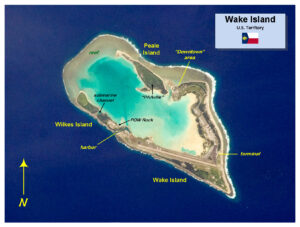
 The Battle of Wake Island was a significant conflict in the Pacific theater of World War II, occurring on Wake Island. The attack began simultaneously with the assault on Pearl Harbor’s naval and air bases in Hawaii on the morning of December 8, 1941 (December 7th in Hawaii) and concluded on December 23rd with the American forces capitulating to the Empire of Japan. The battle took place on the atoll comprising Wake Island and its smaller islets, Peale and Wilkes, involving air, land, and sea forces of the Japanese Empire and the United States, with a notable presence of Marines from both nations. The Japanese forces were formidable, and the majority of the surviving Americans were transported from the island to POW camps by the Japanese. Ninety-seven were left behind to be used as forced labor. The Allies’ response involved intermittent bombing of the island, but no further land invasions occurred. This was in line with a broader Allied strategy to isolate certain Japanese-occupied islands in the South Pacific, effectively leaving them to wither in isolation.
The Battle of Wake Island was a significant conflict in the Pacific theater of World War II, occurring on Wake Island. The attack began simultaneously with the assault on Pearl Harbor’s naval and air bases in Hawaii on the morning of December 8, 1941 (December 7th in Hawaii) and concluded on December 23rd with the American forces capitulating to the Empire of Japan. The battle took place on the atoll comprising Wake Island and its smaller islets, Peale and Wilkes, involving air, land, and sea forces of the Japanese Empire and the United States, with a notable presence of Marines from both nations. The Japanese forces were formidable, and the majority of the surviving Americans were transported from the island to POW camps by the Japanese. Ninety-seven were left behind to be used as forced labor. The Allies’ response involved intermittent bombing of the island, but no further land invasions occurred. This was in line with a broader Allied strategy to isolate certain Japanese-occupied islands in the South Pacific, effectively leaving them to wither in isolation.
On October 5, 1943, American naval aircraft from the USS Yorktown attacked Wake Island. On October 7, 1943, Rear Admiral Shigematsu Sakaibara, commander of the Japanese garrison on the island, orders the execution of a civilian accused of stealing, and 97 Americans POWs, claiming they were trying to make radio contact with US forces, and a civilian accused of stealing. Initially, the 97 POWs were detained to be used as forced labor. Anticipating an invasion, Sakaibara commanded their execution. They were led to the island’s northern end, blindfolded, and shot with a machine gun. One prisoner, whose name remains unknown, escaped and etched “98 US PW 5-10-43” into a large coral rock near the hastily dug mass grave. This American was later recaptured, and Sakaibara personally beheaded him with a katana. The etched message remains visible, marking a somber landmark on Wake Island to this day. The Wake Island Massacre was an outrage.
The Pacific war finally drew to a close starting in August 1945, and the Emperor of Japan announced the surrender to the Japanese people and the agreement was formally signed by September 2, 1945. On September 4, 1945, the remaining Japanese garrison surrendered to a detachment of United States Marines under the command of Brigadier General Lawson H. M. Sanderson, with the handover being officially conducted in a brief ceremony aboard the destroyer escort USS Levy. Earlier, the garrison received news that Imperial Japan’s defeat was imminent, so the mass grave was quickly exhumed, and the bones were moved to the US cemetery that had been established on Peacock Point after the invasion, with wooden crosses erected in preparation for the expected arrival of US forces. During the initial interrogations, the Japanese claimed that the remaining 98 Americans on the island were mostly killed by an American bombing raid, though some escaped and fought to the death after being cornered on the beach at the north end of Wake Island. Several Japanese officers in American custody committed suicide over the incident, leaving written statements that incriminated Sakaibara. Sakaibara and his subordinate, Lieutenant Commander Tachibana, were later sentenced 
 to death after conviction for this and other war crimes. Sakaibara was executed by hanging in Guam on June 19, 1947, while Tachibana’s sentence was commuted to life in prison. The remains of the murdered civilians were exhumed and reburied at Section G of the National Memorial Cemetery of the Pacific, which is commonly known as Punchbowl Crater, on Honolulu.
to death after conviction for this and other war crimes. Sakaibara was executed by hanging in Guam on June 19, 1947, while Tachibana’s sentence was commuted to life in prison. The remains of the murdered civilians were exhumed and reburied at Section G of the National Memorial Cemetery of the Pacific, which is commonly known as Punchbowl Crater, on Honolulu.

 The Sixties Scoop, often referred to simply as The Scoop, was a time when policies in Canada allowed child welfare authorities to remove Indigenous children from their families and communities to place them in foster homes. These children were then adopted by white families. Although it is called the Sixties Scoop, this practice started in the mid-to-late 1950s and continued until the 1980s. There was no given indication that these children were neglected or mistreated, just that they were Indigenous, and supposedly, therefore would be better off in the care of white families. During those years, an estimated 20,000 Indigenous children were removed from their families and placed predominantly with white middle-class families.
The Sixties Scoop, often referred to simply as The Scoop, was a time when policies in Canada allowed child welfare authorities to remove Indigenous children from their families and communities to place them in foster homes. These children were then adopted by white families. Although it is called the Sixties Scoop, this practice started in the mid-to-late 1950s and continued until the 1980s. There was no given indication that these children were neglected or mistreated, just that they were Indigenous, and supposedly, therefore would be better off in the care of white families. During those years, an estimated 20,000 Indigenous children were removed from their families and placed predominantly with white middle-class families.
The program’s policies were not uniform, with each province implementing distinct foster programs and adoption policies. Saskatchewan was unique in having the targeted Indigenous transracial adoption program known as the Adopt Indian Métis (AIM) Program. The term “Sixties Scoop” was first used in the early 1980s by social workers from the British Columbia Department of Social Welfare to describe the practice of child apprehension by their department. This term made its initial appearance in print in a 1983 report by the Canadian Council on Social Development, entitled “Native Children and the Child Welfare System.” Researcher Patrick Johnston cited the term’s origin and utilized it in his report. This term is akin to “Baby Scoop Era,” denoting the time from the late 1950s to the 1980s when many children were removed from unmarried mothers for adoption. These mothers were given no choice in the matter.
The government policies responsible for the Sixties Scoop were abandoned in the mid-1980s following resolutions passed by Ontario chiefs and severe condemnation from a Manitoba judicial inquiry. The inquiry, led by Associate Chief Judge Edwin C. Kimelman, culminated in the release of “No Quiet Place / Review Committee on Indian and Métis Adoptions and Placements,” commonly referred to as the “Kimelman Report.” Numerous lawsuits have been initiated in Canada by individuals who were part of the Sixties Scoop, including class-action suits in five provinces, such as the one initiated in British Columbia in 2011. Chief Marcia Brown Martel of the Beaverhouse First Nation was the lead plaintiff in the Ontario class-action suit filed in 2009. On February 14, 2017, Justice Edward Belobaba of the Ontario Superior Court found the government responsible for damages caused by the Sixties Scoop. Subsequently, on October 6, 2017, an $800-million settlement was disclosed for the Martel case. Currently, Métis and non-status First Nations individuals are not included in the settlement, prompting the National Indigenous Survivors of Child Welfare Network…an organization led by survivors of the Sixties Scoop in Ottawa…to call for the rejection of the settlement unless it encompasses all Indigenous individuals who were removed from their homes and placed into forced adoption.
The Sixties Scoop began during a period when Indigenous families were already grappling with the consequences of the Canadian Indian residential school system. This network of boarding schools for Indigenous peoples adversely affected their social, economic, and living conditions. The residential school system remained operational until the closure of the last school in 1996. Established by the federal government and managed by various churches, the system’s goal was to assimilate Aboriginal children by teaching them Euro-Canadian and Christian values. It enforced policies that prohibited the children from speaking their native languages, communicating with their families, or practicing their cultural traditions. Survivors of residential schools have spoken out about the physical, spiritual, sexual, and psychological abuse they endured from the staff. The enduring cultural impact on First Nations, Métis, and Inuit families and communities is both widespread and profound.
The Sixties Scoop involved the forced removal of children from their Indigenous lands and communities, often without the consent or knowledge of their families or tribes. Siblings were frequently separated and sent to different areas to prevent any communication with their relatives. These children were denied knowledge of their true nationality, history, or family ties. If a child sought to learn about their cultural identity, they required consent from their biological parents. However, due to the government’s efforts to sever ties between the children and their biological families, access to their birth records was impossible. Consequently, while the children might have suspected their cultural heritage, they had no means to verify it with concrete evidence.
The Canadian government began the process of closing the mandatory residential school system in the 1950s and 1960s, believing that Aboriginal children would receive a superior education within the public school system. A summary states: “This transition to provincial services led to a 1951 [Indian Act] amendment that enabled the province to provide services to Aboriginal people where none existed federally. Child protection was one of these areas. In 1951, twenty-nine Aboriginal children were in provincial care in British Columbia; by 1964, that number was 1,466. Aboriginal children, who had comprised only 1 percent of all children in care, came to make up just over 34 percent.”
The Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) of Canada, established as part of the Indian Residential Schools Settlement Agreement, was tasked with recording the experiences of Indigenous children in residential schools. Its mission was to disseminate the truths of survivors, their families, communities, and all those impacted, to the Canadian populace. The TRC’s final report, released in 2015, details these findings: “By the end of the 1970s, the transfer of children from residential schools was nearly complete in Southern Canada, and the impact of the Sixties Scoop was in evidence across the country.” First Nations have persistently resisted such policies through various means, including legal challenges (Natural Parents v. Superintendent of Child Welfare, 1976, 60 D.L.R. 3rd 148 S.C.C) and the establishment of their own policies, like the Spallumcheen Indian Band’s by-law to manage its child welfare program, achieving varying levels of success.
In response to the loss of their children and the subsequent cultural genocide, First Nations communities took 
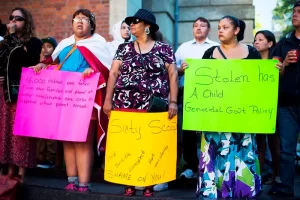 action by repatriating children from failed adoptions and striving to reclaim authority over their children’s welfare practices. This movement began in 1973 with the Blackfoot (Siksika) child welfare agreement in Alberta. Currently, there are approximately 125 First Nations Child and Family Service Agencies in Canada, operating under a variety of agreements that grant them authority from provincial governments to offer services, with funding provided by the federal government.
action by repatriating children from failed adoptions and striving to reclaim authority over their children’s welfare practices. This movement began in 1973 with the Blackfoot (Siksika) child welfare agreement in Alberta. Currently, there are approximately 125 First Nations Child and Family Service Agencies in Canada, operating under a variety of agreements that grant them authority from provincial governments to offer services, with funding provided by the federal government.

 My uncle, Lester “Jim” Wolfe was in the Army during World War II, and as such, was among those who stormed the beaches of Normandy, France on D-Day (June 6, 1944), while my dad, Allen Spencer, his future brother-in-law, was among the B-17s flying cover in the skies above. Thankfully, both of them made it home, and became the men they were destined to be. I really can’t imagine growing up without knowing my Uncle Jim. He was a great guy, with a great sense of humor. He saw a lot of things in his lifetime, and so, he always had great stories to tell. To my child’s mind, my uncle seemed very knowledgeable in things, as did my dad. It was a different era than that of my own, and they knew different things as a result. I guess that is why they always seemed so wise to me.
My uncle, Lester “Jim” Wolfe was in the Army during World War II, and as such, was among those who stormed the beaches of Normandy, France on D-Day (June 6, 1944), while my dad, Allen Spencer, his future brother-in-law, was among the B-17s flying cover in the skies above. Thankfully, both of them made it home, and became the men they were destined to be. I really can’t imagine growing up without knowing my Uncle Jim. He was a great guy, with a great sense of humor. He saw a lot of things in his lifetime, and so, he always had great stories to tell. To my child’s mind, my uncle seemed very knowledgeable in things, as did my dad. It was a different era than that of my own, and they knew different things as a result. I guess that is why they always seemed so wise to me.
While he had a lot of wisdom, Uncle Jim was also a great comedian too. He was always making jokes and loved  to make and hear people laugh. Uncle Jim was a master storyteller, the finest there was. Whenever he began his tales, we’d gather around, eyes wide with amazement. It was always a mystery whether his stories were drawn from life or were pre fiction…until the punchline came. At that moment, we’d burst into laughter, exclaiming, “Oh! Uncle Jim!” He delighted in our reactions, which brought him great amusement. And on the topic of amusement, Uncle Jim was an old hand at tickling. He’d chase and tickle us whenever we pestered him…which, of course, meant we always did. We’d scamper off, trying to escape, though we never really did. Uncle Jim’s heart was as kind as his spirit was playful.
to make and hear people laugh. Uncle Jim was a master storyteller, the finest there was. Whenever he began his tales, we’d gather around, eyes wide with amazement. It was always a mystery whether his stories were drawn from life or were pre fiction…until the punchline came. At that moment, we’d burst into laughter, exclaiming, “Oh! Uncle Jim!” He delighted in our reactions, which brought him great amusement. And on the topic of amusement, Uncle Jim was an old hand at tickling. He’d chase and tickle us whenever we pestered him…which, of course, meant we always did. We’d scamper off, trying to escape, though we never really did. Uncle Jim’s heart was as kind as his spirit was playful.
Uncle Jim was the kind of person who would help anyone in need, whether they were neighbors, friends, or even strangers. His generosity knew no bounds, and he was always ready to offer his assistance. His love for his family was his “above all” priority. He would protect his wife and children at all costs, both in words and actions. He was utterly devoted to them. When he decided to purchase land in Washington to build his final home, he ensured there was enough space for each of his children to have a place of their own nearby. He was determined that none of them would ever be without a home. The property he chose was atop a mountain, offering some of the most stunning views during the ascent. Even in his later years, as Alzheimer’s Disease necessitated his stay in a nursing home, he maintained his happy spirit. He delighted in brightening the day of the nursing staff and 
 visitors alike, often engaging in harmless “mischief” around the nurses’ station. My sisters and I continue to hold him dear in our hearts. Thoughts of him always bring smiles to our faces. Uncle Jim passed away in 2013, reuniting with his beloved wife, my Aunt Ruth, and other departed family members. We’re comforted by the belief that they’re joyfully together, and we look forward to the day we’ll all be reunited. Today marks what would have been Uncle Jim’s 103rd birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Uncle Jim!! We love and miss you very much!!
visitors alike, often engaging in harmless “mischief” around the nurses’ station. My sisters and I continue to hold him dear in our hearts. Thoughts of him always bring smiles to our faces. Uncle Jim passed away in 2013, reuniting with his beloved wife, my Aunt Ruth, and other departed family members. We’re comforted by the belief that they’re joyfully together, and we look forward to the day we’ll all be reunited. Today marks what would have been Uncle Jim’s 103rd birthday. Happy birthday in Heaven, Uncle Jim!! We love and miss you very much!!

 One of the most iconic monuments in the United States, in my opinion is that of Mount Rushmore. I’m sure some people might not agree with me on that, but I have been to Mount Rushmore more times than I could possibly count, and it just never gets old. The monument was the vision of Doane Robinson, a South Dakota historian who was looking to draw more visitors to the state. While that was a cool idea, it was dwarfed, in the end, by the absolute grandeur of the finished product. Maybe it was the vision of the sculptor, Gutzon Borglum, who Robinson commissioned to chisel the faces into the mountain, or maybe it was because it would transform a mountain into an awesome tribute to four really great presidents. I can’t say for sure, but the monument ended up being so much more than a tourist attraction. Every time I am there, I feel the awesomeness of the place, almost as if it is hallowed ground…though not in the Biblical sense.
One of the most iconic monuments in the United States, in my opinion is that of Mount Rushmore. I’m sure some people might not agree with me on that, but I have been to Mount Rushmore more times than I could possibly count, and it just never gets old. The monument was the vision of Doane Robinson, a South Dakota historian who was looking to draw more visitors to the state. While that was a cool idea, it was dwarfed, in the end, by the absolute grandeur of the finished product. Maybe it was the vision of the sculptor, Gutzon Borglum, who Robinson commissioned to chisel the faces into the mountain, or maybe it was because it would transform a mountain into an awesome tribute to four really great presidents. I can’t say for sure, but the monument ended up being so much more than a tourist attraction. Every time I am there, I feel the awesomeness of the place, almost as if it is hallowed ground…though not in the Biblical sense.
The sculpting of Mount Rushmore was a monumental task, particularly in 1927. Nevertheless, the carving began on October 4th on the likenesses of the four great men of Mount Rushmore, located in the Black Hills National Forest of South Dakota. The project was to be far from quickly finished. Instead, it would take an additional 12 years to complete the granite likenesses of four esteemed American presidents…George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Abraham Lincoln, and Theodore Roosevelt. Each time a likeness was completed, it was big news, and people came from miles around to watch the unveiling ceremony. Of course, the project was not without conflict. The Lakota Sioux people, who consider the Black Hills to be sacred ground, strongly opposed the project. The mountain was previously part of the Great Sioux Reservation before being taken away  from them by the US government. Nevertheless, there were no skirmishes over the project, and these days, the likeness of Crazy Horse is also being carved into a mountain in the Black Hills.
from them by the US government. Nevertheless, there were no skirmishes over the project, and these days, the likeness of Crazy Horse is also being carved into a mountain in the Black Hills.
The first face “chiseled” by Borglum, was that of George Washington. Initially, Borglum sculpted the head in an egg shape and added the features afterward. The plan was to place Thomas Jefferson’s likeness to the right of Washington, but after two years, it developed severe cracks. The workers were forced to remove the damaged sculpture with dynamite. They tried going deeper, but the kept coming up with more quartz, which was unsuitable for the enduring sculpture that today exists on Mount Rushmore. So, Borglum repositioned Jefferson on Washington’s left side and started again.
Washington’s face was completed in 1934. Jefferson’s was dedicated in 1936…with then…president Franklin Roosevelt in attendance. Lincoln’s likeness was completed a year later. In 1939, Teddy Roosevelt’s face was completed. The project, which cost $1 million, was funded primarily by the federal government. When we think of sculpting in stone, we think of hammers and chisels, but much of Mount Rushmore was “sculpted” with dynamite. With 450,000 tons of granite to be removed, chisels were definitely not going to be enough. Throughout the fourteen years of carving, from 1927 to 1941, nearly 400 workers, including both men and women, labored at the memorial. The work was demanding, the hours extensive, the wages modest, and job security was unpredictable. Even under severe and perilous conditions, there were no fatalities during the carving process. While for some, this work represented merely a job, for others, it evolved into a profound vocation. For those that embraced the project, I can imagine that they somehow felt the same sense of this being hallowed ground that I feel each time I’m there.
At the time of Borglum’s death, the sculpture was not finished. He continued to touch up his work at Mount Rushmore until he died suddenly in 1941. Borglum had originally hoped to also carve a series of inscriptions into the mountain, outlining the history of the United States. After his passing, his son Lincoln Borglum finished 
 the sculpture to its current point. It isn’t exactly the sculpture Gutzon Borglum has imagined, because it was to have featured the presidents to their waists, but I think it is perfect as it stands today, from its four carved heads to the secret room, known as “The Hall of Records,” behind the structure, that no one is permitted to see without an act of Congress. That is something I would love to be allowed to see someday. As it stands, it too remains unfinished.
the sculpture to its current point. It isn’t exactly the sculpture Gutzon Borglum has imagined, because it was to have featured the presidents to their waists, but I think it is perfect as it stands today, from its four carved heads to the secret room, known as “The Hall of Records,” behind the structure, that no one is permitted to see without an act of Congress. That is something I would love to be allowed to see someday. As it stands, it too remains unfinished.

 The Battle of Coyotepe Hill marked a major conflict in the United States’ occupation of Nicaragua, spanning from August to November 1912. This clash was part of the insurrection led by General Luis Mena Vado, the Minister of War, against President Adolfo Díaz Recinos’ administration. Coyotepe is an ancient fortress perched atop a 500-foot hill, commanding a view of the strategic railway line near Masaya, situated approximately halfway between Managua and Granada in Nicaragua.
The Battle of Coyotepe Hill marked a major conflict in the United States’ occupation of Nicaragua, spanning from August to November 1912. This clash was part of the insurrection led by General Luis Mena Vado, the Minister of War, against President Adolfo Díaz Recinos’ administration. Coyotepe is an ancient fortress perched atop a 500-foot hill, commanding a view of the strategic railway line near Masaya, situated approximately halfway between Managua and Granada in Nicaragua.
Adolfo Díaz Recinos was born on July 15, 1875, in Alajuela, Costa Rica, and he served as the President of Nicaragua from May 9, 1911, to January 1, 1917, and once more from November 14, 1926, to January 1, 1929. A native of Costa Rica to Nicaraguan parents, he was employed as a secretary by the La Luz y Los Angeles Mining Company. This American enterprise, incorporated in Delaware, owned extensive gold mines near Siuna in Eastern Nicaragua. Díaz Recinos played a pivotal role in directing funds to the insurrection against Liberal President José Santos Zelaya, who had angered the United States through his negotiations with Germany and Japan regarding the revival of the Nicaragua Canal project.
Luis Mena Vado, born in 1865, served as the President of Nicaragua from August 27 to 30, 1910, following the  collapse of General José Santos Zelaya’s government. He subsequently assumed the role of acting President during a rebellion. A conservative, Mena Vado was a member of the coalition government alongside liberal Juan Jose Estrada and fellow conservatives Emiliano Chamorro and Adolfo Diaz Recinos.
collapse of General José Santos Zelaya’s government. He subsequently assumed the role of acting President during a rebellion. A conservative, Mena Vado was a member of the coalition government alongside liberal Juan Jose Estrada and fellow conservatives Emiliano Chamorro and Adolfo Diaz Recinos.
From October 2 to 4, 1912, Nicaraguan rebels commanded by General Benjamín Zeledón held positions at Coyotepe and Barranca fort, strategic locations overlooking a vital railway line, and refused to surrender to the forces of President Adolfo Díaz Recinos. Major Smedley Butler of the US Marines, who had previously clashed with Zeledón’s forces on September 19th, led his battalion back from their recent victory in Granada, Nicaragua, on October 3rd and bombarded the insurgents’ stronghold at Coyotepe.
In the pre-dawn hours of October 4th, Butler’s battalion, along with two Marine battalions and another from the USS California under the command of Marine Colonel Joseph H Pendleton, coordinated an assault from various positions to seize the hill. Zeledón was killed in the conflict…most likely by his own troops. With the capture of 
 León, Nicaragua two days later by US Marines and the recapture of Masaya by Nicaraguan government troops, the Nicaraguan revolution of 1912 was essentially over. During the Somoza dictatorship the fortress was used as a prison. Occasionally, various dissidents are imprisoned there would be taken from the fortress in a helicopter and dropped into a nearby volcano.
León, Nicaragua two days later by US Marines and the recapture of Masaya by Nicaraguan government troops, the Nicaraguan revolution of 1912 was essentially over. During the Somoza dictatorship the fortress was used as a prison. Occasionally, various dissidents are imprisoned there would be taken from the fortress in a helicopter and dropped into a nearby volcano.

 For a number of years, I took my dad, Allen Spencer, who was a top turret gunner and flight engineer on a B-17G during World War II, to see the vintage planes when they came into Casper, Wyoming. Included in those old B-17s was the infamous Nine-O-Nine. Dad loved them all, and it was a special time for us. We crawled through those old planes, and Dad showed me his station, as well as the others on the Flying Fortress. Dad passed away on December 12, 2007, and I think of those special outings every time I see a B-17 flying overhead. The sightings are becoming fewer and further between, sadly. It’s quickly becoming the second end of the World War II era.
For a number of years, I took my dad, Allen Spencer, who was a top turret gunner and flight engineer on a B-17G during World War II, to see the vintage planes when they came into Casper, Wyoming. Included in those old B-17s was the infamous Nine-O-Nine. Dad loved them all, and it was a special time for us. We crawled through those old planes, and Dad showed me his station, as well as the others on the Flying Fortress. Dad passed away on December 12, 2007, and I think of those special outings every time I see a B-17 flying overhead. The sightings are becoming fewer and further between, sadly. It’s quickly becoming the second end of the World War II era.
The Nine-O-Nine was privately owned by the Collings Foundation and on October 2, 2019, the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress crashed at Bradley International Airport, Windsor Locks, Connecticut. Sadly, seven of the thirteen people on board were killed, and the other six, as well as one person on the ground, were injured. The precious Nine-O-Nine was destroyed by fire, with only a portion of one wing and the tail remaining. I couldn’t believe it when I heard. It was so tragic.
Before the accident, the Collings Foundation operated the aircraft under the Living History Flight Experience, an FAA program permitting vintage military aircraft owners to provide compensated rides. The Foundation’s executive director, Rob Collings, had sought amendments to permit guests to handle the aircraft’s controls, contending that the FAA’s interpretation of the program’s regulations was overly stringent.
The “living history” flight was delayed by 40 minutes due to a problem starting one of the engines. The pilot shut down the other engines and used a spray can to remove moisture before starting the flight. Departing from Bradley International Airport in Windsor Locks, Connecticut, at 9:48am local time, the aircraft was on a local flight with three crew members and ten passengers. An engine was observed sputtering and emitting smoke. At 9:50am, the pilot reported an issue with the plane’s Number 4 engine, located on the outer right wing. He instructed the crew chief, who also served as the loadmaster, to have the passengers return to their seats. Then, the pilot shut down the Number 4 engine. The control tower cleared the airspace for the aircraft to make an emergency landing on Runway 6. Approaching low, the Nine-O-Nine landed 1,000 feet before the runway, struck the Instrument Landing System (ILS) antenna array, veered right off the runway, crossed a grassy area and a taxiway, and collided with a de-icing facility at 9:54am, bursting into flames. A Connecticut Air National Guardsman, despite sustaining a broken arm and collarbone, successfully opened an escape hatch following the plane crash. Meanwhile, an airport worker, who was in the building struck by the plane, rushed to the crash site to assist in extracting injured passengers from the fiery wreckage. This individual incurred serious burns to his hands and arms and was subsequently transported to the hospital by ambulance. The pilot and co-pilot, aged 75 and 71, were among the seven fatalities. Additionally, one individual on the ground sustained injuries. The airport remained closed for three and a half hours after the incident.
According to the final report released by the NTSB on May 17, 2021, the probable cause of the crash was: “The pilot’s failure to properly manage the airplane’s configuration and airspeed after he shut down the Number 4 engine following its partial loss of power during the initial climb. Contributing to the accident was the inadequate 
 maintenance of the airplane while it was on tour, which resulted in the partial loss of power to the Numbers 3 and 4 engines; the ineffective safety management system (SMS) of the Collings Foundation, which failed to identify and mitigate safety risks; and the FAA’s inadequate oversight of the Collings Foundation’s SMS.”
maintenance of the airplane while it was on tour, which resulted in the partial loss of power to the Numbers 3 and 4 engines; the ineffective safety management system (SMS) of the Collings Foundation, which failed to identify and mitigate safety risks; and the FAA’s inadequate oversight of the Collings Foundation’s SMS.”
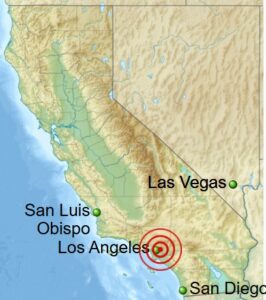
 The quiet morning of October 1, 1987, was suddenly shattered at 7:42 am by the ominous shaking of a 6.1 earthquake. The quake, located in Whittier, California, killed 6 people and injured 100 more that fateful day. The quake, named the 1987 Whittier Narrows Earthquake, lasted 30 seconds, violently waking residents from sleep, with items tumbling to the floor. The quake ruptured gas lines, sparking several fires. As is usually the case, falling debris was the cause of the loss of lives and the injuries. In addition, there were significant highway disruptions. Remarkably, no substantial building collapses occurred despite the intense shaking. It was the largest quake to hit Southern California since 1971. Nevertheless, it was not nearly as damaging as the Northridge quake that would devastate parts of Los Angeles seven years later.
The quiet morning of October 1, 1987, was suddenly shattered at 7:42 am by the ominous shaking of a 6.1 earthquake. The quake, located in Whittier, California, killed 6 people and injured 100 more that fateful day. The quake, named the 1987 Whittier Narrows Earthquake, lasted 30 seconds, violently waking residents from sleep, with items tumbling to the floor. The quake ruptured gas lines, sparking several fires. As is usually the case, falling debris was the cause of the loss of lives and the injuries. In addition, there were significant highway disruptions. Remarkably, no substantial building collapses occurred despite the intense shaking. It was the largest quake to hit Southern California since 1971. Nevertheless, it was not nearly as damaging as the Northridge quake that would devastate parts of Los Angeles seven years later.
Southern California was shaken by a prolonged series of aftershocks in the days following the earthquake. Many people were hesitant to return to their homes, so they chose to camp in public parks for an extended period of time, until things settled down again. As a safety measure, hospitals were preemptively evacuated. While there were isolated incidents of looting amidst the turmoil, they were not widespread.
The earthquake occurred on a blind thrust fault. A blind thrust earthquake happens along a thrust fault that leaves no signs on the Earth’s surface, which is why it’s termed “blind.” These faults, hidden from view, elude standard geological mapping on the surface. Occasionally, they are detected incidentally during oil exploration with seismic methods; otherwise, their presence may remain unsuspected…until the quake occurs.
Whittier, a small town located south of Los Angeles, is primarily known as the birthplace of President Richard Nixon. However, Nixon’s birth was not the only time Whittier was in the news. In fact, this quake was not the first earthquake to strike Whittier. The 1929 Whittier earthquake struck on July 8, registering a local magnitude of 4.7 and a maximum intensity of VII (Very Strong) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The tremor, with a depth of 8.1 miles, was felt most acutely southwest of the city, where it caused significant damage to a school and two houses and led to the collapse of chimneys in other homes. In Santa Fe Springs, oil derricks were affected, and minor ground fissures were observed. That earthquake’s impact was noted from Mount Wilson to Santa Ana, and from Hermosa Beach to Riverside, with numerous aftershocks continuing until early 1931.
The 7:42 am quake was the most intense in the Los Angeles region since the 1971 San Fernando quake, reaching as far as San Diego, San Luis Obispo, and Las Vegas. Communications and local media were disrupted, power outages occurred, and many early workers were trapped in inoperative elevators. Additional 
 devastations included several water and gas main ruptures, broken windows, and partial ceiling collapses. Similar to the San Fernando quake, transportation was impacted, with the Santa Ana and San Gabriel River Freeways closed near Santa Fe Springs due to dislodged concrete and visible cracks. Damage from the 1987 Whittier earthquake is estimated at $100 million.
devastations included several water and gas main ruptures, broken windows, and partial ceiling collapses. Similar to the San Fernando quake, transportation was impacted, with the Santa Ana and San Gabriel River Freeways closed near Santa Fe Springs due to dislodged concrete and visible cracks. Damage from the 1987 Whittier earthquake is estimated at $100 million.

 The Pennsylvania Railroad Company (PRR), known as the “Pennsy,” was a premier American Class I railroad founded in 1846 with its headquarters in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It got its name from the state where it originated. In contrast to other major eastern trunk lines, the Pennsylvania Railroad began operations later. A trunk line railroad is a railroad line providing basic nationwide transportation ties within a country or with neighboring countries. The Baltimore and Ohio, Erie, and New York Central Railroads all had origins dating back to the 1820s and early 1830s. The Pennsy emerged from Pennsylvania’s desire to remain economically competitive. It built a meticulously engineered route from Harrisburg to Pittsburgh and grew primarily through acquisitions. At the height of its operation, the PRR managed an extensive network of routes, catered to millions of passengers, and is often celebrated as the most illustrious of American railroads.
The Pennsylvania Railroad Company (PRR), known as the “Pennsy,” was a premier American Class I railroad founded in 1846 with its headquarters in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It got its name from the state where it originated. In contrast to other major eastern trunk lines, the Pennsylvania Railroad began operations later. A trunk line railroad is a railroad line providing basic nationwide transportation ties within a country or with neighboring countries. The Baltimore and Ohio, Erie, and New York Central Railroads all had origins dating back to the 1820s and early 1830s. The Pennsy emerged from Pennsylvania’s desire to remain economically competitive. It built a meticulously engineered route from Harrisburg to Pittsburgh and grew primarily through acquisitions. At the height of its operation, the PRR managed an extensive network of routes, catered to millions of passengers, and is often celebrated as the most illustrious of American railroads.
In the early 1840s, Philadelphia’s commercial significance faced threats from two fronts. The increasing trade through the Erie Canal directed a growing volume of commerce from the Central West to the northern seaboard. In addition, the burgeoning Baltimore and Ohio Railroad signaled a significant commercial future for Baltimore, Maryland, potentially eclipsing Philadelphia. The Baltimore and Ohio Company, demonstrating remarkable initiative, sought connections with Pittsburgh to reroute western trade away from eastern Pennsylvania. Additionally, Philadelphia’s financial reputation had been tarnished by recent turmoil. The Panic of 1837, which was the United States Bank’s clash with President Andrew Jackson, its subsequent defeat and failure as a state bank, and the resulting distress within local financial sectors, all contributed to the shift of the nation’s monetary hub to New York.
In 1847, the directors of the Pennsylvania Railroad appointed J Edgar Thomson, an engineer from the Georgia Railroad, to survey and build the line. He selected a path that followed the west bank of the Susquehanna River northward to its meeting with the Juniata River, then along its banks to the foothills of the Allegheny Mountains, culminating at what would become Altoona, Pennsylvania. To cross the mountains, the line ascended a moderate incline for 10 miles to a point where it spanned two mountain ravines by constructing a fill and curving the tracks along a 220-degree bend known as the Horseshoe Curve, which kept the grade below 2 percent. The summit was breached by the 3,612-foot Gallitzin Tunnels, after which the route descended to Johnstown on a gentler slope.
The Pennsylvania Railroad’s charter was expanded on March 23, 1853, permitting the purchase and bond guarantees of railroads in other states, limited by its capital stock percentage. The Pennsy supported several lines to attract more traffic. By 1854’s close, it had acquired stakes in the Ohio and Pennsylvania, Ohio and Indiana, Marietta and Cincinnati, Maysville and Big Sandy, and Springfield, Mount Vernon and Pittsburgh railroads, totaling $1,450,000 (equivalent to $49.2 million in 2023). It also backed the Steubenville and Indiana with a $500,000 bond guarantee. In 1856, it gained a majority interest in the Cumberland Valley Railroad and built more lines in Philadelphia. The Main Line of Public Works was bought in 1857 for $7,500,000 ($245 million in 2023).
The Empire Transportation Company, founded in 1865 by Joseph D Potts, evolved into a multi-modal freight transportation subsidiary of the Pennsylvania Railroad. It possessed oil tanker cars, transporting refined oil primarily for independent refiners during the period of John D Rockefeller’s Standard Oil refinery consolidations in the 1870s. Additionally, the company owned grain freighters on the Great Lakes and oil pipelines in Pennsylvania’s oil-rich areas. In 1877, when it sought to acquire and construct oil refineries, Standard Oil took ownership of the company.
The controlling, non-institutional shareholders of the PRR during the early 1960s were Henry Stryker Taylor, who was a part of the Jacob Bunn business dynasty of Illinois, and Howard Butcher III, a principal in the Philadelphia brokerage house of Butcher and Sherrerd (later Butcher and Singer).
On February 1, 1968, the Pennsylvania Railroad merged with its longtime arch-rival, the New York Central Railroad. The Pennsylvania Railroad absorbed the New York Central and eventually went by the name of Penn Central Transportation Company.
In 1969, the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) mandated the inclusion of the struggling New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (NH) into the system. A combination of factors such as inflation, mismanagement, severe weather conditions, and the retraction of a $200 million government-backed operating loan led Penn Central to seek bankruptcy protection on June 21, 1970. By May 1971, its passenger services and equipment 
 were handed over to a newly established government-funded entity known as the National Railroad Passenger Corporation, or Amtrak, to alleviate the financial burdens of passenger transport from Penn Central and other railroads. The Penn Central’s rail lines, including the former Pennsylvania Railroad tracks, were transferred to Conrail in 1976, with Amtrak ultimately acquiring the Northeast and Keystone Corridor lines.
were handed over to a newly established government-funded entity known as the National Railroad Passenger Corporation, or Amtrak, to alleviate the financial burdens of passenger transport from Penn Central and other railroads. The Penn Central’s rail lines, including the former Pennsylvania Railroad tracks, were transferred to Conrail in 1976, with Amtrak ultimately acquiring the Northeast and Keystone Corridor lines.
 I think most of us have heard the name Hindenburg in some version or another. Whether it’s the airship disaster of 1937; the man himself, Paul von Hindenburg; or the Hindenburg Line of World War I, the name is known. Paul von Hindenburg was born into an aristocratic family on October 2, 1847, in Posen, Prussia, which is present-day Pozna?, Poland. His father was a Prussian military officer-turned-government official, who was granted a title of nobility in 1869; and his mother was the daughter of a doctor.
I think most of us have heard the name Hindenburg in some version or another. Whether it’s the airship disaster of 1937; the man himself, Paul von Hindenburg; or the Hindenburg Line of World War I, the name is known. Paul von Hindenburg was born into an aristocratic family on October 2, 1847, in Posen, Prussia, which is present-day Pozna?, Poland. His father was a Prussian military officer-turned-government official, who was granted a title of nobility in 1869; and his mother was the daughter of a doctor.
Hindenburg joined the Prussian army when he was 19, amid the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, which was also referred to as the Seven Weeks’ War…a significant event leading up to the unification of Germany. Hindenburg fulfilled the role of a staff officer in the Franco-Prussian War from 1870 to 1871 and ultimately rose to the rank of lieutenant general.
After a long military career, Hindenburg retired in 1911, at the age of 64. Then, with the onset of World War I in 1914, he was recalled to active service. As commander of the Eighth Army, he was elevated to the rank of field marshal and achieved a string of victories over the Russians on the Eastern Front, cementing his status as a national hero. One battle that stands out was the Battle of Tannenberg in Poland. Under his command, alongside his chief of staff General Erich Ludendorff, it became one of Germany’s most decisive triumphs of the war.
Anna von der Golz wrote a book called Hindenburg, in which she is quotes as saying, “Soon after the outbreak of war Hindenburg became Germany’s major symbol of victory against the enemy and of unity at home–a function traditionally performed by the Emperor in wartime, or perhaps on occasion by the Chief of the General Staff, but certainly not by the commander of a single German army.”
The phrase “Hindenburg will sort it out,” swiftly turned into a catchphrase, and depictions of the field marshal proliferated, she said. Hindenburg was named chief of the German General Staff by Kaiser Wilhelm entrusting him with the army’s command. Still, the Allies still managed to inflict a decisive defeat.
Following Germany’s defeat in World War I, Hindenburg retired from the military for the second time and entered politics. In 1925, at the age of 77, the “Victor of Tannenberg” was elected as the president of the democratic Weimar Republic (1919-1933), becoming Germany’s second president. He was re-elected in 1932.
In an effort to stabilize the region after the war and the harsh conditions of the Armistice of Compiègne, Hindenburg resorted to issuing presidential emergency decrees, not a real good move on his part. Nevertheless, it was permitted by the nation’s constitution in times of disturbance and economic distress. These decrees enabled him to bypass the German parliament’s consent, suppress his political adversaries, curtail free speech and other civil liberties, and permit military leaders to dictate foreign policy.

Hindenburg was initially a critic of Hitler and the Nazi Party, so at first, he declined to bestow upon Hitler the chancellorship he sought. However, under pressure from his conservative advisors and due to the rising influence of the Nazi Party, he eventually named Hitler as chancellor, reassured by his advisors that they could contain the Nazi program. That was likely his biggest mistake. Hitler swiftly utilized Hindenburg’s decree powers to enact several mandates, including the 1933 Reichstag Fire Decree, the Enabling Act, and the Law for the Protection of the People and the State.
As Hindenburg’s health declined, his appointment effectively granted Hitler dictatorial powers. Upon Hindenburg’s death at age 86 on August 2, 1934, Hitler declared himself the Führer of Germany. Hindenburg was buried alongside his wife, Gertrud von Sperling, who passed away in 1921, at the Tannenberg war memorial in Prussia. Their remains were later transferred to Saint Elizabeth Church in Marburg, Germany, in 1946.
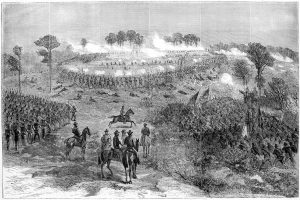
 In the latter part of September 1864, in the middle of the Civil War’s second half, the Union Army targeted Fort Harrison, a key Confederate stronghold. Capturing Richmond, Virginia, hinged on taking Fort Harrison, crucial to General Butler’s offensive strategy. As the most formidable segment of the Confederate defense line, Fort Harrison offered a clear view to the James River, rendering surprise attacks nearly impossible. Following intense summer skirmishes along Petersburg, Virginia’s earthworks, and a toll of around 27,000 casualties since June, a haunting silence had settled over the region. The II Army Corps, led by Major General Winfield Hancock and previously the backbone of Major General George G Meade’s Army of the Potomac, was now severely weakened. Positioned near Petersburg, the II Army Corps was tasked with monitoring and preventing any maneuvering of General Robert E Lee’s combat forces across the James River.
In the latter part of September 1864, in the middle of the Civil War’s second half, the Union Army targeted Fort Harrison, a key Confederate stronghold. Capturing Richmond, Virginia, hinged on taking Fort Harrison, crucial to General Butler’s offensive strategy. As the most formidable segment of the Confederate defense line, Fort Harrison offered a clear view to the James River, rendering surprise attacks nearly impossible. Following intense summer skirmishes along Petersburg, Virginia’s earthworks, and a toll of around 27,000 casualties since June, a haunting silence had settled over the region. The II Army Corps, led by Major General Winfield Hancock and previously the backbone of Major General George G Meade’s Army of the Potomac, was now severely weakened. Positioned near Petersburg, the II Army Corps was tasked with monitoring and preventing any maneuvering of General Robert E Lee’s combat forces across the James River.
At that moment, Major General Benjamin Butler knew he needed to devise a strategy to turn the tide. The pause in activity presented an ideal opportunity for action. Butler considered that during such lulls, there’s often a slight drop in vigilance—just enough, he surmised, for a surprise attack. With this in mind, Butler approached Lieutenant General Ulysses S Grant with a plan. The strategy involved relocating the Army of the James north of the James River to initiate an assault on the Confederate Outer Defenses near Richmond. The objective of the Federal Army of the James was to seize control of the road network southeast of the Confederate Capital, ultimately aiming to capture Richmond itself. 
Before Petersburg, there was little activity, but the situation was changing rapidly in the Shenandoah Valley. The battle at Fisher’s Hill occurred on September 22, 1864, resulting in numerous casualties, notably the death of Brigadier General William Nelson Pendleton’s son. Grant’s staff officers were against the subsequent boat journey up the James River, yet Benjamin Butler persuaded Grant to deploy the Army of the James for a northern offensive. The strategy was straightforward. The Confederates underestimated the Federal Armies’ ability to mount a significant offensive towards Richmond from the north, as they had troops defending the earthworks there, leading them to allocate their forces elsewhere. Even with General Robert E Lee’s focus on the north, the Confederate forces in the outer defenses were critically understrength. It was believed that if a genuine threat emerged in that area, Confederate troops could swiftly reinforce the defenses before an attack could be initiated. On the night of September 28-29, 1864, Major General Benjamin Butler convened his top officers for a briefing on the planned movements of his army. Major General Edward O C Ord of the 18th Army Corps, Major General David B Birney of the 10th Army Corps, and Brigadier General August V Kautz of the Cavalry Division were present.
The strategy involved Major General Ord and the 18th Army Corps making an unexpected crossing of the James River at Aiken’s Landing, then advancing up Varina Road. Their goal was to destroy the Confederate bridges at Chaffin’s Bluff before heading up Osbourne Road towards Richmond. At the same time, the 10th Corps, led by Major General Birney, would push forward from Deep Bottom to seize New Market Heights. Moving northwest, Birney’s divisions would proceed up New Market Road towards the Confederate capital. Meanwhile, Brigadier General Kautz’s cavalry was to dash down Darbytown Road towards Richmond. Unfortunately for the South, on September 29, 1864, the plan partially unraveled when 2,500 Union soldiers from Major General Benjamin Butler’s Army of the James overwhelmed Major Richard Cornelius Taylor’s 200-man Confederate garrison, taking the fort in the Battle of Chaffin’s Farm. The operation saw the unfortunate death of Brigadier General Hiram Burnham, a brigade commander from Maine in the XVIII Corps. In his memory, Fort Harrison was subsequently renamed Fort Burnham after the Union forces assumed control.
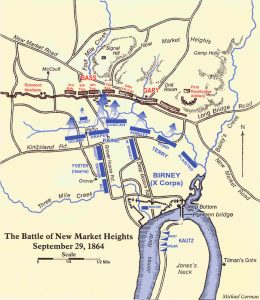
 Ultimately, Fort Harrison stood as the sole victory of the day. Although the attempt to capture Richmond was unsuccessful, it quickly pointed out the region’s marked susceptibility. Recognizing the imminent threat to Richmond, General Robert E Lee then commanded a counterattack on September 30. The offensive was unsuccessful, and Brigadier General George J Stannard lost an arm during the resistance to Lee’s assault. This setback compelled the Confederates to reposition their defenses further west. Fort Harrison, also known as Fort Burnham, stayed under Union control until the war was over on November 6, 1865.
Ultimately, Fort Harrison stood as the sole victory of the day. Although the attempt to capture Richmond was unsuccessful, it quickly pointed out the region’s marked susceptibility. Recognizing the imminent threat to Richmond, General Robert E Lee then commanded a counterattack on September 30. The offensive was unsuccessful, and Brigadier General George J Stannard lost an arm during the resistance to Lee’s assault. This setback compelled the Confederates to reposition their defenses further west. Fort Harrison, also known as Fort Burnham, stayed under Union control until the war was over on November 6, 1865.

