finland
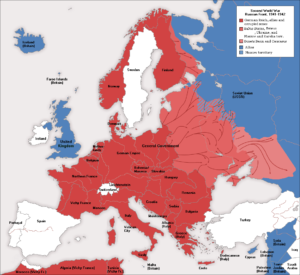
 When countries choose sides in a war, there isn’t normally much chance that they will switch sides, but that is exactly what happened to Romania…and in fact, there were four countries that switched sides in that war, so maybe it isn’t so uncommon after all. At the start of the war Romania was allied and Poland and pro-British. They were trying to stay neutral, but that wasn’t easy. As the war progressed, Romania became more and more concerned about being overrun by the Soviet Union and the Fascist elements already in Romania. Finally, the decision was made to adopt a pro-German dictatorship and became an ‘affiliate state’ of the Axis Powers. The Romanian government signed the Tripartite Pact in November 1940. During the time that Romania supported the Axis powers, they supplied Nazi Germany and the Axis armies with oil, grain, and industrial products. Also, numerous train stations in the country, such as Gara de Nord in Bucharest, served as transit points for troops departing for the Eastern Front.
When countries choose sides in a war, there isn’t normally much chance that they will switch sides, but that is exactly what happened to Romania…and in fact, there were four countries that switched sides in that war, so maybe it isn’t so uncommon after all. At the start of the war Romania was allied and Poland and pro-British. They were trying to stay neutral, but that wasn’t easy. As the war progressed, Romania became more and more concerned about being overrun by the Soviet Union and the Fascist elements already in Romania. Finally, the decision was made to adopt a pro-German dictatorship and became an ‘affiliate state’ of the Axis Powers. The Romanian government signed the Tripartite Pact in November 1940. During the time that Romania supported the Axis powers, they supplied Nazi Germany and the Axis armies with oil, grain, and industrial products. Also, numerous train stations in the country, such as Gara de Nord in Bucharest, served as transit points for troops departing for the Eastern Front.
With all of this, Romania caught the eye of the Allies in 1943, and soon became a target for their aerial bombardment. One of the most notable air bombardments was the attack on the oil fields of Ploie?ti on August 1, 1943, known as Operation Tidal Wave. On April 4 and 15, 1944, Bucharest was subjected to intense Allied bombardment. On August 23, 1944, King Michael I removed the government of Ion Antonescu and declared Romanian support to the Allies. Then the Luftwaffe bombed the city Bucharest on August 24 and 25, 1944 in direct response to the Romania’s decision to switch sides. Some experts believe that by switching sides Romania helped shorten the war by several months. I’m sure that Romania was glad to be on the winning side of the war.
Romania was not the only nation to switch sides in Worls War II. They were Bulgaria, Finland, and Italy. Bulgaria also signed the Tripartite Pact in March of 1941, but Finland never signed it, but was nonetheless a co-belligerent on the side of the Axis Powers. Finland signed the Anti-Comintern Pact, an anti-communist agreement of mainly fascist powers, in November 1941. Italy had its own imperial ambitions, which were partly 
 based on the Roman Empire and similar to the German policy of lebensraum, which clashed with those of Britain and France. No matter wat their aspirations were, all of these nations decided that the ways of Germany and Hitler were simply not ways they could live with, so they switched sides, joined the Allied Nations, further weakened Hitler to the point of causing his demise.
based on the Roman Empire and similar to the German policy of lebensraum, which clashed with those of Britain and France. No matter wat their aspirations were, all of these nations decided that the ways of Germany and Hitler were simply not ways they could live with, so they switched sides, joined the Allied Nations, further weakened Hitler to the point of causing his demise.

 I love to ride on the Ferry boats in Washington state. It’s especially cool to have your car right there with you at the end of your journey. You just get in and go off to the rest of your adventure. Of course, a Ferry boat is just that…a boat, and that always leaves the possibility of one sinking. That has happened on numerous occasions. It seems to me though that most of the time when they sink, it is in open waters, and not the inland waters, such as the Puget Sound.
I love to ride on the Ferry boats in Washington state. It’s especially cool to have your car right there with you at the end of your journey. You just get in and go off to the rest of your adventure. Of course, a Ferry boat is just that…a boat, and that always leaves the possibility of one sinking. That has happened on numerous occasions. It seems to me though that most of the time when they sink, it is in open waters, and not the inland waters, such as the Puget Sound.
One such maritime disaster in open waters, occurred on September 28, 1994, when a large car-and-passenger ferry…MS Estonia, sank in the Baltic Sea, killing 852 people. MS Estonia was a cruiseferry built in 1980 at the West German shipyard Meyer Werft in Papenburg. The ship was sold to Nordström and Thulin in 1993, for use on Estline’s Tallinn–Stockholm route. Estonia departed slightly behind schedule that night, departing at at 7:15pm on September 27. It was expected in Stockholm the next morning at about 9:00am. The ship was carrying 989 people, which included 803 passengers and 186 crew. The seas were rough that night, and it was determined by a 1997 investigation, that the ship’s bow door locks had failed during the storm. However, new underwater footage appears to show a previously unrecorded 13-foot hole in the ship’s hull. Given that information, many people think that it might have been a Russian torpedo that took down the MS Estonia. Whatever the case may be, the sinking of Estonia was one of the worst maritime disasters of the 20th century.
The main reason for the new theory is that Estonia was traveling on an overnight cruise from Tallinn, the capital city of Estonia, to Stockholm, Sweden, when it sank off the coast of Finland. Estonia is a former Soviet republic that gained its independence in 1991, but the last Russian troops actually left in 1994. Tallinn was a popular and affordable travel destination for Swedes. The Estonia was a type of ferry known as a “ro-ro,” which featured a smorgasbord, live music, dancing and drinking, and allowed people to drive vehicles onto one end of the ship and drive off on the other end.
There is no doubt that the stormy weather played a part in the disaster, because in the storm, the waves reached an estimated 15 to 20 feet. The Estonia went down in the middle of the night. It went down so quickly, that many passengers were trapped inside the ship. Some were able to escape and managed to make it into lifeboats. Some of those later drowned in the frigid water or died from hypothermia. Out of the 989 souls on board Estonia, only 137 survived, most of those were rescued by helicopters.
Officially, a joint Swedish-Finnish-Estonian government committee ruled it an accident and blamed it on stormy 
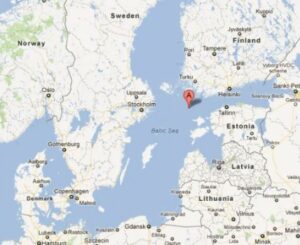 weather that caused water to pour through an open bow door and into the Estonia’s car deck, destabilizing the ship and capsizing it in less than an hour. Nevertheless, there were others, including some family and friends of the Estonia victims, who believed the sinking was the result of a pre-existing hole caused by a collision or explosion. I don’t suppose that the full truth will ever be known, but the loss of life will forever be felt.
weather that caused water to pour through an open bow door and into the Estonia’s car deck, destabilizing the ship and capsizing it in less than an hour. Nevertheless, there were others, including some family and friends of the Estonia victims, who believed the sinking was the result of a pre-existing hole caused by a collision or explosion. I don’t suppose that the full truth will ever be known, but the loss of life will forever be felt.
 While there were those who thought it wasteful to build the lavish Temppeliaukio Church, a Lutheran church in the Toolo neighborhood of Helsinki, Finland. Before the construction of the church was even fully complete it made headlines when on the nights of July 16 and 17, 1968 a group of Christian students painted in large letters “BIAFRA” in several places on the exterior walls of the building to bring attention to the famine then going on in Biafra, which had declared independence from Nigeria in 1967. The students, part of the 1960s student revolutionary movement, thought they were doing a service to the people of Biafra, but they were simply young and naive, and they didn’t know that one thing had nothing to do with the other, because were the funds not used in the church, they would have been used for something else. Building the church or not building the church would make no difference for the people of Biafra.
While there were those who thought it wasteful to build the lavish Temppeliaukio Church, a Lutheran church in the Toolo neighborhood of Helsinki, Finland. Before the construction of the church was even fully complete it made headlines when on the nights of July 16 and 17, 1968 a group of Christian students painted in large letters “BIAFRA” in several places on the exterior walls of the building to bring attention to the famine then going on in Biafra, which had declared independence from Nigeria in 1967. The students, part of the 1960s student revolutionary movement, thought they were doing a service to the people of Biafra, but they were simply young and naive, and they didn’t know that one thing had nothing to do with the other, because were the funds not used in the church, they would have been used for something else. Building the church or not building the church would make no difference for the people of Biafra.
The Temppeliaukio Church was designed by architects and brothers Timo and Tuomo Suomalainen and opened in 1969. It was uniquely built directly into solid rock. It is known as the “Church of the Rock” and “Rock Church.” Plans for the Temppeliaukio/Tempelplatsen (Temple square) began as early as the 1930s when a plot of land was selected for the building. It was decided to hold a competition for the design of the church. The plan by JS Siren, who was the winner of the second competition to design the architecture of the church, was interrupted in its early stages when World War II began in 1939. After the war, that design was scrapped and there was another architectural competition. That competition was won by Timo Suomalainen and Tuomo Suomalainen in 1961. Even that plan had to be somewhat changed when, for economic reasons, it was scaled  back, and the interior space of the church was reduced to about one-quarter of its original plan. I suppose that when you think about it, cutting a church into solid rock would be a complicated and costly operation. The long-awaited Construction finally began in February 1968, and the rock-temple was completed for consecration in September 1969.
back, and the interior space of the church was reduced to about one-quarter of its original plan. I suppose that when you think about it, cutting a church into solid rock would be a complicated and costly operation. The long-awaited Construction finally began in February 1968, and the rock-temple was completed for consecration in September 1969.
As planned, the interior was carved out of solid rock. It is beautifully bathed in natural light which enters through the skylight surrounding the center copper dome. Strangely, the church reminds me of a spaceship, a little bit anyway, but I find it to be beautiful and quite peaceful too. The church is used frequently as a concert venue due to its excellent natural acoustics. The acoustic quality is created by the rough, virtually unworked rock surfaces. The iconic rock walls were not included in the original competition entry, even though the Suomalainen brothers had considered the idea, because they believed that it was too radical for the competition jury. I suppose thy wondered if it would be looked at as sacrilegious or maybe too backward to be beautiful… how very wrong they were about that. But when conductor Paavo Berglund shared his knowledge of acoustics from some of the best music halls and the acoustical engineer Mauri Parjo gave requirements for the wall surfaces, the Suomalainen brothers discovered that they could fulfill all the requirements for the acoustics by leaving the rock walls exposed in the Church Hall. It was also a financial savings both then and, in the future, as it eliminated the need to paint the interior.
Today, the Temppeliaukio church is one of the most popular tourist attractions in the city, with half a million people visiting it annually. The stone-hewn church is located in the heart of Helsinki, giving people easy access  to its beauty and solace. Maintaining the original character of the square is the fundamental concept behind the building. The idiosyncratic choice of form has made it a favorite with professionals and aficionados of architecture. I can imagine that many of them come to see it simply to admire the perfection of this almost artistic masterpiece. The church furnishings were designed by the architects. Organ builder Veikko Virtanen manufactured the church organ, which has 43 stops and 3001 pipes. In an unusual anomaly, there are no bells at the church. Instead, a recording of bells composed by Taneli Kuusisto is played via loudspeakers on the exterior wall calls parishioners to the services.
to its beauty and solace. Maintaining the original character of the square is the fundamental concept behind the building. The idiosyncratic choice of form has made it a favorite with professionals and aficionados of architecture. I can imagine that many of them come to see it simply to admire the perfection of this almost artistic masterpiece. The church furnishings were designed by the architects. Organ builder Veikko Virtanen manufactured the church organ, which has 43 stops and 3001 pipes. In an unusual anomaly, there are no bells at the church. Instead, a recording of bells composed by Taneli Kuusisto is played via loudspeakers on the exterior wall calls parishioners to the services.

 There are different kinds of governments, some good and some bad. The problem these days is that people are confused about which one is the best. On April 13, 1918, the people of Helsinki, Finland were not among the confused. They had lived under a capitalist government, and they had lived under a socialist government, and there was no doubt in their minds that they did not want to live in socialism any longer.
There are different kinds of governments, some good and some bad. The problem these days is that people are confused about which one is the best. On April 13, 1918, the people of Helsinki, Finland were not among the confused. They had lived under a capitalist government, and they had lived under a socialist government, and there was no doubt in their minds that they did not want to live in socialism any longer.
Finland had been under Russian rule since 1809. With the upheaval in Russia in 1917, which included the abdication of Czar Nicholas II in March and the rise to power of Vladimir Lenin and his radical socialist followers, the Bolsheviks, in November, Finland decided to declare its independence in December, 1917. Unfortunately, conflict broke out almost immediately between radical socialists, who were supporters of the Bolsheviks in Russia, and the anti-socialists within the government. In late January 1918, the radical socialist Red Guard launched a rebellion, terrorizing and killing civilians in their attempt to spark a Bolshevik-style revolution. It reminds me of the riots because of the left’s push to socialism in this country. The Whites (as government troops were known) under the command of Baron Karl Gustav Mannerheim found themselves in a bitter struggle to drive the Red Guard (as the Bolsheviks and socialists were known) out of Finland.
On April 3, 1918, German troops who had been sent by Kaiser Wilhelm II, landed in Finland to aid Mannerheim’s White army. Germany had made an agreement to support Finland and its newly declared parliamentary government. German troops, alongside Mannerheim and his force of 16,000 men, fought to take back control of Helsingfors (Helsinki) from the Red Guard, an army of Finnish supporters of the Russian Bolsheviks, on April 13, 1918. That victory was followed by another in Viborg by the end of the month. Another major victory by the Germans and the White Finns took place at Lahti on May 7, 1918. It was that battle that ended the Finnish civil war.
Germany’s close ties with the emerging Finnish government reached a new level in October 1918. Conservative forces in Finland decided to establish monarchal rule in the country, giving the throne to Frederick, a German prince, in the remaining weeks of World War I. However, Kaiser Wilhelm himself had abdicated by the time the Central Powers appealed for an armistice one month later and it seemed certain that the victorious Allies would not look kindly upon a German prince on the Finnish throne, so Frederick abdicated on December 14. The Treaty of Versailles, signed in June 1919, recognized Finland’s hard-won independence. That July, the Finnish parliament adopted a new republican constitution, and liberal Kaarlo J Stahlberg, was elected as the country’s first president.
Today, Finland is considered a republic with representative democracy. The public administration is composed of the highest elected bodies, state administration, local government, and the courts. The highest elected body is 
 made up of the parliament, the president, and the government. The current president of Finland is Sauli Niinistö, who has been president since March 1, 2012. The Parliament of Finland exercises the legislative powers while the executive power is exercised by the cabinet supervised by the premier who heads the government of Finland. The president heads the state and has powers to make a decision concerning some matters such as personal appointments and pardons.
made up of the parliament, the president, and the government. The current president of Finland is Sauli Niinistö, who has been president since March 1, 2012. The Parliament of Finland exercises the legislative powers while the executive power is exercised by the cabinet supervised by the premier who heads the government of Finland. The president heads the state and has powers to make a decision concerning some matters such as personal appointments and pardons.
 On June 26, 2003, a Green Beret was laid to rest at Arlington National Cemetery. That may not seem like such an unusual event, but in reality, it was very unusual. Lauri Allan Torni, aka Larry Thorne, was born in Viipuri, Finland on May 28, 1919. When he grew up, he entered the Finnish military service in 1938. He participated in the war between Finland and the USSR, proving himself in battle, and earning the rank of captain. It would appear that Torni would quite likely have a long and distinguished career in the military service.
On June 26, 2003, a Green Beret was laid to rest at Arlington National Cemetery. That may not seem like such an unusual event, but in reality, it was very unusual. Lauri Allan Torni, aka Larry Thorne, was born in Viipuri, Finland on May 28, 1919. When he grew up, he entered the Finnish military service in 1938. He participated in the war between Finland and the USSR, proving himself in battle, and earning the rank of captain. It would appear that Torni would quite likely have a long and distinguished career in the military service.
All that changed when Finland allied itself with Nazi Germany in 1941. In 1943, Torni put together a unit that was informally called Detachment Torni. This was an infantry unit that penetrated deep behind enemy lines, and they quickly made a reputation for themselves on both sides of the front for its combat effectiveness. For his part, Torni, for his Finnish military service was awarded 8 medals, to include the Mannerheim Cross, for action on July 9, 1944.
When his unit was demobilized, Torni joined a German SS unit in East Prussia and continued to fight the Russians, who at that time were the known enemy. During his time in the German SS, Torni was captured by the British, escaped a POW camp, and returned to Finland, where he was arrested for his German army service. I’m sure that at this point he wondered what was going on. I would think he realized the the German SS was his whole problem, but like many, he was fooled by Hitler and the Nazi party. After being pardoned in 1948, Torni secretly traveled to Sweden, masqueraded as a Swedish seaman, and sailed to the vicinity of Mobile, Alabama,  where he jumped overboard and made it to land. As most people know, getting to land was an opportunity to seek asylum, which Torni did. He was granted residency in 1953 and because he wanted to be loyal to his new country, Torni, now going by Larry Thorne joined the Army. Again, he proved himself in battle, and eventually became a Green Beret assigned to Special Forces. Torni, now Thorne was an incredible soldier, and very loyal to his nation and his fellow soldiers. He served in various high profile capacities around the world in his time of service as a Green Beret.
where he jumped overboard and made it to land. As most people know, getting to land was an opportunity to seek asylum, which Torni did. He was granted residency in 1953 and because he wanted to be loyal to his new country, Torni, now going by Larry Thorne joined the Army. Again, he proved himself in battle, and eventually became a Green Beret assigned to Special Forces. Torni, now Thorne was an incredible soldier, and very loyal to his nation and his fellow soldiers. He served in various high profile capacities around the world in his time of service as a Green Beret.
In 1963 when he was 44 years old, Thorne was deployed to Vietnam as an advisor, but two years later Torni’s remarkable career came to an end when his helicopter crashed during a secret mission. It was a tragic end to a short lived, be remarkable career. His remains were not located until 1999. Finally, on June 26, 2003, a multi-national hero and in the end, a celebrated Green Beret was laid to rest. He was an amazing soldier.
 A declaration of war usually means that the people in both areas within the dispute had better prepare for eminent attack, because the declaration of war is like firing the warning shot before the actual open-fire begins. Of course, it may not be an immediate attack, but the attack always comes…or does it. On September 3, 1939, the United Kingdom and France declared war on Nazi Germany, after the Germans invaded Poland. Over the next eight months, at the start of World War II, there were no major military land operations on the Western Front. Strange, considering that the United Kingdom and France had declared war on Nazi Germany. You would think that they would attack or something, but nothing happened. During those eight months, Poland was overrun. It took about five weeks for the German Invasion of Poland beginning September 1, 1939 and the Soviet invasion beginning on 17 September 1939. Still, the Western Allies did nothing. I guess I don’t understand that. War had been declared by each side, but no Western power would
A declaration of war usually means that the people in both areas within the dispute had better prepare for eminent attack, because the declaration of war is like firing the warning shot before the actual open-fire begins. Of course, it may not be an immediate attack, but the attack always comes…or does it. On September 3, 1939, the United Kingdom and France declared war on Nazi Germany, after the Germans invaded Poland. Over the next eight months, at the start of World War II, there were no major military land operations on the Western Front. Strange, considering that the United Kingdom and France had declared war on Nazi Germany. You would think that they would attack or something, but nothing happened. During those eight months, Poland was overrun. It took about five weeks for the German Invasion of Poland beginning September 1, 1939 and the Soviet invasion beginning on 17 September 1939. Still, the Western Allies did nothing. I guess I don’t understand that. War had been declared by each side, but no Western power would  launch a significant land offensive…even though the terms of the Anglo-Polish and Franco-Polish military alliances obligated the United Kingdom and France to assist Poland. They simply stood by and let it happen.
launch a significant land offensive…even though the terms of the Anglo-Polish and Franco-Polish military alliances obligated the United Kingdom and France to assist Poland. They simply stood by and let it happen.
The quiet of the so-named Phoney War was marked by a few Allied actions. During the Saar Offensive in September, France attacked Germany with the intention of assisting Poland, but the attack fizzled out within days and the French withdrew. In November, the Soviets attacked Finland in the Winter War. This resulted in much debate in France and Britain about helping Finland, but this campaign was delayed until the Winter War ended in March. The Allied discussions about a Scandinavian campaign caused concern in Germany and resulted in the German invasion of Denmark and Norway in April. Then the Allied troops that were previously assembled for Finland were redirected to Norway instead. Fighting there continued until June when the Allies evacuated, ceding Norway to Germany in response to the German invasion of France, which had taken place on May 10, 1940.

The Germans launched attacks at sea during the autumn and winter of 1939, against British aircraft carriers and destroyers, sinking several including the carrier HMS Courageous with the loss of 519 lives. Action in the air began on October 16, 1939 when the Luftwaffe launched air raids on British warships. There were various minor bombing raids and reconnaissance flights on both sides, but nothing that could possibly be viewed as a clear offensive….and during that whole time, people were dying and being subjected to various atrocities, because no one would help. Yes, war was declared, but it was a phony war, and apparently a phony declaration.

