boston

 Out of the blue, in 1722, the readers of a paper published in Boston, called The Courant, were treated to and fascinated by letters that were sent in by a widow with an razor-sharp wit and a gift for sarcasm. Her name was Mrs Silence Dogood. Mrs Dogood had an unusual sense of humor. She liked to poke fun at such illustrious institutions such as Harvard. For that, many of her readers loved her and became avid followers. She wasn’t afraid to speak her mind, and she wasn’t afraid to call a spade a spade. She told it like it was, and she didn’t care what others thought of her.
Out of the blue, in 1722, the readers of a paper published in Boston, called The Courant, were treated to and fascinated by letters that were sent in by a widow with an razor-sharp wit and a gift for sarcasm. Her name was Mrs Silence Dogood. Mrs Dogood had an unusual sense of humor. She liked to poke fun at such illustrious institutions such as Harvard. For that, many of her readers loved her and became avid followers. She wasn’t afraid to speak her mind, and she wasn’t afraid to call a spade a spade. She told it like it was, and she didn’t care what others thought of her.
So…just who was Mrs Dogood? Rumor had it that she was just an old widow woman who had been around long enough to have long lost any concern over what people thought of her. Maybe her many years of life had given her insight that no one else had. I remember reading Ann Lander’s column when I was a girl and a young married woman. Her advise always seemed so wise. I remember a number of articles from various columnists, and there again, my thought was, “How did they know so much?” I was sure they must have multiple degrees. Of course, while they might have had a degree or two, that did not make them any smarter than the next guy…and this type of writing was usually more about logic and common sense, that learned skill. So, who was Mrs Silence Dogood? That is the question of the day.
The answer to that question will most likely shock you. The reality is that Mrs Silence Dogood was the pen name used by Benjamin Franklin. Now, while Benjamin Franklin was a very intelligent man, as we all know. the fact remains that at the time he was writing under the pen name of Mrs Silence Dogood, Franklin was a boy of just 16 years. He was too young to be taken seriously or to have any possibility of getting his writings published, so he came up with an ingenious solution. His goal was to have his work published in the New-England Courant…a newspaper founded and published by his brother James Franklin. He took this goal seriously, especially after he was denied several times when he tried to publish letters under his own name in the Courant. Mrs Silence Dogood wrote 14 letters, which were first printed in 1722, and can be read here.
At the time of the printing of those letters, Franklin worked as an apprentice in his older brother’s printing shop in Boston. Franklin was a boy who had yet to get something he wrote published, so at 16, and desperate to finally receive the respect and recognition he felt he justly deserved. His idea was to create the persona of a 
 middle-aged widow named Silence Dogood. Once every two weeks, Franklin left a letter under the door of his brother’s printing shop. A total of 14 letters were sent. For months no one knew the identity of Mrs Dogood, but everyone was completely enthralled. Those letters were the talk of the town…even after they found out they were written by a 16-year-old Benjamin Franklin.
middle-aged widow named Silence Dogood. Once every two weeks, Franklin left a letter under the door of his brother’s printing shop. A total of 14 letters were sent. For months no one knew the identity of Mrs Dogood, but everyone was completely enthralled. Those letters were the talk of the town…even after they found out they were written by a 16-year-old Benjamin Franklin.

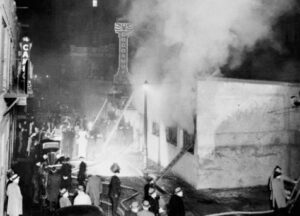 One of the saddest realities is that safety standards are often the result of a tragedy. That is exactly what happened during what is still the deadliest nightclub fire in the world, and the second-deadliest single-building fire…after the Iroquois Theatre fire. On November 28, 1942, Cocoanut Grove was well known as one of Boston’s most popular nightspots. The club attracted many celebrity guests and Boston’s most elite citizens. The fire was a tragedy that later became the catalyst for change in fire prevention, and how to survive a fire. Unfortunately, 492 people have to pay for these lessons with their lives.
One of the saddest realities is that safety standards are often the result of a tragedy. That is exactly what happened during what is still the deadliest nightclub fire in the world, and the second-deadliest single-building fire…after the Iroquois Theatre fire. On November 28, 1942, Cocoanut Grove was well known as one of Boston’s most popular nightspots. The club attracted many celebrity guests and Boston’s most elite citizens. The fire was a tragedy that later became the catalyst for change in fire prevention, and how to survive a fire. Unfortunately, 492 people have to pay for these lessons with their lives.
The Cocoanut Grove was owned by Barnet “Barney” Welansky, who was closely connected to the Mafia and to Mayor Maurice J Tobin. As often happens, anyone connected to the Mafia and/or a politician, also believes they are above the law. They do things the way they want to, cutting corners to save a buck, and then they expect their connections to get them out of trouble when and if it shows up. Welansky was no different. In the building and running of his nightclub, fire regulations had been pretty much disregarded, because as we all know, regulations are for other people to follow, but not, in this case, the Cocoanut Grove. There was a constant concern about people sneaking in the exit doors, so rather than pay for security to prevent such actions, some exit-doors had been locked to prevent said unauthorized entry. The decor wasn’t always checked for safety either, like the elaborate palm tree décor, which contained flammable materials. Also, because of wartime shortages of freon, the air-conditioning used flammable gas to cool the club. Welansky often disregarded the capacity laws to bring in bigger profits, and so it was that during the first Thanksgiving weekend since the United States had entered World War II, the Grove was filled to more than twice its legal capacity.
When disaster struck, it was in the form of a fire that was initiated by an electrical short and fueled by methyl chloride in the air conditioning unit. Once it started, the fire and its associated smoke spread rapidly through all 
 areas of the club. The problem…people were unable to escape due in part to locked exit doors. The only saving grace was that the local hospitals were especially well prepared to treat the casualties, because they had been rehearsing emergency drills in response to possible wartime attacks on the East Coast. Had that not been the case, the death toll would have likely included the 130 survivors too. If “good” can be said to come from tragedy, it would come in the form of the demonstrated value of the new blood banks and stimulated important advances in the treatment of burn victims. As always happens after a tragedy, many new laws were enacted for public establishments, including the banning of flammable decorations, a provision that emergency exits must be kept unlocked (from the inside), and that revolving doors cannot be the only exit.
areas of the club. The problem…people were unable to escape due in part to locked exit doors. The only saving grace was that the local hospitals were especially well prepared to treat the casualties, because they had been rehearsing emergency drills in response to possible wartime attacks on the East Coast. Had that not been the case, the death toll would have likely included the 130 survivors too. If “good” can be said to come from tragedy, it would come in the form of the demonstrated value of the new blood banks and stimulated important advances in the treatment of burn victims. As always happens after a tragedy, many new laws were enacted for public establishments, including the banning of flammable decorations, a provision that emergency exits must be kept unlocked (from the inside), and that revolving doors cannot be the only exit.
The investigation centered around Welansky’s blatant disregard for the safety of the very patrons who gave him his wealth by their continued patronage of his establishment. An official report revealed that “the Cocoanut Grove had been inspected by a captain in the Boston Fire Department (BFD) just ten days before the fire and declared safe. Further, it was found that the Grove had not obtained any licenses for operation for several years. There were no food handlers’ permits and no liquor licenses. Stanley Tomaszewski, the busboy who had allegedly started the fire, was underage and should not have been working there. Moreover, the recent remodeling of the Broadway Lounge had been done without building permits, using unlicensed contractors.” Tomaszewski testified at the inquiry and was exonerated, as he was not responsible for the flammable decorations or the life safety code violations. While declared innocent, Tomaszewski would pay for the “crime” anyway, in the form of being “ostracized for much of his life because of the fire.” Tomaszewski died in 1994. In the end, the blame was rightly assigned to Welansky, for violation of the existing safety standards, and upon 
 his conviction in 1943, Welansky was sentenced to 12–15 years in prison. Welansky served nearly four years before being quietly pardoned by Tobin, who had been elected governor of Massachusetts since the fire. In December 1946, diagnosed with cancer, Welansky was released from Norfolk Prison, telling reporters, “I wish I’d died with the others in the fire.” Nine weeks later on 27 Jan 1947 the cancer took his life. He was 49 years old.
his conviction in 1943, Welansky was sentenced to 12–15 years in prison. Welansky served nearly four years before being quietly pardoned by Tobin, who had been elected governor of Massachusetts since the fire. In December 1946, diagnosed with cancer, Welansky was released from Norfolk Prison, telling reporters, “I wish I’d died with the others in the fire.” Nine weeks later on 27 Jan 1947 the cancer took his life. He was 49 years old.

 Firefighter and Benjamin Franklin…not usually thought of in the same sentence, but really, they should be. In 1736, Benjamin Franklin was already a young man of influence, but his ambitions didn’t stop at just a few. Most of us think of Benjamin Franklin as a scientist, inventor, founding father, prankster, and writer, but firefighter…hmmmmm, not so much. Nevertheless, Benjamin Franklin was a visionary. He saw a problem and decided to fix it.
Firefighter and Benjamin Franklin…not usually thought of in the same sentence, but really, they should be. In 1736, Benjamin Franklin was already a young man of influence, but his ambitions didn’t stop at just a few. Most of us think of Benjamin Franklin as a scientist, inventor, founding father, prankster, and writer, but firefighter…hmmmmm, not so much. Nevertheless, Benjamin Franklin was a visionary. He saw a problem and decided to fix it.
By 1736 Franklin had adopted Philadelphia, Pennsylvania as his home, but during a visit to his hometown of Boston, Massachusetts, he witnessed a fire, and his mind went into overdrive. What he saw was that the safety precautions to keep fire from spreading seemed to be far more advanced in Boston than in Philadelphia. At that time, Philadelphia’s infrastructure was basically a maze of wooden buildings and houses squeezed together in such a way that it was almost like kindling for a bonfire. Franklin saw this decided that something needed to be done. So, he published his findings in his own Philadelphia Gazette. In doing so, he turned up a different kind of heat. Before long, he was able to round up about 30 of his friends and fellow business owners who were interested. So together, the founded the Union Fire Company. Franklin made sure that The Union Fire Company was a non-profit organization…run completely by volunteers. What made this attractive to these business owners is that it was essentially a promise, to always have each other’s backs, if a fire broke out on or close to one of their properties. Not only were they promising to help extinguish the flames and save homes, but each member was required to keep a heavy-duty bag in which to smuggle out any possessions they could salvage as well. It was a code of honor to try, in the midst of disaster, to salvage whatever they could of the lives of the occupants. The Union Fire Company quickly became the biggest fire relief company in the Colonies, or as they later became, the United States.
Never being one to just sit back and tell others what to do, Benjamin Franklin became a volunteer firefighter himself. Soon, there were six volunteer corps established in Philadelphia. This fire company was the first volunteer fire company of its kind in the United States. When people saw how well the system worked, volunteer fire companies sprung up across the city and soon all over the country. We think of Benjamin Franklin 
 as many things, but in reality, we should maybe think of him as much more than we do. He was the brainchild behind the Great Compromise, which created the Congress we still have today. He was also the first fireman in another way. He “put out the fiery debates” and created a sense of compromise and peace among the founding fathers of our nation too, but he was an actual firefighter in that he actually fought the fires in his city.
as many things, but in reality, we should maybe think of him as much more than we do. He was the brainchild behind the Great Compromise, which created the Congress we still have today. He was also the first fireman in another way. He “put out the fiery debates” and created a sense of compromise and peace among the founding fathers of our nation too, but he was an actual firefighter in that he actually fought the fires in his city.

 No country can truly be secure without an army, and the Thirteen Colonies (now the United States) was no different. After the beginning of the Revolutionary War, John Adams began to see the value of an army, so on June 10, 1775, he proposed to Congress, at a meeting in Philadelphia, that the men laying siege to Boston should be considered a Continental Army led by a general. The men who were mostly from New England, had armed themselves and rushed to surround British forces in Boston following the Battle of Lexington and Concord. Adams, who was representing Massachusetts, realized that the military effort would only succeed if the British thought the colonies were united. To achieve his united feel, Adams suggested than they appoint George Washington of Virginia, to command the Continental forces, despite the fact that New Englanders were used to fighting in local militias under officers elected from among their own ranks.
No country can truly be secure without an army, and the Thirteen Colonies (now the United States) was no different. After the beginning of the Revolutionary War, John Adams began to see the value of an army, so on June 10, 1775, he proposed to Congress, at a meeting in Philadelphia, that the men laying siege to Boston should be considered a Continental Army led by a general. The men who were mostly from New England, had armed themselves and rushed to surround British forces in Boston following the Battle of Lexington and Concord. Adams, who was representing Massachusetts, realized that the military effort would only succeed if the British thought the colonies were united. To achieve his united feel, Adams suggested than they appoint George Washington of Virginia, to command the Continental forces, despite the fact that New Englanders were used to fighting in local militias under officers elected from among their own ranks.
Five days later, on June 15th, Adams formally nominated George Washington as commander in chief of the Continental Army. Washington accepted the post on June 16th, and on June 17th, with no rest for the troops, the newly named army fought the Battle of Bunker Hill. John Adam’s wife, Abigail, and son, John Quincy Adams, watched the battle from their hometown of Braintree.
Just as the British had discovered the difficulties of waging war with rowdy and uncontrollable Yankees for soldiers during the Seven Years’ War, Washington was equally unimpressed when he met his supposed army. Just as the British had, he saw “stupidity” among the enlisted men, who were used to the easy familiarity of being commanded by neighbors. Upon arrival outside Boston, General George Washington organized this body of more than 22,000 men, known as the Main Army, into three divisions of two brigades each, promptly 
 insisting that the officers behave with decorum and the enlisted men with respect. Washington had some success with this first Continental Army, but when the New Englanders went home to their farms at the end of 1775, General Washington had to start fresh with new recruits in 1776. In retrospect, I’m sure Washington had better control over the second Continental Army, because they didn’t know any other leadership style. George Washington remained the commander of the Continental Army until the end of the Revolutionary War.
insisting that the officers behave with decorum and the enlisted men with respect. Washington had some success with this first Continental Army, but when the New Englanders went home to their farms at the end of 1775, General Washington had to start fresh with new recruits in 1776. In retrospect, I’m sure Washington had better control over the second Continental Army, because they didn’t know any other leadership style. George Washington remained the commander of the Continental Army until the end of the Revolutionary War.
 I have been to and inside the Statue of Liberty, and it is a place I’ll never forget. I was a teenager at the time, but I can still vividly picture the inside, as well as the outside. I think the thing that most stuck in my head is that to go up into the statue was a rather tight corridor. The arm was closed when we were there, but we didn’t really know why. For a time, especially after 9-11, no one was allowed to go into the Statue of Liberty at all, for fear of another terrorist attack.
I have been to and inside the Statue of Liberty, and it is a place I’ll never forget. I was a teenager at the time, but I can still vividly picture the inside, as well as the outside. I think the thing that most stuck in my head is that to go up into the statue was a rather tight corridor. The arm was closed when we were there, but we didn’t really know why. For a time, especially after 9-11, no one was allowed to go into the Statue of Liberty at all, for fear of another terrorist attack.
Prior to the 9-11 concerns, the Statue of Liberty was examined by French and American engineers for structural stability in 1982, as part of the planning for its centennial in 1986. Following the examination, it was announced that the statue was in need of considerable restoration. Careful examination had revealed that the right arm  had been improperly attached to the main structure. It was swaying more and more when strong winds blew and there was a significant risk of structural failure. This is information that I’m thankful I didn’t have when I went up into the statue in 1973. I recall being disappointed that we couldn’t go up in the arm then, but apparently they knew of the issues even then. Of further concern, the head had been installed 2 feet off center, and one of the rays was wearing a hole in the right arm when the statue moved in the wind. All the problems warranted the repairs done in 1984. She also got a nose job and her arm was shifted slightly to a better position. This information, though not well know, was really bad news, when you think about it. The statue had been standing in this place for 96 years by the time these flaws were discovered. Imagine what could have happened, especially with the arm improperly
had been improperly attached to the main structure. It was swaying more and more when strong winds blew and there was a significant risk of structural failure. This is information that I’m thankful I didn’t have when I went up into the statue in 1973. I recall being disappointed that we couldn’t go up in the arm then, but apparently they knew of the issues even then. Of further concern, the head had been installed 2 feet off center, and one of the rays was wearing a hole in the right arm when the statue moved in the wind. All the problems warranted the repairs done in 1984. She also got a nose job and her arm was shifted slightly to a better position. This information, though not well know, was really bad news, when you think about it. The statue had been standing in this place for 96 years by the time these flaws were discovered. Imagine what could have happened, especially with the arm improperly  installed. The armature structure was badly corroded, and about two percent of the exterior plates needed to be replaced. Although problems with the armature had been recognized as early as 1936, when cast iron replacements for some of the bars had been installed, much of the corrosion had been hidden by layers of paint applied over the years. The whole statue was literally a ticking time bomb. Following the repairs, the statue would be much safer and could again be used, but that was not the end of her secrets.
installed. The armature structure was badly corroded, and about two percent of the exterior plates needed to be replaced. Although problems with the armature had been recognized as early as 1936, when cast iron replacements for some of the bars had been installed, much of the corrosion had been hidden by layers of paint applied over the years. The whole statue was literally a ticking time bomb. Following the repairs, the statue would be much safer and could again be used, but that was not the end of her secrets.
Most people think that the Statue of Liberty was a gift from the nation of France, and while it did come from France, it was actually partly a gift from the manufacturer in France (not the French nation). on top of that, Americans had to pay for the pedestal and partly contributed to the cost of the statue itself. Fundraisers were held in Boston and Philadelphia, in order to win the right to have the statue, but in the end, it went to New York. I’m sure many people who helped with the fundraising were very disappointed. This was another secret of the Statue of Liberty that I did not know.

 Sometimes, a picture can instill such a strange awareness within us that it is hard to get the picture out of our heads. It doesn’t have to be something horrible, bloody, or shocking, but simply something unusual. The phone tower in Stockholm, Sweden, built in 1887 is that kind of a picture, for sure.
Sometimes, a picture can instill such a strange awareness within us that it is hard to get the picture out of our heads. It doesn’t have to be something horrible, bloody, or shocking, but simply something unusual. The phone tower in Stockholm, Sweden, built in 1887 is that kind of a picture, for sure.
Technology has changed so much over the years, and this tower was a relic of the past. That is probably why the image has stuck in my head all this time. The tower served its purpose at the time, connecting 5,000 telephone wires and providing service to all those people, but to me it seemed rather dangerous in many ways. The telephone was an amazing invention, but somehow, the idea of buried cable never occurred to the inventor or the engineers who made it a reality for everyone. The service was very expensive, and so only for the wealthy…a fact that would change in years to come.
Similar towers sprang up around the world, and most residents soon grew to hate the massive amounts of lines that littered their skyline. Still, it was the only way at the time, and the telephone was, after all, an important invention. Too bad they couldn’t immediately come up with the wireless version we all enjoy these days. The telephone towers were used shortly before telephone companies started burying their wires in about 1913.
The change was well received, since most residents hated it, and some of the work was done after a snowstorm downed telephone poles, causing the cities to pay for the changes. Soon the hated phone lines began to disappear. I can see why the towers are hated, and to this day, most photographers hate to have the towers 
 and wires in their photographs. I have often found myself wishing the wires were missing from that perfect shot I got as my husband and I walked along the walking paths in Casper, so I can understand the way the residents of Stockholm, New York, and Boston felt about the monstrosity that was the telephone lines in their cities. Thankfully for the residents, the problem was solved when the tower burned down on July 25, 1953.
and wires in their photographs. I have often found myself wishing the wires were missing from that perfect shot I got as my husband and I walked along the walking paths in Casper, so I can understand the way the residents of Stockholm, New York, and Boston felt about the monstrosity that was the telephone lines in their cities. Thankfully for the residents, the problem was solved when the tower burned down on July 25, 1953.
 Years ago, when the telephone first came out, the only way to call someone, if they had a phone, that is, was to go through the operator. Basically, you picked up your phone, and often, cranked a ringer to get the attention of the operator, and then told them who you wanted to talk to. The operator would then connect you with the person you were calling by way of a switchboard. Of course, that meant that the operator could also stay on the line and listen to the whole conversation, if she chose to do so. The switchboard operator was needed to make any call except if two people had a party line.
Years ago, when the telephone first came out, the only way to call someone, if they had a phone, that is, was to go through the operator. Basically, you picked up your phone, and often, cranked a ringer to get the attention of the operator, and then told them who you wanted to talk to. The operator would then connect you with the person you were calling by way of a switchboard. Of course, that meant that the operator could also stay on the line and listen to the whole conversation, if she chose to do so. The switchboard operator was needed to make any call except if two people had a party line.
Many people have no idea what a party line is, but my friend Gale Dugger Oskolkoff had one when her family lived in the Casper area, and her, her sisters, and I used to have a great time listening in on the calls that were made to a girl who had the unfortunate position of being a teenaged girl with a boyfriend and a party line. She use to get so mad at us. I don’t even know her name, but if she could have, I think she would have reached through the phone and choked us. Of course, I feel sorry for her now, because there was pretty much no privacy in her love life, but it was fun…for us anyway.
Before long, party lines became a thing of the past, and while direct distance dialing came into being before party lines went out, direct distance dialing was a brand new technology on November 10, 1951, when it was first offered on trial basis at Englewood, New Jersey, to 11 selected major cities across the United States. This service grew rapidly across major cities during the 1950s. The first direct-dialed long-distance telephone calls were possible in the New Jersey communities of Englewood and Teaneck. Customers of the ENglewood 3, ENglewood 4 and TEaneck 7 exchanges, who could already dial New York City and area, were able to dial 11 cities across the United States, simply by dialing the three-digit area code and the seven-digit number, which at the time consisted of the first two letters of the central office name and five digits. On November 10, 1951, Englewood Mayor M. Leslie Denning made the first customer-dialed long distance call, to Mayor Frank Osborne of Alameda, California.
The eleven destinations at that time were:
617: Boston, Massachusetts
312: Chicago, Illinois
216: Cleveland, Ohio
313: Detroit, Michigan
414: Milwaukee, Wisconsin
415: Oakland, California
215: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
412: Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
401: Providence, Rhode Island
916: Sacramento, California
318: San Francisco – San Francisco required the special code 318 for temporary routing requirements
Many other cities could not be included, as they did not yet have the necessary toll switching equipment to handle incoming calls automatically on their circuits. As with any technology, these changes take time to implement. Other cities still had either a mixture of local number lengths or were all still six-digit numbers. Montreal, Quebec and Toronto, Ontario in Canada, for example, had a mix of six and seven-digit numbers from 1951 to 1957, and did not have direct distance dialing until 1958. Whitehorse, Yukon, had seven-digit numbers from 1965, but the necessary switching equipment was not in place locally until 1972.

These days, all this seems completely archaic, considering the fact that even the phone lines that were installed on poles and underground are almost not necessary in today’s world. With the implementation of wireless…everything, we no longer need to have a phone line to have a phone, and in fact a home phone is not necessary for most people, because a cellular phone can be taken with us where ever we go, so we never need to miss a call, unless our work does not allow us to have the phone with us. Phones have come a long way since the days of switchboards, operators, and phone lines, and I think most of us would agree that it’s better now, although there are those who like to be disconnected.
 For some reason, there are certain areas on the United States, and the world, where earthquakes are…unexpected. There are just no real fault lines in these places, and no man-made reasons for it, like mining or drilling. So often people think they live in an area that is completely safe from an earthquake. Nevertheless, that does not mean that an earthquake can’t happen, as the people of Charleston, South Carolina found out on August 31, 1886.
For some reason, there are certain areas on the United States, and the world, where earthquakes are…unexpected. There are just no real fault lines in these places, and no man-made reasons for it, like mining or drilling. So often people think they live in an area that is completely safe from an earthquake. Nevertheless, that does not mean that an earthquake can’t happen, as the people of Charleston, South Carolina found out on August 31, 1886.
The first indicator that something strange was going on, came on August 27 and 28, when foreshocks were felt in Summerville, South Carolina, where my first cousin once removed, Stephanie Willard and her family live. While the tremors were odd, the people of the area didn’t think they were a warning for what was coming. Then, at 9:51pm on August 31, the rumbling began. The 7.6 magnitude quake was felt as far away as Boston, Chicago and Cuba. Buildings as far away as far away as Ohio and Alabama were damaged. But, it was Charleston, South Carolina, that took the biggest hit from the quake. Almost all of the buildings in town were seriously damaged. About 14,000 chimneys fell from the earthquake’s shaking. It caused multiple fires, and  water lines and wells were ruptured. The total damage was in excess of $5.5 million, which would be about $112 million today.
water lines and wells were ruptured. The total damage was in excess of $5.5 million, which would be about $112 million today.
While that was a disaster in itself, it was the loss of life that was felt the worst. More that 100 people lost their lives that fateful day, and countless others were injured, in what is still the largest recorded earthquake in the history of the southeastern United States. The quake damaged as many as 2,000 buildings, including buildings as far away as central Alabama, central Ohio, eastern Kentucky, southern Virginia and western West Virginia. The strange part about this quake is the fact that there were no apparent surface cracks as a result of this tremor, railroad tracks were bent in all directions in some locations. Acres of land were liquefied. This quake remained a mystery for many years since there were no known underground faults for 60 miles in any direction. Then, as science and detection methods got better, scientists have recently uncovered a concealed fault along the coastal plains of Virginia and the Carolinas. While this fault is now known, scientists think that another quake of this magnitude remains highly  unlikely, though not impossible, in this location.
unlikely, though not impossible, in this location.
I guess I don’t quite understand that concept, except to say that if it is the only fault and has nothing to connect to, maybe there is less chance of a small tremor turning into a big quake, and maybe that is why they don’t expect another quake of that magnitude. Still, it is always good advise to realize that no place is immune to earthquakes. Oklahoma has found that out in recent years, as underground mining work has created quake situations that weren’t there before. It is still my hope that the Charleston area never has another quake like the one they had in 1886.

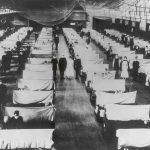 Not everyone agrees with getting the flu shot, and I get that. Still, even though there have been issues with the flu shot, it has also been something, along with medicines that has helped to prevent breakouts like the flu pandemic that hit Philadelphia on this day, September 28, 1918. It is believed that a Liberty Loan parade prompted the outbreak in Philadelphia, and before the outbreak was over, an estimated 30 million people worldwide were dead. As most of us know, influenza is a virus that attacks the respiratory system, is highly contagious, and mutates very quickly to avoid being killed by the human immune system. A prior pandemic of the flu in 1889 killed thousands all over the world, but it was nothing like the 1918 Flu Pandemic in its deadliness.
Not everyone agrees with getting the flu shot, and I get that. Still, even though there have been issues with the flu shot, it has also been something, along with medicines that has helped to prevent breakouts like the flu pandemic that hit Philadelphia on this day, September 28, 1918. It is believed that a Liberty Loan parade prompted the outbreak in Philadelphia, and before the outbreak was over, an estimated 30 million people worldwide were dead. As most of us know, influenza is a virus that attacks the respiratory system, is highly contagious, and mutates very quickly to avoid being killed by the human immune system. A prior pandemic of the flu in 1889 killed thousands all over the world, but it was nothing like the 1918 Flu Pandemic in its deadliness.
It is thought that the 1918 flu pandemic originated with a bird or farm animal in the American Midwest early that year. It may have traveled among birds, pigs, sheep, moose, bison, and elk, eventually mutating to the version that took hold in the human population that year. Like most outbreaks, this one started slowly, but as people moved from place to place, and others came in to help, it began to spread like wildfire. Once it spread to Europe later in the year, through some of the 200,000 American troops shipped out to fight in World War I, it was out of control. It affected every area of life, and people wore masks to avoid contact with the virus.
By June 1918, it had largely disappeared in North America, but only after taking a considerable toll on the people. Over the summer of 1918, it spread quickly over Europe. It’s first stop seems to have been in Spain, and it took so many lives there, that it was named the Spanish Flu. This flu was highly unusual, because it seemed to affect strong people in the prime of their lives rather than babies and the elderly. By the end of the summer, about 10,000 people were dead. In most cases, hemorrhages in the nose and lungs killed victims within three days. By fall, it was completely out of control. By the time it reached London and Boston in 
 September, it was a far worse strain that it had been before. Twelve thousand soldiers came down with the flu in Massachusetts in mid-September. Philadelphia was the hardest hit city in the United States with a loss of nearly 12,000. The whole city was quarantined. In the United States, five out of every thousand people fell victim to the flu. Other countries were far worse, some as much as ten, fifteen or even thirty five per thousand, with 20 million people dying in India alone. In the end, more people died from the influenza pandemic, than from all of the battles of World War I combined.
September, it was a far worse strain that it had been before. Twelve thousand soldiers came down with the flu in Massachusetts in mid-September. Philadelphia was the hardest hit city in the United States with a loss of nearly 12,000. The whole city was quarantined. In the United States, five out of every thousand people fell victim to the flu. Other countries were far worse, some as much as ten, fifteen or even thirty five per thousand, with 20 million people dying in India alone. In the end, more people died from the influenza pandemic, than from all of the battles of World War I combined.
 These days, most tsunami waves come with prior warning…at least since the 1946 wave that hit Alaska and Hawaii. Nevertheless, there are disastrous waves that are largely unpredictable, and those can be as deadly as the ones that the Pacific Tsunami Warning System warns people about. One in particular I had never heard of, until my sister Cheryl Masterson heard about it and mentioned it a few days ago. It happened in Boston, Massachusetts on January 15, 1919, and while it was of a very different variety than most tsunamis, it was deadly nevertheless. This tsunami was so strange, in fact, that most people wouldn’t even believe that this is a true story, but it did happen.
These days, most tsunami waves come with prior warning…at least since the 1946 wave that hit Alaska and Hawaii. Nevertheless, there are disastrous waves that are largely unpredictable, and those can be as deadly as the ones that the Pacific Tsunami Warning System warns people about. One in particular I had never heard of, until my sister Cheryl Masterson heard about it and mentioned it a few days ago. It happened in Boston, Massachusetts on January 15, 1919, and while it was of a very different variety than most tsunamis, it was deadly nevertheless. This tsunami was so strange, in fact, that most people wouldn’t even believe that this is a true story, but it did happen.
Around 12:40pm on January 15, 1919, a storage tank holding 2.3 million gallons of molasses exploded at the Purity Distilling Co. in the North End of Boston, sending waves of molasses rushing through the streets at almost 35 miles per hour. I’m sure that many people wouldn’t even think of this event as being at all dangerous, I mean after all, it’s just molasses. Nevertheless, a 25 foot high wave of molasses coming at you going 35 miles per hour is as deadly as being hit be a car. There was no warning, and in reality, there couldn’t  be. The molasses was being stored in the tank awaiting transfer to another plant and, due to its quickly rising temperature, it set off a tragic and previously unheard of chain of events. According to witnesses, the ground shook as if a tornado or freight train were coming down the street.
be. The molasses was being stored in the tank awaiting transfer to another plant and, due to its quickly rising temperature, it set off a tragic and previously unheard of chain of events. According to witnesses, the ground shook as if a tornado or freight train were coming down the street.
According to The Boston Globe, citizens “were picked up by a rush of air and hurled many feet.” A truck itself was picked up by the gushing wave and thrown into Boston Harbor. The force of the wave was so destructive, it almost tipped a railroad car off of Boston’s elevated railway tracks.” And The Boston Post described the gruesome scene, “Molasses, waist deep, covered the street and swirled and bubbled about the wreckage. Here and there struggled a form — whether it was animal or human being was impossible to tell. Horses died like so many flies on sticky fly-paper. The more they struggled, the deeper in the mess they were ensnared. Human beings — men and women — suffered likewise.”
The final death toll was set at 21, while 150 people were injured. The dead were either crushed by debris filled molasses, or drowned by the molasses itself. People and animals were seen struggling, some for which nothing could be done. The clean up was massive. Fire trucks were brought in to hose down the streets, and welders to  cut the tank up. The harbor was brown until summer. The molasses seeped into every crack, and it is said that on hot summer days, you could smell it for decades. I’m not sure how that could be, but maybe their minds played tricks in them too. In the end, the public outcry made a lawsuit necessary. The townspeople brought a class-action suit against the United States Industrial Alcohol Company, which had recently bought the Purity Distilling Company. Three years of hearings later, the USIAC was found guilty and forced to pay $600,000, which would equate to almost $10 million today, in settlements for negligence. The wave was as deadly as any tsunami could have been, but in reality, no warning could have prevented this tragedy.
cut the tank up. The harbor was brown until summer. The molasses seeped into every crack, and it is said that on hot summer days, you could smell it for decades. I’m not sure how that could be, but maybe their minds played tricks in them too. In the end, the public outcry made a lawsuit necessary. The townspeople brought a class-action suit against the United States Industrial Alcohol Company, which had recently bought the Purity Distilling Company. Three years of hearings later, the USIAC was found guilty and forced to pay $600,000, which would equate to almost $10 million today, in settlements for negligence. The wave was as deadly as any tsunami could have been, but in reality, no warning could have prevented this tragedy.

