World War II
 There was, during the Second World War, a somewhat strange and almost morbid plan that was concocted to dupe the Germans into believing that the Allies were going to invade Greece in 1943, when in fact, they were going to invade Sicily, some 500 miles away. The success of the mission really depended on the element of surprise, and in the end, the Allies needed something that would be believable to the Germans.
There was, during the Second World War, a somewhat strange and almost morbid plan that was concocted to dupe the Germans into believing that the Allies were going to invade Greece in 1943, when in fact, they were going to invade Sicily, some 500 miles away. The success of the mission really depended on the element of surprise, and in the end, the Allies needed something that would be believable to the Germans.
The thing that made the operation morbid was that in the end, they would use a dead body to bring about their deception. In their plan a body was dumped in the sea, to be discovered by Axis forces, carrying fake secret documents suggesting the invasion would be staged in Greece. They were a bit shocked when their plan worked, but work it did. The German troops were diverted to Greece, and Operation Mincemeat became a huge success, but even after it was over, it remained a source of secrecy, confusion, and conspiracy theory. The biggest source of confusion being…just who was this man who was found floating in the ocean, and how did he really die? For most people, the operation remains a mystery to this day, but one man believes that he now knows the true identity of the man found floating in the ocean.
In the 1956 film called “The Man Who Never Was,” one historian claims to have finally established beyond any reasonable doubt the identity of the person who played the part of the dead man, He believes he was a homeless Welshman named Glyndwr Michael. The body, which was given the identity of a fake Royal Marine, Major William Martin, was dropped into the sea off Spain in 1943. Winston Churchill had remarked that “Anyone but a bloody fool would know it was Sicily”, but after the tides carried Major Martin’s body into the clutches of Nazi agents, Hitler and his High Command became convinced Greece was the target. “You can forget about Sicily. We know it’s in Greece,” proclaimed General Alfred Jodl, head of the German supreme command operations staff.
“Mincemeat swallowed, rod, line and sinker” was the message sent to Churchill after the Allies learned the plot had worked. In recent years, there have been repeated claims that Mincemeat’s chief planner, Lieutenant Commander Ewen Montagu, was so intent on deceiving the Germans that he stole the body of a crew member from HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy aircraft carrier which exploded off the Scottish coast in March 1943, and lied to the dead man’s relatives. In 2003, a documentary based on 14 years of research by former police officer Colin 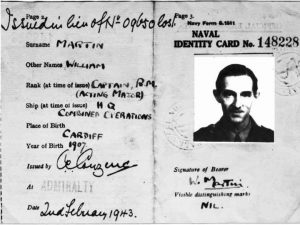 Gibbon claimed that ‘Major Martin’ was Dasher sailor Tom Martin. Then in 2004, official sanction appeared to be given to another candidate, Tom Martin’s crewmate John Melville. At a memorial service on board the current HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy patrol vessel, off the coast of Cyprus, Lieutenant Commander Mark Hill named Mr Melville as Major Martin, describing him as “a man who most certainly was”. Mr Melville’s daughter, Isobel Mackay, later told The Scotsman newspaper: “I feel very honored if my father saved 30,000 Allied lives.” I don’t suppose that we will ever know who the man really was, without exhuming his body, and that hardly seems right. Whoever he was, his family can rest assured that he saved many lives that day.
Gibbon claimed that ‘Major Martin’ was Dasher sailor Tom Martin. Then in 2004, official sanction appeared to be given to another candidate, Tom Martin’s crewmate John Melville. At a memorial service on board the current HMS Dasher, a Royal Navy patrol vessel, off the coast of Cyprus, Lieutenant Commander Mark Hill named Mr Melville as Major Martin, describing him as “a man who most certainly was”. Mr Melville’s daughter, Isobel Mackay, later told The Scotsman newspaper: “I feel very honored if my father saved 30,000 Allied lives.” I don’t suppose that we will ever know who the man really was, without exhuming his body, and that hardly seems right. Whoever he was, his family can rest assured that he saved many lives that day.

 A while back, my sister, Cheryl Masterson and I were talking about our Dad, Allen Spencer’s military training. Like much of Dad’s military service, big discussions about his training days were non-existent. So, I decided to trace his military career, to the best ability I could, and basically take a walk in his footsteps. We knew that he shipped out of Fort Snelling, Minnesota, and then spent time in Salt Lake City, Utah and in Kearney, Nebraska. We weren’t sure exactly where his basic training took place or his training for the B-17. That conversation got my curiosity going, and I decided that I needed to check it out. It’s not always easy to research a persons path through every aspect of their lives, but with the knowledge that he initially started out at Fort Snelling, I hoped to trace the rest of his journey through World War II. Fort Snelling, it turns out was a Reception Center. The men and women started there, received their vaccinations, medical exams, and their gear. They were classified and assigned to a unit. Then they were shipped out for their basic training.
A while back, my sister, Cheryl Masterson and I were talking about our Dad, Allen Spencer’s military training. Like much of Dad’s military service, big discussions about his training days were non-existent. So, I decided to trace his military career, to the best ability I could, and basically take a walk in his footsteps. We knew that he shipped out of Fort Snelling, Minnesota, and then spent time in Salt Lake City, Utah and in Kearney, Nebraska. We weren’t sure exactly where his basic training took place or his training for the B-17. That conversation got my curiosity going, and I decided that I needed to check it out. It’s not always easy to research a persons path through every aspect of their lives, but with the knowledge that he initially started out at Fort Snelling, I hoped to trace the rest of his journey through World War II. Fort Snelling, it turns out was a Reception Center. The men and women started there, received their vaccinations, medical exams, and their gear. They were classified and assigned to a unit. Then they were shipped out for their basic training.
Most of the men in dad’s original unit would go on to become part of the transport or supply teams, but because my dad had a job building airplanes for Douglas Aircraft Company prior to enlisting in the Army Air Force, he was moved to a unit that would spend the war in a B-17G flying Fortress Bomber. For my dad, it was an epic job. He often wrote home to his family about just how amazing the B-17 Bomber was, and how proud 
 he was to be serving on one. Part of dad’s job was to be the flight engineer, another position that stemmed from his vast knowledge of airplanes. The flight engineer knew the all equipment on the B-17 better than the pilot and any other crew member from the engines to the radio equipment to the armament to the engines to the electrical system and to anything else. Many flight engineers served as maintenance crew chiefs before moving to the position of a B-17 flight engineer. The flight engineer was also the top turret gunner. Dad’s training for his work took him to Miami Beach, Florida, then to Gulfport, Mississippi, and Dyersburg, Tennessee.
he was to be serving on one. Part of dad’s job was to be the flight engineer, another position that stemmed from his vast knowledge of airplanes. The flight engineer knew the all equipment on the B-17 better than the pilot and any other crew member from the engines to the radio equipment to the armament to the engines to the electrical system and to anything else. Many flight engineers served as maintenance crew chiefs before moving to the position of a B-17 flight engineer. The flight engineer was also the top turret gunner. Dad’s training for his work took him to Miami Beach, Florida, then to Gulfport, Mississippi, and Dyersburg, Tennessee.
In Gulfport, Mississippi, dad was trained as a flight airplane mechanic, and it was here that he volunteered to become an aerial gunner as well. He received his wings in November 1943, following gunnery training in Las Vegas, Nevada. Dyersburg Army Air Force Base was the largest combat aircrew training school built during the early war years. It was the only inland B-17 Flying Fortress training base east of the Mississippi River. The base was located on 2,541 acres, not including the practice range. Approximately 7,700 crew men received their last phase training at DAAB. From Dyersburg AAB, dad was sent to Kearney, Nebraska. There he and his crew were assigned a brand new B-17G bomber. Shortly thereafter they flew to New York to be dispatched to their base in the European Theater…Great Ashfield, Suffolk, England. Before arriving there, he wasn’t even sure where he was going, because these things were kept top secret, and were revealed on a need-to-know basis. Based out of Great Ashfield, dad flew 36 missions, one more that the required 35, having volunteered to fill in for a sick 
 crewmember on the final flight. In one of his letters, he told his family not to worry about him, because as he said, “I’m not afraid of what the near future might bring. I’m going into combat fully confident of my plane, crew, and myself. And I know that with the help of God, I’ll come home again in just as good a condition as I am right now.” And so he did. Today would have been my dad’s 95th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven Dad. We love and miss you very much and we are so proud of you.
crewmember on the final flight. In one of his letters, he told his family not to worry about him, because as he said, “I’m not afraid of what the near future might bring. I’m going into combat fully confident of my plane, crew, and myself. And I know that with the help of God, I’ll come home again in just as good a condition as I am right now.” And so he did. Today would have been my dad’s 95th birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven Dad. We love and miss you very much and we are so proud of you.
 Most of us think of dogs as pets, and so they are, but they are so much more. Dogs know when their master is sick, lonely, or worried. Dogs ask little of their masters, and give so much back, but there is a group of dogs who are working dogs. In fact, we often see dogs in everyday life and think little of their presence, when in fact, their work is vital to those they work for. One of the most well known working dog groups is the K-9 Units. We think of these dogs as police dogs, and so they are, but originally, the K-9 Corps were founded in World War II. Of course, dogs were used long before that war, but not in the capacity of World War II.
Most of us think of dogs as pets, and so they are, but they are so much more. Dogs know when their master is sick, lonely, or worried. Dogs ask little of their masters, and give so much back, but there is a group of dogs who are working dogs. In fact, we often see dogs in everyday life and think little of their presence, when in fact, their work is vital to those they work for. One of the most well known working dog groups is the K-9 Units. We think of these dogs as police dogs, and so they are, but originally, the K-9 Corps were founded in World War II. Of course, dogs were used long before that war, but not in the capacity of World War II.
The Romans used dogs in battles, sending them in to attack the enemy. Native Americans used them as pack animals, as well as sentry animals. Even in the Middle Ages, dogs were sent into battle equipped with their own armor. Modern European societies had long established traditions of using dogs in war. But, I think that their use was probably made most famous 77 years ago, when in January of 1942, Dogs for Defense, Inc. was established as a national organization to help procure dogs for war training purposes. Although some dogs were acquired through purchase, it was largely through the dog owner population’s patriotic sentiments that most dogs were acquired for training. That really amazes me. I understand patriotism, and how people would volunteer in the service, but it seems strange to me to volunteer your dog.  Nevertheless, they did. It was the job of Dogs For Defense not only to procure the dogs, but also to train them. Once trained, the dogs were to be given to the Quartermaster General, who then turned them over to the Plant Protection Branch and Inspection Division. Many thought the primary use of dogs would be as sentries for civilian war plants and quartermaster depot, but dogs have proven to be a much more.
Nevertheless, they did. It was the job of Dogs For Defense not only to procure the dogs, but also to train them. Once trained, the dogs were to be given to the Quartermaster General, who then turned them over to the Plant Protection Branch and Inspection Division. Many thought the primary use of dogs would be as sentries for civilian war plants and quartermaster depot, but dogs have proven to be a much more.
There are dogs that can sniff out drugs, gun powder…and the enemy. The DFD trained over 10,000 dogs. Most of the dogs were used at home for sentry duty, however, more than 1,800 dogs were sent into combat starting in 1942. The US Marine Corps sent over 1,000 dogs to be trained at their Camp Lejeune facility. Unfortunately, many commanders were unfamiliar, and maybe a little distrusting of the dogs, and didn’t know how to use them to their advantage. Seven Quartermaster Corps War Dog Platoons were sent to the European Theatre of Operations, but they did not have much success, probably due mostly to the lack of training with their handlers. In 1943, the QMC sent a detachment of six scout dogs and two messenger dogs to operate in the  Pacific Theatre. This was a test of their value in combat conditions. The Japanese troops had deeply entrenched themselves on many islands in the Pacific theater of operations. Thousands were hiding in caves and in the dense jungles. They would lie very still, in wait for patrolling Marines and soldiers and then ambush them before the troops ever detected enemy forces. This is where the dogs proved their value. The first war dog platoons took to the Pacific island of New Britain. Here Marine war dogs attached to the Sixth Army first worked on sentry duty. Once a beachhead was established the dogs and handlers began conducting their patrols. They went on forty-eight patrols in fifty-three days. The dog patrols captured or killed 200 Japanese soldiers. This early success of war dog platoons set the standard for what could be expected, and what could not, from a K-9 detachment. I think that the more training given to both dogs and handlers, the better the results will be, as we have seen in K-9 police dogs in modern times.
Pacific Theatre. This was a test of their value in combat conditions. The Japanese troops had deeply entrenched themselves on many islands in the Pacific theater of operations. Thousands were hiding in caves and in the dense jungles. They would lie very still, in wait for patrolling Marines and soldiers and then ambush them before the troops ever detected enemy forces. This is where the dogs proved their value. The first war dog platoons took to the Pacific island of New Britain. Here Marine war dogs attached to the Sixth Army first worked on sentry duty. Once a beachhead was established the dogs and handlers began conducting their patrols. They went on forty-eight patrols in fifty-three days. The dog patrols captured or killed 200 Japanese soldiers. This early success of war dog platoons set the standard for what could be expected, and what could not, from a K-9 detachment. I think that the more training given to both dogs and handlers, the better the results will be, as we have seen in K-9 police dogs in modern times.
 Gunner was a stray male Kelpie, born in August 1941, who became notable for his reliability to accurately alert Allied Air Force personnel that Japanese aircraft were approaching Darwin during the Second World War. Gunner was six months old when he was found whimpering under a destroyed mess hut at Darwin Air Force base where he suffering a broken leg on February 19, 1942, following the first wave of Japanese attacks on Darwin.
Gunner was a stray male Kelpie, born in August 1941, who became notable for his reliability to accurately alert Allied Air Force personnel that Japanese aircraft were approaching Darwin during the Second World War. Gunner was six months old when he was found whimpering under a destroyed mess hut at Darwin Air Force base where he suffering a broken leg on February 19, 1942, following the first wave of Japanese attacks on Darwin.
Gunner was taken to a field hospital, but the doctor insisted he could not fix a “man” with a broken leg without knowing his name and serial number. The doctor repaired and plastered his leg after the air force personnel replied that his name was “Gunner” and his number was “0000”. Gunner entered the airforce on that day. It might have been unofficial, but only is the way he was “drafted.” Gunner’s Air Force career was very real. Leading Aircraftman Percy Westcott, one of the two airmen who found Gunner, took ownership of him and became his master and handler. Gunner was badly shaken after the bombing and quite skittish, but being only six months old he quickly responded to the attention of the men on base.
About a week later, Gunner first demonstrated his remarkable hearing skills. The men were working on the airfield, when Gunner became agitated. He started to whine and jump. A little while later, the sound of approaching airplane engines was heard by the airmen. Suddenly, a wave of Japanese raiders appeared in the skies above Darwin and began bombing and strafing the town. Somehow…Gunner knew. Two days later, Gunner became agitated again, and not long afterwards came another air attack. In the months that followed, the same pattern played out every time an attack occurred. Long before the sirens sounded, Gunner would become agitated and head for shelter. Because of Gunner’s amazing hearing he was able to warn air force personnel of approaching Japanese aircraft up to 20 minutes before they arrived and before they showed up on the radar. Gunner was never agitated when he heard Allied planes taking off or landing….just the enemy aircraft. Somehow Gunner could differentiate the sounds of Allied and enemy aircraft. He was so reliable that Wing Commander McFarlane gave approval for Westcott to sound a portable air raid siren whenever Gunner’s  whining or jumping alerted him. Before long, there were a number of stray dogs roaming the base. McFarlane gave the order that all dogs be shot, with the exception of Gunner. They couldn’t afford any distractions.
whining or jumping alerted him. Before long, there were a number of stray dogs roaming the base. McFarlane gave the order that all dogs be shot, with the exception of Gunner. They couldn’t afford any distractions.
Gunner became such a part of the air force that he slept under Westcott’s bunk, showered with the men in the shower block, sat with the men at the outdoor movie pictures, and went up with the pilots during practice take-off and landings. When Westcott was posted to Melbourne 18 months later, Gunner stayed in Darwin, looked after by the RAAF butcher. It is unknown what happened to Gunner after the war, but he was a most amazing dog.
 One of the most elegant ships ever built, RMS Queen Elizabeth, was one of the two superliners built by John Brown and Company in Clydebank, Scotland, in the 1930s. The ship did not start out as RMS Queen Elizabeth, but rather as Hull 552. Later, it was named in honor of Queen Elizabeth, and launched, on 27 September 1938. The RMS Queen Elizabeth was 1,031 feet long and 118.5 feet wide. It was the largest passenger liner ever constructed…until then anyway.
One of the most elegant ships ever built, RMS Queen Elizabeth, was one of the two superliners built by John Brown and Company in Clydebank, Scotland, in the 1930s. The ship did not start out as RMS Queen Elizabeth, but rather as Hull 552. Later, it was named in honor of Queen Elizabeth, and launched, on 27 September 1938. The RMS Queen Elizabeth was 1,031 feet long and 118.5 feet wide. It was the largest passenger liner ever constructed…until then anyway.
During the late 1930s, workers at a Scottish construction site began building a sea vessel for the Cunard Line ocean liner company that would be larger and more luxurious than anything the world had ever seen. However, the outbreak of World War II in 1939 prevented the completion of the Queen Elizabeth‘s finer points. The vessel was hastily made seaworthy for wartime service and was used as a transport vessel for the Allies, carrying massive amounts of supplies and several hundred thousand troops around the world until the war’s end. Because of the concerns over German bombing, the ship was moved to New York to harbor it in a safer place.
After the war, the ship, which was equipped with a 200,000 horsepower engine, was embellished with an elegant art deco style. It made its public debut in 1946, leaving Southampton, England, on its first luxurious  run across the Atlantic. The ship continued to be a luxury passenger liner until it retirement in 1968.
run across the Atlantic. The ship continued to be a luxury passenger liner until it retirement in 1968.
Then, the Queen Elizabeth was auctioned off to the highest bidder, eventually being purchased in 1970 by C.W. Tung, a Taiwanese shipping tycoon. Tung renamed the vessel Seawise University and began work on converting the ship into a learning center that would tour the world. However, in early 1972, as the mobile university neared completion, a fire destroyed the pride of the Cunard Line. The fire broke out while the ship was docked in Hong Kong Harbor, and by the next morning the famous vessel was a total loss on the bottom of the sea floor.
 While looking at some historic photos, I came across one that was both intriguing, and sad. The title of the photograph was as intriguing as the photograph itself. Shoes on the Danube Banksdepicts a memorial in Budapest, Hungary that was conceived by film director Can Togay. The memorial sits on the east and of the Danube River. Togay worked with sculptor Gyula Pauer to create a memorial to honor the Jews who were killed by fascist Arrow Cross militiamen in Budapest during World War II.
While looking at some historic photos, I came across one that was both intriguing, and sad. The title of the photograph was as intriguing as the photograph itself. Shoes on the Danube Banksdepicts a memorial in Budapest, Hungary that was conceived by film director Can Togay. The memorial sits on the east and of the Danube River. Togay worked with sculptor Gyula Pauer to create a memorial to honor the Jews who were killed by fascist Arrow Cross militiamen in Budapest during World War II.
As I looked at the picture of many pairs of shoes, the magnitude of what had happened there, and exactly what I was looking at hit me. These shoes were not just shoes, they were people…innocent people, who lined up and shot for no other reason than that they were Jewish. These people were told to remove their shoes, and then they were shot. Their lifeless bodies fell into the river and were swept downstream. There was no funeral, no burial…despite the traditions that are set up for Jewish burial. Of course, I know that not every Jewish death can be handles in the Jewish traditions, but these people were murdered in such a way as to humiliate them, including the lack of a traditional burial.
The monument along the Danube River represents the lives of the people who were murdered, there is no way to really represent the people, because no one knows who they were, what they looked like, or even how many there were for sure, but rather the monument depicts their shoes left behind on the bank. It is the only real connection we can have to these victims of such horrible hatred. The brutal treatment of the approximately 3,500 people, 800 of them Jews, and the rest accused of Jewish activities, is beyond horrid. These people were forced to strip naked on the banks of the Danube and face the river. Then, a firing squad shot the prisoners at close range in the back so that they fell into the river to be washed away.
The monument is located on the Pest side of the Danube Promenade in line with where Zoltan Street would meet the Danube if it continued that far, about 980 feet south of the Hungarian Parliament and near the Hungarian Academy of Sciences…between Roosevelt Square and Kossuth square. The sculptor created sixty pairs of period-appropriate shoes out of iron. The shoes are attached to the stone embankment, and behind them lies a 131 foot long, 27 inch high stone bench. At three points are cast iron signs, with the following text in Hungarian, English, and Hebrew: “To the memory of the victims shot into the Danube by Arrow Cross militiamen in 1944–45. Erected 16 April 2005.”
Most of the murders along the edge of the River Danube took place around December 1944 and January 1945, when the members of the Arrow Cross Party police (“Nyilas”) took as many as 20,000 Jews from the newly established Budapest ghetto and executed them along the river bank. There were, of course, some survivors who managed to make it out, and lived to tell their stories. On of those Was Tommy Dick, who wrote the book, “Getting Out Alive.” I have not read the book yet, but after seeing this memorial, I will be reading it very soon.
There were heroes in Budapest too. Valdemar Langlet, head of the Swedish Red Cross in Budapest, with his wife Nina, and later the diplomat Raoul Wallenberg and 250 coworkers were working around the clock to save the Jewish population from being sent to Nazi concentration camps. This group later grew in number to approximately 400. Lars and Edith Ernster, Jacob Steiner, and many others were housed at the Swedish Embassy in Budapest and 32 other buildings throughout the city which Wallenberg had rented and declared as extraterritorially Swedish to try to safeguard the residents. Italian Giorgio Perlasca did the same, sheltering Jews in the Spanish Embassy.
On the night of January 8, 1945, an Arrow Cross execution brigade forced all the inhabitants of the building on  Vadasz Street to the banks of the Danube. At midnight, Karoly Szabo and 20 policemen with drawn bayonets broke into the Arrow Cross house and rescued everyone. Among those saved were Lars Ernster, who fled to Sweden and became a member of the board of the Nobel Foundation from 1977 to 1988, and Jacob Steiner, who fled to Israel and became a professor at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Steiner’s father had been shot dead by Arrow Cross militiamen 25 December 1944, and fell into the Danube. His father had been an officer in World War I and spent four years as a prisoner of war in Russia. These were horrific murders, and after looking at the pictures of this memorial and reading about the horrible murders, my mind cannot unsee the images it has conjured up of this atrocity.
Vadasz Street to the banks of the Danube. At midnight, Karoly Szabo and 20 policemen with drawn bayonets broke into the Arrow Cross house and rescued everyone. Among those saved were Lars Ernster, who fled to Sweden and became a member of the board of the Nobel Foundation from 1977 to 1988, and Jacob Steiner, who fled to Israel and became a professor at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Steiner’s father had been shot dead by Arrow Cross militiamen 25 December 1944, and fell into the Danube. His father had been an officer in World War I and spent four years as a prisoner of war in Russia. These were horrific murders, and after looking at the pictures of this memorial and reading about the horrible murders, my mind cannot unsee the images it has conjured up of this atrocity.
 When disaster strikes, and homes are in ruin, people try to come together to help return a sense of normalcy to the people affected by the disaster. Disasters happen quickly, and the devastation is often heavy. It is a difficult thing to help people heal. While one disaster or event is often the same as another in terms of damage, something we somehow don’t connect to that same kind of devastation, is war. I’m not sure why, but when I think of war,I picture a battle held in the middle of a vast desert, with no civilization in sight. of course, when I really think about it, I now that is not reality, but rather my mind trying to fit war into a box of civility. In reality, there is nothing civil about war. Gun shots, bombs, and land mines aren’t picky about who they hit. Soldier or civilian…all are fair game in a war. And towns…well, there is often little to nothing left after a bomb hits.
When disaster strikes, and homes are in ruin, people try to come together to help return a sense of normalcy to the people affected by the disaster. Disasters happen quickly, and the devastation is often heavy. It is a difficult thing to help people heal. While one disaster or event is often the same as another in terms of damage, something we somehow don’t connect to that same kind of devastation, is war. I’m not sure why, but when I think of war,I picture a battle held in the middle of a vast desert, with no civilization in sight. of course, when I really think about it, I now that is not reality, but rather my mind trying to fit war into a box of civility. In reality, there is nothing civil about war. Gun shots, bombs, and land mines aren’t picky about who they hit. Soldier or civilian…all are fair game in a war. And towns…well, there is often little to nothing left after a bomb hits.
During World War II, London was often the targets of the German Luftwaffe, and the bombs they dropped, devastated many parts of London. From September 7, 1940, London was systematically bombed by the Luftwaffe for 56 out of the following 57 days and nights, in what was called “The Blitz.” Most notable was a large daylight attack against London on September 15th. Of course, these weren’t the only bombings, and the people of London didn’t know when or if it was safe to be out of the bomb shelters. Life in London had taken on eerie gloom,as people continued to seek refuge in the bomb shelters, because that was the only safe place to be. The biggest problem was that the bomb shelters were also gloomy, boring, and generally depressing. The children probably suffered the most, because kids don’t really understand all this hatred and killing. Their world had been turned upside down…and they didn’t know why.
By the end of 1940, 24,000 civilians had been killed in the Blitz and hundreds of thousands made homeless. In November, German bombers had obliterated Coventry city center and there had been particularly fierce raids on Manchester and Liverpool in the days leading up to Christmas. The public were now mourning the loss of their loved ones on the home front and in combat, as well as praying for the 41,000 British soldiers captured on the continent, but it was the children, in my mind, who suffered the most. Their childlike innocence was completely destroyed, along with their homes. Their parents, and other adults made the decision to change their little world, even if it was only for a short time. They didn’t have much, but they put together whatever they could to lift the spirits of these scared children. Christmas parties were held for the children and the shelter walls were decorated with paper chains and decorations, while amateur singing nights, discussion groups, and sewing circles were held regularly.
In order to avoid the bombs, many families spent some of the holidays in air-raid shelters and other places of refuge. They decked out their temporary homes with makeshift decorations…and very short Christmas trees because of the height of the shelters. Even if gas or electricity was available, Christmas dinner would have still been an amazing feat, because turkey was so expensive. Most people made do with other cuts of meat, which were still expensive. A family of four’s weekly meat ration probably wouldn’t even cover the cost of a small chicken. One alternative was home-raised chickens or rabbits, much to the shock of young children who often regarded them as pets. Home-grown vegetables and chutneys would have also made the table. Rations were  scrimped and saved including ham, bacon, butter, suet, and margarine. The tea and sugar rations were increased in the week before Christmas. Very little fruit was imported and nuts were very costly. Consequently, cooks had to improvise Christmas cakes and puddings devoid of dried fruit and marzipan, using instead sponge or other unlikely ingredients. Alcohol was available but, horribly expensive. And there would be no after-dinner French cheeses or brandy due to the German occupation. It was a poor Christmas party in comparison to those in the past, but it served to remind all the people that Christmas is more about the blessings in life, than it is about the things we are given.
scrimped and saved including ham, bacon, butter, suet, and margarine. The tea and sugar rations were increased in the week before Christmas. Very little fruit was imported and nuts were very costly. Consequently, cooks had to improvise Christmas cakes and puddings devoid of dried fruit and marzipan, using instead sponge or other unlikely ingredients. Alcohol was available but, horribly expensive. And there would be no after-dinner French cheeses or brandy due to the German occupation. It was a poor Christmas party in comparison to those in the past, but it served to remind all the people that Christmas is more about the blessings in life, than it is about the things we are given.

 As the chief architect and minister for armaments and war production, Albert Speer designed many of the great buildings that Hitler craved. Hitler loved having the very best. Hitler was always impressed by academic credentials and any kind of artistic or technical talent, so he made Speer his personal architect. Albert Speer was born March 19, 1905, in Mannheim, Germany. At the age of 22, he received his architectural license, having studied at three German technical schools. He became an ardent Nazi after hearing Hitler speak at a rally in late 1930, and joined the party in January 1931. It was his decision to become a Nazi that gave him the opportunity to be noticed by Hitler.
As the chief architect and minister for armaments and war production, Albert Speer designed many of the great buildings that Hitler craved. Hitler loved having the very best. Hitler was always impressed by academic credentials and any kind of artistic or technical talent, so he made Speer his personal architect. Albert Speer was born March 19, 1905, in Mannheim, Germany. At the age of 22, he received his architectural license, having studied at three German technical schools. He became an ardent Nazi after hearing Hitler speak at a rally in late 1930, and joined the party in January 1931. It was his decision to become a Nazi that gave him the opportunity to be noticed by Hitler.
It was the fact that he now worked for Hitler, that gave him the power he craved for himself. Hitler began a massive Berlin building program. Among the projects the Fuhrer entrusted Speer with was the design of the parade grounds for the Nuremberg Party Congress in 1934, which Leni Riefienstahl made famous in her famous propaganda film Triumph of the Will. As minister of armaments and munitions, Speer’s job description expanded to include not only armament production and transportation, but also the direction of raw material use and finally the conscription of slave labor, culled from concentration camps, for war material production. On this day, November 21, 1941, Speer approached Hitler, and asked for 30,000 Soviet prisoners to be slave labor for his projects,telling Hitler that these slave laborers would come in handy for his “new” Berlin. Speer wanted to begin construction even as the war waged. Despite the drain on resources Hitler agreed. Speer beguiled the Fuhrer with models of a Great Hall for the Chancellery and a grand office for Goering. I find it strange to think that someone finally pulled a few things over on Hitler, who always seemed to have the upper hand.
The program was going well, but the times were not in Speer’s favor, or Hitler’s. The war turned against Nazi Germany, the rebuilding plans were scrapped. When the war was over, Hitler was dead by his own hand, and Speer was tried as a war criminal at Nuremberg, the site of his grand parade, and sentenced to 20 years in prison for his role in the Nazi regime, principally for the use of forced labor. Despite repeated attempts to gain early release, he served his full sentence, most of it at Spandau Prison in West Berlin. Following his release in 
 1966, Speer published two bestselling autobiographical works, Inside the Third Reich and Spandau: The Secret Diaries, detailing his close personal relationship with Hitler, and providing readers and historians with a unique perspective on the workings of the Nazi regime. He wrote a third book, Infiltration, about the SS. Speer died of a stroke in 1981 while on a visit to London.
1966, Speer published two bestselling autobiographical works, Inside the Third Reich and Spandau: The Secret Diaries, detailing his close personal relationship with Hitler, and providing readers and historians with a unique perspective on the workings of the Nazi regime. He wrote a third book, Infiltration, about the SS. Speer died of a stroke in 1981 while on a visit to London.

 In the middle of a war, the people of a nation become concerned about anyone who might potentially be the enemy, especially if they are living inside the country’s borders. It is really a natural reaction to enemy personnel. After the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor, the United states became quite concerned about the Japanese immigrants in our country, whether they were here legally or not. Much of the immigration to the United States from Japan began in 1884, when thousands of Japanese arrived in Hawaii to work the sugar cane fields. In the wake of the 1882 Chinese Exclusion Act, which drastically restricted Chinese immigration, Japanese people began arriving and began to prosper and started small businesses or became farmers. Most of them settled along the West Coast, meaning roughly 13,000 people of Japanese descent lived in the Intermountain West prior to World War II. The attack on Pearl Harbor, heightened the level of concern about those people.
In the middle of a war, the people of a nation become concerned about anyone who might potentially be the enemy, especially if they are living inside the country’s borders. It is really a natural reaction to enemy personnel. After the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor, the United states became quite concerned about the Japanese immigrants in our country, whether they were here legally or not. Much of the immigration to the United States from Japan began in 1884, when thousands of Japanese arrived in Hawaii to work the sugar cane fields. In the wake of the 1882 Chinese Exclusion Act, which drastically restricted Chinese immigration, Japanese people began arriving and began to prosper and started small businesses or became farmers. Most of them settled along the West Coast, meaning roughly 13,000 people of Japanese descent lived in the Intermountain West prior to World War II. The attack on Pearl Harbor, heightened the level of concern about those people.
It was decided that, because their loyalties could not positively be confirmed, the Japanese immigrants needed to be rounded up and put in concentration camps. I suppose this might have seemed similar to what the Germans did to the Jewish people, but the Japanese people were not murdered in the camps, like the Jews were. And so it came to be that the people of Japanese descent from Oregon, Washington and California were incarcerated at the Heart Mountain Relocation Center in Park County, Wyoming, by the executive order of President Franklin Roosevelt. The prisoners were held at the camp from August 12, 1942 to November 10, 1945, which was actually two months after the end of the war with Japan. The camp was populated with 10,000 people at its largest, making it the third largest town in the state at the time.
I have tried to imagine what it must have been like for those Japanese immigrants to be held in the Heart Mountain Relocation Center for as much as 2 years and 3 months. Of course, the illegal immigrants of our time immediately came to my mind, but there is a difference between these people and the illegal immigrants of today. These people were here legally, and most of them had already become citizens. Unfortunately, that did not calm the worried minds of the rest of the people of the United States. Our nation had been attacked, and the attackers looked just like the Japanese immigrants. Precautions had to be taken. I’d like to think that if it were me, in that position, that I would understand why this was happening, but I’m not so sure I would. After all, these people were not criminals. They were hard working Americans, and yet they were for a time…the enemy, or possibly the enemy.
Unfortunately, like many prior immigrant groups, the Japanese faced discrimination. Things aren’t always fair, and people aren’t always treated properly. Starting in the early 20th century, Japanese immigrants, as well as Chinese immigrants, were targeted by Alien Land Laws in western states including Wyoming. These laws prevented the Asian immigrants from buying land. In 1924, the United States Congress passed the Asian Exclusion Act, which all but cut off new immigration from Asia. In response, Japanese Americans formed organizations such as the Japanese American Citizens’ League to help address their shared challenges. Despite  the attempts of Japanese Americans to fit in, some people expressed ongoing skepticism regarding the place of Asians in American society.
the attempts of Japanese Americans to fit in, some people expressed ongoing skepticism regarding the place of Asians in American society.
The Heart Mountain facility consisted of 450 barracks, each containing six apartments, when the first internees arrived on August 12, 1942. The largest apartments were simply single rooms measuring 24 feet by 20 feet. The barracks were covered with tar paper. While each unit was eventually outfitted with a potbellied stove, none had bathrooms. The people all used shared latrines. None of the apartments had kitchens. The residents ate their meals in mess halls. When the people first arrived, a barbed-wire fence to surround the camp was not yet complete. The internees protested the construction of this barrier and caused further work to be delayed. In November 1942, they submitted a petition containing 3,000 signatures to the War Relocation Authority (WRA) Director Dillon Meyer. The fence was completed by December, however, and further emphasized the sense of confinement among the internees. Shortly after the construction of the fence, 32 boys were arrested for sledding in the hills beyond the boundary. In response to the perceived overreaction on the part of the camp administration, Rikio Tomo, a Heart Mountain internee, placed an editorial in the Heart Mountain Sentinel asking for clarification about the internees’ citizenship status and constitutional freedoms. Schools were built at Heart Mountain, including a high school, to accommodate the children. These schools served students from elementary school through high school. Roughly 1500 students attended Heart Mountain High School, which included grades 8-12.
The internees provided most of the labor required to run the Heart Mountain camp, while WRA administrators oversaw its general operations. Wages ranged from $12 per month for unskilled labor to $19 per month for skilled labor, including teachers for the schools and doctors in the camp hospitals. In addition, Heart Mountain internees also worked as manual laborers on farms and ranches in Wyoming and nearby states from Nebraska to Oregon. The WRA administrators encouraged activities emphasizing American civics, such as scouting and adult English classes, as part of what they saw as an Americanization process. Committees composed initially of American-born internees provided much of the day-to-day governance of the camps. While these groups provided some measure of self-determination, they disrupted the generational hierarchy. American-born adults in their 20s and 30s were given a higher political status within the camps than their Japanese-born parents.
In 1943, General George Marshall approved the creation of the Japanese-American combat unit. As a result of the low turnout, the War Department extended the draft to the camps. It was decided that while they were not free to go where they chose, these people were needed to serve their country, so a draft was instituted. After they were drafted into the U.S. Army, soldiers from Heart Mountain occasionally returned to visit their families who were still held there. Somehow that doesn’t seem quite fair to me, and many of the prisoners agreed. They thought they should have been given their constitutional rights back before they were drafted. The organization of draft resistance distinguished Heart Mountain from the other relocation centers. The plan, which was given the endorsement of President Roosevelt, was to create an all-Japanese regiment, consisting of soldiers from a previously existing Hawaiian unit and volunteers from the camps. The response from within the camps fell far short of expectations, partly because of a loyalty questionnaire distributed by the WRA. The WRA form was used to determine eligibility for military service and permanent leave. Many of the questions were considered intrusive by prisoners. Others were not as straightforward as the WRA probably intended. Instead of serving as a neutral tool to determine someone’s suitability for service, the questionnaire further alienated many the men. To me it seems that the WRA was somehow not aware of how racist the entire situation really was. For example, question 27 asked about a person’s willingness to serve in the military. For 
 prisoners who felt service should be contingent upon the restoration of constitutional rights to all Japanese Americans, a simple yes or no answer was insufficient. In each of the camps, the draft became a divisive issue. While some prisoners felt military service was an opportunity to exemplify patriotism, others felt that constitutional rights should be restored before agreeing to mandatory service. I doubt if the situation would have ever really been resolved, except that the war ended.
prisoners who felt service should be contingent upon the restoration of constitutional rights to all Japanese Americans, a simple yes or no answer was insufficient. In each of the camps, the draft became a divisive issue. While some prisoners felt military service was an opportunity to exemplify patriotism, others felt that constitutional rights should be restored before agreeing to mandatory service. I doubt if the situation would have ever really been resolved, except that the war ended.
 Anthony Joseph Drexel Biddle I (1874–1948) was an eccentric millionaire whose fortune allowed him to pursue theatricals, self-published writing, athletics, and Christianity on a full-time basis. He was the man upon whom the book “My Philadelphia Father” and the play and film “The Happiest Millionaire” were based, but even before that Biddle was eccentric…to say the least. Biddle was a trainer in hand-to-hand combat in both World War I and World War II. In fact, Biddle was an expert in hand-to-hand combat. He also had an unusual way of training his men. It was not unusual for Biddle to tell his trainees to attempt to kill him!! I can’t say for sure that he allowed them to use live ammunition, but he did give them “chance” to try to kill him before he could disarm them.
Anthony Joseph Drexel Biddle I (1874–1948) was an eccentric millionaire whose fortune allowed him to pursue theatricals, self-published writing, athletics, and Christianity on a full-time basis. He was the man upon whom the book “My Philadelphia Father” and the play and film “The Happiest Millionaire” were based, but even before that Biddle was eccentric…to say the least. Biddle was a trainer in hand-to-hand combat in both World War I and World War II. In fact, Biddle was an expert in hand-to-hand combat. He also had an unusual way of training his men. It was not unusual for Biddle to tell his trainees to attempt to kill him!! I can’t say for sure that he allowed them to use live ammunition, but he did give them “chance” to try to kill him before he could disarm them.
An officer in the United States Marine Corps, Biddle was an expert in close-quarters fighting and the author of “Do or Die: A Supplementary Manual on Individual Combat,” a book on combat methods, including knives and empty-hand skills, training both the United States Marine Corps in two world wars and Special Agents of the Federal Bureau of Investigation. He was considered not just an expert in fighting, but also a pioneer of United States Marine Corps training in the bayonet and hand-to-hand combat. He based his style on fencing, though this approach was sometimes criticized as being unrealistic for military combat. At one point, when it looked like there was no way out of a drill he assigned to his men…they were surrounding him, and for all intents and  purposes, they had him. Nevertheless, the outcome was not what anyone would have expected, because within in a few minutes, Biddle had completely disarmed each and every one of the men.
purposes, they had him. Nevertheless, the outcome was not what anyone would have expected, because within in a few minutes, Biddle had completely disarmed each and every one of the men.
Born on October 1, 1874 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to Edward Biddle II and Emily Drexel, Anthony was grandson of banker Anthony Joseph Drexel, and great-grandson of banker Nicholas Biddle. Biddle was a graduate of Germany’s Heidelberg University. He was a fellow of the American Geographical Society and founded a movement called “Athletic Christianity” that eventually attracted 300,000 members around the world. A 1955 Sports Illustrated article called him “boxing’s greatest amateur” as well as a “major factor in the re-establishment of boxing as a legal and, at that time, estimable sport.” He joined the Marines in 1917 at the age of 41, and convinced his superiors to include boxing in Marine Corps recruit training. In 1919, he was promoted to the rank of major, and became a lieutenant colonel in 1934. In Lansdowne, Pennsylvania, right outside of Philadelphia, Biddle opened a military training facility, where he trained 4,000 men. His training included long hours of calisthenics and gymnastics, and taught skills such as machete, saber, dagger, bayonet combat, hand grenade use, boxing, wrestling, savate and jiujitsu. He also served two years in the National Guard.
 In 1895, he married Cordelia Rundell Bradley. Their marriage was blessed with three children, Anthony Joseph Drexel Biddle Jr. (1897–1961), who married Mary Duke (1887–1960). They were the parents of Mary Duke Biddle (1920–2012) and Nicholas Benjamin Duke Biddle. Their second child was Cordelia Drexel Biddle (1898–1984), who married Angier Buchanan Duke (1884–1923), the son of Benjamin Newton Duke. They were the parents of Angier Biddle Duke (1915–1995) and Anthony Drexel Duke (1918-2014). Their third child was Livingston Ludlow Biddle (1899–1981), who married Kate Raboteau Page (b. 1903), daughter of Robert N. Page. They were the parents of Livingston Ludlow Biddle III. Biddle died May 27, 1948 from a cerebral hemorrhage and uremic poisoning.
In 1895, he married Cordelia Rundell Bradley. Their marriage was blessed with three children, Anthony Joseph Drexel Biddle Jr. (1897–1961), who married Mary Duke (1887–1960). They were the parents of Mary Duke Biddle (1920–2012) and Nicholas Benjamin Duke Biddle. Their second child was Cordelia Drexel Biddle (1898–1984), who married Angier Buchanan Duke (1884–1923), the son of Benjamin Newton Duke. They were the parents of Angier Biddle Duke (1915–1995) and Anthony Drexel Duke (1918-2014). Their third child was Livingston Ludlow Biddle (1899–1981), who married Kate Raboteau Page (b. 1903), daughter of Robert N. Page. They were the parents of Livingston Ludlow Biddle III. Biddle died May 27, 1948 from a cerebral hemorrhage and uremic poisoning.

