assassination

 Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin had just finished speaking at a factory in Moscow, when Fanya Kaplan, a member of the Social Revolutionary party shot him twice. Lenin, the leader of the Bolsheviks was seriously wounded, but survived the attack. The attempted assassination basically set off a “gang war” of sorts, although to a much larger degree…a Civil War, really. That war, known as Red Terror, set off a wave of reprisals by the Bolsheviks against the Social Revolutionaries and other political opponents. As Russia fell deeper into civil war, thousands of people were executed. This had been coming since 1887, but would not fully materialize until the assassination of Petrograd Cheka leader Moisei Uritsky and the attempted assassination of Vladimir Lenin.
Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin had just finished speaking at a factory in Moscow, when Fanya Kaplan, a member of the Social Revolutionary party shot him twice. Lenin, the leader of the Bolsheviks was seriously wounded, but survived the attack. The attempted assassination basically set off a “gang war” of sorts, although to a much larger degree…a Civil War, really. That war, known as Red Terror, set off a wave of reprisals by the Bolsheviks against the Social Revolutionaries and other political opponents. As Russia fell deeper into civil war, thousands of people were executed. This had been coming since 1887, but would not fully materialize until the assassination of Petrograd Cheka leader Moisei Uritsky and the attempted assassination of Vladimir Lenin.
Vladimir Ilich Ulyanov was born on April 22, 1870, in Simbirsk, Russian Empire. After his brother was executed in 1887 for plotting to assassinate Czar Alexander III, Ulyanov became interested in the revolutionary cause, also adopting the pseudonym…Lenin. He decided to study law and upon completion, took up practice in Petrograd, which is now Saint Petersburg. In Petrograd, Lenin began to associate with people from the revolutionary Marxist circles. Soon, he was organizing a Marxist group in the capital to enlist workers to the Marxist cause. He called the new group, “Union for the Struggle for the Liberation of the Working Class.” Following the December 1895, arrest of Lenin and the other leaders of the Union, Lenin was jailed for a year. Upon his release, he was exiled to Siberia for a term of three years.
After his term in jail, and the subsequent exile, Lenin went to Western Europe in 1900, where he continued his revolutionary activity. In 1902, while in Western Europe that he published a pamphlet titled “What Is to Be Done?,” which argued that only a disciplined party of professional revolutionaries could bring socialism to Russia. Of course, most of us know that Lenin was working in the shadows to get back into the Russian Marxist system. In 1903, he met with other Russian Marxists in London and established the Russian Social-Democratic Workers’ Party (RSDWP), but while he tried really hard, there was discord from the start. There remained a split between Lenin’s Bolsheviks (Majoritarians), who advocated militarism, and the Mensheviks (Minoritarians), who advocated a democratic movement toward socialism. There is a saying, about a house divided…it just can’t stand. These two groups increasingly opposed each other within the framework of the RSDWP, and Lenin made the split official at a 1912 conference of the Bolshevik Party.
After the outbreak of the Russian Revolution of 1905, Lenin made his move, and returned to Russia. The revolution, which consisted mainly of strikes throughout the Russian empire, came to an end when Nicholas II promised reforms, including the adoption of a Russian constitution and the establishment of an elected legislature. Then, when order had been restored, as often happens in government, the czar nullified most of these reforms. That forced Lenin to go into exile again in 1907.
Lenin was opposed to World War I, which began in 1914, calling it “an imperialistic conflict” and called on “working-class” soldiers to turn their guns on the capitalist leaders who “sent them down into the murderous trenches.” Lenin was pushing for a socialist agenda by appealing to the middle-income people who felt like they should be given a handout by the government to supplement their income. Little did they know that socialism is never the best solution. War is always hard on the countries involved, but World War I was an unprecedented disaster for Russia. The Russian casualties were greater than those sustained by any other nation in any previous war. The war also left the economy hopelessly disrupted by the costly war effort. By March of 1917, things had gotten so bad that riots and strikes broke out in Petrograd over the scarcity of food. To make matters worse, army troops who had lost confidence in the leadership joined the strikers, and on March 15 Nicholas II was forced to abdicate, which brought to an end centuries of czarist rule. Following the February Revolution, so named because of Russia’s use of the Julian calendar, power was shared between the ineffectual Provincial Government and the soviets, or “councils” of soldiers’ and workers’ committees.
German authorities allowed Lenin and his lieutenants to secretly cross Germany en route from Switzerland to Sweden in a sealed railway car, after the outbreak of the February Revolution. The hope was that the return of the anti-war Socialists to Russia would undermine the Russian war effort, which had been continued under the Provincial Government. Lenin began to push for the overthrow of the Provincial Government by the soviets, an act for which he was condemned as a “German agent” by the government’s leaders. Forced to escape to Finland in July, his call for “peace, land, and bread” met with increasing popular support, and the Bolsheviks won a majority in the Petrograd soviet. Then, in October, Lenin secretly returned to Petrograd, and on November 7th the Bolshevik-led Red Guards took down the Provisional Government and proclaimed soviet rule.
Following the coup, Lenin became the virtual dictator of the world’s first Marxist state. His government made peace with Germany, nationalized industry, and distributed land but beginning in 1918, it all began to fall apart. The nation sank into a devastating civil war against czarist forces. In 1920, the czarists were defeated, and in 
 1922 the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was established. Upon Lenin’s death in early 1924, his body was embalmed and placed in a mausoleum near the Moscow Kremlin. Petrograd was renamed Leningrad in his honor. After a struggle of succession, fellow revolutionary Joseph Stalin succeeded Lenin as leader of the Soviet Union. The Lenin years were finally over.
1922 the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was established. Upon Lenin’s death in early 1924, his body was embalmed and placed in a mausoleum near the Moscow Kremlin. Petrograd was renamed Leningrad in his honor. After a struggle of succession, fellow revolutionary Joseph Stalin succeeded Lenin as leader of the Soviet Union. The Lenin years were finally over.

 It’s not often that a young man “pulls strings” in order to go to war. Most men would rather not go to war, and some will even try to “pull strings” to get out of going. John F Kennedy, who had some health problems, and an old back injury from his college football days, was turned down for the Navy, but his dad managed to pull some strings for his son, who really wanted to go into the navy. Young was desperate, and like most parents, his father wanted to help fulfill that dream. So in 1941, Kennedy’s politically connected father, Joseph Kennedy used his influence to get his sin, John “Jack” into the service. Of course, Joseph might have been thinking ahead to future political maneuvers when he pushed for a military career for his son. Once in the Navy, Kennedy volunteered for PT (motorized torpedo) boat duty in the Pacific in 1942.
It’s not often that a young man “pulls strings” in order to go to war. Most men would rather not go to war, and some will even try to “pull strings” to get out of going. John F Kennedy, who had some health problems, and an old back injury from his college football days, was turned down for the Navy, but his dad managed to pull some strings for his son, who really wanted to go into the navy. Young was desperate, and like most parents, his father wanted to help fulfill that dream. So in 1941, Kennedy’s politically connected father, Joseph Kennedy used his influence to get his sin, John “Jack” into the service. Of course, Joseph might have been thinking ahead to future political maneuvers when he pushed for a military career for his son. Once in the Navy, Kennedy volunteered for PT (motorized torpedo) boat duty in the Pacific in 1942.
“Jack” Kennedy quickly worked to move himself up in rank, and soon he was Lieutenant John F. Kennedy. July 1943 found Lieutenant Kennedy and the crew of PT 109 in combat near the Solomon Islands. People often think that being in the Navy or the Air Force is somehow safer than the Army or Marines, but the reality is that any position in a war 
 can prove to be dangerous. On August 2, 1943, the middle of the night, Kennedy’s boat was rammed by a Japanese destroyer and caught fire. In the ensuing explosion, several of Kennedy’s shipmates were blown overboard into a sea of burning oil. With no regard for his own life, Kennedy dove in to rescue three of the crew and in the process swallowed some of the toxic mixture. Kennedy always blamed his chronic stomach problems on that incident. The ordeal was not quickly over, and for 12 hours, Kennedy and his men clung to the wrecked hull. Finally, he ordered them to abandon ship. Kennedy and the other good swimmers placed the injured on a makeshift raft. They took turns pushing and towing the raft four miles to safety on a nearby island.
can prove to be dangerous. On August 2, 1943, the middle of the night, Kennedy’s boat was rammed by a Japanese destroyer and caught fire. In the ensuing explosion, several of Kennedy’s shipmates were blown overboard into a sea of burning oil. With no regard for his own life, Kennedy dove in to rescue three of the crew and in the process swallowed some of the toxic mixture. Kennedy always blamed his chronic stomach problems on that incident. The ordeal was not quickly over, and for 12 hours, Kennedy and his men clung to the wrecked hull. Finally, he ordered them to abandon ship. Kennedy and the other good swimmers placed the injured on a makeshift raft. They took turns pushing and towing the raft four miles to safety on a nearby island.
Their ordeal still wasn’t over. For six days, Kennedy and his crew waited on the island for rescue. There was little to eat on the island, but the men survived by drinking coconut milk and rainwater until native islanders discovered the sailors and offered food and shelter. While they waited, Kennedy tried every night to signal other US Navy ships in the area. In addition, Kennedy scrawled a message on a coconut husk and gestured to the islanders to take it to a nearby PT base at Rendova. Finally, on August 8, a Navy patrol boat picked up the survivors of PT-109.
The men were taken to the hospital to recuperate, and on June 12, 1944, while Kennedy was in the hospital recuperating from back surgery, he received the Navy and Marine Corps medal for “courage, endurance, and 
 excellent leadership [that] contributed to the saving of several lives and was in keeping with the highest traditions of the United States Naval Service.”
excellent leadership [that] contributed to the saving of several lives and was in keeping with the highest traditions of the United States Naval Service.”
Of course, the rest is history. John F Kennedy went on to become the 35th President of the United States, and on November 22, 1963, Kennedy was assassinated in Dallas. His vice president, Lyndon B Johnson, assumed the presidency upon Kennedy’s death.

 John Wilkes Booth was an actor, and as such, he had an expectation of applause following a performance. That is just what he thought the assassination of President Lincoln was. No, he didn’t think it was fake. He knew he was murdering the President of the United States, but he somehow thought people would consider it one of his greatest performances…the crowning moment of his stage career. It never occurred to him that the people who had loved him as an actor would suddenly turn against him.
John Wilkes Booth was an actor, and as such, he had an expectation of applause following a performance. That is just what he thought the assassination of President Lincoln was. No, he didn’t think it was fake. He knew he was murdering the President of the United States, but he somehow thought people would consider it one of his greatest performances…the crowning moment of his stage career. It never occurred to him that the people who had loved him as an actor would suddenly turn against him.
At the very least, he expected to be greeted with applause and support by those sympathetic to the Confederacy. Instead, he found, much to his shock and great dismay, that he was a hounded man, and few wanted to associate with him. Oh, the loyalists to the Confederacy did their duty by him, but with great reluctance. He first encountered this reaction when he and David Herold, who was an American pharmacist’s assistant and Wilkes accomplice in the assassination of Abraham Lincoln, stumbled upon a man in the dark, while searching for the home of Colonel Cox. The man, a local named Oswell Swann, reluctantly agreed to guide then to the Cox home, but only if he received payment for his services. He considered it just reward for the risk he was taking. Afterward, Swann collected his fee and vanished into the night, leaving the fugitives to the “hospitality” of Colonel Cox. That “hospitality” consisted of a few supplies, including whiskey, and a servant to lead the men to a hiding place in the woods. Cox certainly didn’t want these men to be found in his house.
Cox informed Booth that he was to “remain hidden in the woods until contacted.” Then Cox sent for Thomas Jones, a Confederate agent with experience in smuggling spies and information across the Potomac River into Virginia. Jones agreed to get them out and guide them across the Potomac, for a fee, but when he visited the fugitives in the woods, where they hid in a pine thicket, he told them it would be several days before he could do so. The manhunt for Booth and Herold was massive. Federal troops combed the area, searching properties and interrogating citizens over whether they had seen two men traveling together. Booth was very distressed, because instead of receiving the expected support and appreciation of the south, Booth found himself confined to a pine thicket!! Jones provided the men with newspapers, from which Booth discovered that he was widely considered a villainous murderer, rather than the Confederate hero he had expected to be. He wrote about his “horrible” fate, and the “injustice” of it all, in a diary he kept in an appointment book.
Federal authorities had most of the conspirators who had planned to kidnap Abraham Lincoln in custody by April 20, 1865. Several were not party to the assassination, but because they were involved in the kidnapping plans, they were held anyway. Three men were still not in custody…Booth, Herold, and John Surratt remained at large. The War Department put out wanted poster, released in Washington on April 20, offering a $50,000 reward for Booth, and $25,000 apiece for Herold and Surratt. By then, Surratt was hiding out in Canada, even though he knew that his mother was being held in federal custody. Coward that he was, Surratt was making plans to flee to Europe. Booth and Herold continued to cower in a pine thicket, relatively helpless. They didn’t dare leave, because they would be seen and immediately arrested. A dejected Booth spent his time drinking whiskey and scribbling in his makeshift diary over the unfairness of his reception. He believed his action had made him a martyr to the Confederate cause.
When the fugitives finally attempted to cross the Potomac, on about April 21, Jones’s guidance consisted of verbal instructions directing them to a waiting boat. These men had no boating experience, and the night was windy. The tides and swift current didn’t help matters either. Nor did the gunboats in the area. Booth whined into his diary, “last night being chased by gunboats till I was forced to return wet, cold, and starving.” Needless to say, the crossing was a failure, but Booth’s overly dramatic entry exaggerated what may have been an encounter with USS Juniper, positioned in the river near their point of crossing. Juniper’s log did not include a report of chasing anything that night. Booth likely spotted the gunboat, and in a panic, returned to the Maryland shore. Booth’s fugitive days ended when he was caught on April 26, 1865, near Port Royal, Virginia. As Booth and his co-conspirator, David Herold, cowered inside a barn, the soldiers demanded that they surrender. John Wilkes Booth died in agonizing fashion at the hands of Union soldiers in Port Royal, Virginia, 
 two weeks after he assassinated Abraham Lincoln. When the Union soldiers demanded their surrender, Herold complied. But Booth refused. He didn’t leave the barn until one of the soldiers set it on fire. As he tried to sneak out in the shadows and flame, a shot cracked through the silent night…and found its mark. Booth briefly held on to life, but in the end, the bullet would be his demise…in true disgraced style.
two weeks after he assassinated Abraham Lincoln. When the Union soldiers demanded their surrender, Herold complied. But Booth refused. He didn’t leave the barn until one of the soldiers set it on fire. As he tried to sneak out in the shadows and flame, a shot cracked through the silent night…and found its mark. Booth briefly held on to life, but in the end, the bullet would be his demise…in true disgraced style.

 Since time began, people have hoped for peace, and ended up in a battle. While “world peace” will likely never be an option, at least not in this world, governments continue to try, and those who oppose peace continue to do their best to sabotage the plans for peace. Israel has often been at the center of the battle for peace, which makes no logical sense. The other Arab nations have long been after the land, small as it is, that belongs to Israel. I never understood how they could covet the small piece of land that Israel had. The reality is that the Arab nations simply don’t want Israel to exist at all.
Since time began, people have hoped for peace, and ended up in a battle. While “world peace” will likely never be an option, at least not in this world, governments continue to try, and those who oppose peace continue to do their best to sabotage the plans for peace. Israel has often been at the center of the battle for peace, which makes no logical sense. The other Arab nations have long been after the land, small as it is, that belongs to Israel. I never understood how they could covet the small piece of land that Israel had. The reality is that the Arab nations simply don’t want Israel to exist at all.
In 1995, a rally was being held in support of the Oslo Accords at the Kings of Israel Square in Tel Aviv. A number of people had warned Yitzhak Rabin, the fifth prime minister of Israel, that his life could be in danger, but he would not back down. The Oslo Accords was a pair of agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). The Oslo I Accord was signed in Washington DC, in 1993. The Oslo II Accord was signed in Taba, Egypt, in 1995. The problem with these agreements is that the battle between these two groups goes so much deeper than just who owns the land. These nations are related and have been in a feud since the time of Jacob and Esau in Biblical days. Nevertheless, nations have tried to bring about peace between the two nations ever since the battle began.
On November 4, 1995 (12 Marcheshvan 5756 on the Hebrew calendar) at 9:30pm, at the end of the rally. An Israeli ultranationalist named Yigal Amir, who radically opposed Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin’s peace initiative, and particularly the signing of the Oslo Accords, took it upon himself, to assassinate Yitzhak Rabin. The Likud leader and future prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, told Rabin’s government that withdrawing from any “Jewish” land was heresy, which I would have to agree with, because the land had been given to them by God. They believed that Rabin was probably too secular and too far removed from the Biblical Jewish tradition and Jewish values, but assassination is never the answer.
Conservative rabbis associated with the settlers’ movement prohibited territorial concessions to the Palestinians and forbade soldiers in the Israel Defense Forces from evacuating Jewish settlers under the accords. Some rabbis proclaimed “din rodef” based on a traditional Jewish law of self-defense, against Rabin personally, arguing that the Oslo Accords would endanger Jewish lives. The whole situation, which was “designed” to bring “peace,” took on a completely different tone…chaos. While I would never condone violence or assassination, I 
 don’t think Israel should ever be forced to give up parts of its land, and unfortunately, any peace agreement with the Palestinians always includes taking Israeli land, when Arab land is already far, far bigger. During the trial, Amir admitted to the assassination of Yitzhak Rabin and claimed that he was justified in doing so, saying that Amir he was “satisfied” and was acting on the “orders of God.” Following the trial, Amir was sentenced to life imprisonment for the murder of Rabin.
don’t think Israel should ever be forced to give up parts of its land, and unfortunately, any peace agreement with the Palestinians always includes taking Israeli land, when Arab land is already far, far bigger. During the trial, Amir admitted to the assassination of Yitzhak Rabin and claimed that he was justified in doing so, saying that Amir he was “satisfied” and was acting on the “orders of God.” Following the trial, Amir was sentenced to life imprisonment for the murder of Rabin.

 People are free to call it whatever they want to, but I prefer to follow the Biblical version, in which Joseph was warned in a dream, to move his son, Jesus to Egypt, because the Pharaoh was looking for Him so he could kill Him. Joseph heeded the warning. and the family moved immediately…like in the middle of the night, while those who were a danger to him were sleeping. Thankfully Joseph heeded that dream. Just imagine our world if he had not.
People are free to call it whatever they want to, but I prefer to follow the Biblical version, in which Joseph was warned in a dream, to move his son, Jesus to Egypt, because the Pharaoh was looking for Him so he could kill Him. Joseph heeded the warning. and the family moved immediately…like in the middle of the night, while those who were a danger to him were sleeping. Thankfully Joseph heeded that dream. Just imagine our world if he had not.
There have been other people who have had dream warnings, or prophetic dreams, whether a warning or a great blessing that was coming their way. I believe that our dreams can be a matter of God talking to us. President Abraham Lincoln was one of those people who had a prophetic dream, and it has been well documented through the years, for those of us who have chosen to listen. President Lincoln had his dream on April 4, 1865, and the dream was so troubling that he actually told it to a number of people including his wife, Mary Todd Lincoln and his former law partner, Ward Hill Lamon on April 11, 1865.
According to Lamon’s recollection, President Abraham Lincoln dreams on this night in 1865 “of ‘the subdued sobs of mourners’ and a corpse lying on a catafalque in the White House East Room.” In the dream, Lincoln asked a soldier standing guard “Who is dead in the White House?” to which the soldier replied, “the President. He was killed by an assassin.” Lincoln woke up at that point. On April 11, he told Lamon that the dream had “strangely annoyed” him ever since. Ten days after having the dream, Lincoln was shot dead by an assassin while attending the theater. Abraham Lincoln was shot by John Wilkes Booth while attending a play at Ford’s Theater in Washington DC on April 14, 1865. His assassination was the only successful leg in a conspiracy that also intended on capturing or killing Vice President Andrew Johnson and Secretary of State William Seward.
Interestingly, Lincoln supposedly later insisted to Lamon that the body on display was not his own…so he, himself did not view the dream as a warning of his own death. Some historians have discounted Lamon’s account, which was first published in the 1880s, nearly 20 years after the assassination. Nevertheless, Lamon claimed to have reconstructed the incident based on notes he made in 1865. I suppose the historians believe that since neither he nor Mary Lincoln mentioned the dream right after the president’s murder, it must not have been true. I believe that it was true, and that they were in such shock, that it never occurred to them to bring it up. Still, it is well known that Lincoln was a dreamer and was apparently quite interested in the meaning of dreams and what they have to say about future events both positive and negative. Proof of his curiosity lies in an 1863 letter to his wife, who at the time was in Philadelphia with their 10-year-old son, Tad. Lincoln writes that Mary had better “put Tad’s pistol away” as he “had an ugly dream about him.” Moreover, members of Lincoln’s cabinet recalled that, on the morning of his assassination, the president told them he’d dreamed of sailing across an unknown body of water at great speed. He also apparently revealed that he’d had the same dream repeatedly on previous occasions, before “nearly every great and important event of the War.”
The Secret Service was formed as a result of that assassination, but just imagine if they had all heeded the dream warning and placed a better guard around President Lincoln. If those he told of the dream, had considered the possibility of missing the play, or posted guards around the president, how different could have been the outcome. The world will never know, because one of our greatest presidents was gone before he could finish his second term in office. Lincoln was a very popular president. In his run against Democrat, George B 
 McClellan, Lincoln carried all but three states (Kentucky, New Jersey, and Delaware), and won 55 percent of the vote. He won 212 electoral votes to McClellan’s 21, which goes to show that most of the people approved of his anti-slavery policies, as opposed to the Democrats, who wanted to keep slavery, and who fought against the slaves and minority races…and still do, even to this day.
McClellan, Lincoln carried all but three states (Kentucky, New Jersey, and Delaware), and won 55 percent of the vote. He won 212 electoral votes to McClellan’s 21, which goes to show that most of the people approved of his anti-slavery policies, as opposed to the Democrats, who wanted to keep slavery, and who fought against the slaves and minority races…and still do, even to this day.

 I have always known that I was stubborn, and “bull headed” and if you ask my sisters, they will very much agree with me on that fact, but I seriously doubt if they would ever call me stubborn if I were compared to President Theodore Roosevelt. I don’t think many people are as stubborn as Roosevelt was. Roosevelt didn’t run for his initial term in office, but rather became president of the United States because William McKinley was assassinated while Roosevelt was serving as vice president. He did run for and win a second term in the election of 1904, during which he promised not to run for a third term thereafter. A man of his word to a point, Roosevelt stuck to that promise through the 1908 election, but then he decided to run for President again in 1912, first losing the Republican primary to the incumbent William Taft and then running at the head of a brand-new party, the Progressive “Bull Moose” Party. It is a strange name for a political party, but I think it might have been appropriate for Roosevelt.
I have always known that I was stubborn, and “bull headed” and if you ask my sisters, they will very much agree with me on that fact, but I seriously doubt if they would ever call me stubborn if I were compared to President Theodore Roosevelt. I don’t think many people are as stubborn as Roosevelt was. Roosevelt didn’t run for his initial term in office, but rather became president of the United States because William McKinley was assassinated while Roosevelt was serving as vice president. He did run for and win a second term in the election of 1904, during which he promised not to run for a third term thereafter. A man of his word to a point, Roosevelt stuck to that promise through the 1908 election, but then he decided to run for President again in 1912, first losing the Republican primary to the incumbent William Taft and then running at the head of a brand-new party, the Progressive “Bull Moose” Party. It is a strange name for a political party, but I think it might have been appropriate for Roosevelt.
When Roosevelt decided to run for president again in 1912, a saloon owner named John Schrank became obsessed with him, and after having a nightmare that convinced Schrank that Roosevelt was responsible for McKinley’s assassination. That fueled his obsession, and on October 14, 1912, he walked up to Roosevelt as he exited a Milwaukee hotel on route to a campaign event and fired a .38-caliber revolver right into his chest. For most people, this would be the end of the story, but this is where Roosevelt really earned the name attached to the political party of which he was a member.
Unfortunately, Schrank was not a bad shot, and the bullet hit its mark. Fortunately, the path of the bullet was not an easy one. After passing through Roosevelt’s glasses case and 50 pages worth of notes in his breast pocket, which slowed it down considerably the bullet hit Roosevelt’s chest. The items in its way likely slowed the bullet enough to save Roosevelt’s life. Then, in typical “bull headed” fashion, the former president coughed into his hands to check for blood, and upon finding none, continued on to the Milwaukee Auditorium, where he delivered an 84-minute speech that began with the following lines, “Friends, I shall ask you to be as quiet as possible. I don’t know whether you fully understand that I have just been shot; but it takes more than that to kill a Bull Moose. But fortunately, I had my manuscript, so you see I was going to make a long speech, and there is a bullet – there is where the bullet went through – and it probably saved me from it going into my heart. The bullet is in me now, so that I cannot make a very long speech, but I will try my best.”
The bullet stayed lodged in his ribs throughout the rest of his unsuccessful campaign, and until his passing in 
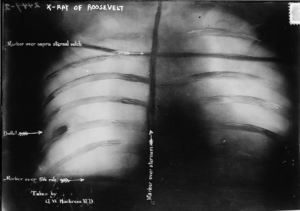 1919. While Roosevelt lost his race, his determination did show the kind of fortitude it takes to be president of this country. Being the leader of the free world, is not something that can be handled easily. The President of the United States must be an anointed position, and it is not one that just anyone can handle. In many ways, the best presidents are a type of “bull moose.” They have to be to take the pounding they have to take, and then keep coming back for more.
1919. While Roosevelt lost his race, his determination did show the kind of fortitude it takes to be president of this country. Being the leader of the free world, is not something that can be handled easily. The President of the United States must be an anointed position, and it is not one that just anyone can handle. In many ways, the best presidents are a type of “bull moose.” They have to be to take the pounding they have to take, and then keep coming back for more.
 In the history of the United States, 4 presidents have been assassinated. Of course the ones we remember the most are Abraham Lincoln and John F Kennedy. The other two were William McKinley and James Garfield. With Lincoln and Kennedy, death was quick, even though with Lincoln it took until the next day. With McKinley, death came 7 days after he was shot, but with Garfield, death needn’t have come at all.
In the history of the United States, 4 presidents have been assassinated. Of course the ones we remember the most are Abraham Lincoln and John F Kennedy. The other two were William McKinley and James Garfield. With Lincoln and Kennedy, death was quick, even though with Lincoln it took until the next day. With McKinley, death came 7 days after he was shot, but with Garfield, death needn’t have come at all.
President James A Garfield had served as the president for just four months when he was shot on July 2, 1881, by Charles Guiteau in Washington DC. Guiteau had been stalking the president for about a month, and he shot him in the arm and the back. Guiteau wasn’t much of a shot I guess. Garfield didn’t die instantly, and in fact he didn’t die for 11 weeks. In the end, it wasn’t the wounds that caused his death, but rather that the wounds became infected which claimed the president’s life in the end. Had the doctors of that age known more about infection, I believe Garfield might have lived. Infection always comes from exposure to a bacteria or virus. Yes, it could have been introduced by the bullets, but with the proper treatment, the infection could also have been thwarted. Of course, I don’t know if President Garfield would have been able to walk, or move in any other way, because I don’t know how bad the wound in his back was. Nevertheless, a would that took 11 weeks to kill the man, could not have been an infection that could not be healed. Of course, I’m no  doctor, but then modern medicine has many more tools in it’s belt now than it did then. Ironically, when you think about it Garfield was not the only one of the assassinated presidents who faced exposure and lost. The others were exposed to their assassins bullet, a sad but true fact. It’s just that Garfield suffered a much longer length of time than the others…and that is truly awful.
doctor, but then modern medicine has many more tools in it’s belt now than it did then. Ironically, when you think about it Garfield was not the only one of the assassinated presidents who faced exposure and lost. The others were exposed to their assassins bullet, a sad but true fact. It’s just that Garfield suffered a much longer length of time than the others…and that is truly awful.
Apparently, Guiteau was angry because the president didn’t appoint him to the office he desired. That is an insane reason to kill a man, and Guiteau must have been a man who could not control his own emotions…sadly. While the assassinations of Lincoln, Kennedy, and McKinley are still steeped in conspiracy theories and political ideology, Guiteau’s motivations were simple…egomania, delusions of grandeur, and the belief that God had willed him to “remove” Garfield from office. Guiteau failed to become the “great man” he was striving to be, and after being convicted of murder, Guiteau was sentenced to death and was hanged in 1882.
 When I think of the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln, I think of John Wilkes Booth shooting the president at the Ford Theater. I don’t think about the assassination being a part of a conspiracy, but in fact, it was. It makes sense, I guess, because it isn’t even logical that someone could simply walk into the Ford Theater and to the President’s box and shoot him. Someone had to tell Booth where the president was going to be. Someone had to clear the way for Booth to get in. Someone had to remove more than just a president. This was a plot to change history.
When I think of the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln, I think of John Wilkes Booth shooting the president at the Ford Theater. I don’t think about the assassination being a part of a conspiracy, but in fact, it was. It makes sense, I guess, because it isn’t even logical that someone could simply walk into the Ford Theater and to the President’s box and shoot him. Someone had to tell Booth where the president was going to be. Someone had to clear the way for Booth to get in. Someone had to remove more than just a president. This was a plot to change history.
Lincoln conspirator Mary Surratt, who was born Mary Elizabeth Jenkins in 1823, was from Maryland. Before her acts of treason, Mary married John Harrison Surratt in 1840, when she was 17. They planed a life together an began buying massive amounts of land near Washington. Together, she and her husband had three children…John Jr, Isaac, Anna. Then After her husband’s death in 1864, when she was just 41, Mary moved to Washington DC, on High Street. To make some money, Mary rented part of her property…a tavern that her husband had built, to a man named John Lloyd, who was a retired police officer.
John Jr, Mary’s eldest son, met John Wilkes Booth during his time as a Confederate spy. Because of this connection, when Booth was plotting Lincoln’s assassination with his co-conspirators, he felt perfectly at home in Mary Surratt’s DC residence, which had by this time, become a boardinghouse. As plans progresses Mary Surratt also became involved with the shooting of Abraham Lincoln, through these men. She even asked Lloyd to help. Her request was that he have some “shooting-irons” ready for some men that would stop by later that night…the night that they murdered Abraham Lincoln. Although drunk, Lloyd was able to provide testimony of the appearance of Booth and a co-conspirator at Mary’s tavern. For her involvement, Mary Surratt was sentenced to death, she was the first woman to be executed by the United States Government. She asked of her executioners only to, “not let her fall” in a very small voice, but as she was hanged on July 7, 1865, her request was not honored.
Lewis Powell (some accounts say Paine) was nicknamed Doc as a child for his love of nursing animals back to health. Powell’s part in the conspiracy was to assassinate Secretary of State Seward. Seward was at home sick in bed the night of the assassination. That should have made his job easier. Powell gained entry to the home claiming to have medicine for Seward, but when he entered Seward’s room, he found Seward’s son, Franklin. They got into a scuffle when Powell refused to hand over the medicine. Powell beat Franklin so badly that he 
 was in a coma for sixty days. He also stabbed Seward’s body guard before stabbing Steward several times. He was pulled off the Secretary by the body guard and two other members of the household. Seward survived, and Powell hid in a cemetery overnight. He was caught when he returned to Mary Surratt’s while she was being questioned by investigators. Powell attempted suicide while waiting for a verdict. He was convicted and hanged on July 7, 1865.
was in a coma for sixty days. He also stabbed Seward’s body guard before stabbing Steward several times. He was pulled off the Secretary by the body guard and two other members of the household. Seward survived, and Powell hid in a cemetery overnight. He was caught when he returned to Mary Surratt’s while she was being questioned by investigators. Powell attempted suicide while waiting for a verdict. He was convicted and hanged on July 7, 1865.
David Herold accompanied Powell to Seward’s house. Herold waited outside with the getaway horses. After Lincoln was assassinated, Herold managed to escape DC that same night, and met up with Booth. He was caught with Booth on April 26. Despite his lawyers many attempts to convince the court his client was innocent, Herold was convicted and was hanged on July 7, 1865.
George Atzerodt was given the task of killing Vice President Johnson. He went to the hotel Johnson was staying at, but was too afraid to kill the vice president. He went to the hotel bar and began drinking, hoping to get his courage up to do his part. Instead, he got very drunk and spent the night wandering the streets of Washington DC. He was arrested after the bartender reported his strange questions the night before. Atzerodt was convicted and hanged on July 7, 1865.
Edman Spangler was at Ford’s Theater the night of the assassination. Witness testimonies were conflicting as to his role in covering up Booth’s escape, but he allegedly took down the man trying to catch Booth before he fled. Spangler was found guilty and sentenced to six years in prison. He was pardoned in 1869 by President Johnson…which is odd considering the group tried to kill him. Spangler died in 1875 on his farm in Maryland.
Samuel Arnold was not involved in the April 14 assassination attempts. However, he was involved in earlier plots to kidnap Lincoln, and was arrested for his connections to Booth. Arnold was convicted and sentenced to life in prison. He was pardoned by President Johnson in 1869. He died in 1906 from tuberculosis.

It is unclear what role Michael O’Laughlen played in the actual assassination attempts. He was surely a conspirator to the group’s plans. He voluntarily surrendered on April 17. O’Laughlen was convicted and sentenced to life in prison. He died from yellow fever two years into his sentence.
It is unclear what part, if any, Mary’s son, John Surratt Jr played in the events of April 14. He claims to have been in New York that night, but he escaped to Canada and an international manhunt ensued for him. After his mother’s execution in July, he escaped to England. He then traveled to Rome and joined the group of soldiers protecting the Pope. It was while visiting Alexandria, Egypt that he was finally recognized and sent back to the United States. Unlike the other co-conspirators, Surratt was tried by a civilian court. On August 10 the trial ended with a hung jury and the charges were dropped in 1868. He died from pneumonia in 1916, and was the last living person with ties to the assassination attempt.
 With Abraham Lincoln’s birthday just behind us…he was born on February 12, 1809. Most of us know that Lincoln had no formal education. We know that he gave amazing speeches and that he freed the slaves. We also know that he was assassinated, but there are a number of other Lincoln Facts that I didn’t know, and maybe you didn’t either. One sad fact is that Lincoln lost his mother at the tender age of 9 years old, when she drank poison milk. She wasn’t poisoned, but it turns out that many people died of a strange “milk sickness” that was caused by a cow eating a “poisonous to humans” plant called White Snakeroot. I’m sure it was a horrible time for Lincoln, but his father remarried, and the widow, Sarah Bush Johnston was a kind woman, who got along well with her step-son.
With Abraham Lincoln’s birthday just behind us…he was born on February 12, 1809. Most of us know that Lincoln had no formal education. We know that he gave amazing speeches and that he freed the slaves. We also know that he was assassinated, but there are a number of other Lincoln Facts that I didn’t know, and maybe you didn’t either. One sad fact is that Lincoln lost his mother at the tender age of 9 years old, when she drank poison milk. She wasn’t poisoned, but it turns out that many people died of a strange “milk sickness” that was caused by a cow eating a “poisonous to humans” plant called White Snakeroot. I’m sure it was a horrible time for Lincoln, but his father remarried, and the widow, Sarah Bush Johnston was a kind woman, who got along well with her step-son.
At the age of 21, Abraham Lincoln became a champion wrestler. I don’t know how he would have fared in WWE, but then that is a lot of drama and show too. Nevertheless, he wrestled in approximately 300 matches, and only lost once. It is thought that his long legs helped him lock his opponent down. Lincoln reportedly talked a little smack in the ring too. According to Carl Sandburg’s biography of Lincoln, “Honest Abe once challenged an entire crowd of onlookers after dispatching an opponent: ‘I’m the big buck of this lick. If any of you want to try it, come on and whet your  horns.’ There were no takers.” Lincoln’s grappling exploits earned him an “Outstanding American” honor in the National Wrestling Hall of Fame.
horns.’ There were no takers.” Lincoln’s grappling exploits earned him an “Outstanding American” honor in the National Wrestling Hall of Fame.
Lincoln is also the only president to have personally test-fired rifles outside the White House, including one by my ancestor, Christopher Spencer who was the inventor of the Spencer Repeating Rifle. When Spencer signed his new rifle up for adoption right after the Civil War broke out, it was not well received by the Department of War Ordnance, that felt soldiers would waste ammunition by firing too rapidly with repeating rifles. The unit was also more expensive than Springfield Model 1861 rifled musket in use at the time. Nevertheless, shortly after the famous Battle of Gettysburg, Spencer was able to gain an audience with President Abraham Lincoln, who invited him to a shooting match and demonstration of the weapon on the lawn of the White House. President Lincoln was so impressed with the weapon that he ordered General James Wolfe Ripley to adopt it for production.  Unfortunately, Ripley disobeyed the order and continued to use the old single-shooters.
Unfortunately, Ripley disobeyed the order and continued to use the old single-shooters.
President Lincoln is also responsible for the safety of the presidents that followed him. Yes, there were failures, but without Lincoln’s decision to create the Secret Service on April 14, 1865, just hours before he was assassinated, many presidents in the future would not have had the quality of protection they did. The Secret Service did protect President Lincoln after his death, when grave robbers attempted to steal his body and hold it for a ransom of $200,000 and the release of one of their gang from prison. Their attempt was foiled by the Secret Service that President Lincoln had initiated.

 Imagine being a witness to a part of history. Of course, we all are. We witness our part of history, because history happens all around us. It’s just that some events are more. More what you might ask. More devastating, more tragic, more exciting, just more. One such event was the assassination of President Lincoln. I can’t begin to imagine what it would have been like to go out for a night at the theater only to have the evening shattered be gunfire…and then to look up and see that your President was slumped over, bleeding, and dying. Now imagine you were just a child at the time.
Imagine being a witness to a part of history. Of course, we all are. We witness our part of history, because history happens all around us. It’s just that some events are more. More what you might ask. More devastating, more tragic, more exciting, just more. One such event was the assassination of President Lincoln. I can’t begin to imagine what it would have been like to go out for a night at the theater only to have the evening shattered be gunfire…and then to look up and see that your President was slumped over, bleeding, and dying. Now imagine you were just a child at the time.
That was the situation Samuel Seymour found himself in on April 14, 1865. On April 14, 1865, Seymour was five years old, when his godmother, who was the wife of his father’s employer took him to see Our American Cousin at Ford’s Theater in Washington DC. They were sitting in the balcony across the theater from the Presidential box. Everyone knew President Lincoln. I don’t know how star struck people got back then. Not nearly as much as today, but everyone knew him. A while later, says Seymour, “All of a sudden a shot rang out…and someone in the President’s box screamed. I saw Lincoln slumped forward in his seat.” Suddenly, John Wilkes Booth jumped from the box to the stage. What five year old boy wouldn’t remember those two events. Of course, Seymour didn’t understand what had happened to President Lincoln,  but he was very concerned for Booth, who broke his leg in the jump. He was just a child.
but he was very concerned for Booth, who broke his leg in the jump. He was just a child.
As a child, Seymour was the youngest person in the theater. Most, if not all of the people there were adults. Two months before his death, Seymour appeared on the February 9, 1956, broadcast of the CBS TV panel show “I’ve Got a Secret.” Seymour was hurt in a fall prior to the show, and the show’s producers had urged Seymour to postpone his appearance on the show. Seymour’s doctor left the choice up to Seymour, Seymour chose to go on. During the panelists correctly guessed that Seymour witnessed the assassination of Lincoln. Seymour died on April 12, 1956, and with that, the last witness to Lincoln’s assassination was gone.

