new york city
 Since people began moving around the world there was a need for mail service, but people hated to wait months to hear from their loved ones…especially if it was with bad news. There had to be a way to get he mail faster and with the invention of the airplane, in late 1903, the possibility of a new way to deliver the mail was on the horizon. It really didn’t take very long for someone to make the metal leap from driving the mail to flying the mail from place to place. Where there is a need, there must be a solution. That solution came on May 15, 1918, when the United States officially established airmail service between New York and Washington DC, using Army aircraft and pilots. Prior to this date, the Post Office Department used new transportation systems such as railroads or steamboats to transport mail. They contracted with the owners of the lines to carry the mail. There were no commercial airlines to contract with, so no one had thought about that yet, but that was about to change.
Since people began moving around the world there was a need for mail service, but people hated to wait months to hear from their loved ones…especially if it was with bad news. There had to be a way to get he mail faster and with the invention of the airplane, in late 1903, the possibility of a new way to deliver the mail was on the horizon. It really didn’t take very long for someone to make the metal leap from driving the mail to flying the mail from place to place. Where there is a need, there must be a solution. That solution came on May 15, 1918, when the United States officially established airmail service between New York and Washington DC, using Army aircraft and pilots. Prior to this date, the Post Office Department used new transportation systems such as railroads or steamboats to transport mail. They contracted with the owners of the lines to carry the mail. There were no commercial airlines to contract with, so no one had thought about that yet, but that was about to change.
Army Major Reuben H. Fleet was charged with setting up the first US airmail service, scheduled to operate beginning May 15, 1918 between Washington DC, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and New York City. The army pilots chosen to fly that day were Lieutenants Howard Culver, Torrey Webb, Walter Miller and Stephen Bonsal, all chosen by Major Fleet, and Lieutenants James Edgerton and George Boyle, both chosen by postal officials. Edgerton and Boyle had only recently graduated from the flight school at Ellington Field, Texas and neither had more than 60 hours of piloting time. While I’m sure they were a bit nervous, I’m also sure they were excited to be standing on the threshold of history.
The project got off to a bit of an embarrassingly rocky start, when Lieutenant Boyle, who was engaged to the daughter of Interstate Commerce Commissioner Charles McChord, was selected to pilot the first plane out of Washington DC that day. After all his preparations, Boyle hopped into his plane and was unable to start it. The plane had not been fueled. I’m sure that added a bit of nervousness to the situation. Nevertheless, he finally got his Curtiss Jenny, loaded with 124 pounds of airmail, into the air and made his way to Washington DC. His assignment was to fly to Philadelphia, the mid-way stop between the Washington and New York ends of the service. He did not make it there that day. The novice pilot got lost and low on gas, crash landed in rural Maryland, less than 25 miles away from Washington.
Fortunately for the service, the other flights operated as scheduled that day. Thanks to his political connections, Lieutenant Boyle was given a second chance to fly the airmail out of Washington DC. This time, he was given an escort who flew him out of the city, having given him directions to “follow the Chesapeake Bay” towards Philadelphia. Unfortunately, Boyle followed those instructions too literally, following the curve of the bay over to Maryland’s eastern shore, where he landed, out of fuel again. Not even Boyle’s connections could help him now, and he was removed from the pilots list for the service. I’m sure that didn’t help his standing with his future father-in-law either.
The other rookie pilot, Lieutenant James Edgerton, did much better on his flights and stayed with the service. Edgerton managed to keep his plane aloft during a violent storm that struck while he was on another flight, even as the propeller was pelted by hail. He stayed with the mail service until the next year, and became the Chief of Flying Operations. Then in August, the Post Office Department took over airmail operations with airplanes and civilian pilots of its own. Captain Benjamin Lipsner was named the first superintendent of the U.S. Airmail Service.
The first flight operated by the Post Office Department took off from College Park, Maryland, on August 12, 1918. The destination was New York. Max Miller flew that historic flight. Miller flew the new Curtiss R-4 aircraft. These new planes had more powerful Liberty 400 horsepower engines. Miller was the first pilot hired by the Post Office Department. He died when his plane caught fire and crashed on September 1, 1920. The Post Office Department decided to launch pathfinding flights from New York to Chicago in September 1918. A major obstacle was the Allegheny Mountains, considered by some to be the most dangerous territory on the route. U.S. Airmail Service Superintendent Benjamin Lipsner chose two of his best pilots, Eddie Gardner and Max Miller, for these flights. Eager competitors, Gardner and Miller turned the test into a race. On September 5,  1918, the pair left New York. Miller flew in a Standard airmail plane with a 150-horsepower Hispano-Suiza engine. Gardner followed in a Curtiss R-4 with a 400-horsepower Liberty engine and was accompanied by Eddie Radel, a mechanic. As each pilot landed to refuel or make repairs, he eagerly called Lipsner in Chicago to find out where the other one was. A set of telegrams now in the National Postal Museum tracked their progress. Miller landed in Chicago first, at 6:55 p.m. on September 6. Gardner arrived the next morning, landing at 8:17 at Grant Park. Sometimes it isn’t about the size of the engine I guess. Of course, today, very few people use the postal service, not called “snail mail.” With the internet and texting we have almost instant access to our loved ones.
1918, the pair left New York. Miller flew in a Standard airmail plane with a 150-horsepower Hispano-Suiza engine. Gardner followed in a Curtiss R-4 with a 400-horsepower Liberty engine and was accompanied by Eddie Radel, a mechanic. As each pilot landed to refuel or make repairs, he eagerly called Lipsner in Chicago to find out where the other one was. A set of telegrams now in the National Postal Museum tracked their progress. Miller landed in Chicago first, at 6:55 p.m. on September 6. Gardner arrived the next morning, landing at 8:17 at Grant Park. Sometimes it isn’t about the size of the engine I guess. Of course, today, very few people use the postal service, not called “snail mail.” With the internet and texting we have almost instant access to our loved ones.
 For a long time, people in the 19th century, living in urban apartments, didn’t regularly take their children outside so they could get some fresh air. Then, the doctors started to recommend that these children really needed to get outside for fresh air. Now that doesn’t necessarily mean that the parents were real excited about the idea of loading up their child and taking them for a walk…just to get the recommended amount of fresh air. Nevertheless, it was important, as the doctors told them that it would strengthen their immune system, and with the number of pandemics that had gone around, the parents really tried to do whatever they could to make this happen.
For a long time, people in the 19th century, living in urban apartments, didn’t regularly take their children outside so they could get some fresh air. Then, the doctors started to recommend that these children really needed to get outside for fresh air. Now that doesn’t necessarily mean that the parents were real excited about the idea of loading up their child and taking them for a walk…just to get the recommended amount of fresh air. Nevertheless, it was important, as the doctors told them that it would strengthen their immune system, and with the number of pandemics that had gone around, the parents really tried to do whatever they could to make this happen.
While physicians such as Dr. Luther Emmett Holt advised simply placing an infant’s basket near an open window, some parents took it a step further. Enter the Baby Cage. The baby cage was just what it sounded like. It was a platform, with chicken wire all around it to keep the baby in. This whole contraption was then suspended outside the window…even if the window was on the sixth floor or something.  Personally, I can’t imagine hanging my baby outside my window for a dose of fresh air, but it was an actual thing in those days.
Personally, I can’t imagine hanging my baby outside my window for a dose of fresh air, but it was an actual thing in those days.
Eleanor Roosevelt, who by her own admission “knew absolutely nothing about handling or feeding a baby,” bought a chicken-wire cage after the birth of her daughter, Anna. She hung it out the window of her New York City apartment and placed Anna inside for her naps…until a concerned neighbor threatened to report her to the authorities. I would think so. If the brackets that suspended the cage to the window came loose…so long baby. I couldn’t find any incidence of such a thing happening, however. The first commercial patent for a baby cage was filed in 1922 by Emma Read of Spokane, Washington. The cages became popular in London in the 1930s among apartment dwellers without access to backyards. Ultimately, their popularity declined. It is possible that this was connected to safety concerns. As I said, I can imagine. I would have nightmares about that if it were my child.
 New York City…a place as glamorous as any city in the world, the financial center of the world…and a target. Most of us know about the attacks on the World Trade Center in 1993, and again on September 11, 2001, but there was another attack that was planned for New York City, and in the end…foiled. This attack is most likely one you don’t recall…in fact, I think very few people even knew about it. The United States has enemies, as most nations do, and one of the best know enemies of the United States was Adolf Hitler.
New York City…a place as glamorous as any city in the world, the financial center of the world…and a target. Most of us know about the attacks on the World Trade Center in 1993, and again on September 11, 2001, but there was another attack that was planned for New York City, and in the end…foiled. This attack is most likely one you don’t recall…in fact, I think very few people even knew about it. The United States has enemies, as most nations do, and one of the best know enemies of the United States was Adolf Hitler.
According to an article I read recently, two men. Laureano Clavero and Pere Cardona, interviewed a Nazi pilot from World War II, who passed away in 2013. According to their research and their interview, the two claimed that they had proven the planned attack was real in an interview as they promoted their new book, The Diary of Peter Brill, a Nazi pilot during World War Two. In the interview, Peter Brill, who has been dubbed The Last Luftwaffe Pilot, claimed that Hitler was developing a plan to send a huge bomber from Germany to the United States. The New York mission has long been considered a myth, but Clavero and Cardona insist Brill admitted his involvement when they interviewed him. They claimed that Brill was a part of the secret project.

Clavero came across Brill and his history in 2010, when he was investigating the crash of two German bombers in the Pyrenees during the conflict. I’m always amazed at how often looking for one piece of information leads to another discovery. Brill agreed to give the authors an interview, and told them that he had been asked to take part in a secret mission to cross the Atlantic and launch the huge bombardment. While Brill was not specific, the two authors believe the project was convened in 1943, with Hitler’s enthusiastic support. The huge Heinkel plane was to be modified to allow it to fly 12,000 miles…the distance from Berlin to New York and back.
Brill and five others received top-secret training in the Polish city of Thorn, where they learned to fly at high altitude. They had to brave the frequent fires in the bomber’s engines. Before long, it became clear that the Heinkel was incapable of flying to New York and back. The authors claim that, when it became clear that the “Junker” could not fly such a long distance, the German engineers toyed with various workarounds, including  the creation of a halfway house and the coupling of the bomber to a Mescherschmitt. Nevertheless, it soon became clear to everyone that the mission would have to be scrapped, as there were more pressing difficulties taking precedence. “What is certain is that they were close to realizing their objective, but all the crazy dreams of Hitler were left to one side after the battle of Stalingrad,” Cardona said. “They were pushed aside for the day-to-day problems.” Clavero and Cardona have written their new book using the interviews given by Brill, and the memoirs gifted to them by his family when he died. The book sounds very interesting, and I, for one, plan to read about this…almost attack on New York City.
the creation of a halfway house and the coupling of the bomber to a Mescherschmitt. Nevertheless, it soon became clear to everyone that the mission would have to be scrapped, as there were more pressing difficulties taking precedence. “What is certain is that they were close to realizing their objective, but all the crazy dreams of Hitler were left to one side after the battle of Stalingrad,” Cardona said. “They were pushed aside for the day-to-day problems.” Clavero and Cardona have written their new book using the interviews given by Brill, and the memoirs gifted to them by his family when he died. The book sounds very interesting, and I, for one, plan to read about this…almost attack on New York City.

 My nephew, Shannon Moore, who is married to my niece Lindsay, is the Special Teams Coordinator and Tight Ends coach at East Carolina University…Home of the Pirates. Shannon is totally in his element as a coach, having come from the Wyoming Cavalry team, where he and Lindsay met; to Brookings, South Dakota; to Miami, Florida; to Greenville, North Carolina, where he is today. Every move he has made has been a move up in status. For Shannon, Greenville is a personal favorite place. The town is a real football town, and game day is lots of fun. As the coach, it’s like a big celebration, and he gets to be right there in the middle of it all. Shannon thrives on all things football, and I’m quite sure all of the other sports as well.
My nephew, Shannon Moore, who is married to my niece Lindsay, is the Special Teams Coordinator and Tight Ends coach at East Carolina University…Home of the Pirates. Shannon is totally in his element as a coach, having come from the Wyoming Cavalry team, where he and Lindsay met; to Brookings, South Dakota; to Miami, Florida; to Greenville, North Carolina, where he is today. Every move he has made has been a move up in status. For Shannon, Greenville is a personal favorite place. The town is a real football town, and game day is lots of fun. As the coach, it’s like a big celebration, and he gets to be right there in the middle of it all. Shannon thrives on all things football, and I’m quite sure all of the other sports as well.
The cool thing for Shannon and Lindsay is the fact that he has the summers off. They have been spending the summer taking trips here and there. This year, they did a tour of the Northeast. The trip started out in Niagara Falls for Independence Day. Now, I think that would be a very cool place to be for the holiday. Shannon and Lindsay rode on the Maid of the Mist ferry boat to the base of the falls, which is an amazing ride. From Niagara Falls, their trip took them to Portland, Maine. Then they went to New Hampshire and Massachusetts, where 
 they went to the Baseball Hall of Fame. The next leg of their trip took them to Vermont for a nice dinner. And what tour of the Northeast would be complete without a trip to New York City. They went to the Statue of Liberty, Ellis island, and the Brooklyn bridge, as well as taking in a Yankees game. They had been there before, but it was right after Hurricane Sandy, so they were unable to go to those places. They also toured the sites for Seinfeld and You’ve Got Mail. Lindsay tells me that it was “waaaay fun!!” The next leg of their trip was a ride on the Amtrak to Philadelphia to see a Phillies Game, the Liberty Bell and the Rocky Statue. Finally they took the Amtrak back to North Carolina. Their grand tour of the Northeast took them on a plane, train, automobile, and ferry. Lindsay and Shannon have set a goal to see all 50 states. In the Northeast, they have seven states left. They only check off the states, when both of them have been to the state.
they went to the Baseball Hall of Fame. The next leg of their trip took them to Vermont for a nice dinner. And what tour of the Northeast would be complete without a trip to New York City. They went to the Statue of Liberty, Ellis island, and the Brooklyn bridge, as well as taking in a Yankees game. They had been there before, but it was right after Hurricane Sandy, so they were unable to go to those places. They also toured the sites for Seinfeld and You’ve Got Mail. Lindsay tells me that it was “waaaay fun!!” The next leg of their trip was a ride on the Amtrak to Philadelphia to see a Phillies Game, the Liberty Bell and the Rocky Statue. Finally they took the Amtrak back to North Carolina. Their grand tour of the Northeast took them on a plane, train, automobile, and ferry. Lindsay and Shannon have set a goal to see all 50 states. In the Northeast, they have seven states left. They only check off the states, when both of them have been to the state.
As if the summer hasn’t been busy enough, Shannon has also been keeping himself busy with golfing and yard work. They will try to get to the beach a few times before fall, and they did make a trip back home to Wyoming 
 for a visit, stopping to see Shannon’s folks too along the way. I think it’s been a long time since they have driven back to Wyoming. Lindsay was kind of amazed that it took three days to drive home. In the fall, it will be back too football training again. Lindsay is so cute. Every time I ask her for information, she always adds one little thing, this time she said, “Oh yeah AND I know I am biased but man…he is the best husband ever and the nicest person ever!! Such a kind and generous person!!” I love to see that!! Today is Shannon’s birthday. Happy birthday Shannon!! Have a great day!! We love you!!
for a visit, stopping to see Shannon’s folks too along the way. I think it’s been a long time since they have driven back to Wyoming. Lindsay was kind of amazed that it took three days to drive home. In the fall, it will be back too football training again. Lindsay is so cute. Every time I ask her for information, she always adds one little thing, this time she said, “Oh yeah AND I know I am biased but man…he is the best husband ever and the nicest person ever!! Such a kind and generous person!!” I love to see that!! Today is Shannon’s birthday. Happy birthday Shannon!! Have a great day!! We love you!!

 Most of us have heard the name Sandy Hook because of the school shooting that took place in an elementary school with the same name in Newtown, Connecticut. That tragedy was not the first time the name Sandy Hook had been at the center of attention, however. Most people know that along United States coastal areas, there are many lighthouses. The lighthouses might not be so necessary these days, because of GPS tracking, but before all of the technology that we have today, lighthouses were the only way for a ship to know if they were coming dangerously close to a stretch of land. Such was the case with the Sandy Hook lighthouse in 1776. The problem they were having with the lighthouse, however, is that it was thought that the lighthouse would also help the British ships to invade New York City. It was a very real concern, and posed a grave danger to the Provincial Congress of New York.
Most of us have heard the name Sandy Hook because of the school shooting that took place in an elementary school with the same name in Newtown, Connecticut. That tragedy was not the first time the name Sandy Hook had been at the center of attention, however. Most people know that along United States coastal areas, there are many lighthouses. The lighthouses might not be so necessary these days, because of GPS tracking, but before all of the technology that we have today, lighthouses were the only way for a ship to know if they were coming dangerously close to a stretch of land. Such was the case with the Sandy Hook lighthouse in 1776. The problem they were having with the lighthouse, however, is that it was thought that the lighthouse would also help the British ships to invade New York City. It was a very real concern, and posed a grave danger to the Provincial Congress of New York.
The Sandy Hook lighthouse was located on a piece of land that was disputed territory in those days. The land sits directly across the bay from New York City, making it an important shipping lane, but a dangerous one too. In early 1761, the Provincial Congress of New York set up lotteries to raise money for the construction of a lighthouse. A lighthouse in this area had been under discussion for nearly a century before it was initiated by Colonial Governor Edmund Andread. Forty three New York merchants proposed the lotteries to the Provincial Council, after losing 20,000 sterling pounds to shipwrecks in 1761. The money was collected, and the Sandy Hook lighthouse was built. It first shone its beam on June 11, 1764. It served it’s purpose quite well…in fact maybe too well…at least during the Revolutionary War. Ships weren’t sinking, but in a big way, it left New York City quite vulnerable to attack. So, after just fifteen years of use, the New York Provincial Congress decided that the lighthouse had to be dismantled. Then came the controversy. A committee of the New York Provincial Congress told Major William Malcolm to “use your best discretion to render the light-house entirely useless.” They wanted him to remove the lens and lamps so that the lighthouse could no longer warn ships of possible hazards on the rocky shore. He succeeded. Colonel George Taylor reported to the committee six days later, that Malcolm had given him eight copper lamps, two tackle falls and blocks, three casks, and a part of a cast of oil from the dismantling of the beacon.
Malcolm’s efforts failed, because the lighthouse was quickly put back into service by the merchants in the area, with the installation of lamps and reflectors. The Patriots attempted to knock the light out again on June 1st, by placing cannon on boats and attempting to blow away the British paraphernalia, damaging some of it before 
 they were chased away. Malcolm’s efforts did not prevent the British from invading New York City. The new states of New York and New Jersey fought over ownership of the lighthouse until the federal government assumed control of all US lighthouses in 1787. As of 1996, the Sandy Hook lighthouse, the oldest original lighthouse in the United States, became a historic landmark, and passed into the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. It is still in operation as part of the Gateway National Recreation Area.
they were chased away. Malcolm’s efforts did not prevent the British from invading New York City. The new states of New York and New Jersey fought over ownership of the lighthouse until the federal government assumed control of all US lighthouses in 1787. As of 1996, the Sandy Hook lighthouse, the oldest original lighthouse in the United States, became a historic landmark, and passed into the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. It is still in operation as part of the Gateway National Recreation Area.
 Living in New Jersey, does not necessarily mean that people work or shop in New Jersey. Since Manhattan is just across the Hudson River, many people work and shop there…who wouldn’t, given the chance. I suppose that at some point it was decided that there might soon be too many bridges over the river, and maybe a tunnel under it could be built. The first known underwater tunnel to be built was the Thames Tunnel, built beneath the River Thames in London, connecting Rotherhithe and Wapping. It was built between 1825 and 1843 using Marc Isambard Brunel’s and Thomas Cochrane’s newly invented tunneling shield technology, by Brunel and his son Isambard Kingdom Brunel. So the idea was not new, and in fact, not even new to New York City. The Port Authority had acquired the Holland Tunnel in 1930, and soon after New York and New Jersey authorized the agency to proceed with its plan to build what was then called the Midtown Hudson Tunnel or the Midtown Vehicular Tunnel. Creating a 1.5-mile-long structure, even above ground, would be no small accomplishment, but to build it under a riverbed was a monumental task. Hundreds of huge iron rings, each weighing 21 tons, had to be assembled and bolstered together on site to form the lining of the tunnel. At some point it was decided that Midtown Vehicular Tunnel was not grand enough…so in the spirit of patriotism they named it the Lincoln Tunnel, because of the George Washington Bridge. On this day, December 22, 1937 the 8,216 foot center tube opened in 1937, followed by the 7,482 foot north tube in 1945. The 8,006 foot south tube was the last to open, in 1957.
Living in New Jersey, does not necessarily mean that people work or shop in New Jersey. Since Manhattan is just across the Hudson River, many people work and shop there…who wouldn’t, given the chance. I suppose that at some point it was decided that there might soon be too many bridges over the river, and maybe a tunnel under it could be built. The first known underwater tunnel to be built was the Thames Tunnel, built beneath the River Thames in London, connecting Rotherhithe and Wapping. It was built between 1825 and 1843 using Marc Isambard Brunel’s and Thomas Cochrane’s newly invented tunneling shield technology, by Brunel and his son Isambard Kingdom Brunel. So the idea was not new, and in fact, not even new to New York City. The Port Authority had acquired the Holland Tunnel in 1930, and soon after New York and New Jersey authorized the agency to proceed with its plan to build what was then called the Midtown Hudson Tunnel or the Midtown Vehicular Tunnel. Creating a 1.5-mile-long structure, even above ground, would be no small accomplishment, but to build it under a riverbed was a monumental task. Hundreds of huge iron rings, each weighing 21 tons, had to be assembled and bolstered together on site to form the lining of the tunnel. At some point it was decided that Midtown Vehicular Tunnel was not grand enough…so in the spirit of patriotism they named it the Lincoln Tunnel, because of the George Washington Bridge. On this day, December 22, 1937 the 8,216 foot center tube opened in 1937, followed by the 7,482 foot north tube in 1945. The 8,006 foot south tube was the last to open, in 1957.
On average, the Lincoln Tunnel sees upwards of 120,000 cars passing through every day. It is one of the busiest roadways in the country. On the afternoon of September 8, 1953, the tunnel became famous when two men, who had attempted to rob a house in South Orange New Jersey were chased away by its residents. Their car’s license plate was relayed to the police. Peter Simon and John Metcalf escaped into the Lincoln Tunnel and were spotted by transit authorities upon entering. A car chase ensued amid the traffic through the tunnel. Police commandeered a delivery truck and fired shots at the getaway car as it swerved around other vehicles. In all 28 shots were fired, and the driver, Peter Simon, was shot in the head about three quarters of the way to the other side of the tunnel. The gunfight was reported by The New York Times the next morning.
The Hudson River current has historically stayed close to the edge of Lower Manhattan, but with the construction of Battery Park City, which juts out into the river, part of the current has been rerouted. Its new location brings it more toward the river’s center and it’s uncovering much of the soil lying on top of the walls and ceiling of the Tunnel. As of 2009, some parts of the tunnel’s walls have seen a soil coverage decrease of about 25%, making them far more susceptible to shifting or cracking in the coming years. Not good!!
The process of building the 1.5 mile tunnel was grueling. To support the cavities that the workers dug out, they  installed a series of 21 ton iron rings set into the walls. The workers who dug the tunnels, called sandhogs, had to use a series of airlocks to depressurize and re-pressurize their bodies while entering a new section of the tunnel. With no ventilation, the air in each pressurized section got stale quickly. The excavation involved digging, lining the walls with the rings, pouring cement into every crease and crack to the keep the water out, and finally they moved along to the next airlock. Clifford Holland, chief engineer and namesake of the Holland Tunnel, died of a heart attack at 41 years of age due to immense stress during the construction, as well as the growing toxicity of the air in the airlocks. The Lincoln Tunnel faired better, with no reported work-related deaths.
installed a series of 21 ton iron rings set into the walls. The workers who dug the tunnels, called sandhogs, had to use a series of airlocks to depressurize and re-pressurize their bodies while entering a new section of the tunnel. With no ventilation, the air in each pressurized section got stale quickly. The excavation involved digging, lining the walls with the rings, pouring cement into every crease and crack to the keep the water out, and finally they moved along to the next airlock. Clifford Holland, chief engineer and namesake of the Holland Tunnel, died of a heart attack at 41 years of age due to immense stress during the construction, as well as the growing toxicity of the air in the airlocks. The Lincoln Tunnel faired better, with no reported work-related deaths.

 When you think of a town within a town or city, you often think of New York City, where you might find Queens, Harlem, or Yonkers. Or you might think of New Orleans, where you might find the French Quarter or the 9th Ward, but people really never think of a town within a town, when the town is a small town, like Forsyth, Montana, population of about 1,777. Nevertheless, Forsyth, Montana was a town that had within it a town…so to speak. When my husband, Bob Schulenberg’s grandpa, Andrew Schulenberg was a young married man, he built a couple of houses there. The houses were next door to each other. Andy’s parents lived in one house, and he and his wife, lived in the other. Across the street was another house owned by Schulenberg family relative, Bob’s Great Aunt Hennie. Being such a small town, there were other Schulenberg families very nearby, and since Andy’s parents, Max and Julia Schulenberg had ten children, it made for a lot of Schulenberg relation living in a neighborhood in Forsyth, Montana. Well, before long, the people of the town found themselves calling that neighborhood, Schulenbergville. I’m not sure just exactly when
When you think of a town within a town or city, you often think of New York City, where you might find Queens, Harlem, or Yonkers. Or you might think of New Orleans, where you might find the French Quarter or the 9th Ward, but people really never think of a town within a town, when the town is a small town, like Forsyth, Montana, population of about 1,777. Nevertheless, Forsyth, Montana was a town that had within it a town…so to speak. When my husband, Bob Schulenberg’s grandpa, Andrew Schulenberg was a young married man, he built a couple of houses there. The houses were next door to each other. Andy’s parents lived in one house, and he and his wife, lived in the other. Across the street was another house owned by Schulenberg family relative, Bob’s Great Aunt Hennie. Being such a small town, there were other Schulenberg families very nearby, and since Andy’s parents, Max and Julia Schulenberg had ten children, it made for a lot of Schulenberg relation living in a neighborhood in Forsyth, Montana. Well, before long, the people of the town found themselves calling that neighborhood, Schulenbergville. I’m not sure just exactly when  the neighborhood got its name, but since Andy was the sheriff of Rosebud County from 1955 to 1972, my guess is that it was either during that time, or it was his job as sheriff that solidified the name to that area of town.
the neighborhood got its name, but since Andy was the sheriff of Rosebud County from 1955 to 1972, my guess is that it was either during that time, or it was his job as sheriff that solidified the name to that area of town.
I had the chance to see the two houses that Andy Schulenberg built, and to find out that the second one was the house that Bob’s Uncle Butch Schulenberg was born in. I love to see the homes where loved ones were born, partly I suppose, because so few people are born at home these days. In those days, however, being born at home was a very common practice, and it makes me think about the history that the house has witnessed. The house got to see little Butch Schulenberg growing up…or at least starting his life, since I don’t know when the family might have moved out of the house. Nevertheless, the area remained Schulenbergville for a number of years, and I don’t think the locals have forgotten it to this day.
Nor have they forgotten the sheriff who really made the Schulenberg name a household word in the little town of Forsyth. Andy was a different kind of sheriff from those you normally meet, and that is a story I will tell sometime, but it’s too long for this story. Suffice it to say that he was dearly loved, and there is more than one 
 adult who owes the fact that they weren’t in prison…or worse as kids, to Sheriff Andy Schulenberg, and they will be happy to tell you so. The two houses Andy built still stand, as do the houses of the neighboring Schulenberg clan members, although some are no longer occupied. I find that a bit sad, but it is a testament to good construction work. Now they stand as a treasured memory for those who knew Schulenbergville well.
adult who owes the fact that they weren’t in prison…or worse as kids, to Sheriff Andy Schulenberg, and they will be happy to tell you so. The two houses Andy built still stand, as do the houses of the neighboring Schulenberg clan members, although some are no longer occupied. I find that a bit sad, but it is a testament to good construction work. Now they stand as a treasured memory for those who knew Schulenbergville well.

 So often, when we have a holiday, people tend to think that it is just another day to have a family dinner and a day off of work. Often, they are celebrating the day for the wrong reason, but not so today. Labor Day is a day for our nation to pay tribute to its workers. No nation can be strong if it has no workers. So, as a show of gratitude, Labor Day was set aside to allow a day of rest for the American worker. When our nation was founded, there was largely nothing here. The native Americans lived in Teepees, so they could be mobile. They needed to follow the buffalo because that was their food supply. But, we had come from nations where there were houses and farms, and ways to get the things we needed.
So often, when we have a holiday, people tend to think that it is just another day to have a family dinner and a day off of work. Often, they are celebrating the day for the wrong reason, but not so today. Labor Day is a day for our nation to pay tribute to its workers. No nation can be strong if it has no workers. So, as a show of gratitude, Labor Day was set aside to allow a day of rest for the American worker. When our nation was founded, there was largely nothing here. The native Americans lived in Teepees, so they could be mobile. They needed to follow the buffalo because that was their food supply. But, we had come from nations where there were houses and farms, and ways to get the things we needed.
Nevertheless, this was a new nation, and it was going to take a lot of hard work to turn it into the great nation it has become. The work was going to be a lot of hard physical labor. We would also need those who would teach our children and others so that they could become doctors, scientists, inventors, and all the other jobs that would be needed to take this from a vast empty land, to a thriving nation that would be able to bring about the dreams that we all came over here to fulfill.
After a time of hard work, and much growth, the nation began to give increasing emphasis to a Labor Day holiday. It was decided that we, as a nation, needed to thank our laborers for all they had done to build this country. The first bill to be introduced was into the New York legislature, but the first state to pass a law was Oregon, on February 21, 1887. Over the course of that year, four more states passed legislation to honor laborers through a Labor Day holiday that was created by legislative enactment. Those states were Colorado, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and New York. By the end of the decade, Connecticut, Nebraska, and Pennsylvania were also listed among the states honoring laborers with a Labor Day holiday. By 1894, 23 other states had adopted the holiday in honor of workers, and on June 28 of that year, Congress passed an act making the first Monday in September of each year a legal holiday in the District of Columbia and the territories.
The first Labor Day holiday was celebrated on Tuesday, September 5, 1882, in New York City, in accordance with the plans of the Central Labor Union. The day began with a parade and continued on with lots of festivities. The Central Labor Union held its second Labor Day holiday just a year later, on September 5, 1883. That was rather odd, considering the fact that the holiday didn’t become official until 1887, and then it wasn’t in New York City. Later, like many holidays, it began to make less sense to keep the holiday on the fifth, and so the first Monday in September was chosen to be the permanent time to celebrate it. That makes sense when you think about it. If you are going to celebrate the laborers, give them a three day weekend. After all, that is 
 cause for celebration for most laborers. Of course, as we all know, the holiday doesn’t give every worker the day off. That would be almost impossible for all the obvious reasons. Nevertheless, as Labor Day arrives, I hope that each and every worker knows that whether they get the day off or not, this grateful nation has set aside this day to celebrate them, and to thank them for making this nation great. Happy Labor Day to workers everywhere!!
cause for celebration for most laborers. Of course, as we all know, the holiday doesn’t give every worker the day off. That would be almost impossible for all the obvious reasons. Nevertheless, as Labor Day arrives, I hope that each and every worker knows that whether they get the day off or not, this grateful nation has set aside this day to celebrate them, and to thank them for making this nation great. Happy Labor Day to workers everywhere!!
 Years ago, many people thought that anyone who was trying to invent an airplane was pretty much insane…saying, that “if man were meant to fly, God would have given him wings” as their reasoning. I’m sure that those same people reiterated their thoughts on the matter, with each new plane crash…basically jumping on the chance to say, “I told you so!” Of course, these days, no one thinks that way, whether they like to fly or not. I guess a fear of flying and the idea that it is a foolish pipe dream aren’t the same things at all. Still, while man has proven over the years that flight is possible, and in fact mostly safe, there are some airplane crashes that that will forever be embedded in our minds. For me, of course, the one that I can picture in my mind at the drop of a hat, is Flight 232 that crashed in Sioux City, Iowa. This was the crash that took the life of my Great Aunt Gladys Pattan Byer Cooper. That pilot was so close to landing that plane safely, and would have, in fact, if the plane hadn’t put in one last effort to turn over due to a major loss of hydraulics. The resulting crash made me wonder how anyone survived…much less the 185 out of 296 people on board. The only reason they survived was the skill of the pilot…and much prayer.
Years ago, many people thought that anyone who was trying to invent an airplane was pretty much insane…saying, that “if man were meant to fly, God would have given him wings” as their reasoning. I’m sure that those same people reiterated their thoughts on the matter, with each new plane crash…basically jumping on the chance to say, “I told you so!” Of course, these days, no one thinks that way, whether they like to fly or not. I guess a fear of flying and the idea that it is a foolish pipe dream aren’t the same things at all. Still, while man has proven over the years that flight is possible, and in fact mostly safe, there are some airplane crashes that that will forever be embedded in our minds. For me, of course, the one that I can picture in my mind at the drop of a hat, is Flight 232 that crashed in Sioux City, Iowa. This was the crash that took the life of my Great Aunt Gladys Pattan Byer Cooper. That pilot was so close to landing that plane safely, and would have, in fact, if the plane hadn’t put in one last effort to turn over due to a major loss of hydraulics. The resulting crash made me wonder how anyone survived…much less the 185 out of 296 people on board. The only reason they survived was the skill of the pilot…and much prayer.
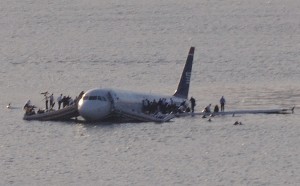
Another plane crash that has stayed in my memory was the crash of the Concorde, that occurred on this day, July 25, 2000. The Concord was a beautiful plane, and by far the most luxurious one of its time. I’m not sure there are even any planes that are more luxurious today…although the Boeing 787 might be. Dubbed the Dreamliner, it gives the indication that it might out class the Concorde. Nevertheless, in its day, the Concorde was the end all, beat all of airplanes. The thing that always amazes me is that sometimes it is the tiniest of things that ends up bringing down a plane. Much like the bird strike that brought down US Airways Flight 1549 on the Hudson River.
The Concorde was downed be a small piece of metal on the runway…that had fallen off of another plane. Air France Flight 4590 left DE Gaulle Airport for New York carrying nine crew members and 96 German tourists who were planning to take a cruise to Ecuador. That piece of metal shredded the tire that ran over it, throwing  pieces of the tire into one of the engines and fuel tanks, causing a disabling fire. The pilot had no idea what was about to happen, but just moments later the plane plunged to the ground near a hotel in Gonesse, France. A huge fireball erupted and all 105 people on the plane were killed immediately. The Concorde, the world’s fastest commercial jet, had enjoyed an exemplary safety record up to that point, with no crashes in the plane’s 31 year history. That crash, however, marked the beginning of the end for the Concorde. The last flight of the Concorde was on October 24, 2003. What was supposed to mark the first of a future of supersonic, fast paced air travel, was brought to a disappointing halt. Air travel has taken on a much slower pace since that time.
pieces of the tire into one of the engines and fuel tanks, causing a disabling fire. The pilot had no idea what was about to happen, but just moments later the plane plunged to the ground near a hotel in Gonesse, France. A huge fireball erupted and all 105 people on the plane were killed immediately. The Concorde, the world’s fastest commercial jet, had enjoyed an exemplary safety record up to that point, with no crashes in the plane’s 31 year history. That crash, however, marked the beginning of the end for the Concorde. The last flight of the Concorde was on October 24, 2003. What was supposed to mark the first of a future of supersonic, fast paced air travel, was brought to a disappointing halt. Air travel has taken on a much slower pace since that time.

 For a time it seemed that our nation couldn’t decide where to put the capitol. The first capitol…for a very short time, was New York City. President George Washington occupied two executive mansions in New York City…the Samuel Osgood House and the Alexander Macomb House. New York began building Government House, but Washington never occupied it. The capitol was moved to Philadelphia. Few people realize that it all began in New York City, nor do they realize that Philadelphia was the first official capitol of the United States. Washington DC became the capitol in December, 1800.
For a time it seemed that our nation couldn’t decide where to put the capitol. The first capitol…for a very short time, was New York City. President George Washington occupied two executive mansions in New York City…the Samuel Osgood House and the Alexander Macomb House. New York began building Government House, but Washington never occupied it. The capitol was moved to Philadelphia. Few people realize that it all began in New York City, nor do they realize that Philadelphia was the first official capitol of the United States. Washington DC became the capitol in December, 1800.
The 1790 Residence Act named Philadelphia the temporary capital for ten years untile the White House could be built on the Potomac River in what is now Washington DC. Philadelphia housed both Continental Congresses and the Constitutional Congress. Both the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution were written in Philadelphia. When it was decided that Washington DC would become the capitol, there was a bit of a fight over the move. While President Washington lived in Philadelphia, he lived in the Market Street mansion, which he altered in ways that may have influenced the White House. In an effort to keep the capitol in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania built a grand presidential mansion a few blocks from the Market Street mansion, but President Washigton declined to occupy it.
President Washington’s term would end before the White House was completed. John Quincy Adams became president and lived in the Market Street mansion from March 1797 to May 1800, having also declined to move into the grand presidential mansion that Pennsylvania had built. Then on June 3, 1800, President Adams moved to Washington DC. The White House was still not finished, so in what I found a shocking move, he moved into the Washington City Hotel, as it was properly named. It was called, and rightfully so, Tunnicliff’s, named after William Tunnicliff, who had it build, and owned it. The Washington City Hotel was in reality, a tavern. A tavern!! That is such a strange place for a US president to choose to live. I’m sure he was excited about 
 moving into the White House, but it would not be finished unto the end of October. President Adams finally moved into the White House on November 1, 1800, making him the only president to live in the Philadelphia mansion, a tavern, and the White House.
moving into the White House, but it would not be finished unto the end of October. President Adams finally moved into the White House on November 1, 1800, making him the only president to live in the Philadelphia mansion, a tavern, and the White House.
Things were much different in those days, of course. I’m sure that there was no big pre-move check of the tavern and the surrouning area, like there would be now. I suppose that there was security to some degree, but in reality most Americans wouldn’t have even known that the president had moved at that time, much less that he was living in a tavern.

