new jersy
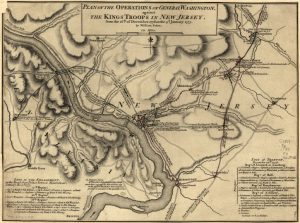 The year was 1776, and it was Christmas Day, but for the men with George Washington, it was not a day of celebration…not exactly anyway. They were in the middle of fighting a war, and the fighting didn’t just stop because it was Christmas, not this year anyway. This was to be an unusual Christmas as far as wartime Christmases went. In 1776, it was difficult to fight a war in the wintertime, because the slower modes of travel. Most times in a war, the armies took the Winter off from warring, but this army was not laying up for the Winter. This war would continue on…no matter what the weather was like.
The year was 1776, and it was Christmas Day, but for the men with George Washington, it was not a day of celebration…not exactly anyway. They were in the middle of fighting a war, and the fighting didn’t just stop because it was Christmas, not this year anyway. This was to be an unusual Christmas as far as wartime Christmases went. In 1776, it was difficult to fight a war in the wintertime, because the slower modes of travel. Most times in a war, the armies took the Winter off from warring, but this army was not laying up for the Winter. This war would continue on…no matter what the weather was like.
Things looked bad that year. The Continental Army had suffered a series of defeats in their battle against the British oppression. After some successful maneuvers, Colonel Henry Knox came to the attention of General George Washington who worked to place him in overall command to the Continental Army. Under his command, the Continentals brought 18 cannon over the river…3  Pounders, 4 Pounders, some 6 Pounders, horses to pull the carriages, and enough ammunition for the coming battle. The 6 Pounders, weighing as much as 1,750 pounds were the most difficult to transport to the far side of the river. But in the end all the trouble of moving this large artillery train to Trenton proved its worth. Knox would place the bulk of his artillery at the top of the town where its fire commanded the center of Trenton.
Pounders, 4 Pounders, some 6 Pounders, horses to pull the carriages, and enough ammunition for the coming battle. The 6 Pounders, weighing as much as 1,750 pounds were the most difficult to transport to the far side of the river. But in the end all the trouble of moving this large artillery train to Trenton proved its worth. Knox would place the bulk of his artillery at the top of the town where its fire commanded the center of Trenton.
The plan devised by Knox and Washington was to conduct a surprise attack upon a Hessian garrison of roughly 1,400 soldiers located in and around Trenton, New Jersey. Washington hoped that a quick victory at Trenton would bolster sagging morale in his army and encourage more men to join the ranks of the Continentals in the coming new year. After several councils of war, General George Washington set the date for the river crossing for Christmas night 1776. It was an unprecedented plan, because the expectation was always that the armies would hold up somewhere for the winter. No one had attacked in winter before, and especially on Christmas. George Washington led 2,400 troops on a daring nighttime crossing of the icy Delaware River. Stealing into New Jersey, on December 26 the Continental forces launched the surprise attack on Trenton.
 The gamble paid off. Many of the Hessians were still disoriented from the previous night’s holiday bender, and colonial forces defeated them with minimal bloodshed. While Washington had pulled off a shock victory, his army was unequipped to hold the city and he was forced to re-cross the Delaware that same day…with nearly 1,000 Hessian prisoners in tow. Washington would go on to score successive victories at the Battles of the Assunpink Creek and Princeton, and his audacious crossing of the frozen Delaware served as a crucial rallying cry for the beleaguered Continental Army. The Revolutionary War would be won by the Continental Army of course, and the rules of warfare changed forever.
The gamble paid off. Many of the Hessians were still disoriented from the previous night’s holiday bender, and colonial forces defeated them with minimal bloodshed. While Washington had pulled off a shock victory, his army was unequipped to hold the city and he was forced to re-cross the Delaware that same day…with nearly 1,000 Hessian prisoners in tow. Washington would go on to score successive victories at the Battles of the Assunpink Creek and Princeton, and his audacious crossing of the frozen Delaware served as a crucial rallying cry for the beleaguered Continental Army. The Revolutionary War would be won by the Continental Army of course, and the rules of warfare changed forever.
 Through the years, or at least since the dawning of flight, man has tried to build flying machines that are more and more creative. Some of these have had amazing runs, like the B-17 Bomber, which was a World War II era plane, that still flies today. Others, like the Hindenburg, went down in a ball of flames. I don’t think it’s usually easy to predict which ones will succeed and which ones won’t. I seriously doubt that people would have predicted that the Concord would ever have the problems it had, or that the Goodyear Blimp would prove successful, where the Hindenburg failed. Sometimes, it’s all about finding yourself with just the right set of components, or making just one slight mistake…and sometimes, the mistake is more obvious.
Through the years, or at least since the dawning of flight, man has tried to build flying machines that are more and more creative. Some of these have had amazing runs, like the B-17 Bomber, which was a World War II era plane, that still flies today. Others, like the Hindenburg, went down in a ball of flames. I don’t think it’s usually easy to predict which ones will succeed and which ones won’t. I seriously doubt that people would have predicted that the Concord would ever have the problems it had, or that the Goodyear Blimp would prove successful, where the Hindenburg failed. Sometimes, it’s all about finding yourself with just the right set of components, or making just one slight mistake…and sometimes, the mistake is more obvious.
The Hindenburg disaster, which occurred on this day, May 6, 1937, was probably the worst slight mistake in history. The Hindenburg was Germany’s version of the most luxurious way to fly in existence at that time. It was over 800 feet long and with its state of the art Mercedes Benz engine, it flew at 85 miles per hour, and had a range of 8,000 miles. The Hindenburg carried 97 passengers, and made ten successful ocean crossings the year before the disaster. It was Germany’s Nazi government’s symbol of national pride, but it held a secret mistake that, on May 6, 1937, exploded into one of Germany’s biggest failures.
The Hindenburg was filled with seven million cubic feet of Hydrogen. The Germans used Hydrogen because of its maneuverability, even though Helium would have been much safer. The Hindenburg was supposed to arrive in New Jersey at 5:00am on that fateful day, but bad weather delayed its arrival until the later afternoon. Even then, the weather was not ideal. Rain further delayed the docking at Lakehurst. When they were finally cleared to dock, Captain Max Pruss brought the ship in too fast and had to order a reverse engine thrust. At 7:20pm a gas leak was noticed. Within minutes, the tail blew up, sending flames hundreds of feet in the air and as far down as the ground below.
The chain reaction that followed caused the entire vessel to burst into flames. There were nearly 1,000 spectators awaiting the arival, who could feel the heat of the fire from a mile away. Those on the Hindenburg  tried to jump. Some tried to jump to the docking cables, and when they fell, they were killed or critically injured. Others tried to jump as they got closer to the ground. Many were critically burned. In all 36 people lost their lives, while 56 managed to survive. Probably the main reason this crash has stayed in the minds of people over the years is that there were so many cameras to document the event. The photographs have become well known. Announcer Herbert Morrison, on WLS radio gave an unforgettably harrowing live account of the disaster, “Oh, oh, oh. It’s burst into flames. Get out of the way, please . . . this is terrible . . . it’s burning, bursting into flames, and is falling . . . Oh! This is one of the worst . . . it’s a terrific sight . . .oh, the humanity.” This truly was a disaster of monumental proportion, and it will never be forgotten.
tried to jump. Some tried to jump to the docking cables, and when they fell, they were killed or critically injured. Others tried to jump as they got closer to the ground. Many were critically burned. In all 36 people lost their lives, while 56 managed to survive. Probably the main reason this crash has stayed in the minds of people over the years is that there were so many cameras to document the event. The photographs have become well known. Announcer Herbert Morrison, on WLS radio gave an unforgettably harrowing live account of the disaster, “Oh, oh, oh. It’s burst into flames. Get out of the way, please . . . this is terrible . . . it’s burning, bursting into flames, and is falling . . . Oh! This is one of the worst . . . it’s a terrific sight . . .oh, the humanity.” This truly was a disaster of monumental proportion, and it will never be forgotten.

