axis of evil

 When we think about the enemies of war, we usually think of two nations that unequivocally hate each other. It is thought that every member of teach nation totally hates every member of the other, but that is not even logical. It doesn’t matter what nation you are talking about, the people of those nations are thoughts to hate each other, and many of them do, but nt all of them do. Not everyone loved war, and not everyone loves killing.
When we think about the enemies of war, we usually think of two nations that unequivocally hate each other. It is thought that every member of teach nation totally hates every member of the other, but that is not even logical. It doesn’t matter what nation you are talking about, the people of those nations are thoughts to hate each other, and many of them do, but nt all of them do. Not everyone loved war, and not everyone loves killing.
World War II was the deadliest wars in world history. It seemed that everyone hated everyone else, or at least that those from the one side (the Allied Powers) hated the other (the Axis of Evil). That wasn’t true either. The leaders probably hated each other, but the people of the nations were caught in the middle of the hatred of their leaders. Many of the people, civilians and military alike were family people, they had a love of others. Many of the people who fought in World War II had no idea of the horrors that were taking place. When they finally found out about it, they were absolutely horrified.
Still, those who fought in the war, knew some of the casualties of the war. A fighter pilot can’t fly over an expanse of an ocean battlefield and not see the losses taking place. For a fighter pilot or a bomber crew, it was not only possible to see the devastation, but they could also imagine what was going on below them as ships sink so quickly that the men onboard cannot escape. To add to the horror, the fact that these ships were his by torpedoes, bombs from the planes, bullets from the planes, and the planes themselves brought the added horror of fire and burning bodies. If a pilot let himself think about it, I think it would be possible to become physically ill at the thought of the horrors going on below them.
One fighter pilot felt that very deeply. During a sea battle in the Pacific Ocean in December 1940, two Royal Navy ships, the HMS Prince of Wales and the HMS Repulse were sunk by Japanese fighters. The scene must have been horrific for the pilots above, whether they were British or Japanese, they knew that men were dying horrific deaths below them. The loss of life so impacted on Japanese fighter pilot that he came back to the spot 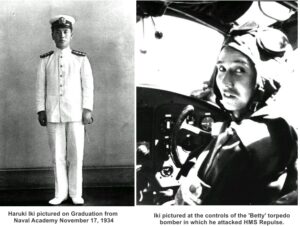
 the next day and dropped two wreaths on the water. His action was to commemorate the dead from both sides during WWII. Japanese Flight Lieutenant Haruki Iki flew to the location of the battle and dropped the two wreaths over the seas. It was a simple act, but it was also a profound act. It showed that while the nations were enemies, the people of the nations were not necessarily enemies too. It also showed that even enemies can have compassion on the other side. War is not all about hate, it is also about being caught in the middle, with no way out but to fight.
the next day and dropped two wreaths on the water. His action was to commemorate the dead from both sides during WWII. Japanese Flight Lieutenant Haruki Iki flew to the location of the battle and dropped the two wreaths over the seas. It was a simple act, but it was also a profound act. It showed that while the nations were enemies, the people of the nations were not necessarily enemies too. It also showed that even enemies can have compassion on the other side. War is not all about hate, it is also about being caught in the middle, with no way out but to fight.
 There have always been wars, and wars include bombs of some kind. It is a fact that everyone seems to understand, and to a degree accept. I suppose they look at it as collateral damage, but the reality is that it is people, property, homes, and businesses. Sometimes I wonder if mankind will ever get to a point where collateral damage is too much to pay. Of course, that will not happen. War means death and destruction, and there will be wars as long as time endures.
There have always been wars, and wars include bombs of some kind. It is a fact that everyone seems to understand, and to a degree accept. I suppose they look at it as collateral damage, but the reality is that it is people, property, homes, and businesses. Sometimes I wonder if mankind will ever get to a point where collateral damage is too much to pay. Of course, that will not happen. War means death and destruction, and there will be wars as long as time endures.
The fact is that no sane human being likes the collateral damage that war brings, but there are, unfortunately, many insane heads of states. These people kill thousands of their own people for almost no reason. They simply disagree, or they look different, or they have a different religion, and that means they must die. So, war begins, and more people die to try to free the people who have been oppressed by their hateful dictators.
World War II took in the Axis of Evil nations and the Allies, who were fighting against regimes like the Nazis, and Japanese. Both were terrible, and neither wanted to give up. Finally, when it was decided that Japan had to be stopped at all costs, the United States made the decision to drop the atomic bomb on Hiroshima, on August 6, 1945, and on Nagasaki on August 9, 1945. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians. It was another in a long list of bombing events of World War II and many other wars. It was all the same old story, right? Wrong.
The two Atomic Bombs dropped, changed the world. They were both the first, and the last times Atomic Bombs were dropped in war. It was as if the world finally saw what these bombs did to people. It was as if they finally felt sick to their stomach…both sides!! During the Cold War, there were a couple of times when the United States and the Soviet Union came close to using the Atomic Bomb, but they decided that they just couldn’t do it. That said, they decided that there really was a line that should never be crossed. Since 1945, and the dropping of two of the most devastating bombs ever, mankind has finally decided that we should not go there again, thankfully.
 A while back, my sister, Cheryl Masterson suggested a book to me because she knew that I liked World War II history. The book, Midnight In Broad Daylight, by Pamela Rotner Sakamoto, was about, among other things, the plight of the Japanese American citizens that followed the attack on Pearl Harbor. The book covered a couple of specific families, but as I listened to it through Audible, I began to consider just how the Japanese American citizens, many of whom were born in the United States to legal immigrants from Japan long before the war and the attack on Pearl Harbor ever happened.
A while back, my sister, Cheryl Masterson suggested a book to me because she knew that I liked World War II history. The book, Midnight In Broad Daylight, by Pamela Rotner Sakamoto, was about, among other things, the plight of the Japanese American citizens that followed the attack on Pearl Harbor. The book covered a couple of specific families, but as I listened to it through Audible, I began to consider just how the Japanese American citizens, many of whom were born in the United States to legal immigrants from Japan long before the war and the attack on Pearl Harbor ever happened.
For all intents and purposes, it seemed that these people were loyal to their new country. Many wanted to serve in the US military to fight against the Axis of Evil countries, including Japan. I could see that, but I could also see the other side of the coin. The rest of the American people were scared. They didn’t know if they could trust these Japanese American citizens. They wondered if they were spies, sent to infiltrate our defenses. Before anyone could really give the situation a second thought, if was decided that the Japanese American citizens and the legal immigrants awaiting naturalization, had to be placed in Japanese internment camps which were established by President Franklin Roosevelt through his Executive Order 9066. At the time, no one could really look rationally at both sides of the situation. It was an awful time for many people.
I thought about the people who really were loyal to the United States. They wanted to help, but no one trusted them. Many of them still had family in Japan, so their loyalties might have been divided, even if they didn’t agree with the attack on Pearl Harbor. I suppose some might have actually been loyal the Japan, I don’t know if we will ever really know for sure. It didn’t matter anyway, because their lives were put on hold…indefinitely. Some people got out of the camps because they had language skills the US military needed. These people were give a chance to get out of the camps, in exchange for serving in the military and making valuable translations. There weren’t a lot of them, but those who did this important work proved themselves to be loyal. Some had been trained in Japanese schools, prior to coming to America. Some had family in Japan, and even family in the Japanese military. I couldn’t imagine how torn they must have been, but they did their jobs. I don’t know if they knew about what was coming for Hiroshima or Nagasaki, but the people in the true story of the book, had  family in Hiroshima on the day of the atomic bombings, as well as family in the Japanese military. They had no way to tell them to get out of town, although civilians were warned to get out. People didn’t trust what they were told, or just didn’t understand what was going on. Somehow, the family in the book survived, but so many didn’t. I can’t feel sorry for any of the Japanese people who agreed with what the Japanese government was doing, but there were people there, as there always are, who didn’t have a choice. They were caught on the wrong side and they couldn’t leave. Those Japanese Americans were caught too. They were on the right side, but they were caught on the wrong side of the right side…if that makes any sense at all.
family in Hiroshima on the day of the atomic bombings, as well as family in the Japanese military. They had no way to tell them to get out of town, although civilians were warned to get out. People didn’t trust what they were told, or just didn’t understand what was going on. Somehow, the family in the book survived, but so many didn’t. I can’t feel sorry for any of the Japanese people who agreed with what the Japanese government was doing, but there were people there, as there always are, who didn’t have a choice. They were caught on the wrong side and they couldn’t leave. Those Japanese Americans were caught too. They were on the right side, but they were caught on the wrong side of the right side…if that makes any sense at all.
 World War II had dragged on long enough. The Axis of Evil nations didn’t seem to care how many of their own people were killed, as long as victory was theirs…typical of any evil nation. It was time to put a stop to this, and the United States, along with the Allied Nations, could see no other solution to the problem, other than fighting fire with fire…literally. This would be the beginning of a horrible new kind of warfare. I’m sure they didn’t come to that decision lightly. While the Japanese were our enemies, the civilian people didn’t really have much say in what they did. Nevertheless, in a war, sometimes civilians are killed. Collateral damage, they call it. It’s a term for deaths, injuries, or other damage inflicted on an unintended target. In American military terminology, it is used for the incidental killing or wounding of non-combatants or damage to non-combatant property during an attack on a legitimate military target. Knowing that the loss of civilian lives is considered “acceptable” in a war, doesn’t make it easy to live with.
World War II had dragged on long enough. The Axis of Evil nations didn’t seem to care how many of their own people were killed, as long as victory was theirs…typical of any evil nation. It was time to put a stop to this, and the United States, along with the Allied Nations, could see no other solution to the problem, other than fighting fire with fire…literally. This would be the beginning of a horrible new kind of warfare. I’m sure they didn’t come to that decision lightly. While the Japanese were our enemies, the civilian people didn’t really have much say in what they did. Nevertheless, in a war, sometimes civilians are killed. Collateral damage, they call it. It’s a term for deaths, injuries, or other damage inflicted on an unintended target. In American military terminology, it is used for the incidental killing or wounding of non-combatants or damage to non-combatant property during an attack on a legitimate military target. Knowing that the loss of civilian lives is considered “acceptable” in a war, doesn’t make it easy to live with.
The prospect was sickening, but something had to be done. So, on March 10, 1945, 300 American bombers  continue to drop almost 2,000 tons of incendiaries on Tokyo, Japan, in a mission that had begun the previous day. The attack destroyed large portions of the Japanese capital and killed 100,000 civilians. Early in the morning on March 10th, the B-29s dropped their bombs of napalm and magnesium incendiaries over the packed residential districts along the Sumida River in eastern Tokyo. The resulting inferno quickly engulfed Tokyo’s wooden residential structures, and the subsequent firestorm replaced oxygen with lethal gases, superheated the atmosphere, and caused hurricane-like winds that blew a wall of fire across the city. The majority of the 100,000 who perished died from carbon monoxide poisoning and the sudden lack of oxygen, but others died horrible deaths within the firestorm, such as those who attempted to find protection in the Sumida River and were boiled alive, or those who were trampled to death in the rush to escape the burning city. As a result of the attack, 10 square miles of eastern Tokyo were entirely obliterated, and an estimated 250,000 buildings were destroyed. When I think about the loss of life brought on by a complete lack of the Japanese government to surrender when they should have.
continue to drop almost 2,000 tons of incendiaries on Tokyo, Japan, in a mission that had begun the previous day. The attack destroyed large portions of the Japanese capital and killed 100,000 civilians. Early in the morning on March 10th, the B-29s dropped their bombs of napalm and magnesium incendiaries over the packed residential districts along the Sumida River in eastern Tokyo. The resulting inferno quickly engulfed Tokyo’s wooden residential structures, and the subsequent firestorm replaced oxygen with lethal gases, superheated the atmosphere, and caused hurricane-like winds that blew a wall of fire across the city. The majority of the 100,000 who perished died from carbon monoxide poisoning and the sudden lack of oxygen, but others died horrible deaths within the firestorm, such as those who attempted to find protection in the Sumida River and were boiled alive, or those who were trampled to death in the rush to escape the burning city. As a result of the attack, 10 square miles of eastern Tokyo were entirely obliterated, and an estimated 250,000 buildings were destroyed. When I think about the loss of life brought on by a complete lack of the Japanese government to surrender when they should have.

This type of bombing was known as area bombing, and was designed to break Japanese morale and force a surrender. I would imagine that morale was seriously broken after such devastating loss of life and property. The firebombing of Tokyo was the first major firebombing operation of this kind against Japan. Over the next nine days, United States bombers flew similar missions against Nagoya, Osaka, and Kobe. Then in August, United States atomic attacks against Hiroshima and Nagasaki finally forced the Japanese surrender. It was an ugly way to have for fight a war, but the Japanese did not seem to care if their own citizens were sacrificed for their evil cause. All they cared about was winning. Thankfully, they didn’t do that either.

