british empire
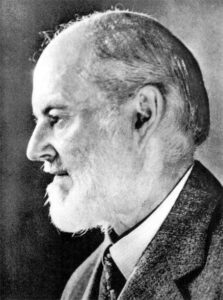 We have all heard of the Rolls Royce, and these days it is a car that is close to my heart, not because I own one, but because I’m pretty sure there are family ties to my son-in-law, Travis Royce and now, my daughter, Amy Royce, and their children, Shai and Caalab. I don’t know that for sure, but I have a hunch, and it’s not just the name. Time will tell as I research further.
We have all heard of the Rolls Royce, and these days it is a car that is close to my heart, not because I own one, but because I’m pretty sure there are family ties to my son-in-law, Travis Royce and now, my daughter, Amy Royce, and their children, Shai and Caalab. I don’t know that for sure, but I have a hunch, and it’s not just the name. Time will tell as I research further.
Sir Frederick Henry Royce, 1st Baronet, OBE, was an English engineer. OBE stands for “The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire and is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organizations, and public service outside the civil service.” Sir Royce was famous for his designs of car and aeroplane engines with a reputation for reliability and longevity. Of course, we probably know much more about the product that brought him fame, than we do the man and his partners, who brought that product to life.
Sir Frederick Henry Royce was born in Alwalton, Huntingdonshire, near Peterborough on March 27, 1863, to James and Mary Royce (née King). He was youngest of their five children. His father ran a flour mill which he leased from the Ecclesiastical Commissioners. Unfortunately, the business failed, and the family moved to London. After his father died in 1872, Royce had to go out to work selling newspapers and delivering telegrams after only one year of formal schooling. With such a beginning, it would seem quite unlikely that Sir Royce would ever amount to anything, but in 1878 with the financial help of an aunt, Royce  was able to start an apprenticeship with the Great Northern Railway company at its works in Peterborough. Unfortunately, the money ran out after three years, and Royce was again forced to change careers. He worked for a short time with a tool-making company in Leeds, and then returned to London and joined the Electric Light and Power Company. In 1882, he moved to their Liverpool office and began working on street and theatre lighting.
was able to start an apprenticeship with the Great Northern Railway company at its works in Peterborough. Unfortunately, the money ran out after three years, and Royce was again forced to change careers. He worked for a short time with a tool-making company in Leeds, and then returned to London and joined the Electric Light and Power Company. In 1882, he moved to their Liverpool office and began working on street and theatre lighting.
Following a few other ventures that produced minimal success, Royce partnered with Charles Rolls (1877–1910) and Claude Johnson (1864–1926) and founded Rolls-Royce. The new company initially focused on large 40-50 horsepower motor cars, the Silver Ghost and its successors. Royce produced his first aero engine shortly after the outbreak of the First World War and aircraft engines became Rolls-Royce’s principal product. While the Rolls Royce aeroplane engine was a much-needed product during the war, it will always be the famous Rolls Royce automobiles that people will remember. They are beautifully elegant, and to be desired by those who have the means to afford them, as well as those who wish they could afford them.

Henry Royce married Minnie Punt in 1893, but they had no children. The couple separated in 1912. Royce, who lived by the motto “Whatever is rightly done, however humble, is noble,” was appointed OBE in 1918, and was created a baronet, of Seaton in the County of Rutland, in 1930 for his services to British Aviation. Sir Royce’s health began to fail him in 1911 and he was finally forced to leave his factory in the Midlands at Derby. He took a team of designers and moved to the south of England, while spending winters in the south of France. He died at his home in Sussex on April 22, 1933. With no children, the baronetcy became extinct on his death.
 Through the years, Russia, also known as the Soviet Union and the USSR, has been sometimes ally and sometimes enemy of the United States. World War I and World War II found the Soviet Union once again on the side of good as a part of the Allied Forces. The main countries in the Allied powers of World War I were France, the British Empire and the Russian Empire. The main Allied powers of World War II were France, Great Britain, the United States, China, and the Soviet Union. So in these two wars anyway, the United States and Russia were on the same side. The three principal partners in the Axis alliance in World War II were Germany, Italy, and Japan. They were joined by Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania and Thailand, who also signed the Tri-Partite Pact as member states.
Through the years, Russia, also known as the Soviet Union and the USSR, has been sometimes ally and sometimes enemy of the United States. World War I and World War II found the Soviet Union once again on the side of good as a part of the Allied Forces. The main countries in the Allied powers of World War I were France, the British Empire and the Russian Empire. The main Allied powers of World War II were France, Great Britain, the United States, China, and the Soviet Union. So in these two wars anyway, the United States and Russia were on the same side. The three principal partners in the Axis alliance in World War II were Germany, Italy, and Japan. They were joined by Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania and Thailand, who also signed the Tri-Partite Pact as member states.
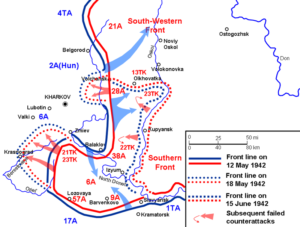
On May 12, 1942, Soviet forces under the command of Marshal Semyon Timoshenko attacked the German 6th  Army from a vulnerable point established during the winter counter-offensive. After a promising start, the offensive was stopped on May 15th by massive airstrikes. There were a number of critical Soviet errors by several staff officers and by Joseph Stalin, who failed to accurately estimate the 6th Army’s potential and overestimated their own newly raised forces, facilitated a German pincer attack on May 17th which cut off three Soviet field armies from the rest of the front by May 22nd. The Soviet Army was hemmed into a narrow area, and the 250,000-strong Soviet force inside the pocket was exterminated from all sides by German armored, artillery, and machine gun firepower, as well as 7,700 tons of air-dropped bombs. After six days of encirclement by the German Army, the Soviet resistance ended as their troops were killed or taken prisoner. It was a devastating loss for the Soviets.
Army from a vulnerable point established during the winter counter-offensive. After a promising start, the offensive was stopped on May 15th by massive airstrikes. There were a number of critical Soviet errors by several staff officers and by Joseph Stalin, who failed to accurately estimate the 6th Army’s potential and overestimated their own newly raised forces, facilitated a German pincer attack on May 17th which cut off three Soviet field armies from the rest of the front by May 22nd. The Soviet Army was hemmed into a narrow area, and the 250,000-strong Soviet force inside the pocket was exterminated from all sides by German armored, artillery, and machine gun firepower, as well as 7,700 tons of air-dropped bombs. After six days of encirclement by the German Army, the Soviet resistance ended as their troops were killed or taken prisoner. It was a devastating loss for the Soviets.
The Counter-offensive of the Second Battle of Kharkov, was called Operation Fredericus, and was launched by the Axis forces in the region around Kharkov against the Red Army Izium bridgehead offensive, and was conducted from May 12 to May 28, 1942, on the Eastern Front during World War II. The objective was to  eliminate the Izium bridgehead over Seversky Donets, also known as the “Barvenkovo bulge,” which was one of the Soviet offensive’s staging areas. A winter counter-offensive drove German troops away from Moscow, but depleted the Red Army’s reserves. The Kharkov offensive was next Soviet attempt to expand their strategic initiative, although it failed to secure a significant element of surprise. The battle ended up being an overwhelming German victory, with 280,000 Soviet casualties compared to just 20,000 for the Germans and their allies. The German Army Group South pressed its advantage, encircling the Soviet 28th Army on June 13 in Operation Wilhelm and pushing back the 38th and 9th Armies on June 22.
eliminate the Izium bridgehead over Seversky Donets, also known as the “Barvenkovo bulge,” which was one of the Soviet offensive’s staging areas. A winter counter-offensive drove German troops away from Moscow, but depleted the Red Army’s reserves. The Kharkov offensive was next Soviet attempt to expand their strategic initiative, although it failed to secure a significant element of surprise. The battle ended up being an overwhelming German victory, with 280,000 Soviet casualties compared to just 20,000 for the Germans and their allies. The German Army Group South pressed its advantage, encircling the Soviet 28th Army on June 13 in Operation Wilhelm and pushing back the 38th and 9th Armies on June 22.

