britain
 The American Revolution was a serious embarrassment to Britain, and especially to King George III. The king had to admit that things weren’t going well in the colonies…at least not where Britain was concerned. By now, the colonists had signed the Declaration of Independence that summer, and they were not going to be moved from achieving their goal to be a sovereign nation.
The American Revolution was a serious embarrassment to Britain, and especially to King George III. The king had to admit that things weren’t going well in the colonies…at least not where Britain was concerned. By now, the colonists had signed the Declaration of Independence that summer, and they were not going to be moved from achieving their goal to be a sovereign nation.
On this day, October 31, 1776, the king give a speech to the British Parliament, telling them about the signing of the United States Declaration of Independence and the revolutionary leaders who signed it, saying, “for daring and desperate is the spirit of those leaders, whose object has always been dominion and power, that they have now openly renounced all allegiance to the crown, and all political connection with this country.” I’m sure he felt that the colonists were rebels, who were not worth wasting time on by now, and he  hoped he could walk away from them without losing face any more than he already had. The British never intended for the United States to be anything more than the colones. The king went on to inform Parliament of the successful British victory over General George Washington and the Continental Army at the Battle of Long Island on August 27, 1776, but warned them that, “notwithstanding the fair prospect, it was necessary to prepare for another campaign.” Somehow, the king had the idea that there was still hope to keep the colonies.
hoped he could walk away from them without losing face any more than he already had. The British never intended for the United States to be anything more than the colones. The king went on to inform Parliament of the successful British victory over General George Washington and the Continental Army at the Battle of Long Island on August 27, 1776, but warned them that, “notwithstanding the fair prospect, it was necessary to prepare for another campaign.” Somehow, the king had the idea that there was still hope to keep the colonies.
Despite George III’s harsh words, General William Howe and his brother, Admiral Richard Howe, still hoped to convince the Americans to rejoin the British empire in the wake of the colonists’ humiliating defeat at the Battle of Long Island. They hoped to do  thing peacefully, but that was just not to be. The British could easily have prevented Washington’s retreat from Long Island and captured most of the Patriot officer corps, including the commander in chief. However, instead of forcing the former colonies into submission by executing Washington and his officers as traitors, the Howe brothers let them go with the hope of swaying Patriot opinion towards a return to the mother country. The Howe brothers’ attempts at negotiation failed, and the War for Independence dragged on for another four years, until the formal surrender of the British to the Americans on October 19, 1781, after the Battle of Yorktown. The freedom of the United States was not going to be taken from them…and that was a serious embarrassment to Britain.
thing peacefully, but that was just not to be. The British could easily have prevented Washington’s retreat from Long Island and captured most of the Patriot officer corps, including the commander in chief. However, instead of forcing the former colonies into submission by executing Washington and his officers as traitors, the Howe brothers let them go with the hope of swaying Patriot opinion towards a return to the mother country. The Howe brothers’ attempts at negotiation failed, and the War for Independence dragged on for another four years, until the formal surrender of the British to the Americans on October 19, 1781, after the Battle of Yorktown. The freedom of the United States was not going to be taken from them…and that was a serious embarrassment to Britain.
 During World War I, Britain, like the United States would have to do in World War II, had to employ large numbers of women into jobs vacated by men who had gone to fight in the war. They also had to create new jobs as part of the war effort. As an example, women were hired in munitions factories. The high demand for weapons resulted in the munitions factories becoming the largest single employer of women during 1918. It was a job that many people resisted, mainly because it was seen as “men’s work.” When I think about the work these women were doing, I find myself much more concerned with the toxicity and danger of the materials they were working with, than whether or not the job should be done by a man. Of course, the materials would present the same danger to the men, but the men had always felt like the dangerous work should fall to them.
During World War I, Britain, like the United States would have to do in World War II, had to employ large numbers of women into jobs vacated by men who had gone to fight in the war. They also had to create new jobs as part of the war effort. As an example, women were hired in munitions factories. The high demand for weapons resulted in the munitions factories becoming the largest single employer of women during 1918. It was a job that many people resisted, mainly because it was seen as “men’s work.” When I think about the work these women were doing, I find myself much more concerned with the toxicity and danger of the materials they were working with, than whether or not the job should be done by a man. Of course, the materials would present the same danger to the men, but the men had always felt like the dangerous work should fall to them.
Nevertheless, with the introduction of conscription in 1916 everything changed. Conscription refers to the process of automatically calling up men and women for military service. During the First World War men (it only applied to men at this time) who were conscripted into the armed forces had no choice but to go and fight, even if they did not want to. Around 1916, with the need becoming serious, the government began  coordinating the employment of women through campaigns and recruitment drives. This led to women working in areas of work that were formerly reserved for men. Jobs such as, for example railway guards, ticket collectors, buses, tram conductors, postal workers, police, firefighters, as well as bank tellers and clerks. Some women also worked heavy or precision machinery in engineering, led cart horses on farms, and worked in the civil service and factories.
coordinating the employment of women through campaigns and recruitment drives. This led to women working in areas of work that were formerly reserved for men. Jobs such as, for example railway guards, ticket collectors, buses, tram conductors, postal workers, police, firefighters, as well as bank tellers and clerks. Some women also worked heavy or precision machinery in engineering, led cart horses on farms, and worked in the civil service and factories.
By 1917 the British munitions factories, which by this time, primarily employed women workers, produced 80% of the weapons and shells used by the British Army. The women working there soon became known as “canaries” because they had to handle TNT (the chemical compound trinitrotoluene that is used as an explosive agent in munitions) which caused their skin to turn yellow. The nickname might have been a cute joke, but the job the women did was far from funny. These women risked their lives working with poisonous substances without adequate protective clothing or the required safety measures, that we know are needed now. During the years of World War I, around 400 women died from overexposure to TNT. I wonder too, how many died in  the years that followed the war, from exposure to the same chemicals that had killed the original 400 women.
the years that followed the war, from exposure to the same chemicals that had killed the original 400 women.
As if the dangerous working conditions weren’t enough, women were also paid significantly less than men in comparable positions. In 1918, women workers on London’s buses, trams, and subways organized a strike and managed to win equal pay for equal work. When the war ended, many women were fired to free up jobs for returning veterans. Some thanks that was. I’m sure many of the women were glad to go back to their prior jobs, or go home to take care of their families, but to be fired” was just wrong in every way. Nevertheless, in return for their hard work, these women were fired so that the returning men could have a job again.
 In March or 1941, the United States was largely considered neutral, so we could provide the countries, who were fighting Adolf Hitler, with war material. It was during this period of time, that the United Kingdom, an old enemy of the United States, since the United States fought against them for our independence, needed our help. Of course, we were allies by that time, and so the thought of a loan to the UK was not out o the question. The UK had been fighting against Adolf Hitler’s Germany army for a while by then, and funds were dwindling. The US loaned $4.33 billion to Britain in 1945, while Canada loaned US$1.19 billion in 1946, at a rate of 2% annual interest. It was a good deal, but in the end, the amount paid back was nearly double the amounts loaned in 1945 and 1946.
In March or 1941, the United States was largely considered neutral, so we could provide the countries, who were fighting Adolf Hitler, with war material. It was during this period of time, that the United Kingdom, an old enemy of the United States, since the United States fought against them for our independence, needed our help. Of course, we were allies by that time, and so the thought of a loan to the UK was not out o the question. The UK had been fighting against Adolf Hitler’s Germany army for a while by then, and funds were dwindling. The US loaned $4.33 billion to Britain in 1945, while Canada loaned US$1.19 billion in 1946, at a rate of 2% annual interest. It was a good deal, but in the end, the amount paid back was nearly double the amounts loaned in 1945 and 1946.
The United States was pulled into World War II shortly after, when Japan attacked Pearl Harbor. That marked to end of the program to provide military materials, because the United States was no longer considered neutral. At this point, the United States was very much needed in a very different way, and could not be neutral and be an effective help, but they also had a score to settle, and it could not be handled on the sidelines. The United States had hoped to sit this one out, but that was not to be. The Axis of Evil was winning against the Allied Nations, and they needed help, but it was the boldness of the attack on Pearl Harbor that finally awoke the sleeping giant that was the United States. The United States victory over Japan in the Battle of Midway was the turning point of the war in the Pacific. Then Germany invaded the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union defeated Germany at Stalingrad, marking the turning point of the war in Eastern Europe. As we all know, in the end the Allies were victorious in World War II.
There are still World War I debts owed to and by Britain. Since a moratorium on all debts from that conflict was agreed at the height of the Great Depression, no repayments have been made to or received from other nations since 1934. Despite the favorable rates there were six years in which Britain deferred payment because of economic or political crises. Britain settled its World War II debts to the United States and Canada when it paid the final  two installments in 2006. The payments of $83.25 million to the US and US$22.7 million to Canada are the last of 50 installments since 1950. Upon the final payments, the UK will have paid back a total of $7.5 billion to the US and US$2 billion to Canada. “This week we finally honor in full our commitments to the United States and Canada for the support they gave us 60 years ago,” said Treasury Minister Ed Balls at the time of those final payments. “It was vital support which helped Britain defeat Nazi Germany and secure peace and prosperity in the post-war period. We honor our commitments to them now as they honored their commitments to us all those years ago,” he added.
two installments in 2006. The payments of $83.25 million to the US and US$22.7 million to Canada are the last of 50 installments since 1950. Upon the final payments, the UK will have paid back a total of $7.5 billion to the US and US$2 billion to Canada. “This week we finally honor in full our commitments to the United States and Canada for the support they gave us 60 years ago,” said Treasury Minister Ed Balls at the time of those final payments. “It was vital support which helped Britain defeat Nazi Germany and secure peace and prosperity in the post-war period. We honor our commitments to them now as they honored their commitments to us all those years ago,” he added.
 The reasons that Britain decided to start a Penal Colony at Botany Bay, Australia are not fully agreed upon. Some say that that there were deeper motives than just a place to house their criminals. The soil at Botany Bay was perfect for growing flax. I suppose that the prisoners would need to be doing some kind of work as penance for their crimes. Nevertheless, Britain would be making a profit from the flax that was produced thee, and the bay was perfect for a port, which would be necessary to assist with trade. All in all, Botany Bay seemed like the best option for a penal colony for Britain, so the plans were put in place, and before long the penal colony became a reality.
The reasons that Britain decided to start a Penal Colony at Botany Bay, Australia are not fully agreed upon. Some say that that there were deeper motives than just a place to house their criminals. The soil at Botany Bay was perfect for growing flax. I suppose that the prisoners would need to be doing some kind of work as penance for their crimes. Nevertheless, Britain would be making a profit from the flax that was produced thee, and the bay was perfect for a port, which would be necessary to assist with trade. All in all, Botany Bay seemed like the best option for a penal colony for Britain, so the plans were put in place, and before long the penal colony became a reality.
When Governor Phillip arrived in 1788, he asked for carpenters, masons, bricklayers to help set up the colony, along with many tools of the trades. In January of 1788, the first 736 convicts banished from England to Australia arrived in Botany Bay. Over the next 60 years, approximately 50,000 criminals were transported from Great Britain to the Botany Bay in one of the strangest episodes in criminal-justice history. I think many of us have thought that some criminals should be place on a deserted island, but Britain basically did just that…with every criminal, it seems.
The accepted wisdom of the upper and ruling classes in 18th century England was that criminals were inherently defective. They did not believe criminals could be rehabilitated and that they simply required separation from the genetically pure, law-abiding citizens. Consequently, lawbreakers had to be either killed or exiled, because prisons were too expensive, and they criminals were not worth the money. With the American victory in the Revolutionary War, transgressors could no longer be shipped off across the Atlantic, so the English had to look for a colony in some other direction.
Captain Arthur Phillip, a tough but fair career naval officer, was charged with setting up the first penal colony in Australia. The convicts were chained beneath the deck during the entire hellish six-month voyage. The first voyage claimed the lives of nearly 10 percent of the prisoners, which remarkably proved to be a rather good rate. On later trips, up to a third of the unwilling passengers died on the way. These were not hardened criminals by any measure; only a small minority were transported for violent offenses. Among the first group was a 70-year-old woman who had stolen cheese to eat.
Although not confined behind bars, most convicts in Australia had an extremely tough life. The guards who volunteered for duty in Australia seemed to be driven by exceptional sadism. Even small violations of the rules could result in a punishment of 100  lashes with a whip. It was said that blood was usually drawn after five lashes, but they didn’t stop there. Convicts usually ended up walking home in boots filled with their own blood, if they could walk at all. Convicts who attempted to escape were sent to tiny Norfolk Island, 600 miles east of Australia. The conditions there were even more inhumane. The only hope of escape from the horror of Norfolk Island was a “game” in which groups of three prisoners drew straws. The short straw was killed as painlessly as possible and a judge was then shipped in to put the other two on trial, one playing the role of killer, the other as witness. I guess the only hope of escape was, in reality, death. There were no second chances for them.
lashes with a whip. It was said that blood was usually drawn after five lashes, but they didn’t stop there. Convicts usually ended up walking home in boots filled with their own blood, if they could walk at all. Convicts who attempted to escape were sent to tiny Norfolk Island, 600 miles east of Australia. The conditions there were even more inhumane. The only hope of escape from the horror of Norfolk Island was a “game” in which groups of three prisoners drew straws. The short straw was killed as painlessly as possible and a judge was then shipped in to put the other two on trial, one playing the role of killer, the other as witness. I guess the only hope of escape was, in reality, death. There were no second chances for them.
 Religious beliefs have caused a number of issues in governments over the centuries, sometimes pitting family members against family members. They were, in fact, the main reason that the United States was founded…to get away from religious persecution. Such was also the case in the coup that was called Britain’s Bloodless Glorious Revolution. At the time, King James II was the king in Britain, and he was a Catholic. At first that didn’t seem like a huge problem, but King James’s policies of religious tolerance after 1685 began to meet with increasing opposition from members of leading political circles, who were troubled by the King’s Catholicism and his close ties with France. The crisis facing the King came to a head in 1688, with the birth of his son, James Francis Edward Stuart, on June 10. This changed the existing line of succession by displacing the heir presumptive, his daughter Mary, a Protestant and the wife of William of Orange, with young James Francis Edward as heir apparent, because at that time it was the first born “son” who inherited the throne. The establishment of a Roman Catholic dynasty in the kingdoms now seemed likely, and the people weren’t happy about it.
Religious beliefs have caused a number of issues in governments over the centuries, sometimes pitting family members against family members. They were, in fact, the main reason that the United States was founded…to get away from religious persecution. Such was also the case in the coup that was called Britain’s Bloodless Glorious Revolution. At the time, King James II was the king in Britain, and he was a Catholic. At first that didn’t seem like a huge problem, but King James’s policies of religious tolerance after 1685 began to meet with increasing opposition from members of leading political circles, who were troubled by the King’s Catholicism and his close ties with France. The crisis facing the King came to a head in 1688, with the birth of his son, James Francis Edward Stuart, on June 10. This changed the existing line of succession by displacing the heir presumptive, his daughter Mary, a Protestant and the wife of William of Orange, with young James Francis Edward as heir apparent, because at that time it was the first born “son” who inherited the throne. The establishment of a Roman Catholic dynasty in the kingdoms now seemed likely, and the people weren’t happy about it.
Some Tory (conservative) members of parliament worked with members of the opposition Whigs in an attempt to resolve the crisis by secretly initiating dialogue with William of Orange to come to England…outside the jurisdiction of the English Parliament. Stadtholder William, the de facto head of state of the Dutch United Provinces, feared a Catholic Anglo–French alliance and had already been planning a military intervention in England, so he was very much open to the plan. After consolidating political and financial support, William crossed the North Sea and English Channel with a large invasion fleet in November 1688, landing at Torbay in Devonshire with an army of 15,000 men, William advanced to London, meeting no opposition from James’ army, which had deserted the king. After only two minor clashes between the two opposing armies in England, and anti-Catholic riots in several towns, King James’s regime collapsed, largely because of a lack of resolve shown by the king. Following Britain’s Bloodless Glorious Revolution, Mary, the daughter of the deposed king, and William of Orange, her husband, are proclaimed joint sovereigns of Great Britain under Britain’s new Bill of Rights. At first I thought that odd, because by rights she would have been in the royal line, but I suppose you would have to honor the warrior who made it all possible.
King James was allowed to escape to France, and in February 1689 Parliament offered the crown jointly to  William and Mary, provided they accept the Bill of Rights. The Bill of Rights, which greatly limited royal power and broadened constitutional law, granted Parliament control of finances and the army and prescribed the future line of royal succession, declaring that no Roman Catholic would ever be sovereign of England. The document also stated that Englishmen possessed certain inviolable civil and political rights, a political concept that was a major influence in the composition of the United States Bill of Rights, composed almost exactly a century later. The Glorious Revolution, the ascension of William and Mary, and the acceptance of the Bill of Rights were decisive victories for Parliament in its long struggle against the crown.
William and Mary, provided they accept the Bill of Rights. The Bill of Rights, which greatly limited royal power and broadened constitutional law, granted Parliament control of finances and the army and prescribed the future line of royal succession, declaring that no Roman Catholic would ever be sovereign of England. The document also stated that Englishmen possessed certain inviolable civil and political rights, a political concept that was a major influence in the composition of the United States Bill of Rights, composed almost exactly a century later. The Glorious Revolution, the ascension of William and Mary, and the acceptance of the Bill of Rights were decisive victories for Parliament in its long struggle against the crown.
 Donald Maclean and Guy Burgess were senior officials in the British Foreign Office and in 1951. They were trusted diplomats, but they had a dark side. They were well known to have left-leaning ideas, and eventually their ideas moved them so far out of line with the jobs they had that it was suspected, if not known that they had become spies for the Soviet Union. Maclean and Burgess were two of the original members of the notorious Cambridge Spy Ring, which was a ring of spies in the United Kingdom, who passed information to the Soviet Union during World War II. They were active at least into the early 1950s. Four members of the ring were originally identified: Kim Philby (cryptonym: Stanley), Donald Duart Maclean (cryptonym: Homer), Guy Burgess (cryptonym: Hicks) and Anthony Blunt (cryptonyms: Tony, Johnson). Once jointly known as the Cambridge Four and later as the Cambridge Five, the number increased as more evidence came to light.
Donald Maclean and Guy Burgess were senior officials in the British Foreign Office and in 1951. They were trusted diplomats, but they had a dark side. They were well known to have left-leaning ideas, and eventually their ideas moved them so far out of line with the jobs they had that it was suspected, if not known that they had become spies for the Soviet Union. Maclean and Burgess were two of the original members of the notorious Cambridge Spy Ring, which was a ring of spies in the United Kingdom, who passed information to the Soviet Union during World War II. They were active at least into the early 1950s. Four members of the ring were originally identified: Kim Philby (cryptonym: Stanley), Donald Duart Maclean (cryptonym: Homer), Guy Burgess (cryptonym: Hicks) and Anthony Blunt (cryptonyms: Tony, Johnson). Once jointly known as the Cambridge Four and later as the Cambridge Five, the number increased as more evidence came to light.
The group was recruited during their education at the University of Cambridge in the 1930s…hence the term Cambridge. There is much debate as to the exact timing of their recruitment by Soviet intelligence. Anthony Blunt claimed that they were not recruited as agents until they had graduated. Blunt, an Honorary Fellow of Trinity College, was several years older than Burgess, Maclean, and Philby; he acted as a talent-spotter and recruiter for most of the group save Burgess. Several people have been suspected of being additional members of the group; John Cairncross (cryptonym: Liszt) was identified as such by Oleg Gordievsky, although many others have also been accused of membership in the Cambridge ring. Both Blunt and Burgess were members of the Cambridge Apostles, an exclusive and prestigious society based at Trinity and King’s Colleges. Cairncross was also an Apostle. Other Apostles accused of having spied for the Soviets include Michael Whitney Straight and Guy Liddell.
The group was radical in their dealings, so I’m not sure that anyone was overly surprised when both Maclean and Burgess disappeared from England in 1951, although they may have assumed that they were assassinated. For years there was no trace of them, and I suppose people began to forget all about them. Nevertheless, there were rumors that they had been spies for the Soviet Union and had left England to avoid prosecution. For five years, nothing was heard of the pair. British intelligence suspected that they were in the Soviet Union, but Russian officials consistently denied any knowledge of their whereabouts.
Then, on February 11, 1956, the pair resurfaced and invited a group of journalists to a hotel room in Moscow. Burgess and Maclean were there to greet them, give a brief interview, and hand out a typed joint statement. In the statement, both men denied having served as Soviet spies. However, they very strongly declared their sympathy with the Soviet Union and stated that they had both been “increasingly alarmed by the post-war character of Anglo-American policy.” They claimed that the decision to leave England and live in Russia was due to their belief that only in Russia would there be “some chance of putting into practice in some form the convictions they had always had.” They were convinced that the Soviet Union desired a policy of “mutual understanding” with the West, but many officials in the United States and Great Britain were adamant in  their opposition to any working relationship with the Russians. They concluded by stating, “Our life in the Soviet Union convinced us we took at the time the correct decision.”
their opposition to any working relationship with the Russians. They concluded by stating, “Our life in the Soviet Union convinced us we took at the time the correct decision.”
While the surprise news conference solved the mystery of where Burgess and Maclean had been for the past five years, it did little to settle the question of why they had gone to the Soviet Union in the first place. Their statement also did not clear up the issue of whether or not they had spied for the Soviet Union. Evidence from both British and American intelligence agencies strongly suggested that the two, together with fellow Foreign Office workers Kim Philby and Sir Anthony Blunt, had engaged in espionage for the Russians. Both men spent the rest of their lives in the Soviet Union. Burgess died in 1963 and Maclean passed away in 1983. I don’t suppose we will ever know all of the British and possibly American secrets they shared with the Russians during those years, only that they were treasonous traitors.

 During the years of growing pains for the United States, it was not considered a nation with any power, or in fact, a nation at all. The British wanted to keep he American Colonies under its power for tax purposes, and for the power that comes when a nation owns large areas of land around the globe. The young country…still under the bonds of British rule, was rebelling against what they considered tyranny, however, they would not get very far without military help coming from somewhere. So, on November 29, 1775, the Second Continental Congress, met in Philadelphia, to establish a Committee of Secret Correspondence. The committee’s goal was to provide European nations with a Patriot interpretation of events in Britain’s North American colonies, in the hope of soliciting aid for the American war effort. The committee consisted of Benjamin Franklin, Benjamin Harrison, John Dickinson, John Hay, and Robert Morris. Following the meeting, the committee instructed Silas Deane to meet with French Foreign Minister Charles Gravier, Count de Vergennes, to stress America’s need for military stores and assure the French that the colonies were moving toward “total separation” from Great Britain. Covert French aid began filtering into the colonies soon after the outbreak of hostilities in 1775, but it was not enough. The Americans had to figure out a way to get more aid.
During the years of growing pains for the United States, it was not considered a nation with any power, or in fact, a nation at all. The British wanted to keep he American Colonies under its power for tax purposes, and for the power that comes when a nation owns large areas of land around the globe. The young country…still under the bonds of British rule, was rebelling against what they considered tyranny, however, they would not get very far without military help coming from somewhere. So, on November 29, 1775, the Second Continental Congress, met in Philadelphia, to establish a Committee of Secret Correspondence. The committee’s goal was to provide European nations with a Patriot interpretation of events in Britain’s North American colonies, in the hope of soliciting aid for the American war effort. The committee consisted of Benjamin Franklin, Benjamin Harrison, John Dickinson, John Hay, and Robert Morris. Following the meeting, the committee instructed Silas Deane to meet with French Foreign Minister Charles Gravier, Count de Vergennes, to stress America’s need for military stores and assure the French that the colonies were moving toward “total separation” from Great Britain. Covert French aid began filtering into the colonies soon after the outbreak of hostilities in 1775, but it was not enough. The Americans had to figure out a way to get more aid.
Deane, a Connecticut delegate to the Continental Congress, left for France on the secret mission on March 3, 1776. He managed to negotiate for unofficial assistance from France, in the form of ships containing military supplies, and recruited Gilbert du Motier, the marquis de Lafayette to share his military expertise with the Continental Army’s officer corps. The aid helped some, but America needed a real commitment from France. That was not so easy to obtain, until after the arrival of the charming Benjamin Franklin in France in December 1776. Then, after the American victory at the Battle of Saratoga in October 1777, the French became convinced that it was worth backing the Americans in a formal treaty. On February 6, 1778, the Treaties of Amity and Commerce and Alliance were signed, and in May 1778 the Continental Congress ratified them.

 One month later, war between Britain and France formally began when a British squadron fired on two French ships. During the American Revolution, French naval fleets proved critical in the defeat of the British, which was assured after the Battle of Yorktown in October 1781. In reality, this was a spy thriller right out of the likes of James Bond, in that every step of this maneuver was critical to the survival of the United States of America, and everything pretty much went exactly as planned.
One month later, war between Britain and France formally began when a British squadron fired on two French ships. During the American Revolution, French naval fleets proved critical in the defeat of the British, which was assured after the Battle of Yorktown in October 1781. In reality, this was a spy thriller right out of the likes of James Bond, in that every step of this maneuver was critical to the survival of the United States of America, and everything pretty much went exactly as planned.
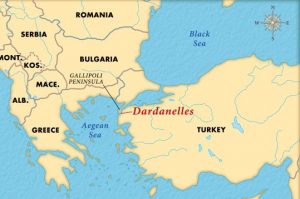
 The Dardanelles is a narrow strait running between the Black Sea in the east and the Mediterranean Sea in the west. In World War I it was a much contested area right from the start. It was the subject of a naval attack, spearheaded by Winston Churchill, who was at that time Britain’s young first lord of the Admiralty. On March 18, 1915, six English and four French battleships headed toward the strait. When they reached the area, Turkish mines blasted five of the ships, sinking three of them and forcing the Allied navy to draw back until land troops could be coordinated to begin an invasion of the Gallipoli peninsula. With troops from the Ottoman Empire and Germany mounting a spirited defense of the peninsula, however, the Gallipoli offensive turned into a significant setback for the Allies, with 205,000 casualties among British Empire troops and nearly 50,000 among the French.
The Dardanelles is a narrow strait running between the Black Sea in the east and the Mediterranean Sea in the west. In World War I it was a much contested area right from the start. It was the subject of a naval attack, spearheaded by Winston Churchill, who was at that time Britain’s young first lord of the Admiralty. On March 18, 1915, six English and four French battleships headed toward the strait. When they reached the area, Turkish mines blasted five of the ships, sinking three of them and forcing the Allied navy to draw back until land troops could be coordinated to begin an invasion of the Gallipoli peninsula. With troops from the Ottoman Empire and Germany mounting a spirited defense of the peninsula, however, the Gallipoli offensive turned into a significant setback for the Allies, with 205,000 casualties among British Empire troops and nearly 50,000 among the French.
When the Allies got involved, the latter offensives in Mesopotamia and Palestine saw more success. By September 1917, the crucial cities of Jerusalem and Baghdad were both in British hands. As the war stretched into the following year, these defeats and an Arab revolt had combined to destroy the Ottoman economy and devastate its land. Some 6 million people were dead and millions more starving. In early October 1918, unable to bank on a German victory any longer, the Turkish government in Constantinople decided to cut its losses and approached the Allies about brokering a peace deal. On October 30, 1918, British and Turkish representatives signed the Treaty of Mudros, which ended Ottoman participation in World War I. According to the terms of the treaty, Turkey had to demobilize its army, release all prisoners of war, and evacuate its Arab provinces, the majority of which were already under Allied control…and open the Dardanelles and Bosporus to Allied warships.
This last condition was fulfilled on November 12, 1918, the day after the armistice, when a squadron of British warships steamed through the Dardanelles, past the ruins of the ancient city of Troy, toward 
 Constantinople. By the post-war terms worked out by the Allies in the Treaty of Sevres in 1920, the waterways that were formerly under Ottoman rule…including the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmora and the Bosporus…were now placed under international control, with the designation that their “navigation…shall in future be open, both in peace and war, to every vessel of commerce or of war and to military and commercial aircraft, without distinction of flag.”
Constantinople. By the post-war terms worked out by the Allies in the Treaty of Sevres in 1920, the waterways that were formerly under Ottoman rule…including the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmora and the Bosporus…were now placed under international control, with the designation that their “navigation…shall in future be open, both in peace and war, to every vessel of commerce or of war and to military and commercial aircraft, without distinction of flag.”
 These days, some people are disenchanted with our country, and even willing to disrespect our flag, so I thought that today might be a good day to talk about our flag, our nation, and our national anthem. In the early days of our nation’s history, war was a rather common. The Revolutionary war and the freedom that came with it, did not mean that our enemies were done battling with us. In 1812, Britain was again at war with the United States, in the War of 1812, which lasted until 1815. British attempts to restrict United States trade, the Royal Navy’s impressment of American seamen and America’s desire to expand its territory, all contributed to the breakout of war. While there were defeats in battle, including the capture and burning of the nation’s capital, Washington DC, in August 1814, American troops were able to repulse British invasions in New York, Baltimore and New Orleans, which boosted national confidence and fostered a new spirit of patriotism. The ratification of the Treaty of Ghent on February 17, 1815, ended the war but left many of the most contentious questions unresolved. Nonetheless, many in the United States celebrated the War of 1812 as a “second war of independence,” beginning an era of partisan agreement and national pride. When I think of how things have changed since those days, I and both extremely sad and extremely mad.
These days, some people are disenchanted with our country, and even willing to disrespect our flag, so I thought that today might be a good day to talk about our flag, our nation, and our national anthem. In the early days of our nation’s history, war was a rather common. The Revolutionary war and the freedom that came with it, did not mean that our enemies were done battling with us. In 1812, Britain was again at war with the United States, in the War of 1812, which lasted until 1815. British attempts to restrict United States trade, the Royal Navy’s impressment of American seamen and America’s desire to expand its territory, all contributed to the breakout of war. While there were defeats in battle, including the capture and burning of the nation’s capital, Washington DC, in August 1814, American troops were able to repulse British invasions in New York, Baltimore and New Orleans, which boosted national confidence and fostered a new spirit of patriotism. The ratification of the Treaty of Ghent on February 17, 1815, ended the war but left many of the most contentious questions unresolved. Nonetheless, many in the United States celebrated the War of 1812 as a “second war of independence,” beginning an era of partisan agreement and national pride. When I think of how things have changed since those days, I and both extremely sad and extremely mad.
During the War of 1812, the friend of a man named Francis Scott Key was taken prisoner by the British. His  name was Dr William Beanes. Key went down to Baltimore, Maryland located the ship where Beanes was being held and negotiated his release. The British agreed to release Beanes, but would not let either of the men leave the ship until after the British bombardment of Fort McHenry. Key watched the bombing campaign unfold from aboard a ship located about eight miles away. After a day, the British were unable to destroy the fort and gave up. Key was relieved to see the American flag still flying over Fort McHenry and quickly penned a few lines in tribute to what he had witnessed. The date was September 13, 1814. The poem Key wrote that day…originally called “The Defense of Fort McHenry,” was changed to “The Star-Spangled Banner” in 1931. Most people would recognize that as our national anthem. The song told of the battle that Key was forced to watch, while praying that Fort McHenry could withstand the attack. That was probably one of the longest days of his life, but when the rockets would flash, he could see the flag, proudly waving…and afterward proclaiming the victory.
name was Dr William Beanes. Key went down to Baltimore, Maryland located the ship where Beanes was being held and negotiated his release. The British agreed to release Beanes, but would not let either of the men leave the ship until after the British bombardment of Fort McHenry. Key watched the bombing campaign unfold from aboard a ship located about eight miles away. After a day, the British were unable to destroy the fort and gave up. Key was relieved to see the American flag still flying over Fort McHenry and quickly penned a few lines in tribute to what he had witnessed. The date was September 13, 1814. The poem Key wrote that day…originally called “The Defense of Fort McHenry,” was changed to “The Star-Spangled Banner” in 1931. Most people would recognize that as our national anthem. The song told of the battle that Key was forced to watch, while praying that Fort McHenry could withstand the attack. That was probably one of the longest days of his life, but when the rockets would flash, he could see the flag, proudly waving…and afterward proclaiming the victory.
That flag and that song are both tributes to the brae men, and now women, who willingly fought and even gave  up their lives for this nation…for our freedom, the very freedom that allows it’s citizens to have free speech, which so many now use to disrespect our flag, our national anthem, our soldiers, and every respectful citizen of this country. These same people somehow wonder how we can be so upset with them…or maybe they know and like the drama queens they are, they love the drama of being on the wrong side of right and wrong. They just don’t like the consequences…such as people’s refusal to support them in their treason. As for me…I don’t believe in giving them any place in my story. I am a patriot…I will always be a patriot, and I will always honor our nation’s flag, anthem, and the soldiers who fought for our freedom.
up their lives for this nation…for our freedom, the very freedom that allows it’s citizens to have free speech, which so many now use to disrespect our flag, our national anthem, our soldiers, and every respectful citizen of this country. These same people somehow wonder how we can be so upset with them…or maybe they know and like the drama queens they are, they love the drama of being on the wrong side of right and wrong. They just don’t like the consequences…such as people’s refusal to support them in their treason. As for me…I don’t believe in giving them any place in my story. I am a patriot…I will always be a patriot, and I will always honor our nation’s flag, anthem, and the soldiers who fought for our freedom.

 After the Revolutionary War, and the United States independence that followed, the relationship between the two nations was quite strained. The United States did not like having British military posts on our northern and western borders, and Britain’s violation of American neutrality in 1794 when the Royal Navy seized American ships in the West Indies during England’s war with France. Finally, in an attempt to smooth things over, Supreme Court Chief Justice John Jay, who was appointed by President Washington, came up with a treaty. The treaty officially known as the “Treaty of Amity Commerce and Navigation, between His Britannic Majesty; and The United States of America” was signed by Britain’s King George III on November 19, 1794 in London. However, after Jay returned home with news of the treaty’s signing, President Washington, who was now in his second term, had encountered fierce Congressional opposition to the treaty. By 1795, its ratification was still uncertain, and there was work to be done to change things.
After the Revolutionary War, and the United States independence that followed, the relationship between the two nations was quite strained. The United States did not like having British military posts on our northern and western borders, and Britain’s violation of American neutrality in 1794 when the Royal Navy seized American ships in the West Indies during England’s war with France. Finally, in an attempt to smooth things over, Supreme Court Chief Justice John Jay, who was appointed by President Washington, came up with a treaty. The treaty officially known as the “Treaty of Amity Commerce and Navigation, between His Britannic Majesty; and The United States of America” was signed by Britain’s King George III on November 19, 1794 in London. However, after Jay returned home with news of the treaty’s signing, President Washington, who was now in his second term, had encountered fierce Congressional opposition to the treaty. By 1795, its ratification was still uncertain, and there was work to be done to change things.
The two biggest opponents to the treaty were two future presidents…Thomas Jefferson and James Madison. Jefferson was, at the time, in between political positions. He had just completed a term as Washington’s secretary of state from 1789 to 1793 and had not yet become John Adams’ vice president. Fellow Virginian, James Madison was a member of the House of Representatives. Jefferson, Madison and other opponents feared the treaty gave too many concessions to the British. They argued that Jay’s negotiations actually weakened American trade rights and complained that it committed the United States to paying pre-revolutionary debts to English merchants. Washington himself was not completely satisfied with the treaty, but considered preventing another war with America’s former colonial master a priority.
The treaty was finally approved by Congress on August 14, 1795, with exactly the two-thirds majority it needed 
 to pass. President Washington signed the treaty just four days later, on August 18, 1795. Washington and Jay may have won the legislative battle and averted war temporarily, but it created a conflict at home that highlighted a deepening division between those of different political ideologies in Washington DC, much like what we see these days. Jefferson and Madison mistrusted Washington’s attachment to maintaining friendly relations with England over revolutionary France, who would have welcomed the United States as a partner in an expanded war against England.
to pass. President Washington signed the treaty just four days later, on August 18, 1795. Washington and Jay may have won the legislative battle and averted war temporarily, but it created a conflict at home that highlighted a deepening division between those of different political ideologies in Washington DC, much like what we see these days. Jefferson and Madison mistrusted Washington’s attachment to maintaining friendly relations with England over revolutionary France, who would have welcomed the United States as a partner in an expanded war against England.

