World War II

 World War II brought with it necessary changes to war ships. Suddenly, the world had planes that could fly greater distances, and even had the ability to land on a ship, provided the ship was big enough to have a relatively short runway. I say relatively short, because the runways on ships seemed like they would be too short to safely land a plane, but they did. One such ship was the HMS Ark Royal.
World War II brought with it necessary changes to war ships. Suddenly, the world had planes that could fly greater distances, and even had the ability to land on a ship, provided the ship was big enough to have a relatively short runway. I say relatively short, because the runways on ships seemed like they would be too short to safely land a plane, but they did. One such ship was the HMS Ark Royal.
The Ark Royal was an English ship designed in 1934 to fit the restrictions of the Washington Naval Treaty. The ship was built by Cammell Laird at Birkenhead, England, and was completed in November 1938. The design of this ship differed from previous aircraft carriers, in that Ark Royal was the first ship on which the hangars and flight deck were an integral part of the hull, instead of an add-on or part of the superstructure. This ship was designed to carry a large number of aircraft. There were two hangar deck levels. HMS Ark Royal served during a period of time during which we first saw the extensive use of naval air power. The Ark Royal played an integral part in developing and refining several carrier tactics.
HNS Ark Royal served in some of the most active naval theatres of the World War II. The ship was involved in the first aerial and U-boat kills of the war, operations off Norway, the search for the German battleship Bismarck, and the Malta Convoys. After Ark Royal survived several near misses, she became known as a “lucky ship” and the reputation stuck…at least until November 13, 1941, when the German submarine U-81 torpedoed her and she sank the following day. Nevertheless, only one of her 1,488 crew members was killed. Her sinking was the subject of several inquiries. While only one man was killed, investigators still couldn’t figure out how the carrier was lost…in spite of efforts to tow her to the naval base at Gibraltar. In the end, they found that several design flaws contributed to the loss. These flaws were rectified in subsequent British carriers. There was, of course, no time to look for the ship then. The war was still going on.


The wreck was discovered in December 2002 by an American underwater survey company using sonar mounted on an autonomous underwater vehicle. The company was under contract from the BBC for the filming of a documentary about the HMS Ark Royal. The ship was at a depth of about 3,300 feet and approximately 30 nautical miles from Gibraltar. So close, and yet so far away.
 Every four years, Americans go to the polls to elect a new president. Looking at the first time that a president is elected, quite often, we know little about the person running for president. Even if they have been in Congress, it takes some digging to really discover who they are, and what they can do for our nation. We rely on things like the political party they belong to or the campaign promises they make. Still, we have no idea what the candidate will really do, until they are in office.
Every four years, Americans go to the polls to elect a new president. Looking at the first time that a president is elected, quite often, we know little about the person running for president. Even if they have been in Congress, it takes some digging to really discover who they are, and what they can do for our nation. We rely on things like the political party they belong to or the campaign promises they make. Still, we have no idea what the candidate will really do, until they are in office.
Sometimes, there are exceptions to that basic rule, however. Such was the case with Dwight D Eisenhower, who was the supreme commander of Allied forces in Western Europe during World War II. Of course, running a nation is not the same as running a war, unless the nation happens to be at war, that is. Nevertheless, a commander who excelled at leading a war, was by definition, a leader…making it a good bet that he could also lead a nation. Eisenhower was that kind of leader, and the people of the United States could see it clearly. He led the massive invasion of Nazi-occupied Europe that began on D-Day…June 6, 1944. Then in 1952, with victory under his belt, leading Republicans convinced Eisenhower, who by then was in command of NATO forces in Europe, to run for president. As the campaign progressed, it would remain to be seen, just how much the people of the United States thought that he would make a good leader for the nation. The election would be the telling point.
And so it went. Eisenhower won a convincing victory over Democrat Adlai Stevenson and would serve two terms in the White House (1953-1961). Even more amazing than his victory was the fact that General Dwight D Eisenhower won the American presidential elections with the largest number of popular votes ever recorded for a presidential candidate. It was a landslide victory. The people had spoken. Also of note, is that Eisenhower was the only other president to win the presidential election, having never served in any other political office. I’m sure everyone knows that the other president to do that is our current president…Donald Trump. That is an almost unheard of feat. A general and a businessman, both of whom had not been politically inclined, and yet, here they were. During his presidency, Eisenhower managed Cold War-era tensions with the Soviet Union under the looming threat of nuclear weapons, ended the war in Korea in 1953 and authorized a number of covert anti-communist operations by the CIA around the world. Here at home, America was in a period of relative prosperity, nevertheless, Eisenhower strengthened Social Security and created the massive new Interstate Highway System. Eisenhower was so well liked that he would beat Stevenson again four years later in a landslide to win re-election, despite health concerns after suffering a heart attack in 1955.

Eisenhower was born in Denison, Texas, on October 14, 1890. He grew up in Abilene, Kansas, as the third of seven sons in a poor family. His mother, a devout Mennonite and pacifist, was quite distressed when young Ike…as he was known…won an appointment to the US Military Academy at West Point, New York. Nevertheless, he went on to graduate in the middle of his class in 1915. While stationed as a second lieutenant in San Antonio, Texas, Eisenhower met Mamie Geneva Doud. The couple married in 1916 and had two sons, Doud Dwight, who died of scarlet fever as a small child, and John. World War I ended just before Eisenhower was scheduled to go to Europe, which was frustrating to the young officer, but he soon managed to acquire an appointment to the Command and General Staff College at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas. Graduating first in his class of 245, he served as a military aide to General John J Pershing, commander of US forces during World War I, and later to General Douglas MacArthur, US Army chief of staff. During his seven years serving under MacArthur, Eisenhower was stationed in the Philippines from 1935 to 1939.
Eisenhower returned soon after Nazi Germany’s invasion of Poland sparked the outbreak of World War II in Europe. In September 1941, he received his first general’s star with a promotion to brigadier general. After Japan attacked Pearl Harbor that December, US Army Chief of Staff General George C Marshall called Eisenhower to Washington, DC to work as a planning officer. Beginning in November 1942, Eisenhower headed Operation Torch, the successful Allied invasion of North Africa. He then directed the amphibious invasion of Sicily and the Italian mainland in 1943 that led to the fall of Rome in June 1944. In early 1943, he was made a full general. Eisenhower was appointed supreme commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force in December of that year and given the responsibility of spearheading the planned Allied invasion of Nazi-occupied Europe. On D-Day…June 6, 1944, more than 150,000 Allied forces crossed the English Channel and stormed the beaches of Normandy. The invasion led to the liberation of Paris on August 25 and turned the tide of the war in Europe decisively in the Allied direction. Having risen from lieutenant colonel in the Philippines to supreme commander of the victorious forces in Europe in only five years, Eisenhower returned home to a hero’s welcome in 1945 to serve as chief of staff of the US Army.
In 1948, Eisenhower left active duty and became president of New York City’s Columbia University. His brief 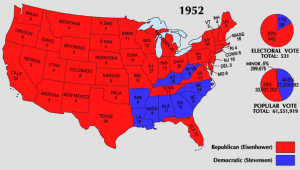 return to civilian life ended in 1950, however, when President Harry S Truman asked him to take command of the new North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) forces in Europe. In that position, Eisenhower worked to create a unified military organization that would combat potential communist aggression around the globe. As President of the United States, while weathering criticism from both left and right, Eisenhower enjoyed high approval ratings throughout his administration. After leaving office in January 1961, he retired to his farm in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. He worked largely on his memoirs, and would publish several books over the following years. He died on March 28, 1969, after a long illness.
return to civilian life ended in 1950, however, when President Harry S Truman asked him to take command of the new North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) forces in Europe. In that position, Eisenhower worked to create a unified military organization that would combat potential communist aggression around the globe. As President of the United States, while weathering criticism from both left and right, Eisenhower enjoyed high approval ratings throughout his administration. After leaving office in January 1961, he retired to his farm in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. He worked largely on his memoirs, and would publish several books over the following years. He died on March 28, 1969, after a long illness.

 When a person travels for business, they find that they really understand the importance of home. My niece, Susan Griffith is one of the many people who travel as part of their job. Susan works for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Wyoming, as a Client Development Executive, basically she is a health insurance agent. She travels to Cheyenne about twice a year around the time people have to update their insurance…open enrollment. She has to go for training. She has to travel around the Bighorn Basin for getting different companies signed up for Blue Cross. Because Susan has to travel for work, she knows how it feels to have to spend that time away from family. Everyone I have talked to about traveling for work has told me that they had little tricks to make a hotel room feel more like home. I don’t know if Susan has a way that helps her or not, but I do know that her home and her family are the most important things in her life. Nevertheless, travel time aside, Susan loves her job!!
When a person travels for business, they find that they really understand the importance of home. My niece, Susan Griffith is one of the many people who travel as part of their job. Susan works for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Wyoming, as a Client Development Executive, basically she is a health insurance agent. She travels to Cheyenne about twice a year around the time people have to update their insurance…open enrollment. She has to go for training. She has to travel around the Bighorn Basin for getting different companies signed up for Blue Cross. Because Susan has to travel for work, she knows how it feels to have to spend that time away from family. Everyone I have talked to about traveling for work has told me that they had little tricks to make a hotel room feel more like home. I don’t know if Susan has a way that helps her or not, but I do know that her home and her family are the most important things in her life. Nevertheless, travel time aside, Susan loves her job!!
Susan and her husband, Josh Griffith love to go camping in the mountains. They, like other members of her 
 family, would live in the mountains, if it weren’t for jobs or school for their girls, Jala Satterwhite and Kaytlyn Griffith. They go camping every chance they get. They love to hike, and this year, they hiked Heart Mountain, which is relatively near their home in Powell, Wyoming. Heart Mountain gained world fame in World War II, when it was used as a concentration camp to hold Japanese-American citizen, after the attack on Pearl Harbor. Many people weren’t sure where Japanese-American loyalties lay, so the didn’t take a chance, and moved the people to camps. It was a sad, but understandable time. Susan’s family also hiked to Copper Lake in the Beartooth Mountains, but they don’t think they will try that one again, because in Susan’s own words, “It was crazy hard!!” This past year, they did something a little different too. San Diego can’t exactly be considered camping in the mountains. Nevertheless, they had a great time. They went to Sea World, and all the other great attractions of the area, including the ocean.
family, would live in the mountains, if it weren’t for jobs or school for their girls, Jala Satterwhite and Kaytlyn Griffith. They go camping every chance they get. They love to hike, and this year, they hiked Heart Mountain, which is relatively near their home in Powell, Wyoming. Heart Mountain gained world fame in World War II, when it was used as a concentration camp to hold Japanese-American citizen, after the attack on Pearl Harbor. Many people weren’t sure where Japanese-American loyalties lay, so the didn’t take a chance, and moved the people to camps. It was a sad, but understandable time. Susan’s family also hiked to Copper Lake in the Beartooth Mountains, but they don’t think they will try that one again, because in Susan’s own words, “It was crazy hard!!” This past year, they did something a little different too. San Diego can’t exactly be considered camping in the mountains. Nevertheless, they had a great time. They went to Sea World, and all the other great attractions of the area, including the ocean.

 With all her traveling nearby, and far away, Susan somehow still finds time to grow a garden. This year, she had a good crop of onions and asparagus…just to name a couple. When she isn’t traveling or camping/hiking, Susan likes to be home. She enjoys nesting, and being with her family. In all, Susan lives a well rounded life, and finds herself very happy in it. Today is Susan’s birthday. Happy birthday Susan!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
With all her traveling nearby, and far away, Susan somehow still finds time to grow a garden. This year, she had a good crop of onions and asparagus…just to name a couple. When she isn’t traveling or camping/hiking, Susan likes to be home. She enjoys nesting, and being with her family. In all, Susan lives a well rounded life, and finds herself very happy in it. Today is Susan’s birthday. Happy birthday Susan!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
 Sometimes, it’s a close call that saves the life of a person, because a difference of inches could have meant the difference between life and death. That was the case for young Corporal Adolf Hitler when he was temporarily blinded on October 14, 1918, by a gas shell that was close enough to temporarily blind him, but unfortunately for the rest of the world, not close enough to kill him. The British shell was part of an attack at Ypres Salient in Belgium, and in the aftermath, Hitler found himself evacuated to a German military hospital at Pasewalk, in Pomerania. Of course, Hitler considered this a great good fortune, with the exception of the temporary blindness. I find myself wishing that the shell had been closer, because the difference of inches could have changed the world, and especially the victims of the Holocaust.
Sometimes, it’s a close call that saves the life of a person, because a difference of inches could have meant the difference between life and death. That was the case for young Corporal Adolf Hitler when he was temporarily blinded on October 14, 1918, by a gas shell that was close enough to temporarily blind him, but unfortunately for the rest of the world, not close enough to kill him. The British shell was part of an attack at Ypres Salient in Belgium, and in the aftermath, Hitler found himself evacuated to a German military hospital at Pasewalk, in Pomerania. Of course, Hitler considered this a great good fortune, with the exception of the temporary blindness. I find myself wishing that the shell had been closer, because the difference of inches could have changed the world, and especially the victims of the Holocaust.
Like many young men of the period, Hitler was drafted for Austrian military service, but when he reported, he was turned down due to lack of fitness. In the summer of 1914, Hitler had moved to Munich. When World War I began, he asked for and received special permission to enlist as a German soldier. It all seemed like a noble thing to do. Hitler was a member of the 16th Bavarian Reserve Infantry Regiment. He traveled to France in October 1914. There, he saw heavy action during the First Battle of Ypres, earning the Iron Cross that December for dragging a wounded comrade to safety. These things rather surprise me, give Hitler’s reputation for thinking only of himself.
Over the course of the next two years, Hitler took part in some of the fiercest struggles of the war, including  the Battle of Neuve Chapelle, the Second Battle of Ypres and the Battle of the Somme. He was wounded in the leg by a shell blast on October 7, 1916, near Bapaume, France. Following his hospital stay. Hitler was sent to recover near Berlin, after which he returned to his old unit by February 1917. According to Hans Mend, a comrade of Hitler, he was given to rants on the dismal state of morale and dedication to the cause on the home front in Germany. According to Mend, “He sat in the corner of our mess holding his head between his hands in deep contemplation. Suddenly he would leap up, and running about excitedly, say that in spite of our big guns victory would be denied us, for the invisible foes of the German people were a greater danger than the biggest cannon of the enemy.” It would seem that Hitler’s crazed mind was beginning to present itself. As I look at a picture of Hitler as a young man, I wonder what happened to him that changed him so much. Yung Hitler didn’t look like the crazed, evil dictator the world knew
the Battle of Neuve Chapelle, the Second Battle of Ypres and the Battle of the Somme. He was wounded in the leg by a shell blast on October 7, 1916, near Bapaume, France. Following his hospital stay. Hitler was sent to recover near Berlin, after which he returned to his old unit by February 1917. According to Hans Mend, a comrade of Hitler, he was given to rants on the dismal state of morale and dedication to the cause on the home front in Germany. According to Mend, “He sat in the corner of our mess holding his head between his hands in deep contemplation. Suddenly he would leap up, and running about excitedly, say that in spite of our big guns victory would be denied us, for the invisible foes of the German people were a greater danger than the biggest cannon of the enemy.” It would seem that Hitler’s crazed mind was beginning to present itself. As I look at a picture of Hitler as a young man, I wonder what happened to him that changed him so much. Yung Hitler didn’t look like the crazed, evil dictator the world knew
Hitler continued to earn citations for bravery over the next year, including an Iron Cross 1st Class for “personal bravery and general merit” in August 1918 for single-handedly capturing a group of French soldiers hiding in a shell hole during the final German offensive on the Western Front. Then, on October 14, 1918, Hitler received the injury that put an end to his service in World War I. He learned of the German surrender while recovering at Pasewalk. Hitler was furious and frustrated by the news. He said, “I staggered and stumbled back to my  ward and buried my aching head between the blankets and pillow.” Hitler felt he and his fellow soldiers had been betrayed by the German people. I’m amazed that he did not put them in the camps too. In 1941, Hitler as Führer would reveal the degree to which his career and its terrible legacy had been shaped by the World War I, writing that “I brought back home with me my experiences at the front; out of them I built my National Socialist community.”
ward and buried my aching head between the blankets and pillow.” Hitler felt he and his fellow soldiers had been betrayed by the German people. I’m amazed that he did not put them in the camps too. In 1941, Hitler as Führer would reveal the degree to which his career and its terrible legacy had been shaped by the World War I, writing that “I brought back home with me my experiences at the front; out of them I built my National Socialist community.”
When I think of what might have been, but for a difference of inches, I find it very ironic. If that shell had hit just a few inches closer, perhaps Hitler would have died a hero in his nation, before he could become the epitome of evil…to the world, and to many of his own people. I suppose World War I and II, as well as the other wars, would have still happened, but maybe, quite likely, the Holocaust would not have happened. Just a few inches. If only.
 There is good that comes from science, and there is bad too, unfortunately. Things like weapons of warfare would most likely fall into the bad that comes from science. Still, weapons are necessary, and maybe it isn’t the weapon that is bad, but rather the user. Wernher von Braun was a rocket scientist in Hitler’s Germany. His job was to build bigger and more dangerous weapons. The V-2 missile was the culmination of von Braun’s work so far. On October 3, 1942, von Braun tested the V-2 missile. The missile was fired successfully from Peenemunde, as island off Germany’s Baltic coast. It traveled 118 miles in that test; and later, in evil weapon style, it proved extraordinarily deadly in the war. The V-2 missile was the precursor to the Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) of the postwar era.
There is good that comes from science, and there is bad too, unfortunately. Things like weapons of warfare would most likely fall into the bad that comes from science. Still, weapons are necessary, and maybe it isn’t the weapon that is bad, but rather the user. Wernher von Braun was a rocket scientist in Hitler’s Germany. His job was to build bigger and more dangerous weapons. The V-2 missile was the culmination of von Braun’s work so far. On October 3, 1942, von Braun tested the V-2 missile. The missile was fired successfully from Peenemunde, as island off Germany’s Baltic coast. It traveled 118 miles in that test; and later, in evil weapon style, it proved extraordinarily deadly in the war. The V-2 missile was the precursor to the Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) of the postwar era.
German scientists, led by von Braun, had been working on the development of these long-range missiles since the 1930s. I don’t know if von Braun was doing this work by choice, which would make him very likely as evil as the weapons of destruction he made, or whether, like so many of the German people under Hitler’s evil rule, he simply had no say in the matter. Whatever the case may be, von Braun was good at what he did. The science, which clearly must have fascinated him, was a work to which he was well suited. He understood it. He knew how to make it do hat he wanted it to do, and become what he wanted it to become…or, at least what he was told to make it become. Still, it took time to perfect. Three trial launches had already failed. The fourth in the series, known as A-4,  finally saw the V-2, a 12-ton rocket capable of carrying a one-ton warhead, successfully launched. I wonder just how much pressure was on von Braun at that fourth launch attempt. Could it have cost him his life, or his freedom, if he did not successfully create this weapon that Hitler wanted so badly.
finally saw the V-2, a 12-ton rocket capable of carrying a one-ton warhead, successfully launched. I wonder just how much pressure was on von Braun at that fourth launch attempt. Could it have cost him his life, or his freedom, if he did not successfully create this weapon that Hitler wanted so badly.
The V-2 was unique in several ways. First, it was virtually impossible to intercept, making it a serious threat to anyone it was aimed at. Upon launching, the missile rises six miles straight up. Then, it proceeds on an arced course, cutting off its own fuel according to the range desired. The missile then tips over and falls on its target-at a speed of almost 4,000 miles per hour. That would make it extremely difficult to blow up in flight, since hitting something moving at that speed would take serious accuracy, and heat seeking missiles were not developed yet. The missile hits with such force that it burrows itself several feet into the ground before exploding. In addition, the missile had the potential of flying a distance of 200 miles, and the launch pads were portable, making them impossible to detect before firing.
September 6, 1944 became the first real use of the V-2, when two missiles were fired at Paris. On September 8, two more were fired at England, which would be followed by more than 1,100 more during the next six months. More than 2,700 British citizens died because of the rocket attacks. After the war, both the United States and the Soviet Union captured samples of the rockets for reproduction. They also captured the scientists  responsible for their creation. Following the war, von Braun was secretly moved to the United States, along with about 1,600 other German scientists, engineers, and technicians, as part of Operation Paperclip. He worked for the United States Army on an intermediate-range ballistic missile program, and he developed the rockets that launched the United States’ first space satellite Explorer 1.
responsible for their creation. Following the war, von Braun was secretly moved to the United States, along with about 1,600 other German scientists, engineers, and technicians, as part of Operation Paperclip. He worked for the United States Army on an intermediate-range ballistic missile program, and he developed the rockets that launched the United States’ first space satellite Explorer 1.
His group was assimilated into NASA, where he served as director of the newly formed Marshall Space Flight Center and as the chief architect of the Saturn V super heavy-lift launch vehicle that propelled the Apollo spacecraft to the Moon. He also advocated for a human mission to Mars. In 1967, von Braun was inducted into the National Academy of Engineering and in 1975, he received the National Medal of Science. Von Braun died on June 16, 1977 of pancreatic cancer in Alexandria, Virginia at age 65. He was buried at the Ivy Hill Cemetery. His gravestone quotes Psalm 19:1: “The heavens declare the glory of God; and the firmament sheweth his handywork” (KJV).
 After World War II, the GIs who had fought in the war, came home, eager to start their lives over. Many went to the car dealerships to buy new cars, only to find that there were no new cars to be found. What a bizarre thought!! In my entire lifetime, I don’t know of a time that new cars weren’t available, but there was a reason for the lack of new cars.
After World War II, the GIs who had fought in the war, came home, eager to start their lives over. Many went to the car dealerships to buy new cars, only to find that there were no new cars to be found. What a bizarre thought!! In my entire lifetime, I don’t know of a time that new cars weren’t available, but there was a reason for the lack of new cars.
During World War II, the whole United States “kicked in” on the war effort. The automobile industry changed the production in their factories from automobiles to whatever was needed for the war effort. The United States automakers manufactured a wide variety of vehicles, munitions, and more  for the government. They made tanks like the Fisher Body Grand Blanc, the Ford M10 Wolverine, and the M18 Hellcat, which were produced by the Buick Motor Car Division of General Motors. Some of the automakers were tasked with producing parts for planes, including the infamous Enola Gay. The 18-foot nose section of the fuselage was built by Chrysler. Chevrolet alone produced 60,000 engines for Pratt and Whitney cargo and bomber planes between 1942 and 1945, along with 500,000 trucks, 8 million artillery shells, and much more. The tire company, Firestone Tire and Rubber Company produced the 40 mm cannon gun mount one of which was placed on the deck of the USS Cod, while another was mounted on the
for the government. They made tanks like the Fisher Body Grand Blanc, the Ford M10 Wolverine, and the M18 Hellcat, which were produced by the Buick Motor Car Division of General Motors. Some of the automakers were tasked with producing parts for planes, including the infamous Enola Gay. The 18-foot nose section of the fuselage was built by Chrysler. Chevrolet alone produced 60,000 engines for Pratt and Whitney cargo and bomber planes between 1942 and 1945, along with 500,000 trucks, 8 million artillery shells, and much more. The tire company, Firestone Tire and Rubber Company produced the 40 mm cannon gun mount one of which was placed on the deck of the USS Cod, while another was mounted on the  stern of PT-305. Pontiac Motor Car Division built aerial launched torpedoes at its facilities in Pontiac, Michigan.
stern of PT-305. Pontiac Motor Car Division built aerial launched torpedoes at its facilities in Pontiac, Michigan.
By the time the World War II ended in 1945, the total value of goods produced by the United States auto industry for the war would exceed $29 million, equal to nearly $400,000,000 today. There had been no new cars built in the United States between early 1942 and late 1945. Once the war was over, automakers were again free to begin manufacturing new cars for the American public. That was all well and good, but it would take time to bring production of automobiles back up to speed. The first car built for civilian sale after World War II, was a Super Deluxe Ford. It rolled off the assembly line on July 3, 1945.

 As I have researched the infantry soldiers of World War II, my thought was that I was really thankful that my dad, Allen Spencer was not one of those men on the ground during the fighting. I felt bad for those men who were on the ground, fighting from the foxholes. I still do, because they were in constant danger. Bombs fall from the sky, and bullets fly from across the battlefield. If those things didn’t kill a soldier, the freezing cold, trench foot, or dysentery from the horribly unsanitary conditions could. It seemed that my dad’s situation was by far safer, but now, I’m not so sure that’s true.
As I have researched the infantry soldiers of World War II, my thought was that I was really thankful that my dad, Allen Spencer was not one of those men on the ground during the fighting. I felt bad for those men who were on the ground, fighting from the foxholes. I still do, because they were in constant danger. Bombs fall from the sky, and bullets fly from across the battlefield. If those things didn’t kill a soldier, the freezing cold, trench foot, or dysentery from the horribly unsanitary conditions could. It seemed that my dad’s situation was by far safer, but now, I’m not so sure that’s true.
The book I had been listening to, that took in World War II from D-Day to The Battle of the Bulge, talked mostly about the ground war, but then at the end, the reader said something that really struck me. It was about the look that crossed the face of a bomber crew’s faces before certain missions…those that would inevitably find the plane flying through flak. The look was one of fear. I knew flak was dangerous, but somehow I didn’t really connect flak with bringing down a plane, or seriously injuring its occupants. Nevertheless, it is quite dangerous for them.
As I researched the dangers of flak, a shocking revelation made itself known. I had written a story about the life expectancy of the ball turret gunner. My findings were that that life expectancy was about 12 seconds. That may be true when one is talking about the prospect of being shot, but when it comes to flak, that cannot be said. Apparently, where flak is concerned, the best place to be is in the plexiglass structure of the ball turret. Plexiglass holds up better against flak than other areas of the plane, so the ball turret gunner is much more protected…at least from flak. The same cannot be said for the bullets flying through the area. I was thankful that my dad was not a ball turret gunner, and that he only filled in as a waist gunner periodically. The waist gunners were in the open, where protection from bullets, and from flak was minimal…at best, non-existent at worst. I can’t imagine how those memories must have affected my dad, but in the book I listened to, the main reason many of the men didn’t want to talk about their experiences in World War II, or any war, was because talking about it brought those memories flooding in again.
After researching flak, and how it works, I can see why the men would get a look of fear on their faces as they prepared to go through areas anti-aircraft weapons shooting flak into the air. Some men said that they could see the red hot glow in the center of the flak, if it was very close. That tells me that it was like a small explosive devise. No wonder it could bring so much damage to a plane. I had known that flak could put holes in the fuselage, but somehow I hadn’t tied that with bringing down a plane. I surmise that it was the B-17 
 bomber top turret gunner’s daughter in me that wouldn’t allow me to place that danger around my dad. I didn’t want to think about the dangers of his every mission in World War II. My mind seems to have placed his plane in a bubble or a force field, so that no danger could come near him. I think every veteran wonders why they were spared, when others didn’t make it back home. I don’t think anyone can answer that question. As a Christian, I have to credit God for bringing my future dad home.
bomber top turret gunner’s daughter in me that wouldn’t allow me to place that danger around my dad. I didn’t want to think about the dangers of his every mission in World War II. My mind seems to have placed his plane in a bubble or a force field, so that no danger could come near him. I think every veteran wonders why they were spared, when others didn’t make it back home. I don’t think anyone can answer that question. As a Christian, I have to credit God for bringing my future dad home.

 On July 19, 1989, in the skies over Alta, Iowa, United Airlines Flight 232, on which my great aunt, Gladys Cooper was a passenger, began the fateful journey to a catastrophic end. At 3:16pm, the rear engine’s fan disk broke apart due to a previously undetected metallurgical defect located in a critical area of the titanium-alloy. Basically that meant that the fan disk shattered, sending shrapnel through the hydraulic lines of all three independent hydraulic systems on board the aircraft. This horrific event caused the rapid loss of all the hydraulic fluid. The subsequent catastrophic disintegration of the disk had resulted in a spray of debris with energy levels that exceeded the level of protection provided by design features of the hydraulic systems that operate the DC-10’s flight controls. The flight crew lost its ability to operate nearly all of them. In the resulting crash landing, the right wing just tapped the runway, causing the plane to cartwheel and break apart as it went careening down the runway and into a corn field. While my Great Aunt Gladys was killed in the crash, the skill of the pilot and flight crew saved 185 lives, including their own.
On July 19, 1989, in the skies over Alta, Iowa, United Airlines Flight 232, on which my great aunt, Gladys Cooper was a passenger, began the fateful journey to a catastrophic end. At 3:16pm, the rear engine’s fan disk broke apart due to a previously undetected metallurgical defect located in a critical area of the titanium-alloy. Basically that meant that the fan disk shattered, sending shrapnel through the hydraulic lines of all three independent hydraulic systems on board the aircraft. This horrific event caused the rapid loss of all the hydraulic fluid. The subsequent catastrophic disintegration of the disk had resulted in a spray of debris with energy levels that exceeded the level of protection provided by design features of the hydraulic systems that operate the DC-10’s flight controls. The flight crew lost its ability to operate nearly all of them. In the resulting crash landing, the right wing just tapped the runway, causing the plane to cartwheel and break apart as it went careening down the runway and into a corn field. While my Great Aunt Gladys was killed in the crash, the skill of the pilot and flight crew saved 185 lives, including their own.
While listening to an audio book about World War II, and what happens when bombers flew through flak (Fl(ieger)a(bwehr)k(anone)). I knew that on at least one occasion, my dad, Allen Spencer, a Flight Engineer and Top Turret Gunner on a B-17 in World War II, was tasked with the job of cranking down the landing gear for landing. I don’t know what I had been thinking happened to the landing gear, maybe a close bit of flak the bent something in the gear perhaps, but what had not occurred to me was a catastrophic hit of that flak, causing all hydraulics to be lost. Nevertheless, quite likely that is what happened. It was one of the scenarios discussed in the book. As the hydraulics were lost, the red fluid was all over the floor of the aircraft, and the next thing that was required was to crank down the landing gear, because the gear could not be lowered without hydraulic fluid. Somehow, Dad’s precarious position of hanging out in the open bomb bay doors seemed like such a simple solution to the problem, albeit a heroic act, but the loss of hydraulics could have meant death to the crew. Getting the landing gear down was only part of the problem. What about the flaps, brakes, and such. These planes were in a really bad way.
Of course, my dad’s plane did land safely, given that he became my dad, but years later, when my mother, Collene Spencer’s Aunt Gladys was on a plane crippled by the loss of all hydraulics, I now realize…finally, that when my dad heard about what happened with Flight 232, as we all eventually did, he understood full well, 
 what the flight crew had been faced with. Something I only understood from the view of a spectator…for lack of a better word. He had been there. The Flight 232 situation quite likely took my dad back some 45 years to that day when he had to crank down the landing gear on a B-17 Bomber that had been damaged by flak, probably spilling hydraulic fluid all over the floor where the crew was standing. The experience must have been awful to go through, and the thought of what happened to Flight 232, almost as bad. And yet, in typical World War II veteran style, Dad said nothing, but rather set about comforting his family over the loss.
what the flight crew had been faced with. Something I only understood from the view of a spectator…for lack of a better word. He had been there. The Flight 232 situation quite likely took my dad back some 45 years to that day when he had to crank down the landing gear on a B-17 Bomber that had been damaged by flak, probably spilling hydraulic fluid all over the floor where the crew was standing. The experience must have been awful to go through, and the thought of what happened to Flight 232, almost as bad. And yet, in typical World War II veteran style, Dad said nothing, but rather set about comforting his family over the loss.
 Sometimes we see a picture that looks so far-fetched that we assume that we are looking at a picture that has been photoshopped, and sometimes we are. Nevertheless, some pictures, unbelievable as they may seem, are the real deal. A while back, I stumbled upon an unbelievable photo of a plane crash, or rather the moment before the plane crashed. I was instantly intrigued. Could this be real? Or was it just a big ruse?
Sometimes we see a picture that looks so far-fetched that we assume that we are looking at a picture that has been photoshopped, and sometimes we are. Nevertheless, some pictures, unbelievable as they may seem, are the real deal. A while back, I stumbled upon an unbelievable photo of a plane crash, or rather the moment before the plane crashed. I was instantly intrigued. Could this be real? Or was it just a big ruse?
At the end of World War II, the English Electric Aviation Company received a contract to develop a jet bomber. The resulting bomber was the English Electric Lightning F1. The ER103 design study was sufficiently impressive for English Electric to be awarded the contract for two prototypes and a structural-test airframe. The early prototypes evolved into the Lightning, an airplane which was to span the time from when the Spitfire was our primary front-line fighter to the end of the Cold War. The Lightning was the only British designed and built fighter capable of speeds in excess of Mach 2 to serve with the Royal Air Force. The aircraft in the photograph was XG332. It was built in 1959, one of 20 pre-production Lightnings. Alan Sinfield took a photograph of XG332 in 1960 at Farnborough. However, it was the very last photograph taken of XG332, in 1962, that became the famous one, and deservedly so. How does someone manage to take a photograph like this? Jim Meads is the man who took the picture, but this was not the picture he expected to take that day. He was a professional photographer who lived near the airfield. In fact, he lived next door to de Havilland test pilot Bob Sowray.
Meads says that Bob Sowray mentioned that he was going to fly the Lightning that day. An excited Meads took his kids for a walk, taking his camera along, hoping to get a shot of the plane, and give his kids something amazing to remember. Well, that part of the walk went according to plan. It was a walk his kids would not soon forget. He had planned to take a photograph of the children with the airfield in the background, just as the Lightning came in to land. They found a good view of the final approach path and waited for the Lightning to return. As it turned out, Bob Sowray didn’t fly the Lightning that day. The pilot was George Aird, another test pilot working for De Havilland. George Aird was involved in the Red Top Air-to-Air Missile program. He was a well-respected test pilot.
The flight was to take place on September 19, 1962. The day did not go as planned in any way. George Aird was in the Lightning doing a demonstration flight off of the south coast. As he approached Hatfield from the north east, he realized that he had trouble. During the flight there was a fire in the aircraft’s reheat zone. “Un-burnt fuel in the rear fuselage had been ignited by a small crack in the jet pipe and had weakened the tailplane actuator anchorage. This weakened the tailplane control system which failed with the aircraft at 100 feet on final approach.” The plane suddenly pitched up, quite violently…just as Aird was coming in to land. Aird lost control of the aircraft and ejected. Had the nose of the plane not pitched up suddenly, Aird would not have had enough time to eject.
The tractor in the photograph was a Fordson Super Major. Upon close inspection of the grill, one can see that it reads D H Goblin, which is the name of another de Havilland jet engine…the Goblin. The tractor driver was 15-year-old Mick Sutterby, who spent that summer working on the airfield. He would play an amazing, but unexpected part in the amazing picture. He wasn’t posing for the camera, but rather, was telling the photographer, Jim Mead, to move on, because he shouldn’t be there. Mead saw the plane coming in and the nose pitch up. Then Aird ejected and Mead says he had just enough time to line up the shot as the Lightning came down nose first.
Sutterby recalls, “I followed my father into work at de Havilland, Hatfield in 1954 when I was 15. My father was the foreman in charge of the aerodrome and gardens. My job in the summer was gang-mowing the airfield and at the time of the crash in 1962 the grass had stopped growing and we were trimming round the ‘overshoot’ of the runway with a ‘side-mower’. I stopped to talk to a chap with a camera who was walking up a ditch to the overshoot. I stopped to tell him that he shouldn’t be here, I heard a roar and turned round and he took the picture! He turned out to be a friend of the pilot and had walked up the ditch to photograph his friend in the Lightning. I saw some bits fly off the plane before it crashed, but it was the photographer who told me he had ejected. There was not a big explosion when it crashed, just a loud ‘whhooooof’.”
“I was about 200 yards from the crash scene. I saw men running out of the greenhouses and checking the scene of the crash. The works fire brigade were on the scene within a minute. Somewhere at home I have a picture of it burning. Although the picture shows it nose diving to the ground, in fact it was slowly turning over and it hit the ground upside down nose first. I was later told that if the pilot had ejected a split second later he would have ejected himself into the ground. I was very lucky. If I had known he was coming into land, I would have been positioned near the ILS (Instrument Landing System) aerial which was only 20 yards or so from the crash site! I believe the photographer had his photo restricted by the Air Ministry for – I think – about 3 months because the plane was secret,” Sutterby said, almost as if in thought.
“He then took it to the Daily Mail who said it was a fake. The photo was eventually published by the Daily  Mirror. From there it went round the world, and I remember seeing a copy in the RAF museum at Hendon. I recollect the photographer usually photographed hunting scenes for magazines like The Field. I recollect that the pilot broke his legs but really was very lucky. I hope this is interesting. All from memory,” finished Sutterby.
Mirror. From there it went round the world, and I remember seeing a copy in the RAF museum at Hendon. I recollect the photographer usually photographed hunting scenes for magazines like The Field. I recollect that the pilot broke his legs but really was very lucky. I hope this is interesting. All from memory,” finished Sutterby.
George Aird didn’t have an easy landing, and in fact, landed on a greenhouse and fell through the roof. The fall broke both of his legs, and he landed on the ground, unconscious. The water from the sprinkler system for the tomatoes woke him up and he reportedly said that his first thought was that he must be in heaven. In the end no one was killed, but the resulting picture by Jim Meads is nothing short of spectacular!!
 Opinions vary as to who the worst generals of World War II were, and I can’t say where I stand on the issue, but after researching several of the battles fought, whether won or lost, I can see how people could make up their own minds on the issue. It must also be noted that even the worst general can have enough good men under him to bring success through multiple blunders on the part of the general. Then, the general is considered a war hero. It doesn’t always happen, but sometimes, it does.
Opinions vary as to who the worst generals of World War II were, and I can’t say where I stand on the issue, but after researching several of the battles fought, whether won or lost, I can see how people could make up their own minds on the issue. It must also be noted that even the worst general can have enough good men under him to bring success through multiple blunders on the part of the general. Then, the general is considered a war hero. It doesn’t always happen, but sometimes, it does.
On September 14, 1944, the US 1st Marine Division landed on the island of Peleliu, one of the Palau Islands in the Pacific. It was part of a larger operation to provide support for General Douglas MacArthur, who was preparing to invade the Philippines. The Palaus were part of the Caroline Islands. They were among the mandated islands taken from Germany and given to Japan as one of the terms of the Treaty of Versailles at the close of World War I. The US military was unfamiliar with the islands, and Admiral William Halsey had argued against Operation Stalemate, which included the Army invasion of Morotai in the Dutch East Indies. He believed that MacArthur would meet minimal resistance in the Philippines, making this operation unnecessary, especially given the risks involved.
General William Henry Rupertus was the commander of the 1st Marine Division when they attacked the Japanese-held island Peleliu. Rupertus mistakenly predicted that the island would fall within 4 days. With that in mind, he sent his troops ashore with minimal water supplies. The battle was a horror show that dragged on for nearly 75 days. The Marines thought they knew how to attack the island, but the Japanese were using some new, innovative tactics, and so the Marines were unprepared. Nevertheless, Rupertus stuck to his original plan, even as casualties mounted, even withdrawing tank support for a critical assault, mistakenly believing it wasn’t needed. It’s actions like this that make you wonder how he ever got to be a general, I guess the Marines agreed, because Rupertus was pulled from command and soon died of a heart attack. The 1st Marine Division was pulled out after a month of vicious combat. They were in such bad shape that the division didn’t fight again for six months.
The pre-invasion bombardment of Peleliu had somehow seemed important, at the time, but it proved to be of no real help. The Japanese defenders of the island were buried too deep in the jungle, and the target intelligence given the Americans was faulty. Upon landing, the Marines met little immediate resistance, but that was a maneuver to get them further onto the island. Shortly thereafter, Japanese machine guns opened fire, knocking out more than two dozen landing craft. Scores of Japanese tanks and troops immediately stormed upon the marines. The shocked 1st and 5th Marine regiments fought for their lives. Jungle caves seemingly exploded with Japanese soldiers. Within one week of the invasion, the Marines lost 4,000 men. By the time it was all over, that number would surpass 9,000. The Japanese lost more than 13,000 men. Flamethrowers and bombs finally subdued the island for the Americans, but in the end, it all proved pointless. MacArthur invaded the Philippines without need of Army or Marine protection from either Peleliu or Morotai.

While MacArthur has a reputation as one of the most innovative and courageous generals in US history, he also committed inexplicable blunders at multiple points in the war. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, MacArthur was ordered to carry out pre-war attack plans on Japanese bases, but he gave no reply. As a result, Japanese planes immediately attacked, wiping out his air force. His thinly spaced and poorly supplied US and Filipino forces crumbled, and he was ordered to evacuate Manila with his command staff. About 150,000 Allied troops had been killed, wounded, or captured. His bold conduct over the next four years gained him a justifiable reputation as a war hero, but he was also reckless, arrogant, and careerist. He saw his role as the occupational governor of Japan as a stepping-stone to running for president and pardoned Japanese war criminals involved in human experimentation. These are not things that a general in the United States military should be doing, and while he was considered a hero by some, there were many others who would seriously disagree.

