that sprung up with the promise of becoming a bustling city, but it was in the wrong place, and life could not be sustained there, so eventually it withered and died off, leaving only the buildings to tell of its presence, and then only to those who happened to pass by.
 Anytime a group of people goes on strike, there are side effects that go beyond the management having to do more work. One of the industries in which a strike can have devastating side effects is the airline industry. When air traffic controllers strike, and the people filling in for them are not used to doing that job, even if they are trained, things can get out of hand quickly. They are likely understaffed, and stressed, but you can’t let these planes fly without guidance, so you use people in management, who probably haven’t done this work in a long time. Such was the case on March 5, 1973, over France when two Spanish aircraft, a DC9 and a Coronado 990 collided 27,000 feet above Nantes, in western France.
Anytime a group of people goes on strike, there are side effects that go beyond the management having to do more work. One of the industries in which a strike can have devastating side effects is the airline industry. When air traffic controllers strike, and the people filling in for them are not used to doing that job, even if they are trained, things can get out of hand quickly. They are likely understaffed, and stressed, but you can’t let these planes fly without guidance, so you use people in management, who probably haven’t done this work in a long time. Such was the case on March 5, 1973, over France when two Spanish aircraft, a DC9 and a Coronado 990 collided 27,000 feet above Nantes, in western France.
Sixty eight people were killed when the two Spanish aircraft collided in mid-air over France that morning,  where air traffic controllers are on strike. The dead, who included a two year old child and 47 Britons, were on board a Spanish Airlines DC9 from Palma, Majorca to London. Eye witnesses said that the DC9 exploded and broke up in mid-air following the collision. Max Chevalier, British Honorary vice-consul at Nantes, said, “Suddenly a streak of red light appeared and part of the aircraft came down with bodies flying out. It was a horrible sight.”
where air traffic controllers are on strike. The dead, who included a two year old child and 47 Britons, were on board a Spanish Airlines DC9 from Palma, Majorca to London. Eye witnesses said that the DC9 exploded and broke up in mid-air following the collision. Max Chevalier, British Honorary vice-consul at Nantes, said, “Suddenly a streak of red light appeared and part of the aircraft came down with bodies flying out. It was a horrible sight.”
The pilot of the Coronado 990, Captain Antonio Arenas-Rodriguez, was able to land his damaged aircraft safely at a military airfield in Cognac. All 108 people on board survived without injury. A passenger on board the Coronado aircraft, Leonard Wareham, 59, who lives in Madrid, said, “We were sitting on the port side of the aircraft. My wife had the window seat. There was an enormous bump and then everything seemed to fall about. No-one knew what was happening except that the aircraft was falling fast. The next thing I  noticed was that a French fighter plane was flying around us and evidently he guided us in to land.”
noticed was that a French fighter plane was flying around us and evidently he guided us in to land.”
At least 16 airlines, including British European Airlines (BEA) and Caledonian, cancelled flights over France following news of the accident. Members of the French Civilian Air Controllers Association (SNCTA), have been on strike illegally since February 20, 1973 hoping to gain improved pension benefits and obtain the right to strike which was outlawed for air traffic controllers in 1964. Military air traffic controllers were put in place to operate France’s air control system on February 26.
 During World War II, the Japanese had a tendency to be very sneaky. Our troops had to watch them very closely, because if they could get into a position to execute a sneak attack, they would do it. Of course, war is war, and the whole idea of war is to get the drop on the enemy, and the Japanese were quite good at it. On 28 February 1943, a convoy, comprised of eight destroyers and eight troop transports with an escort of approximately 100 fighters, set out from Simpson Harbour in Rabaul. On March 1, 1943, United States reconnaissance planes spotted the 16 Japanese ships that were en route to Lae and Salamaua in New Guinea. The Japanese were attempting to keep from losing the island and their garrisons there by sending in 7,000 reinforcements and aircraft fuel and supplies. The Japanese convoy was a result of a Japanese Imperial General Headquarters decision in December 1942 to reinforce their position in the South West Pacific.
During World War II, the Japanese had a tendency to be very sneaky. Our troops had to watch them very closely, because if they could get into a position to execute a sneak attack, they would do it. Of course, war is war, and the whole idea of war is to get the drop on the enemy, and the Japanese were quite good at it. On 28 February 1943, a convoy, comprised of eight destroyers and eight troop transports with an escort of approximately 100 fighters, set out from Simpson Harbour in Rabaul. On March 1, 1943, United States reconnaissance planes spotted the 16 Japanese ships that were en route to Lae and Salamaua in New Guinea. The Japanese were attempting to keep from losing the island and their garrisons there by sending in 7,000 reinforcements and aircraft fuel and supplies. The Japanese convoy was a result of a Japanese Imperial General Headquarters decision in December 1942 to reinforce their position in the South West Pacific.
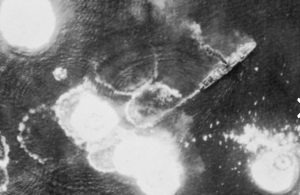 A United States bombing campaign, beginning March 2 and lasting until the March 4, consisting of 137 American bombers supported by United States and Australian fighters, destroyed eight Japanese troop transports and four Japanese destroyers. More than 3,000 Japanese troops and sailors drowned as a consequence, and the supplies sunk with their ships. Of 150 Japanese fighter planes that attempted to engage the American bombers, 102 were shot down. It was a complete and utter disaster for the Japanese. The United States 5th Air Force and the Royal Australian Air Force dropped a total of 213 tons of bombs on the Japanese convoy. The Japanese made no further attempts to reinforce Lae by ship, greatly hindering their ultimately unsuccessful efforts to stop Allied offensives in New Guinea.
A United States bombing campaign, beginning March 2 and lasting until the March 4, consisting of 137 American bombers supported by United States and Australian fighters, destroyed eight Japanese troop transports and four Japanese destroyers. More than 3,000 Japanese troops and sailors drowned as a consequence, and the supplies sunk with their ships. Of 150 Japanese fighter planes that attempted to engage the American bombers, 102 were shot down. It was a complete and utter disaster for the Japanese. The United States 5th Air Force and the Royal Australian Air Force dropped a total of 213 tons of bombs on the Japanese convoy. The Japanese made no further attempts to reinforce Lae by ship, greatly hindering their ultimately unsuccessful efforts to stop Allied offensives in New Guinea.

British Prime Minister Winston Churchill chose March 4, the official end of the battle, to congratulate President Franklin D. Roosevelt, since that day was also the 10th anniversary of the president’s first inauguration. “Accept my warmest congratulations on your brilliant victory in the Pacific, which fitly salutes the end of your first 10 years.” President Franklin Roosevelt was one of the very few president who held the office of president for more than two terms…an almost unheard of amount of time, and a recipe for disaster with some presidents we have had. When you think about it, however, what a great way to mark his first inauguration.
 Hospitals and hospital ships should be off limits during a war…even to the enemy. Some things should be considered sacred n the work hospitals do, should not be attacked. Unfortunately, that doesn’t always seem to matter. The Glenart Castle was a hospital ship during World War I. On March 1, 1917, the ship suffered damaged when she struck a mine in the English Channel 8 nautical miles northwest of the Owers Lightship on 1 March 1917. The ship was repaired and returned to service. That damage was accidental. What happened later was not.
Hospitals and hospital ships should be off limits during a war…even to the enemy. Some things should be considered sacred n the work hospitals do, should not be attacked. Unfortunately, that doesn’t always seem to matter. The Glenart Castle was a hospital ship during World War I. On March 1, 1917, the ship suffered damaged when she struck a mine in the English Channel 8 nautical miles northwest of the Owers Lightship on 1 March 1917. The ship was repaired and returned to service. That damage was accidental. What happened later was not.
On February 26, 1918, Glenart Castle was leaving Newport, South Wales, on its way to Brest, France. Fishermen in the Bristol Channel saw her clearly lit up as a hospital ship. That was supposed to let everyone know that they were not to fire on the ship. John Hill, a fisherman on Swansea Castle, remembered “I saw the Hospital Ship with green lights all around her – around the saloon. She had her red side lights showing and mast-head light, and also another red light which I suppose was the Red Cross light.” Nevertheless, being lit up did nothing for the Glenart Castle. At 04:00, Glenart Castle was hit by a torpedo in the number 3 hold. The blast destroyed most of the lifeboats, and the subsequent pitch of the vessel as I listed hindered attempts to launch the remaining boats. In the eight minutes the ship took to sink, only seven lifeboats were launched. Rough seas and inexperienced rowers swamped most of the boats.
Of the 194 people o board, only 32 survived. A total of 162 people were killed, including the Captain, Bernard Burt, eight nurses of the Queen Alexandra’s Imperial Military Nursing Service, seven Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC) medical officers and 47 medical orderlies. Of the hospital patients being treated on board, a total of 99 died. The matron of Glenart Castle, Miss Kate Beaufoy (1868-1918), was among those killed in the sinking. Beaufoy was a veteran of the South African War and the Gallipoli campaign. She kept a diary of her time on the ship. It is all her family has now. Evidence was found suggesting that the submarine that fired the torpedo may have shot at initial survivors of the sinking in an effort to cover up the sinking of Glenart Castle. It wasn’t bad enough that the hospital ship had been sunk, but they tried to make sure there were no survivors too. The body of a junior officer of Glenart Castle was recovered from the water close to the position of the sinking. It was marked with two gunshot wounds, one in the neck and the other in the thigh. The body also had a life vest indicating he was shot while in the water.
After the war, the British Admiralty sought the captains of U-Boats who sank hospital ships, in order to charge them with war crimes. Kapitänleutnant Wilhelm Kiesewetter, the commander of UC-56, was arrested after the  war on his voyage back to Germany and interned in the Tower of London. He was released on the grounds that Britain had no right to hold a detainee during the Armistice. To my knowledge, he never paid for his crimes. A memorial plaque was dedicated on the 84th anniversary of the sinking, February 26, 2002 near Hartland Point. The plaque’s inscription read, “In proud and grateful memory of those who gave their lives in the hospital ship Glenart Castle. Please remember, Master Lieutenant Commander Burt, Matron Katy Beaufoy, the ships officers, crew and medical staff who died when their ship was torpedoed by UC-56 in the early hours of 26th Feb 1918. The ship lies 20 miles WNW from this stone. For those in peril on the sea. R.I.P. Dedicated 26.02.2002.”
war on his voyage back to Germany and interned in the Tower of London. He was released on the grounds that Britain had no right to hold a detainee during the Armistice. To my knowledge, he never paid for his crimes. A memorial plaque was dedicated on the 84th anniversary of the sinking, February 26, 2002 near Hartland Point. The plaque’s inscription read, “In proud and grateful memory of those who gave their lives in the hospital ship Glenart Castle. Please remember, Master Lieutenant Commander Burt, Matron Katy Beaufoy, the ships officers, crew and medical staff who died when their ship was torpedoed by UC-56 in the early hours of 26th Feb 1918. The ship lies 20 miles WNW from this stone. For those in peril on the sea. R.I.P. Dedicated 26.02.2002.”
 The United States has tried to stay out of most of the wars the rest of the world has become involved in, but sometimes circumstances have drawn us into wars we didn’t want to enter. World War I is a prime example of just such a situation. On February 26, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson learns of the so-called Zimmermann Telegram. The telegram was a message from German Foreign Secretary Arthur Zimmermann to the German ambassador to Mexico proposing a Mexican-German alliance in the event of a war between the United States and Germany. This telegram was a crucial step toward the entry of the United States into World War I.
The United States has tried to stay out of most of the wars the rest of the world has become involved in, but sometimes circumstances have drawn us into wars we didn’t want to enter. World War I is a prime example of just such a situation. On February 26, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson learns of the so-called Zimmermann Telegram. The telegram was a message from German Foreign Secretary Arthur Zimmermann to the German ambassador to Mexico proposing a Mexican-German alliance in the event of a war between the United States and Germany. This telegram was a crucial step toward the entry of the United States into World War I.
On February 24, 1917, British authorities gave Walter Hines Page, the United States ambassador to Britain, a copy of the Zimmermann Telegram. It was a coded message from Zimmermann to Count Johann von Bernstorff, the German ambassador to Mexico. 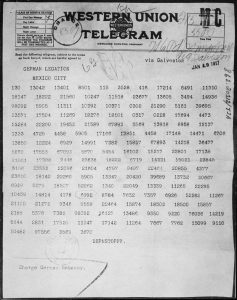 In the telegram, which was intercepted and deciphered by British intelligence in late January, Zimmermann instructed his ambassador, that in the event of a German war with the United States, to offer significant financial aid to Mexico, provided Mexico agreed to enter the conflict as a German ally. Germany also promised to restore to Mexico the lost territories of Texas, New Mexico and Arizona. Now, when you think about it, that is some big promises for Germany to be making, but I supposed that if the event of a loss in the war, all promises were null and void.
In the telegram, which was intercepted and deciphered by British intelligence in late January, Zimmermann instructed his ambassador, that in the event of a German war with the United States, to offer significant financial aid to Mexico, provided Mexico agreed to enter the conflict as a German ally. Germany also promised to restore to Mexico the lost territories of Texas, New Mexico and Arizona. Now, when you think about it, that is some big promises for Germany to be making, but I supposed that if the event of a loss in the war, all promises were null and void.
Upon learning about the proposed agreement between Germany and Mexico, the State Department was quick to send a copy of the Zimmermann Telegram to  President Wilson. The president was shocked by the note’s content and the next day proposed to Congress that the United States should start arming its ships against possible German attacks. Wilson also authorized the State Department to publish the telegram. It appeared on the front pages of American newspapers on March 1, and it left many Americans horrified. The telegram was quickly declared a forgery by the public, but two days later, Zimmermann himself announced that it was genuine.
President Wilson. The president was shocked by the note’s content and the next day proposed to Congress that the United States should start arming its ships against possible German attacks. Wilson also authorized the State Department to publish the telegram. It appeared on the front pages of American newspapers on March 1, and it left many Americans horrified. The telegram was quickly declared a forgery by the public, but two days later, Zimmermann himself announced that it was genuine.
The Zimmermann Telegram helped turn the American public, already angered by repeated German attacks on United States ships, firmly against Germany. On April 2, President Wilson, who had initially sought a peaceful resolution to World War I, urged immediate United States entrance into the war. Four days later, Congress declared war against Germany, and the United States entered World War I on April 6, 1917.

 The “Dust Bowl” was an environmental disaster that hit the Midwest in the 1930s. A combination of a severe water shortage and harsh farming techniques caused the disaster. Some scientists believe it was the worst drought in North America in 300 years. The lack of rain killed the crops that kept the soil in place. When winds blew, they raised enormous clouds of dust. It deposited mounds of dirt on everything, even covering houses. With the Dust Bow came the failure of many farms in the Midwest, and the people had no choice but to move, in order to find a way to make a living.
The “Dust Bowl” was an environmental disaster that hit the Midwest in the 1930s. A combination of a severe water shortage and harsh farming techniques caused the disaster. Some scientists believe it was the worst drought in North America in 300 years. The lack of rain killed the crops that kept the soil in place. When winds blew, they raised enormous clouds of dust. It deposited mounds of dirt on everything, even covering houses. With the Dust Bow came the failure of many farms in the Midwest, and the people had no choice but to move, in order to find a way to make a living.
I suppose that the invasion that followed might have been similar to the current refugees. It wasn’t just one family that moved, but hundreds of families. Los Angeles Police Chief James E. Davis, seeking to halt the “invasion” of dust-bowl Depression refugees in February, 1936, declared a “Bum Blockade” to stop the mass emigration of poverty stricken families fleeing from the dust-torn states of the Midwest. These days, he would have met with severe criticism, not so much for the blockade, as for the name of the blockade.
By 1934, 75% of the United States was severely affected by this terrible drought. The region most affected was the Great Plains, and included more than 100 million acres, centered in Oklahoma, the Texas Panhandle, Kansas, and parts of Colorado and New Mexico. These millions of acres of farmland became useless and soon, hundreds of thousands of people were forced to leave their homes. Many of these destitute families packed up their belongings and migrated west, hoping to find work and a better life, about 200,000 of which were California bound. Instead of finding the promised land of their dreams, however, they found that the available labor pool was vastly disproportionate to the number of job openings that could be filled. Migrants who found employment soon learned that this surplus of workers caused a significant reduction in the going wage rate, and even when the entire family worked, they were unable to support themselves.
Many set up “ditchbank” camps along irrigation canals in the farmers’ fields, which brought with them poor sanitary conditions and created a public health problem. And, of those who could find work in agriculture, it did not put an end to their travels. Instead, their lives were characterized by transience, if they wanted to maintain a steady income, which required them to follow the various harvests around the state. In the meantime, California was overwhelmed, trying to figure out how to absorb as many as 6,000 migrants crossing its borders daily. Also feeling the effects of the Depression, California infrastructures were already overburdened, and the steady stream of newly arriving migrants was more than the system could bear. Though these refugees came from a number of states, Californians often lumped them together as “Okies” or “Arkies,” who became the butt of derogatory jokes and the focus of political campaigns in which candidates made them the scapegoat for a shattered economy. They were accused of many crimes, as well as shiftlessness, lack of ambition, school overcrowding and stealing jobs from native Californians.
California’s Indigent Act was passed in 1933, which made it a crime to bring indigent persons into the state, Davis contended that his men needed no special approval because “any officer has the authority to enforce the state law.” Asking border-county sheriffs to deputize his officers, most complied. However, some refused, including Modoc County, who forced 14 LAPD officers to leave after they turned away local residents trying to 
 return home. On August 24, 1935, the Los Angeles Herald-Express ran an article warning emigrants to stay away from California. It read: Stay Away From California: Warning To Transient Hordes. Those days were very different from the California of today, and not in a good way. I don’t agree with derogatory name calling, but common sense tells us that sometimes you have to try to stop a flood, even if it’s a flood of people.
return home. On August 24, 1935, the Los Angeles Herald-Express ran an article warning emigrants to stay away from California. It read: Stay Away From California: Warning To Transient Hordes. Those days were very different from the California of today, and not in a good way. I don’t agree with derogatory name calling, but common sense tells us that sometimes you have to try to stop a flood, even if it’s a flood of people.

